Augustin Žídek
A scalable and real-time neural decoder for topological quantum codes
Dec 08, 2025Abstract:Fault-tolerant quantum computing will require error rates far below those achievable with physical qubits. Quantum error correction (QEC) bridges this gap, but depends on decoders being simultaneously fast, accurate, and scalable. This combination of requirements has not yet been met by a machine-learning decoder, nor by any decoder for promising resource-efficient codes such as the colour code. Here we introduce AlphaQubit 2, a neural-network decoder that achieves near-optimal logical error rates for both surface and colour codes at large scales under realistic noise. For the colour code, it is orders of magnitude faster than other high-accuracy decoders. For the surface code, we demonstrate real-time decoding faster than 1 microsecond per cycle up to distance 11 on current commercial accelerators with better accuracy than leading real-time decoders. These results support the practical application of a wider class of promising QEC codes, and establish a credible path towards high-accuracy, real-time neural decoding at the scales required for fault-tolerant quantum computation.
Transfer in Deep Reinforcement Learning Using Successor Features and Generalised Policy Improvement
Jan 30, 2019



Abstract:The ability to transfer skills across tasks has the potential to scale up reinforcement learning (RL) agents to environments currently out of reach. Recently, a framework based on two ideas, successor features (SFs) and generalised policy improvement (GPI), has been introduced as a principled way of transferring skills. In this paper we extend the SFs & GPI framework in two ways. One of the basic assumptions underlying the original formulation of SFs & GPI is that rewards for all tasks of interest can be computed as linear combinations of a fixed set of features. We relax this constraint and show that the theoretical guarantees supporting the framework can be extended to any set of tasks that only differ in the reward function. Our second contribution is to show that one can use the reward functions themselves as features for future tasks, without any loss of expressiveness, thus removing the need to specify a set of features beforehand. This makes it possible to combine SFs & GPI with deep learning in a more stable way. We empirically verify this claim on a complex 3D environment where observations are images from a first-person perspective. We show that the transfer promoted by SFs & GPI leads to very good policies on unseen tasks almost instantaneously. We also describe how to learn policies specialised to the new tasks in a way that allows them to be added to the agent's set of skills, and thus be reused in the future.
Unicorn: Continual Learning with a Universal, Off-policy Agent
Jul 03, 2018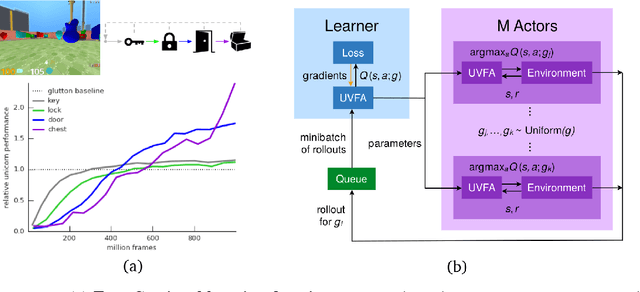
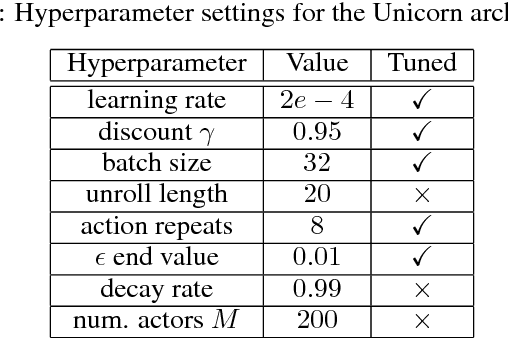
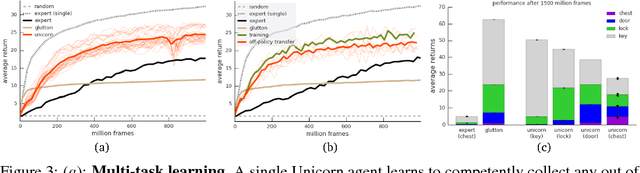
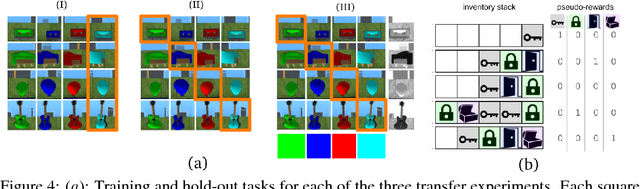
Abstract:Some real-world domains are best characterized as a single task, but for others this perspective is limiting. Instead, some tasks continually grow in complexity, in tandem with the agent's competence. In continual learning, also referred to as lifelong learning, there are no explicit task boundaries or curricula. As learning agents have become more powerful, continual learning remains one of the frontiers that has resisted quick progress. To test continual learning capabilities we consider a challenging 3D domain with an implicit sequence of tasks and sparse rewards. We propose a novel agent architecture called Unicorn, which demonstrates strong continual learning and outperforms several baseline agents on the proposed domain. The agent achieves this by jointly representing and learning multiple policies efficiently, using a parallel off-policy learning setup.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge