Rafael Pardinas
TapeAgents: a Holistic Framework for Agent Development and Optimization
Dec 11, 2024



Abstract:We present TapeAgents, an agent framework built around a granular, structured log tape of the agent session that also plays the role of the session's resumable state. In TapeAgents we leverage tapes to facilitate all stages of the LLM Agent development lifecycle. The agent reasons by processing the tape and the LLM output to produce new thought and action steps and append them to the tape. The environment then reacts to the agent's actions by likewise appending observation steps to the tape. By virtue of this tape-centred design, TapeAgents can provide AI practitioners with holistic end-to-end support. At the development stage, tapes facilitate session persistence, agent auditing, and step-by-step debugging. Post-deployment, one can reuse tapes for evaluation, fine-tuning, and prompt-tuning; crucially, one can adapt tapes from other agents or use revised historical tapes. In this report, we explain the TapeAgents design in detail. We demonstrate possible applications of TapeAgents with several concrete examples of building monolithic agents and multi-agent teams, of optimizing agent prompts and finetuning the agent's LLM. We present tooling prototypes and report a case study where we use TapeAgents to finetune a Llama-3.1-8B form-filling assistant to perform as well as GPT-4o while being orders of magnitude cheaper. Lastly, our comparative analysis shows that TapeAgents's advantages over prior frameworks stem from our novel design of the LLM agent as a resumable, modular state machine with a structured configuration, that generates granular, structured logs and that can transform these logs into training text -- a unique combination of features absent in previous work.
LOOC: Localize Overlapping Objects with Count Supervision
Jul 03, 2020



Abstract:Acquiring count annotations generally requires less human effort than point-level and bounding box annotations. Thus, we propose the novel problem setup of localizing objects in dense scenes under this weaker supervision. We propose LOOC, a method to Localize Overlapping Objects with Count supervision. We train LOOC by alternating between two stages. In the first stage, LOOC learns to generate pseudo point-level annotations in a semi-supervised manner. In the second stage, LOOC uses a fully-supervised localization method that trains on these pseudo labels. The localization method is used to progressively improve the quality of the pseudo labels. We conducted experiments on popular counting datasets. For localization, LOOC achieves a strong new baseline in the novel problem setup where only count supervision is available. For counting, LOOC outperforms current state-of-the-art methods that only use count as their supervision. Code is available at: https://github.com/ElementAI/looc.
Objects of violence: synthetic data for practical ML in human rights investigations
Apr 01, 2020
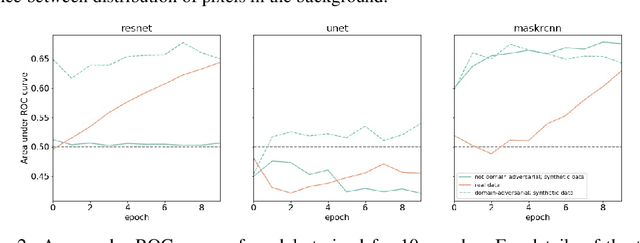
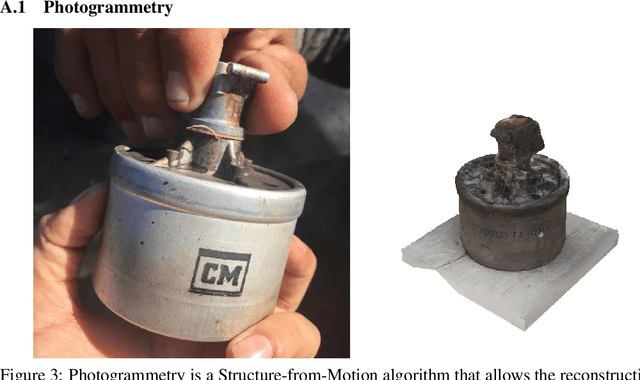

Abstract:We introduce a machine learning workflow to search for, identify, and meaningfully triage videos and images of munitions, weapons, and military equipment, even when limited training data exists for the object of interest. This workflow is designed to expedite the work of OSINT ("open source intelligence") researchers in human rights investigations. It consists of three components: automatic rendering and annotating of synthetic datasets that make up for a lack of training data; training image classifiers from combined sets of photographic and synthetic data; and mtriage, an open source software that orchestrates these classifiers' deployment to triage public domain media, and visualise predictions in a web interface. We show that synthetic data helps to train classifiers more effectively, and that certain approaches yield better results for different architectures. We then demonstrate our workflow in two real-world human rights investigations: the use of the Triple-Chaser tear gas grenade against civilians, and the verification of allegations of military presence in Ukraine in 2014.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge