Olga Vechtomova
Between Predictability and Randomness: Seeking Artistic Inspiration from AI Generative Models
Jun 14, 2025Abstract:Artistic inspiration often emerges from language that is open to interpretation. This paper explores the use of AI-generated poetic lines as stimuli for creativity. Through analysis of two generative AI approaches--lines generated by Long Short-Term Memory Variational Autoencoders (LSTM-VAE) and complete poems by Large Language Models (LLMs)--I demonstrate that LSTM-VAE lines achieve their evocative impact through a combination of resonant imagery and productive indeterminacy. While LLMs produce technically accomplished poetry with conventional patterns, LSTM-VAE lines can engage the artist through semantic openness, unconventional combinations, and fragments that resist closure. Through the composition of an original poem, where narrative emerged organically through engagement with LSTM-VAE generated lines rather than following a predetermined structure, I demonstrate how these characteristics can serve as evocative starting points for authentic artistic expression.
Reimagining Dance: Real-time Music Co-creation between Dancers and AI
Jun 13, 2025Abstract:Dance performance traditionally follows a unidirectional relationship where movement responds to music. While AI has advanced in various creative domains, its application in dance has primarily focused on generating choreography from musical input. We present a system that enables dancers to dynamically shape musical environments through their movements. Our multi-modal architecture creates a coherent musical composition by intelligently combining pre-recorded musical clips in response to dance movements, establishing a bidirectional creative partnership where dancers function as both performers and composers. Through correlation analysis of performance data, we demonstrate emergent communication patterns between movement qualities and audio features. This approach reconceptualizes the role of AI in performing arts as a responsive collaborator that expands possibilities for both professional dance performance and improvisational artistic expression across broader populations.
No Stupid Questions: An Analysis of Question Query Generation for Citation Recommendation
Jun 09, 2025Abstract:Existing techniques for citation recommendation are constrained by their adherence to article contents and metadata. We leverage GPT-4o-mini's latent expertise as an inquisitive assistant by instructing it to ask questions which, when answered, could expose new insights about an excerpt from a scientific article. We evaluate the utility of these questions as retrieval queries, measuring their effectiveness in retrieving and ranking masked target documents. In some cases, generated questions ended up being better queries than extractive keyword queries generated by the same model. We additionally propose MMR-RBO, a variation of Maximal Marginal Relevance (MMR) using Rank-Biased Overlap (RBO) to identify which questions will perform competitively with the keyword baseline. As all question queries yield unique result sets, we contend that there are no stupid questions.
Computational Modeling of Artistic Inspiration: A Framework for Predicting Aesthetic Preferences in Lyrical Lines Using Linguistic and Stylistic Features
Oct 03, 2024Abstract:Artistic inspiration remains one of the least understood aspects of the creative process. It plays a crucial role in producing works that resonate deeply with audiences, but the complexity and unpredictability of aesthetic stimuli that evoke inspiration have eluded systematic study. This work proposes a novel framework for computationally modeling artistic preferences in different individuals through key linguistic and stylistic properties, with a focus on lyrical content. In addition to the framework, we introduce \textit{EvocativeLines}, a dataset of annotated lyric lines, categorized as either "inspiring" or "not inspiring," to facilitate the evaluation of our framework across diverse preference profiles. Our computational model leverages the proposed linguistic and poetic features and applies a calibration network on top of it to accurately forecast artistic preferences among different creative individuals. Our experiments demonstrate that our framework outperforms an out-of-the-box LLaMA-3-70b, a state-of-the-art open-source language model, by nearly 18 points. Overall, this work contributes an interpretable and flexible framework that can be adapted to analyze any type of artistic preferences that are inherently subjective across a wide spectrum of skill levels.
Enchancing Semi-Supervised Learning for Extractive Summarization with an LLM-based pseudolabeler
Nov 16, 2023Abstract:This work tackles the task of extractive text summarization in a limited labeled data scenario using a semi-supervised approach. Specifically, we propose a prompt-based pseudolabel selection strategy using GPT-4. We evaluate our method on three text summarization datasets: TweetSumm, WikiHow, and ArXiv/PubMed. Our experiments show that by using an LLM to evaluate and generate pseudolabels, we can improve the ROUGE-1 by 10-20\% on the different datasets, which is akin to enhancing pretrained models. We also show that such a method needs a smaller pool of unlabeled examples to perform better.
PromptMix: A Class Boundary Augmentation Method for Large Language Model Distillation
Oct 22, 2023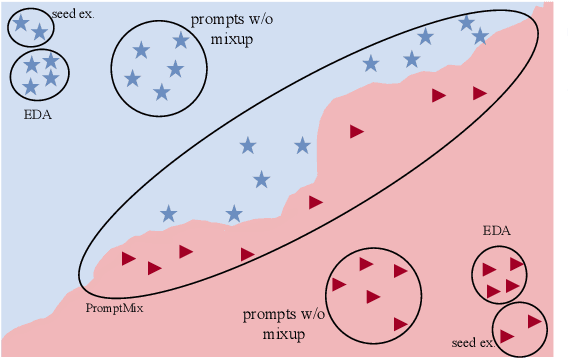
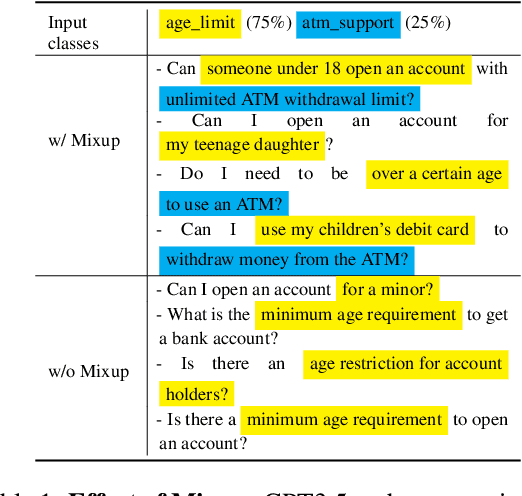
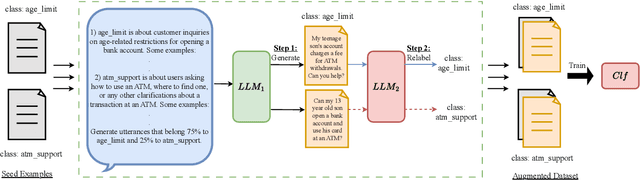
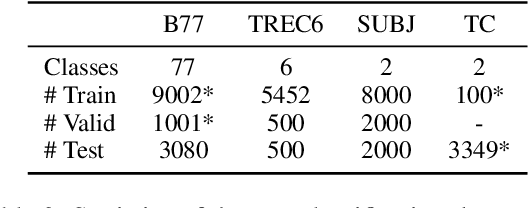
Abstract:Data augmentation is a widely used technique to address the problem of text classification when there is a limited amount of training data. Recent work often tackles this problem using large language models (LLMs) like GPT3 that can generate new examples given already available ones. In this work, we propose a method to generate more helpful augmented data by utilizing the LLM's abilities to follow instructions and perform few-shot classifications. Our specific PromptMix method consists of two steps: 1) generate challenging text augmentations near class boundaries; however, generating borderline examples increases the risk of false positives in the dataset, so we 2) relabel the text augmentations using a prompting-based LLM classifier to enhance the correctness of labels in the generated data. We evaluate the proposed method in challenging 2-shot and zero-shot settings on four text classification datasets: Banking77, TREC6, Subjectivity (SUBJ), and Twitter Complaints. Our experiments show that generating and, crucially, relabeling borderline examples facilitates the transfer of knowledge of a massive LLM like GPT3.5-turbo into smaller and cheaper classifiers like DistilBERT$_{base}$ and BERT$_{base}$. Furthermore, 2-shot PromptMix outperforms multiple 5-shot data augmentation methods on the four datasets. Our code is available at https://github.com/ServiceNow/PromptMix-EMNLP-2023.
Future Sight: Dynamic Story Generation with Large Pretrained Language Models
Dec 20, 2022



Abstract:Recent advances in deep learning research, such as transformers, have bolstered the ability for automated agents to generate creative texts similar to those that a human would write. By default, transformer decoders can only generate new text with respect to previously generated text. The output distribution of candidate tokens at any position is conditioned on previously selected tokens using a self-attention mechanism to emulate the property of autoregression. This is inherently limiting for tasks such as controllable story generation where it may be necessary to condition on future plot events when writing a story. In this work, we propose Future Sight, a method for finetuning a pretrained generative transformer on the task of future conditioning. Transformer decoders are typically pretrained on the task of completing a context, one token at a time, by means of self-attention. Future Sight additionally enables a decoder to attend to an encoded future plot event. This motivates the decoder to expand on the context in a way that logically concludes with the provided future. During inference, the future plot event can be written by a human author to steer the narrative being generated in a certain direction. We evaluate the efficacy of our approach on a story generation task with human evaluators.
LyricJam Sonic: A Generative System for Real-Time Composition and Musical Improvisation
Oct 27, 2022



Abstract:Electronic music artists and sound designers have unique workflow practices that necessitate specialized approaches for developing music information retrieval and creativity support tools. Furthermore, electronic music instruments, such as modular synthesizers, have near-infinite possibilities for sound creation and can be combined to create unique and complex audio paths. The process of discovering interesting sounds is often serendipitous and impossible to replicate. For this reason, many musicians in electronic genres record audio output at all times while they work in the studio. Subsequently, it is difficult for artists to rediscover audio segments that might be suitable for use in their compositions from thousands of hours of recordings. In this paper, we describe LyricJam Sonic -- a novel creative tool for musicians to rediscover their previous recordings, re-contextualize them with other recordings, and create original live music compositions in real-time. A bi-modal AI-driven approach uses generated lyric lines to find matching audio clips from the artist's past studio recordings, and uses them to generate new lyric lines, which in turn are used to find other clips, thus creating a continuous and evolving stream of music and lyrics. The intent is to keep the artists in a state of creative flow conducive to music creation rather than taking them into an analytical/critical state of deliberately searching for past audio segments. The system can run in either a fully autonomous mode without user input, or in a live performance mode, where the artist plays live music, while the system "listens" and creates a continuous stream of music and lyrics in response.
LyricJam: A system for generating lyrics for live instrumental music
Jun 03, 2021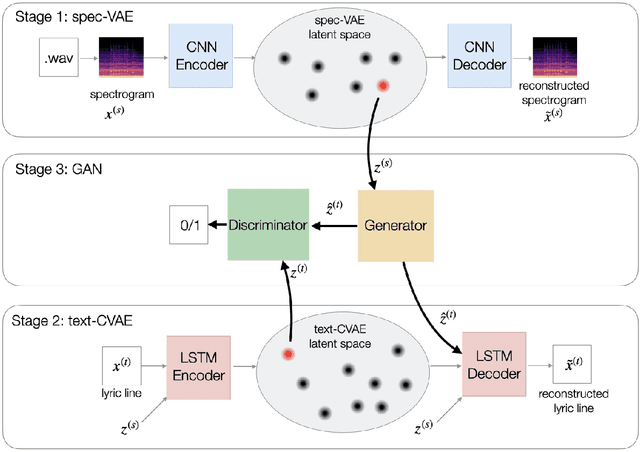

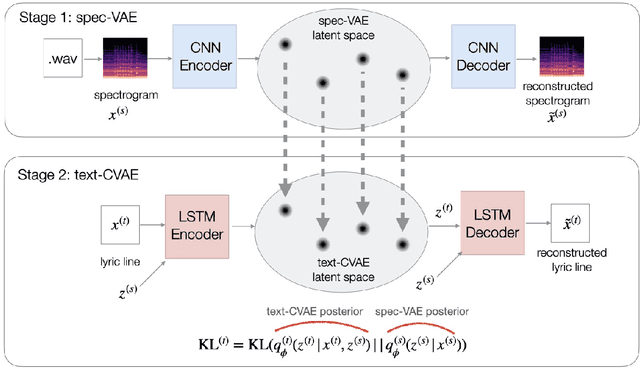
Abstract:We describe a real-time system that receives a live audio stream from a jam session and generates lyric lines that are congruent with the live music being played. Two novel approaches are proposed to align the learned latent spaces of audio and text representations that allow the system to generate novel lyric lines matching live instrumental music. One approach is based on adversarial alignment of latent representations of audio and lyrics, while the other approach learns to transfer the topology from the music latent space to the lyric latent space. A user study with music artists using the system showed that the system was useful not only in lyric composition, but also encouraged the artists to improvise and find new musical expressions. Another user study demonstrated that users preferred the lines generated using the proposed methods to the lines generated by a baseline model.
Towards A Multi-agent System for Online Hate Speech Detection
May 03, 2021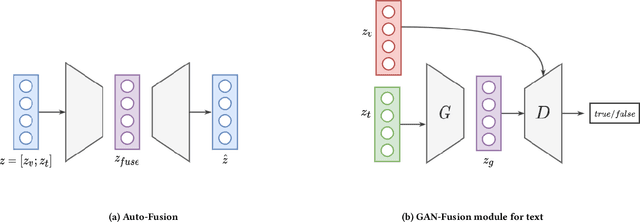
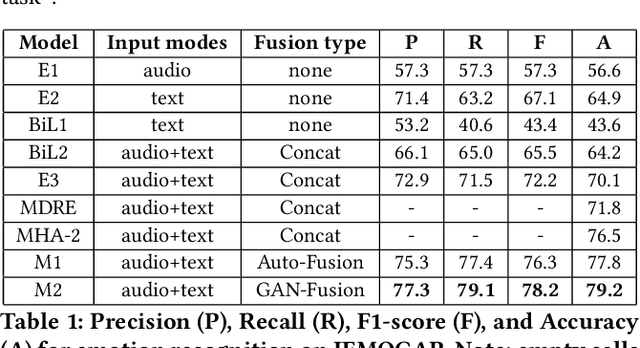
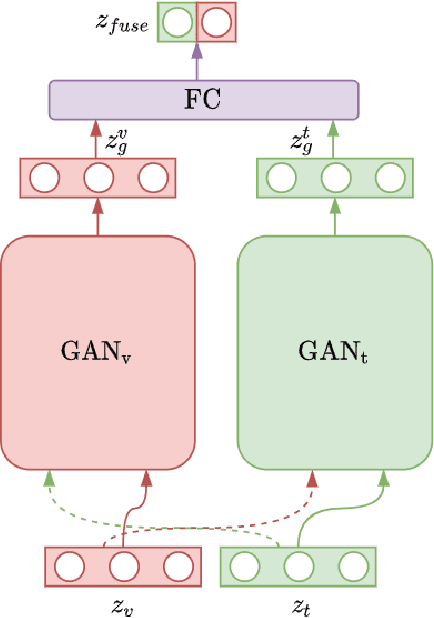
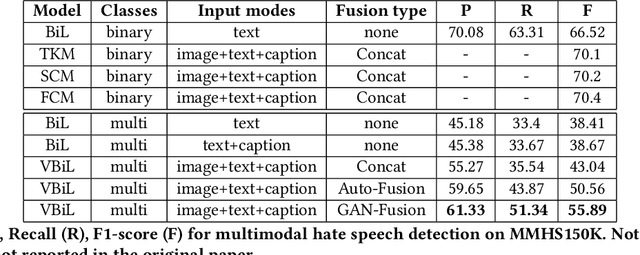
Abstract:This paper envisions a multi-agent system for detecting the presence of hate speech in online social media platforms such as Twitter and Facebook. We introduce a novel framework employing deep learning techniques to coordinate the channels of textual and im-age processing. Our experimental results aim to demonstrate the effectiveness of our methods for classifying online content, training the proposed neural network model to effectively detect hateful instances in the input. We conclude with a discussion of how our system may be of use to provide recommendations to users who are managing online social networks, showcasing the immense potential of intelligent multi-agent systems towards delivering social good.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge