Daniel Mankowitz
Transformers Meet Directed Graphs
Jan 31, 2023Abstract:Transformers were originally proposed as a sequence-to-sequence model for text but have become vital for a wide range of modalities, including images, audio, video, and undirected graphs. However, transformers for directed graphs are a surprisingly underexplored topic, despite their applicability to ubiquitous domains including source code and logic circuits. In this work, we propose two direction- and structure-aware positional encodings for directed graphs: (1) the eigenvectors of the Magnetic Laplacian - a direction-aware generalization of the combinatorial Laplacian; (2) directional random walk encodings. Empirically, we show that the extra directionality information is useful in various downstream tasks, including correctness testing of sorting networks and source code understanding. Together with a data-flow-centric graph construction, our model outperforms the prior state of the art on the Open Graph Benchmark Code2 relatively by 14.7%.
Local Search for Policy Iteration in Continuous Control
Oct 12, 2020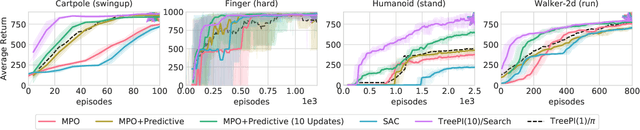
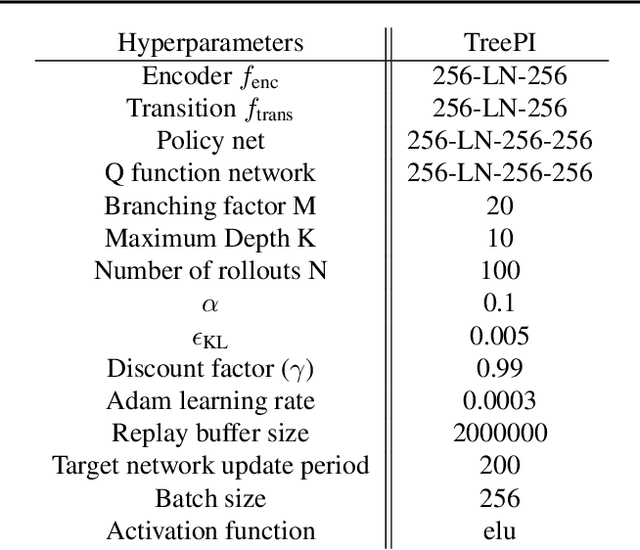
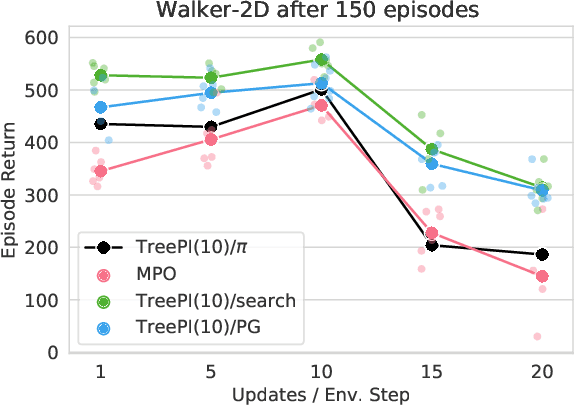
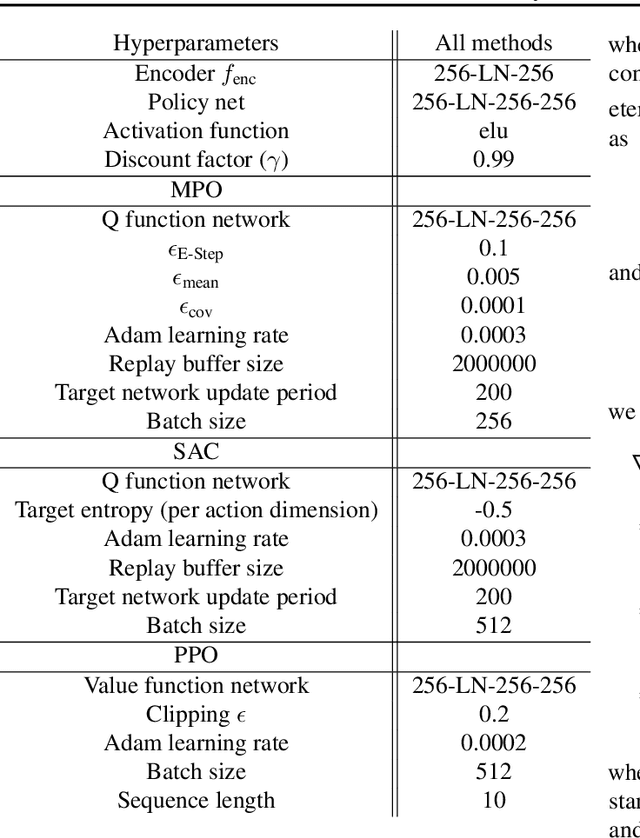
Abstract:We present an algorithm for local, regularized, policy improvement in reinforcement learning (RL) that allows us to formulate model-based and model-free variants in a single framework. Our algorithm can be interpreted as a natural extension of work on KL-regularized RL and introduces a form of tree search for continuous action spaces. We demonstrate that additional computation spent on model-based policy improvement during learning can improve data efficiency, and confirm that model-based policy improvement during action selection can also be beneficial. Quantitatively, our algorithm improves data efficiency on several continuous control benchmarks (when a model is learned in parallel), and it provides significant improvements in wall-clock time in high-dimensional domains (when a ground truth model is available). The unified framework also helps us to better understand the space of model-based and model-free algorithms. In particular, we demonstrate that some benefits attributed to model-based RL can be obtained without a model, simply by utilizing more computation.
RL Unplugged: Benchmarks for Offline Reinforcement Learning
Jul 02, 2020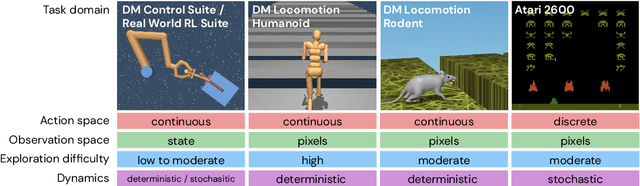
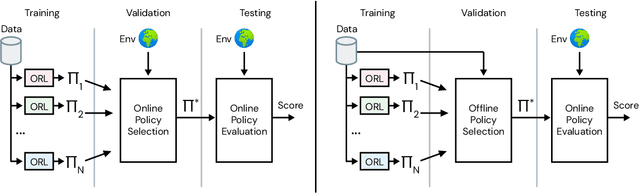
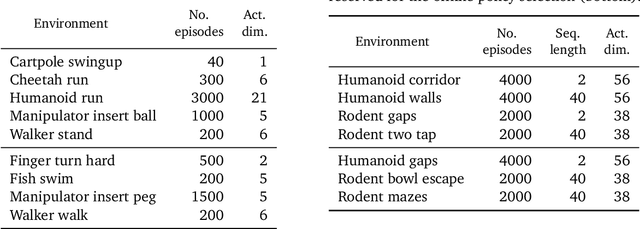
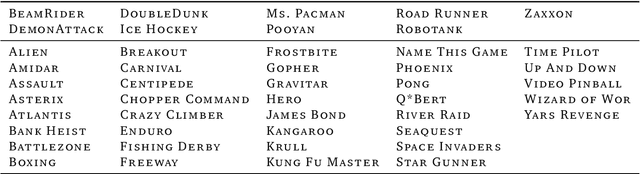
Abstract:Offline methods for reinforcement learning have a potential to help bridge the gap between reinforcement learning research and real-world applications. They make it possible to learn policies from offline datasets, thus overcoming concerns associated with online data collection in the real-world, including cost, safety, or ethical concerns. In this paper, we propose a benchmark called RL Unplugged to evaluate and compare offline RL methods. RL Unplugged includes data from a diverse range of domains including games ({\em e.g.,} Atari benchmark) and simulated motor control problems ({\em e.g.,} DM Control Suite). The datasets include domains that are partially or fully observable, use continuous or discrete actions, and have stochastic vs. deterministic dynamics. We propose detailed evaluation protocols for each domain in RL Unplugged and provide an extensive analysis of supervised learning and offline RL methods using these protocols. We will release data for all our tasks and open-source all algorithms presented in this paper. We hope that our suite of benchmarks will increase the reproducibility of experiments and make it possible to study challenging tasks with a limited computational budget, thus making RL research both more systematic and more accessible across the community. Moving forward, we view RL Unplugged as a living benchmark suite that will evolve and grow with datasets contributed by the research community and ourselves. Our project page is available on github (https://git.io/JJUhd).
A Bayesian Approach to Robust Reinforcement Learning
May 20, 2019



Abstract:Robust Markov Decision Processes (RMDPs) intend to ensure robustness with respect to changing or adversarial system behavior. In this framework, transitions are modeled as arbitrary elements of a known and properly structured uncertainty set and a robust optimal policy can be derived under the worst-case scenario. In this study, we address the issue of learning in RMDPs using a Bayesian approach. We introduce the Uncertainty Robust Bellman Equation (URBE) which encourages safe exploration for adapting the uncertainty set to new observations while preserving robustness. We propose a URBE-based algorithm, DQN-URBE, that scales this method to higher dimensional domains. Our experiments show that the derived URBE-based strategy leads to a better trade-off between less conservative solutions and robustness in the presence of model misspecification. In addition, we show that the DQN-URBE algorithm can adapt significantly faster to changing dynamics online compared to existing robust techniques with fixed uncertainty sets.
Challenges of Real-World Reinforcement Learning
Apr 29, 2019



Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) has proven its worth in a series of artificial domains, and is beginning to show some successes in real-world scenarios. However, much of the research advances in RL are often hard to leverage in real-world systems due to a series of assumptions that are rarely satisfied in practice. We present a set of nine unique challenges that must be addressed to productionize RL to real world problems. For each of these challenges, we specify the exact meaning of the challenge, present some approaches from the literature, and specify some metrics for evaluating that challenge. An approach that addresses all nine challenges would be applicable to a large number of real world problems. We also present an example domain that has been modified to present these challenges as a testbed for practical RL research.
Transfer in Deep Reinforcement Learning Using Successor Features and Generalised Policy Improvement
Jan 30, 2019



Abstract:The ability to transfer skills across tasks has the potential to scale up reinforcement learning (RL) agents to environments currently out of reach. Recently, a framework based on two ideas, successor features (SFs) and generalised policy improvement (GPI), has been introduced as a principled way of transferring skills. In this paper we extend the SFs & GPI framework in two ways. One of the basic assumptions underlying the original formulation of SFs & GPI is that rewards for all tasks of interest can be computed as linear combinations of a fixed set of features. We relax this constraint and show that the theoretical guarantees supporting the framework can be extended to any set of tasks that only differ in the reward function. Our second contribution is to show that one can use the reward functions themselves as features for future tasks, without any loss of expressiveness, thus removing the need to specify a set of features beforehand. This makes it possible to combine SFs & GPI with deep learning in a more stable way. We empirically verify this claim on a complex 3D environment where observations are images from a first-person perspective. We show that the transfer promoted by SFs & GPI leads to very good policies on unseen tasks almost instantaneously. We also describe how to learn policies specialised to the new tasks in a way that allows them to be added to the agent's set of skills, and thus be reused in the future.
Universal Successor Features Approximators
Dec 18, 2018



Abstract:The ability of a reinforcement learning (RL) agent to learn about many reward functions at the same time has many potential benefits, such as the decomposition of complex tasks into simpler ones, the exchange of information between tasks, and the reuse of skills. We focus on one aspect in particular, namely the ability to generalise to unseen tasks. Parametric generalisation relies on the interpolation power of a function approximator that is given the task description as input; one of its most common form are universal value function approximators (UVFAs). Another way to generalise to new tasks is to exploit structure in the RL problem itself. Generalised policy improvement (GPI) combines solutions of previous tasks into a policy for the unseen task; this relies on instantaneous policy evaluation of old policies under the new reward function, which is made possible through successor features (SFs). Our proposed universal successor features approximators (USFAs) combine the advantages of all of these, namely the scalability of UVFAs, the instant inference of SFs, and the strong generalisation of GPI. We discuss the challenges involved in training a USFA, its generalisation properties and demonstrate its practical benefits and transfer abilities on a large-scale domain in which the agent has to navigate in a first-person perspective three-dimensional environment.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge