Koray Kavukcuoglu
Dima
Gemma 3 Technical Report
Mar 25, 2025Abstract:We introduce Gemma 3, a multimodal addition to the Gemma family of lightweight open models, ranging in scale from 1 to 27 billion parameters. This version introduces vision understanding abilities, a wider coverage of languages and longer context - at least 128K tokens. We also change the architecture of the model to reduce the KV-cache memory that tends to explode with long context. This is achieved by increasing the ratio of local to global attention layers, and keeping the span on local attention short. The Gemma 3 models are trained with distillation and achieve superior performance to Gemma 2 for both pre-trained and instruction finetuned versions. In particular, our novel post-training recipe significantly improves the math, chat, instruction-following and multilingual abilities, making Gemma3-4B-IT competitive with Gemma2-27B-IT and Gemma3-27B-IT comparable to Gemini-1.5-Pro across benchmarks. We release all our models to the community.
Imagen 3
Aug 13, 2024Abstract:We introduce Imagen 3, a latent diffusion model that generates high quality images from text prompts. We describe our quality and responsibility evaluations. Imagen 3 is preferred over other state-of-the-art (SOTA) models at the time of evaluation. In addition, we discuss issues around safety and representation, as well as methods we used to minimize the potential harm of our models.
Gemma 2: Improving Open Language Models at a Practical Size
Aug 02, 2024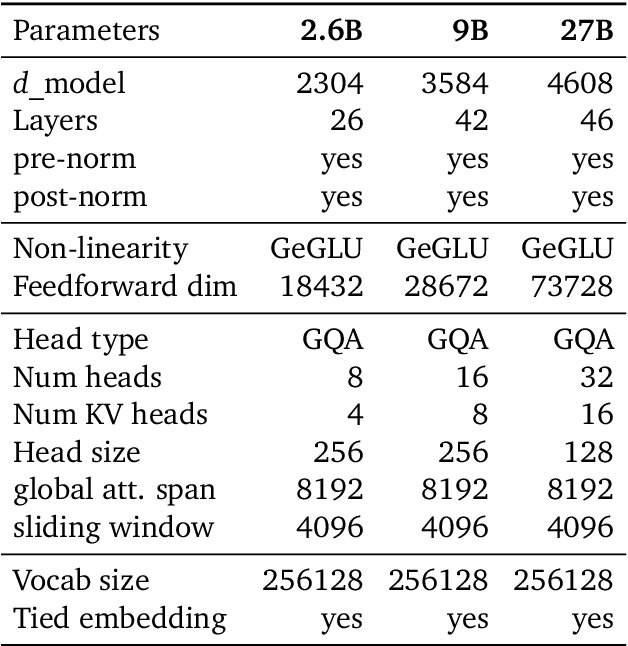
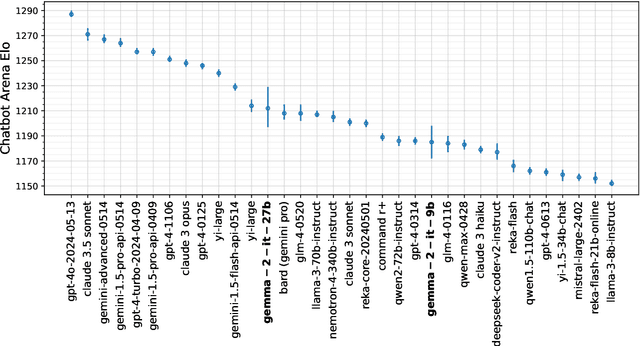
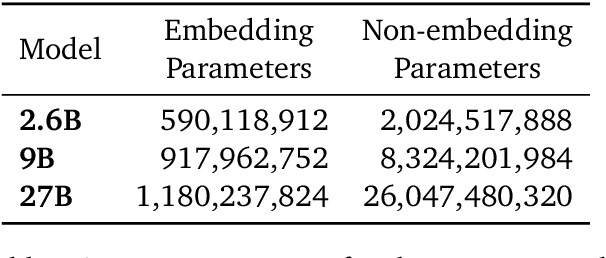
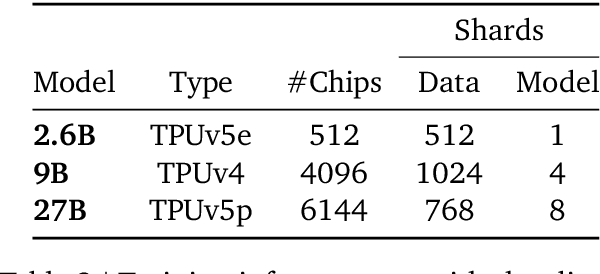
Abstract:In this work, we introduce Gemma 2, a new addition to the Gemma family of lightweight, state-of-the-art open models, ranging in scale from 2 billion to 27 billion parameters. In this new version, we apply several known technical modifications to the Transformer architecture, such as interleaving local-global attentions (Beltagy et al., 2020a) and group-query attention (Ainslie et al., 2023). We also train the 2B and 9B models with knowledge distillation (Hinton et al., 2015) instead of next token prediction. The resulting models deliver the best performance for their size, and even offer competitive alternatives to models that are 2-3 times bigger. We release all our models to the community.
Capabilities of Gemini Models in Medicine
May 01, 2024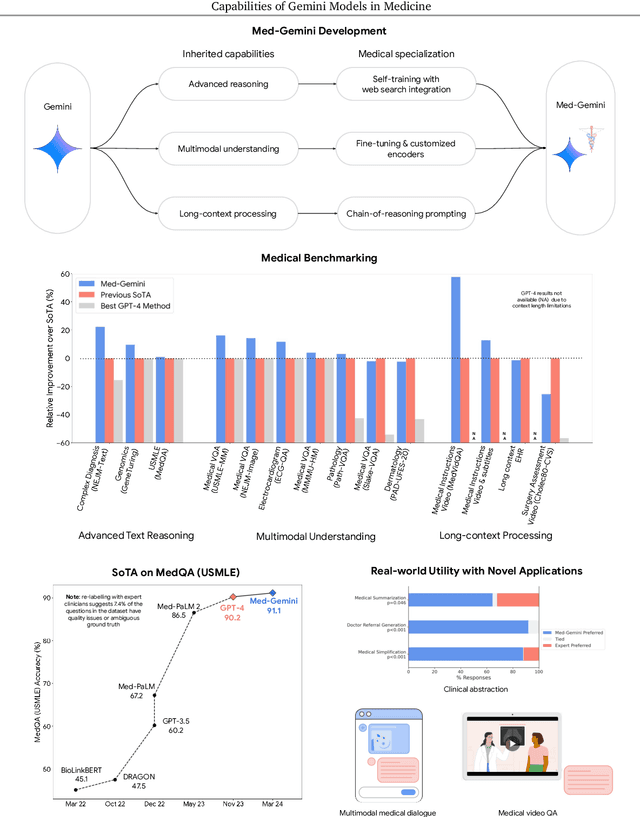
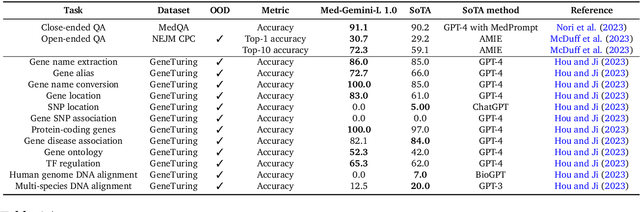
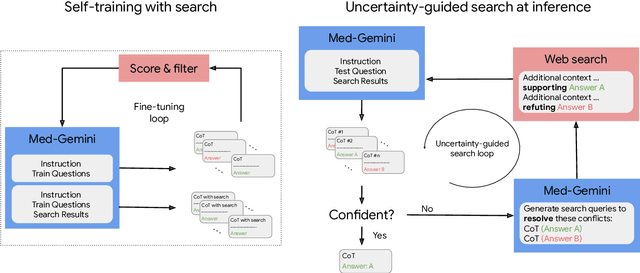
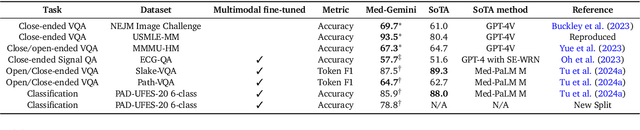
Abstract:Excellence in a wide variety of medical applications poses considerable challenges for AI, requiring advanced reasoning, access to up-to-date medical knowledge and understanding of complex multimodal data. Gemini models, with strong general capabilities in multimodal and long-context reasoning, offer exciting possibilities in medicine. Building on these core strengths of Gemini, we introduce Med-Gemini, a family of highly capable multimodal models that are specialized in medicine with the ability to seamlessly use web search, and that can be efficiently tailored to novel modalities using custom encoders. We evaluate Med-Gemini on 14 medical benchmarks, establishing new state-of-the-art (SoTA) performance on 10 of them, and surpass the GPT-4 model family on every benchmark where a direct comparison is viable, often by a wide margin. On the popular MedQA (USMLE) benchmark, our best-performing Med-Gemini model achieves SoTA performance of 91.1% accuracy, using a novel uncertainty-guided search strategy. On 7 multimodal benchmarks including NEJM Image Challenges and MMMU (health & medicine), Med-Gemini improves over GPT-4V by an average relative margin of 44.5%. We demonstrate the effectiveness of Med-Gemini's long-context capabilities through SoTA performance on a needle-in-a-haystack retrieval task from long de-identified health records and medical video question answering, surpassing prior bespoke methods using only in-context learning. Finally, Med-Gemini's performance suggests real-world utility by surpassing human experts on tasks such as medical text summarization, alongside demonstrations of promising potential for multimodal medical dialogue, medical research and education. Taken together, our results offer compelling evidence for Med-Gemini's potential, although further rigorous evaluation will be crucial before real-world deployment in this safety-critical domain.
RecurrentGemma: Moving Past Transformers for Efficient Open Language Models
Apr 11, 2024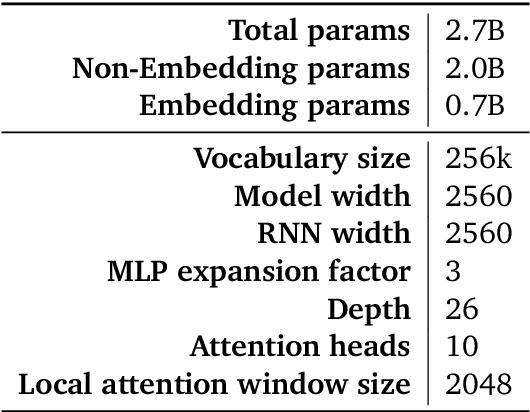
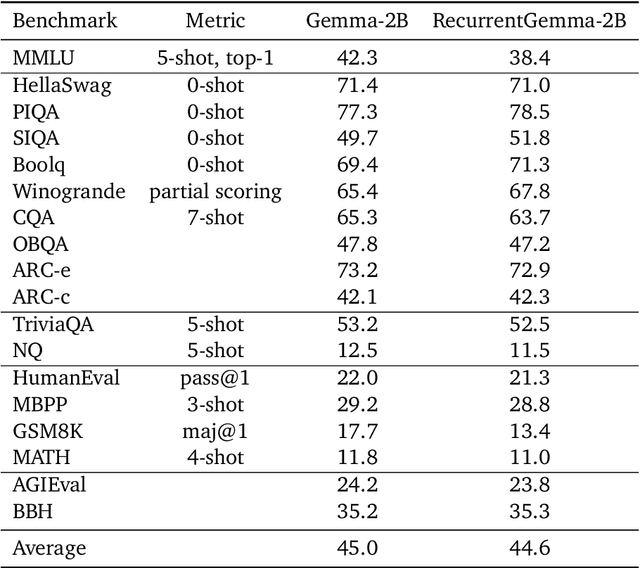

Abstract:We introduce RecurrentGemma, an open language model which uses Google's novel Griffin architecture. Griffin combines linear recurrences with local attention to achieve excellent performance on language. It has a fixed-sized state, which reduces memory use and enables efficient inference on long sequences. We provide a pre-trained model with 2B non-embedding parameters, and an instruction tuned variant. Both models achieve comparable performance to Gemma-2B despite being trained on fewer tokens.
Gemma: Open Models Based on Gemini Research and Technology
Mar 13, 2024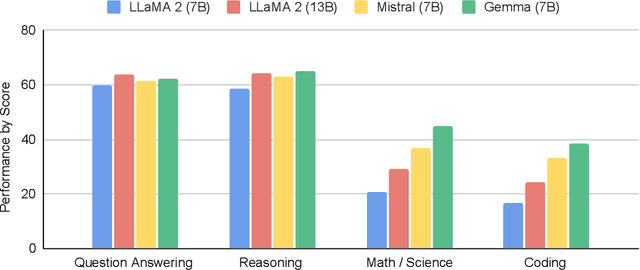
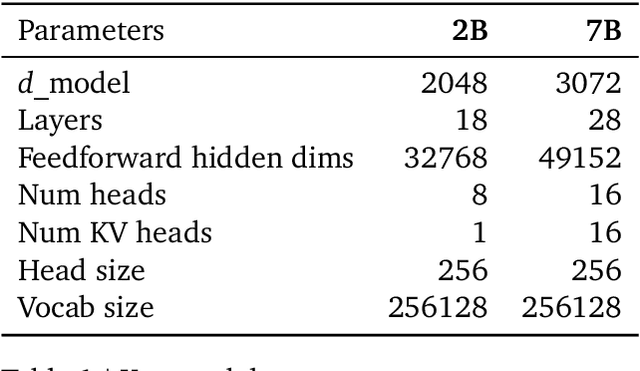
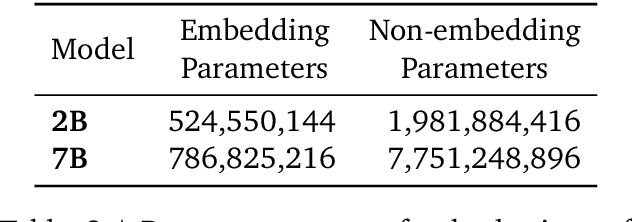
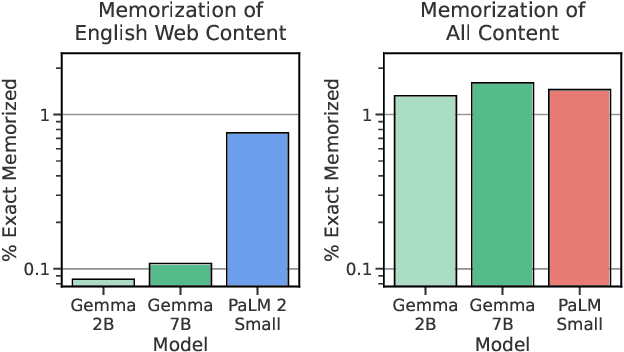
Abstract:This work introduces Gemma, a family of lightweight, state-of-the art open models built from the research and technology used to create Gemini models. Gemma models demonstrate strong performance across academic benchmarks for language understanding, reasoning, and safety. We release two sizes of models (2 billion and 7 billion parameters), and provide both pretrained and fine-tuned checkpoints. Gemma outperforms similarly sized open models on 11 out of 18 text-based tasks, and we present comprehensive evaluations of safety and responsibility aspects of the models, alongside a detailed description of model development. We believe the responsible release of LLMs is critical for improving the safety of frontier models, and for enabling the next wave of LLM innovations.
Gemini 1.5: Unlocking multimodal understanding across millions of tokens of context
Mar 08, 2024Abstract:In this report, we present the latest model of the Gemini family, Gemini 1.5 Pro, a highly compute-efficient multimodal mixture-of-experts model capable of recalling and reasoning over fine-grained information from millions of tokens of context, including multiple long documents and hours of video and audio. Gemini 1.5 Pro achieves near-perfect recall on long-context retrieval tasks across modalities, improves the state-of-the-art in long-document QA, long-video QA and long-context ASR, and matches or surpasses Gemini 1.0 Ultra's state-of-the-art performance across a broad set of benchmarks. Studying the limits of Gemini 1.5 Pro's long-context ability, we find continued improvement in next-token prediction and near-perfect retrieval (>99%) up to at least 10M tokens, a generational leap over existing models such as Claude 2.1 (200k) and GPT-4 Turbo (128k). Finally, we highlight surprising new capabilities of large language models at the frontier; when given a grammar manual for Kalamang, a language with fewer than 200 speakers worldwide, the model learns to translate English to Kalamang at a similar level to a person who learned from the same content.
Gemini: A Family of Highly Capable Multimodal Models
Dec 19, 2023Abstract:This report introduces a new family of multimodal models, Gemini, that exhibit remarkable capabilities across image, audio, video, and text understanding. The Gemini family consists of Ultra, Pro, and Nano sizes, suitable for applications ranging from complex reasoning tasks to on-device memory-constrained use-cases. Evaluation on a broad range of benchmarks shows that our most-capable Gemini Ultra model advances the state of the art in 30 of 32 of these benchmarks - notably being the first model to achieve human-expert performance on the well-studied exam benchmark MMLU, and improving the state of the art in every one of the 20 multimodal benchmarks we examined. We believe that the new capabilities of Gemini models in cross-modal reasoning and language understanding will enable a wide variety of use cases and we discuss our approach toward deploying them responsibly to users.
Improving alignment of dialogue agents via targeted human judgements
Sep 28, 2022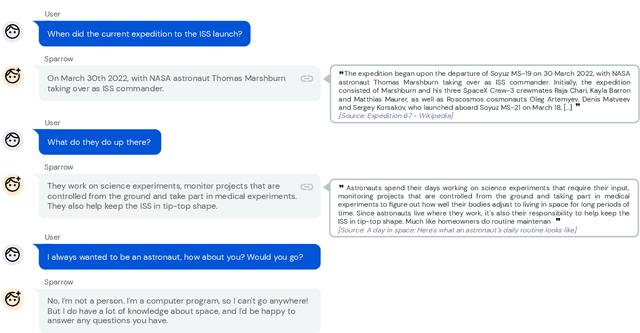

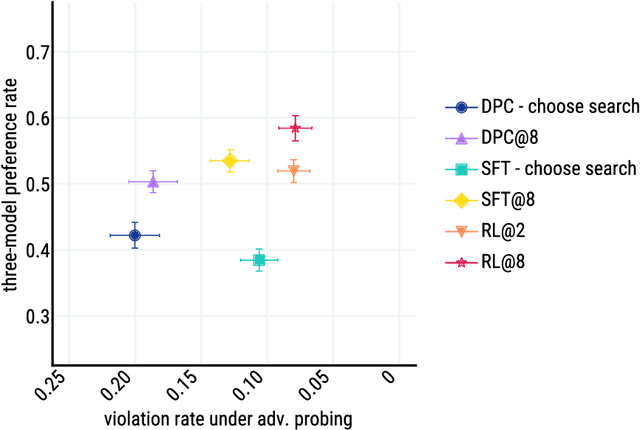
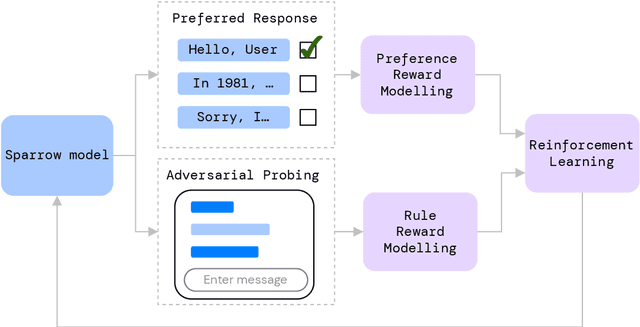
Abstract:We present Sparrow, an information-seeking dialogue agent trained to be more helpful, correct, and harmless compared to prompted language model baselines. We use reinforcement learning from human feedback to train our models with two new additions to help human raters judge agent behaviour. First, to make our agent more helpful and harmless, we break down the requirements for good dialogue into natural language rules the agent should follow, and ask raters about each rule separately. We demonstrate that this breakdown enables us to collect more targeted human judgements of agent behaviour and allows for more efficient rule-conditional reward models. Second, our agent provides evidence from sources supporting factual claims when collecting preference judgements over model statements. For factual questions, evidence provided by Sparrow supports the sampled response 78% of the time. Sparrow is preferred more often than baselines while being more resilient to adversarial probing by humans, violating our rules only 8% of the time when probed. Finally, we conduct extensive analyses showing that though our model learns to follow our rules it can exhibit distributional biases.
Unified Scaling Laws for Routed Language Models
Feb 09, 2022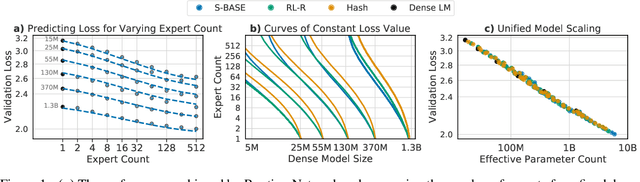

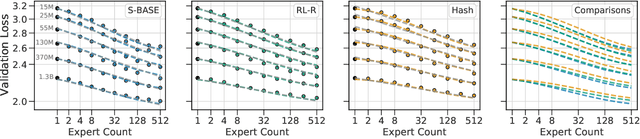
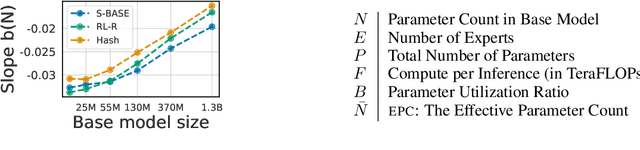
Abstract:The performance of a language model has been shown to be effectively modeled as a power-law in its parameter count. Here we study the scaling behaviors of Routing Networks: architectures that conditionally use only a subset of their parameters while processing an input. For these models, parameter count and computational requirement form two independent axes along which an increase leads to better performance. In this work we derive and justify scaling laws defined on these two variables which generalize those known for standard language models and describe the performance of a wide range of routing architectures trained via three different techniques. Afterwards we provide two applications of these laws: first deriving an Effective Parameter Count along which all models scale at the same rate, and then using the scaling coefficients to give a quantitative comparison of the three routing techniques considered. Our analysis derives from an extensive evaluation of Routing Networks across five orders of magnitude of size, including models with hundreds of experts and hundreds of billions of parameters.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge