Edward Lockhart
Mastering the Game of Stratego with Model-Free Multiagent Reinforcement Learning
Jun 30, 2022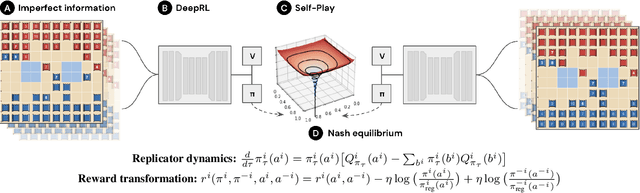
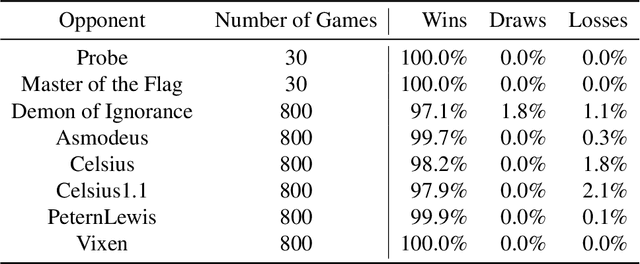
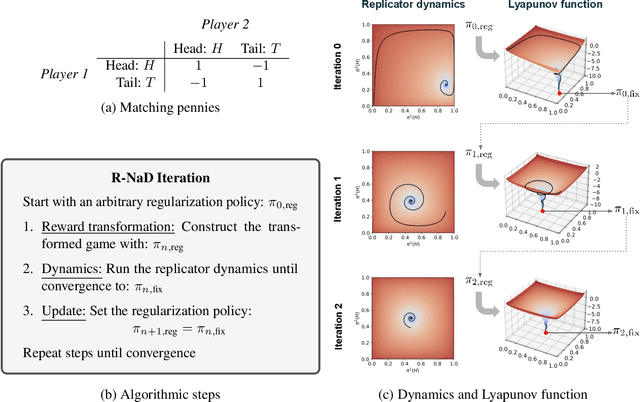

Abstract:We introduce DeepNash, an autonomous agent capable of learning to play the imperfect information game Stratego from scratch, up to a human expert level. Stratego is one of the few iconic board games that Artificial Intelligence (AI) has not yet mastered. This popular game has an enormous game tree on the order of $10^{535}$ nodes, i.e., $10^{175}$ times larger than that of Go. It has the additional complexity of requiring decision-making under imperfect information, similar to Texas hold'em poker, which has a significantly smaller game tree (on the order of $10^{164}$ nodes). Decisions in Stratego are made over a large number of discrete actions with no obvious link between action and outcome. Episodes are long, with often hundreds of moves before a player wins, and situations in Stratego can not easily be broken down into manageably-sized sub-problems as in poker. For these reasons, Stratego has been a grand challenge for the field of AI for decades, and existing AI methods barely reach an amateur level of play. DeepNash uses a game-theoretic, model-free deep reinforcement learning method, without search, that learns to master Stratego via self-play. The Regularised Nash Dynamics (R-NaD) algorithm, a key component of DeepNash, converges to an approximate Nash equilibrium, instead of 'cycling' around it, by directly modifying the underlying multi-agent learning dynamics. DeepNash beats existing state-of-the-art AI methods in Stratego and achieved a yearly (2022) and all-time top-3 rank on the Gravon games platform, competing with human expert players.
Solving Common-Payoff Games with Approximate Policy Iteration
Jan 11, 2021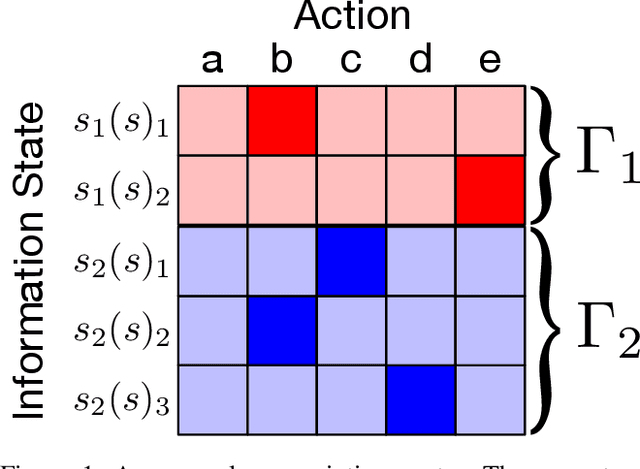
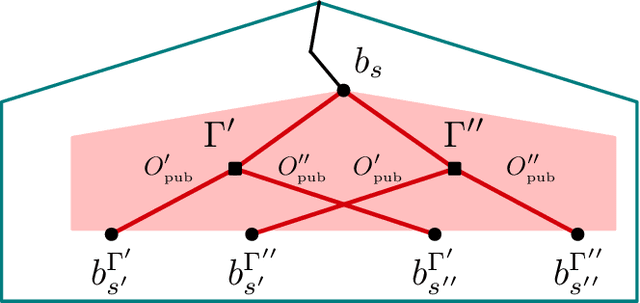
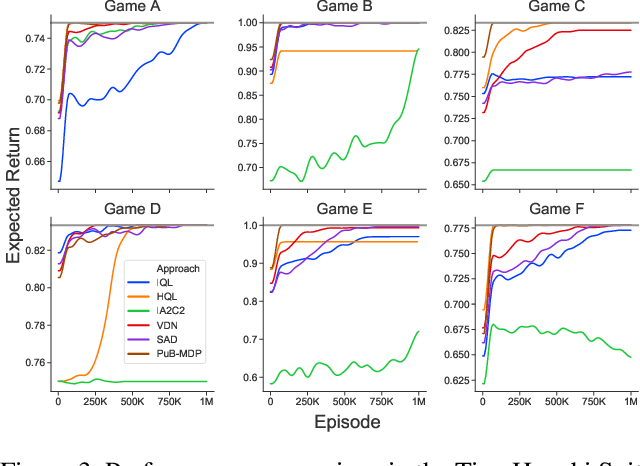
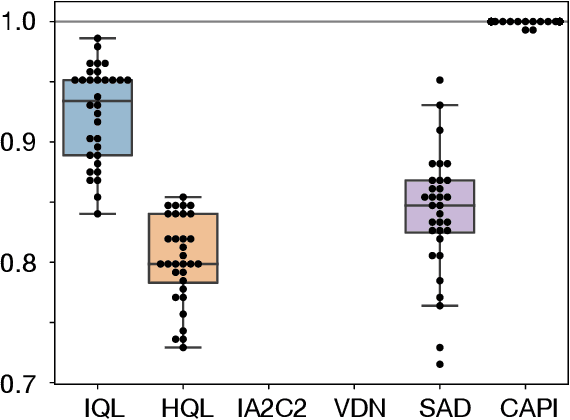
Abstract:For artificially intelligent learning systems to have widespread applicability in real-world settings, it is important that they be able to operate decentrally. Unfortunately, decentralized control is difficult -- computing even an epsilon-optimal joint policy is a NEXP complete problem. Nevertheless, a recently rediscovered insight -- that a team of agents can coordinate via common knowledge -- has given rise to algorithms capable of finding optimal joint policies in small common-payoff games. The Bayesian action decoder (BAD) leverages this insight and deep reinforcement learning to scale to games as large as two-player Hanabi. However, the approximations it uses to do so prevent it from discovering optimal joint policies even in games small enough to brute force optimal solutions. This work proposes CAPI, a novel algorithm which, like BAD, combines common knowledge with deep reinforcement learning. However, unlike BAD, CAPI prioritizes the propensity to discover optimal joint policies over scalability. While this choice precludes CAPI from scaling to games as large as Hanabi, empirical results demonstrate that, on the games to which CAPI does scale, it is capable of discovering optimal joint policies even when other modern multi-agent reinforcement learning algorithms are unable to do so. Code is available at https://github.com/ssokota/capi .
Human-Agent Cooperation in Bridge Bidding
Nov 28, 2020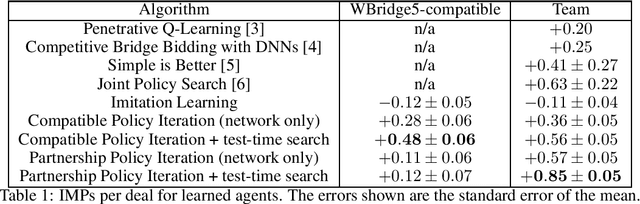
Abstract:We introduce a human-compatible reinforcement-learning approach to a cooperative game, making use of a third-party hand-coded human-compatible bot to generate initial training data and to perform initial evaluation. Our learning approach consists of imitation learning, search, and policy iteration. Our trained agents achieve a new state-of-the-art for bridge bidding in three settings: an agent playing in partnership with a copy of itself; an agent partnering a pre-existing bot; and an agent partnering a human player.
Approximate exploitability: Learning a best response in large games
Apr 20, 2020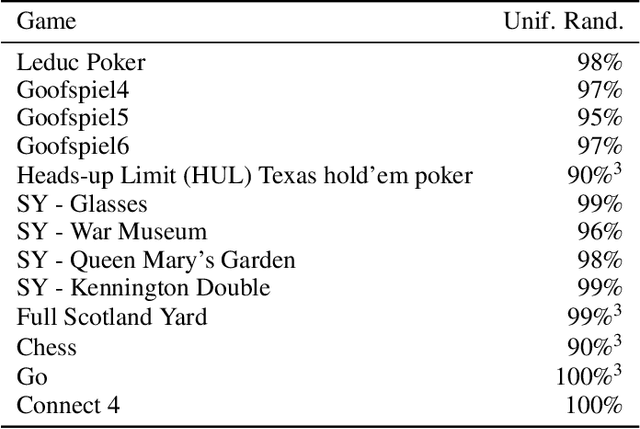
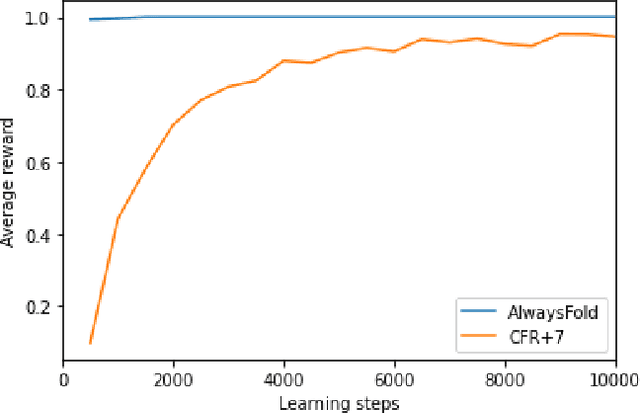

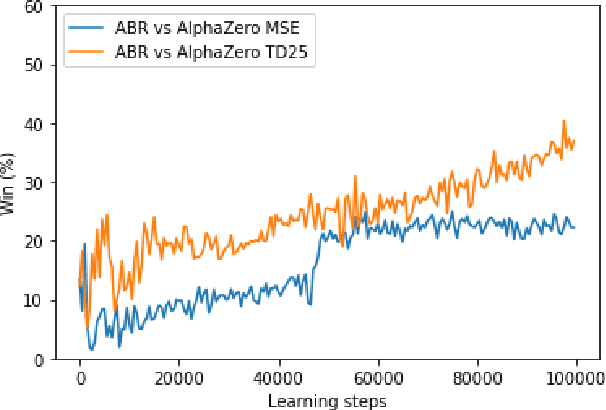
Abstract:A common metric in games of imperfect information is exploitability, i.e. the performance of a policy against the worst-case opponent. This metric has many nice properties, but is intractable to compute in large games as it requires a full search of the game tree to calculate a best response to the given policy. We introduce a new metric, approximate exploitability, that calculates an analogous metric to exploitability using an approximate best response. This method scales to large games with tractable belief spaces. We focus only on the two-player, zero-sum case. Additionally, we provide empirical results for a specific instance of the method, demonstrating that it can effectively exploit agents in large games. We demonstrate that our method converges to exploitability in the tabular setting and the function approximation setting for small games, and demonstrate that it can consistently find exploits for weak policies in large games, showing results on Chess, Go, Heads-up No Limit Texas Hold'em, and other games.
Mastering Atari, Go, Chess and Shogi by Planning with a Learned Model
Nov 19, 2019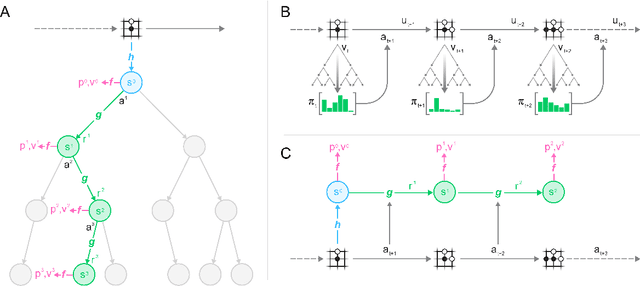
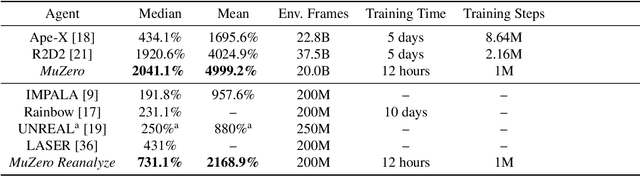
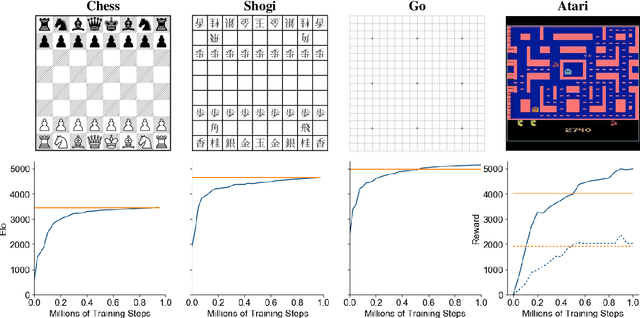
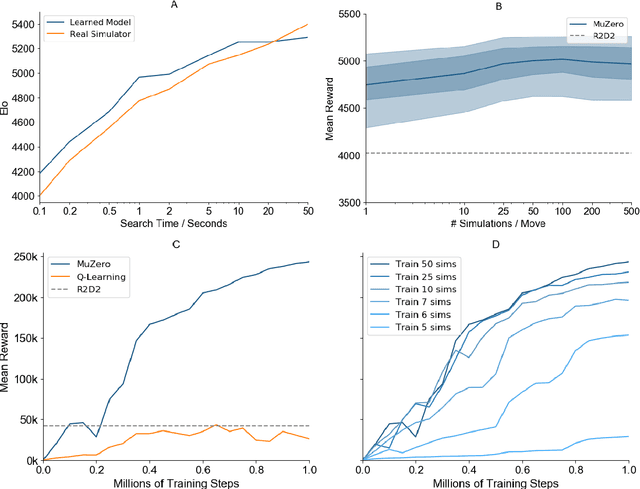
Abstract:Constructing agents with planning capabilities has long been one of the main challenges in the pursuit of artificial intelligence. Tree-based planning methods have enjoyed huge success in challenging domains, such as chess and Go, where a perfect simulator is available. However, in real-world problems the dynamics governing the environment are often complex and unknown. In this work we present the MuZero algorithm which, by combining a tree-based search with a learned model, achieves superhuman performance in a range of challenging and visually complex domains, without any knowledge of their underlying dynamics. MuZero learns a model that, when applied iteratively, predicts the quantities most directly relevant to planning: the reward, the action-selection policy, and the value function. When evaluated on 57 different Atari games - the canonical video game environment for testing AI techniques, in which model-based planning approaches have historically struggled - our new algorithm achieved a new state of the art. When evaluated on Go, chess and shogi, without any knowledge of the game rules, MuZero matched the superhuman performance of the AlphaZero algorithm that was supplied with the game rules.
OpenSpiel: A Framework for Reinforcement Learning in Games
Oct 10, 2019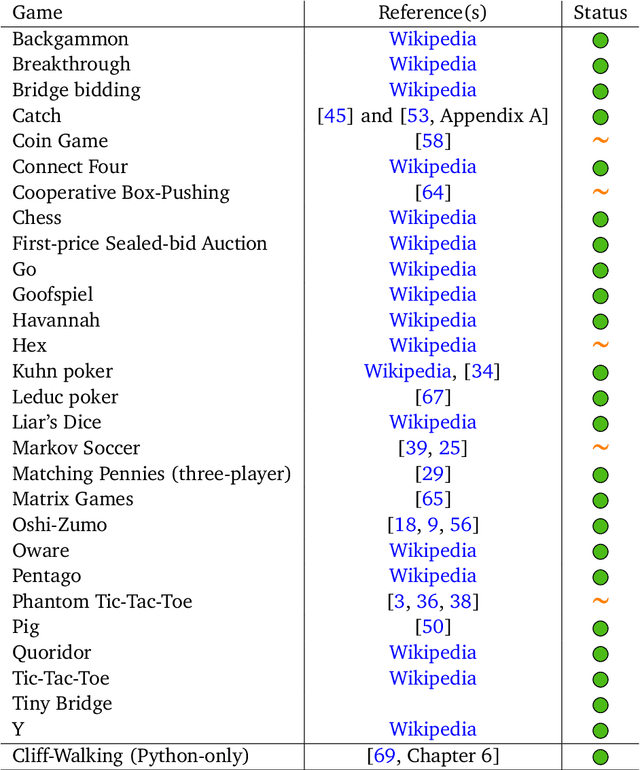
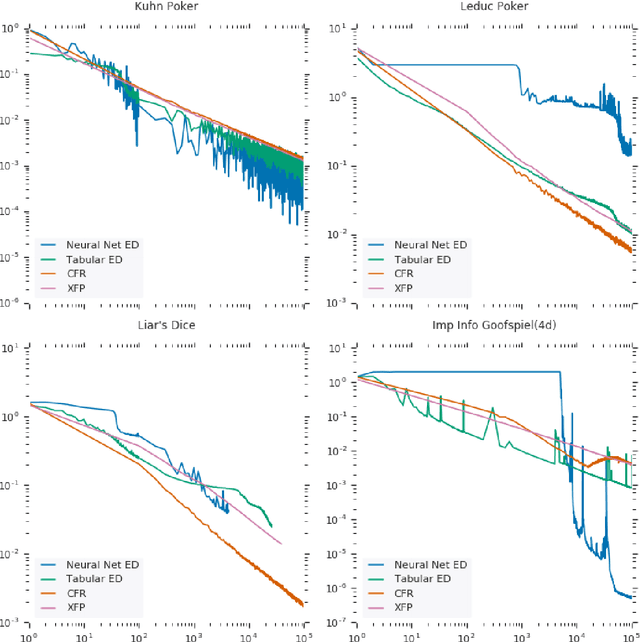
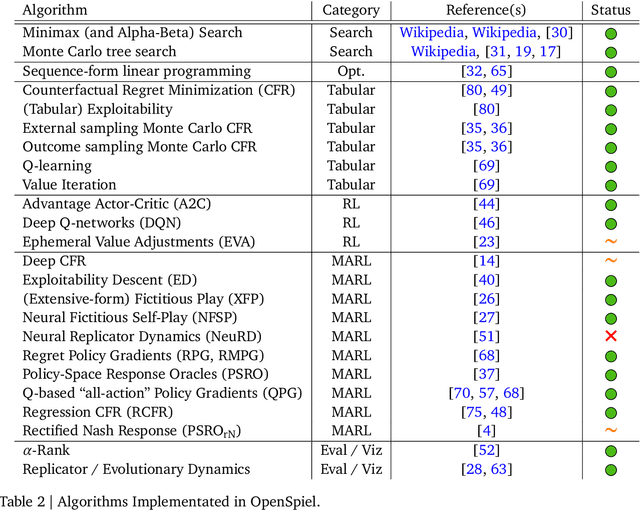
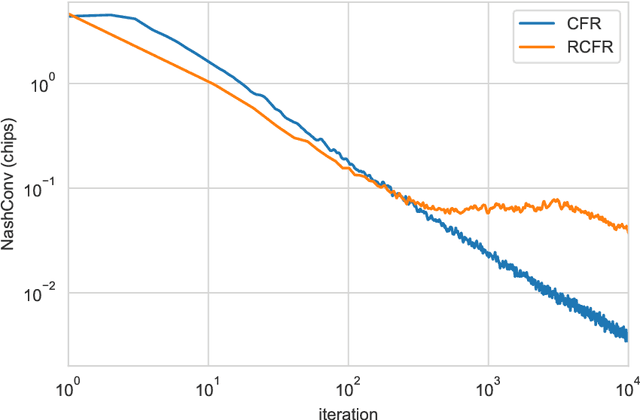
Abstract:OpenSpiel is a collection of environments and algorithms for research in general reinforcement learning and search/planning in games. OpenSpiel supports n-player (single- and multi- agent) zero-sum, cooperative and general-sum, one-shot and sequential, strictly turn-taking and simultaneous-move, perfect and imperfect information games, as well as traditional multiagent environments such as (partially- and fully- observable) grid worlds and social dilemmas. OpenSpiel also includes tools to analyze learning dynamics and other common evaluation metrics. This document serves both as an overview of the code base and an introduction to the terminology, core concepts, and algorithms across the fields of reinforcement learning, computational game theory, and search.
Computing Approximate Equilibria in Sequential Adversarial Games by Exploitability Descent
Mar 21, 2019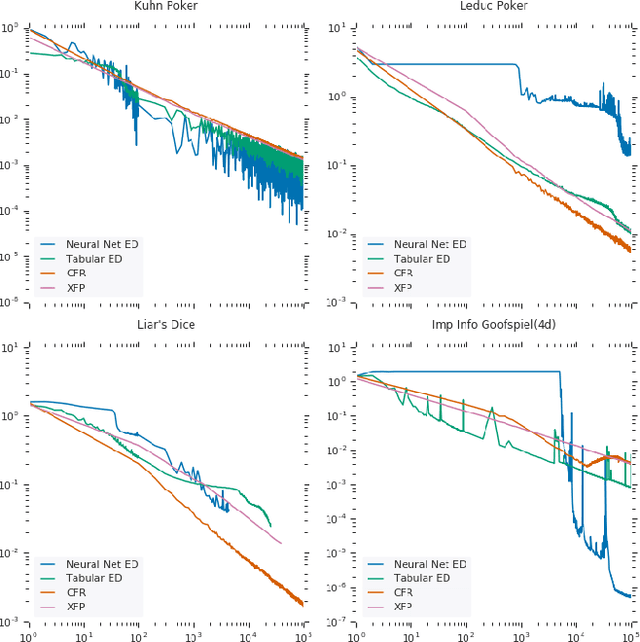
Abstract:In this paper, we present exploitability descent, a new algorithm to compute approximate equilibria in two-player zero-sum extensive-form games with imperfect information, by direct policy optimization against worst-case opponents. We prove that when following this optimization, the exploitability of a player's strategy converges asymptotically to zero, and hence when both players employ this optimization, the joint policies converge to a Nash equilibrium. Unlike fictitious play (XFP) and counterfactual regret minimization (CFR), our convergence result pertains to the policies being optimized rather than the average policies. Our experiments demonstrate convergence rates comparable to XFP and CFR in four benchmark games in the tabular case. Using function approximation, we find that our algorithm outperforms the tabular version in two of the games, which, to the best of our knowledge, is the first such result in imperfect information games among this class of algorithms.
Consistent Jumpy Predictions for Videos and Scenes
Oct 02, 2018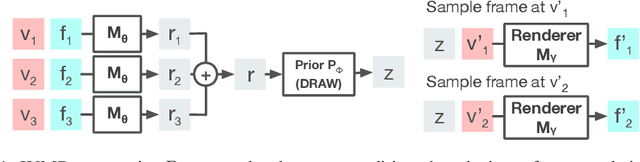
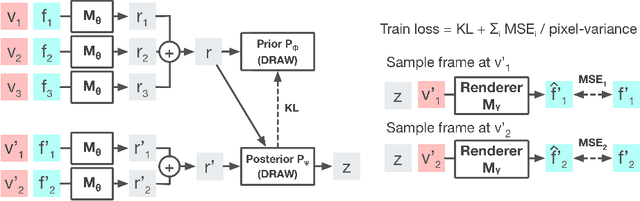

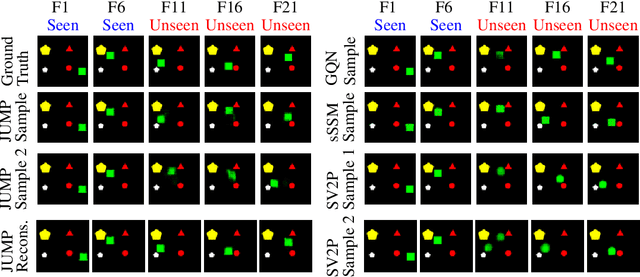
Abstract:Stochastic video prediction models take in a sequence of image frames, and generate a sequence of consecutive future image frames. These models typically generate future frames in an autoregressive fashion, which is slow and requires the input and output frames to be consecutive. We introduce a model that overcomes these drawbacks by generating a latent representation from an arbitrary set of frames that can then be used to simultaneously and efficiently sample temporally consistent frames at arbitrary time-points. For example, our model can "jump" and directly sample frames at the end of the video, without sampling intermediate frames. Synthetic video evaluations confirm substantial gains in speed and functionality without loss in fidelity. We also apply our framework to a 3D scene reconstruction dataset. Here, our model is conditioned on camera location and can sample consistent sets of images for what an occluded region of a 3D scene might look like, even if there are multiple possibilities for what that region might contain. Reconstructions and videos are available at https://bit.ly/2O4Pc4R.
Relational Deep Reinforcement Learning
Jun 28, 2018
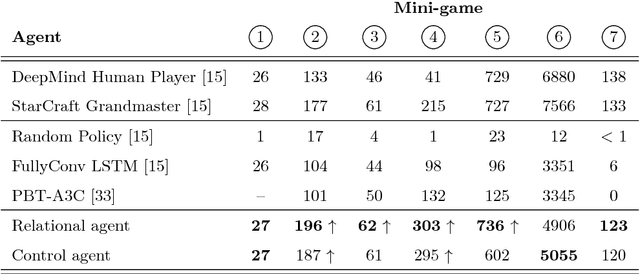
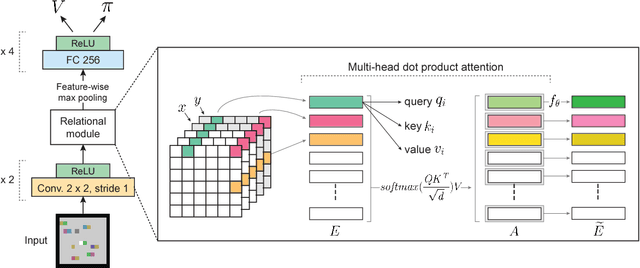
Abstract:We introduce an approach for deep reinforcement learning (RL) that improves upon the efficiency, generalization capacity, and interpretability of conventional approaches through structured perception and relational reasoning. It uses self-attention to iteratively reason about the relations between entities in a scene and to guide a model-free policy. Our results show that in a novel navigation and planning task called Box-World, our agent finds interpretable solutions that improve upon baselines in terms of sample complexity, ability to generalize to more complex scenes than experienced during training, and overall performance. In the StarCraft II Learning Environment, our agent achieves state-of-the-art performance on six mini-games -- surpassing human grandmaster performance on four. By considering architectural inductive biases, our work opens new directions for overcoming important, but stubborn, challenges in deep RL.
Efficient Neural Audio Synthesis
Jun 25, 2018
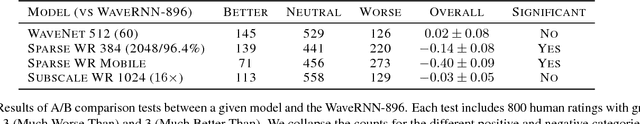
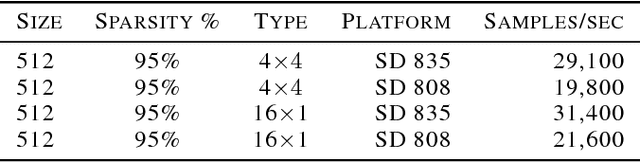
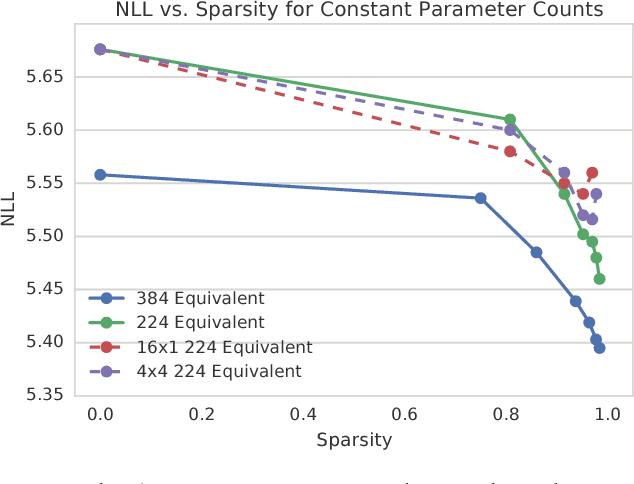
Abstract:Sequential models achieve state-of-the-art results in audio, visual and textual domains with respect to both estimating the data distribution and generating high-quality samples. Efficient sampling for this class of models has however remained an elusive problem. With a focus on text-to-speech synthesis, we describe a set of general techniques for reducing sampling time while maintaining high output quality. We first describe a single-layer recurrent neural network, the WaveRNN, with a dual softmax layer that matches the quality of the state-of-the-art WaveNet model. The compact form of the network makes it possible to generate 24kHz 16-bit audio 4x faster than real time on a GPU. Second, we apply a weight pruning technique to reduce the number of weights in the WaveRNN. We find that, for a constant number of parameters, large sparse networks perform better than small dense networks and this relationship holds for sparsity levels beyond 96%. The small number of weights in a Sparse WaveRNN makes it possible to sample high-fidelity audio on a mobile CPU in real time. Finally, we propose a new generation scheme based on subscaling that folds a long sequence into a batch of shorter sequences and allows one to generate multiple samples at once. The Subscale WaveRNN produces 16 samples per step without loss of quality and offers an orthogonal method for increasing sampling efficiency.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge