Ryutaro Tanno
Centre for Medical Image Computing and Department of Computer Science - University College London - UK, Machine Intelligence and Perception Group - Microsoft Research Cambridge - UK
Advancing Conversational Diagnostic AI with Multimodal Reasoning
May 06, 2025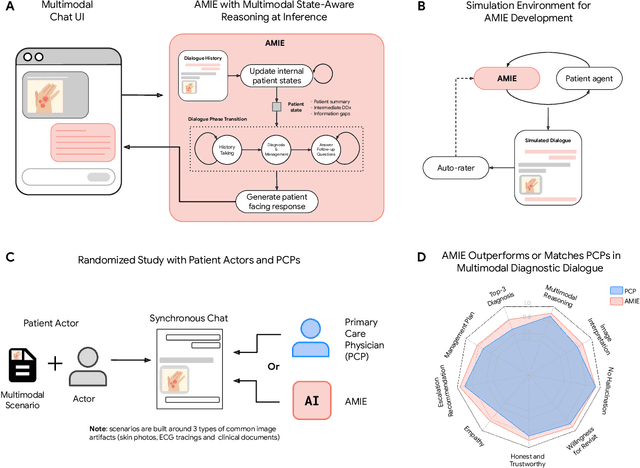
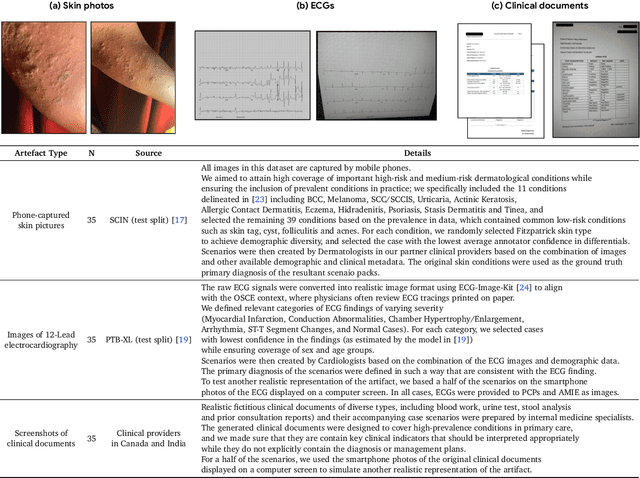
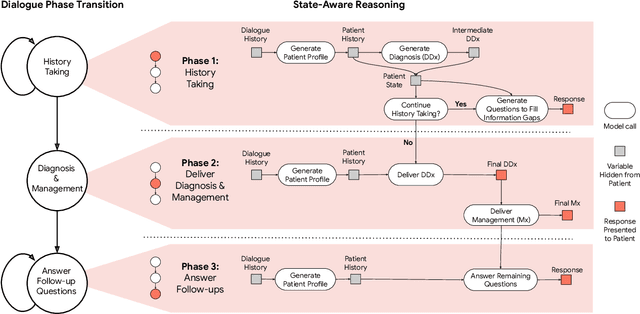
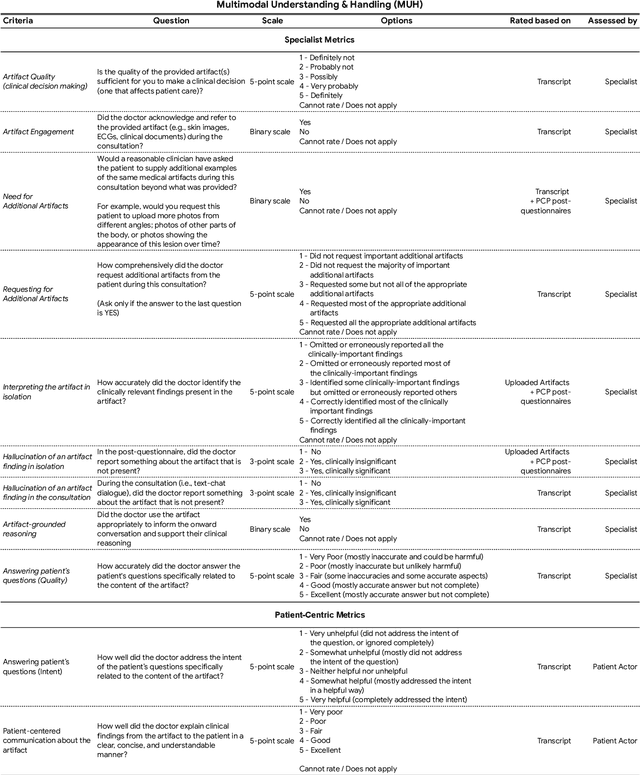
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated great potential for conducting diagnostic conversations but evaluation has been largely limited to language-only interactions, deviating from the real-world requirements of remote care delivery. Instant messaging platforms permit clinicians and patients to upload and discuss multimodal medical artifacts seamlessly in medical consultation, but the ability of LLMs to reason over such data while preserving other attributes of competent diagnostic conversation remains unknown. Here we advance the conversational diagnosis and management performance of the Articulate Medical Intelligence Explorer (AMIE) through a new capability to gather and interpret multimodal data, and reason about this precisely during consultations. Leveraging Gemini 2.0 Flash, our system implements a state-aware dialogue framework, where conversation flow is dynamically controlled by intermediate model outputs reflecting patient states and evolving diagnoses. Follow-up questions are strategically directed by uncertainty in such patient states, leading to a more structured multimodal history-taking process that emulates experienced clinicians. We compared AMIE to primary care physicians (PCPs) in a randomized, blinded, OSCE-style study of chat-based consultations with patient actors. We constructed 105 evaluation scenarios using artifacts like smartphone skin photos, ECGs, and PDFs of clinical documents across diverse conditions and demographics. Our rubric assessed multimodal capabilities and other clinically meaningful axes like history-taking, diagnostic accuracy, management reasoning, communication, and empathy. Specialist evaluation showed AMIE to be superior to PCPs on 7/9 multimodal and 29/32 non-multimodal axes (including diagnostic accuracy). The results show clear progress in multimodal conversational diagnostic AI, but real-world translation needs further research.
Towards Conversational AI for Disease Management
Mar 08, 2025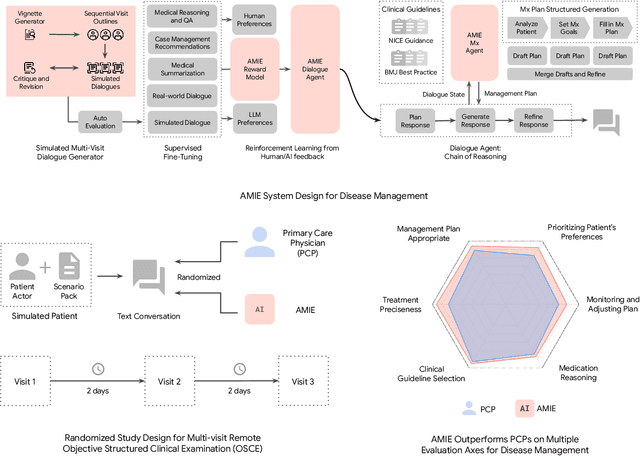
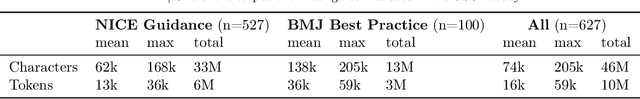
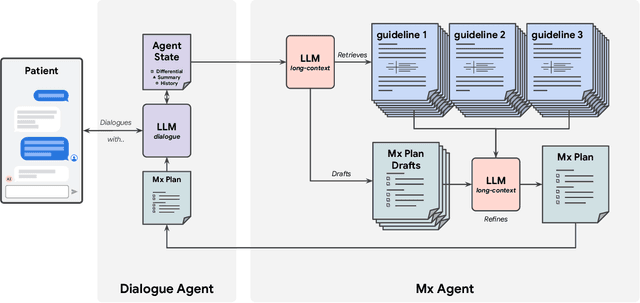
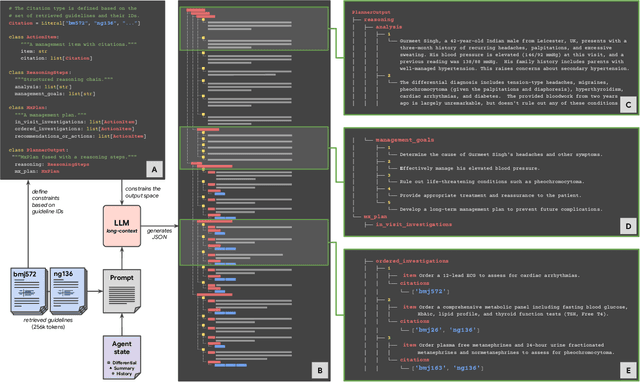
Abstract:While large language models (LLMs) have shown promise in diagnostic dialogue, their capabilities for effective management reasoning - including disease progression, therapeutic response, and safe medication prescription - remain under-explored. We advance the previously demonstrated diagnostic capabilities of the Articulate Medical Intelligence Explorer (AMIE) through a new LLM-based agentic system optimised for clinical management and dialogue, incorporating reasoning over the evolution of disease and multiple patient visit encounters, response to therapy, and professional competence in medication prescription. To ground its reasoning in authoritative clinical knowledge, AMIE leverages Gemini's long-context capabilities, combining in-context retrieval with structured reasoning to align its output with relevant and up-to-date clinical practice guidelines and drug formularies. In a randomized, blinded virtual Objective Structured Clinical Examination (OSCE) study, AMIE was compared to 21 primary care physicians (PCPs) across 100 multi-visit case scenarios designed to reflect UK NICE Guidance and BMJ Best Practice guidelines. AMIE was non-inferior to PCPs in management reasoning as assessed by specialist physicians and scored better in both preciseness of treatments and investigations, and in its alignment with and grounding of management plans in clinical guidelines. To benchmark medication reasoning, we developed RxQA, a multiple-choice question benchmark derived from two national drug formularies (US, UK) and validated by board-certified pharmacists. While AMIE and PCPs both benefited from the ability to access external drug information, AMIE outperformed PCPs on higher difficulty questions. While further research would be needed before real-world translation, AMIE's strong performance across evaluations marks a significant step towards conversational AI as a tool in disease management.
Towards an AI co-scientist
Feb 26, 2025Abstract:Scientific discovery relies on scientists generating novel hypotheses that undergo rigorous experimental validation. To augment this process, we introduce an AI co-scientist, a multi-agent system built on Gemini 2.0. The AI co-scientist is intended to help uncover new, original knowledge and to formulate demonstrably novel research hypotheses and proposals, building upon prior evidence and aligned to scientist-provided research objectives and guidance. The system's design incorporates a generate, debate, and evolve approach to hypothesis generation, inspired by the scientific method and accelerated by scaling test-time compute. Key contributions include: (1) a multi-agent architecture with an asynchronous task execution framework for flexible compute scaling; (2) a tournament evolution process for self-improving hypotheses generation. Automated evaluations show continued benefits of test-time compute, improving hypothesis quality. While general purpose, we focus development and validation in three biomedical areas: drug repurposing, novel target discovery, and explaining mechanisms of bacterial evolution and anti-microbial resistance. For drug repurposing, the system proposes candidates with promising validation findings, including candidates for acute myeloid leukemia that show tumor inhibition in vitro at clinically applicable concentrations. For novel target discovery, the AI co-scientist proposed new epigenetic targets for liver fibrosis, validated by anti-fibrotic activity and liver cell regeneration in human hepatic organoids. Finally, the AI co-scientist recapitulated unpublished experimental results via a parallel in silico discovery of a novel gene transfer mechanism in bacterial evolution. These results, detailed in separate, co-timed reports, demonstrate the potential to augment biomedical and scientific discovery and usher an era of AI empowered scientists.
Advancing Multimodal Medical Capabilities of Gemini
May 06, 2024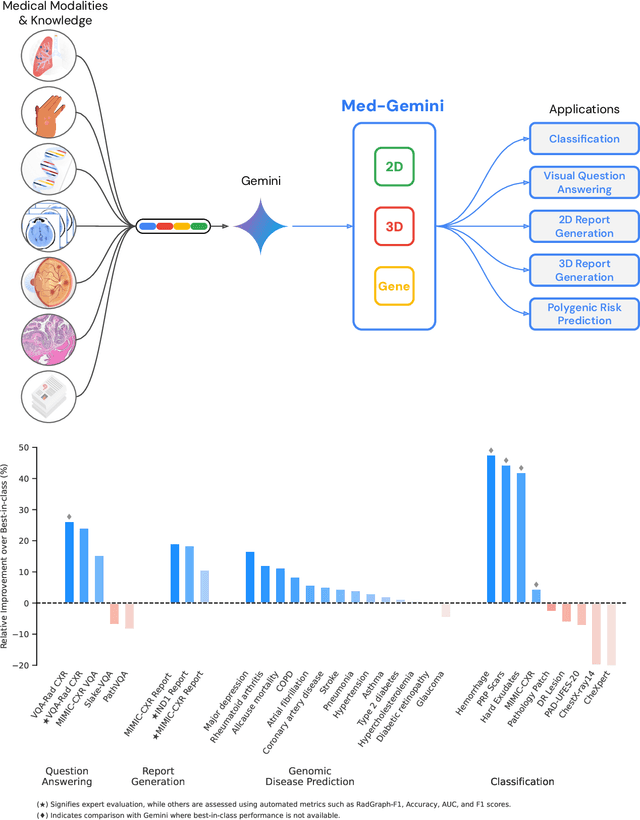
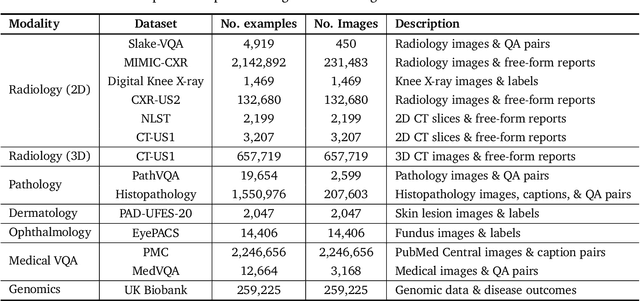

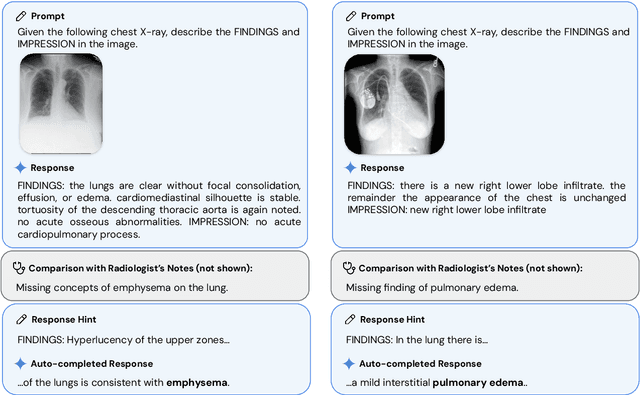
Abstract:Many clinical tasks require an understanding of specialized data, such as medical images and genomics, which is not typically found in general-purpose large multimodal models. Building upon Gemini's multimodal models, we develop several models within the new Med-Gemini family that inherit core capabilities of Gemini and are optimized for medical use via fine-tuning with 2D and 3D radiology, histopathology, ophthalmology, dermatology and genomic data. Med-Gemini-2D sets a new standard for AI-based chest X-ray (CXR) report generation based on expert evaluation, exceeding previous best results across two separate datasets by an absolute margin of 1% and 12%, where 57% and 96% of AI reports on normal cases, and 43% and 65% on abnormal cases, are evaluated as "equivalent or better" than the original radiologists' reports. We demonstrate the first ever large multimodal model-based report generation for 3D computed tomography (CT) volumes using Med-Gemini-3D, with 53% of AI reports considered clinically acceptable, although additional research is needed to meet expert radiologist reporting quality. Beyond report generation, Med-Gemini-2D surpasses the previous best performance in CXR visual question answering (VQA) and performs well in CXR classification and radiology VQA, exceeding SoTA or baselines on 17 of 20 tasks. In histopathology, ophthalmology, and dermatology image classification, Med-Gemini-2D surpasses baselines across 18 out of 20 tasks and approaches task-specific model performance. Beyond imaging, Med-Gemini-Polygenic outperforms the standard linear polygenic risk score-based approach for disease risk prediction and generalizes to genetically correlated diseases for which it has never been trained. Although further development and evaluation are necessary in the safety-critical medical domain, our results highlight the potential of Med-Gemini across a wide range of medical tasks.
Capabilities of Gemini Models in Medicine
May 01, 2024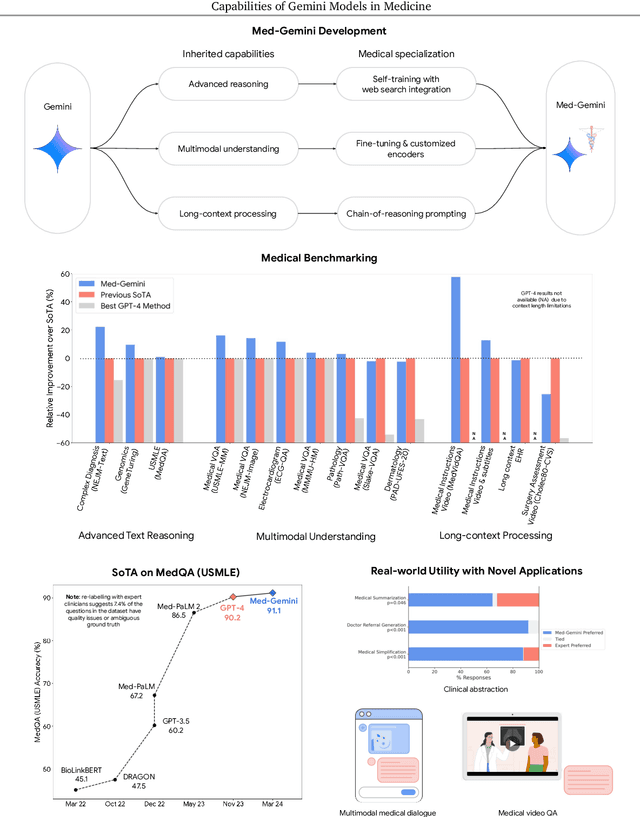
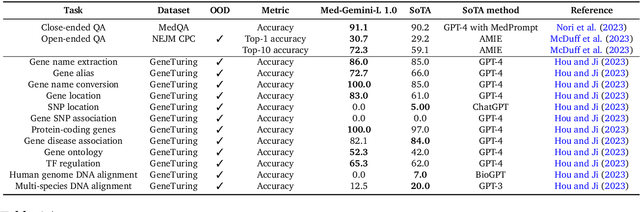
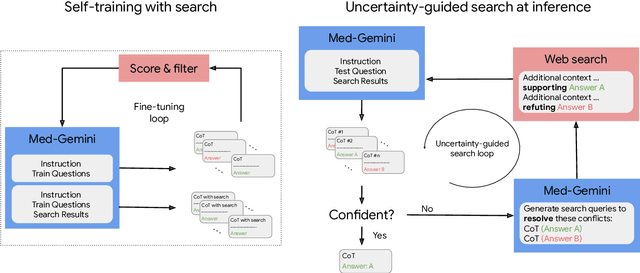
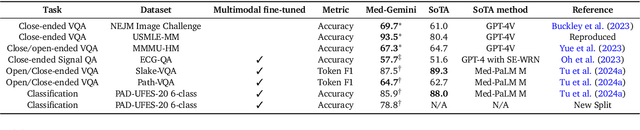
Abstract:Excellence in a wide variety of medical applications poses considerable challenges for AI, requiring advanced reasoning, access to up-to-date medical knowledge and understanding of complex multimodal data. Gemini models, with strong general capabilities in multimodal and long-context reasoning, offer exciting possibilities in medicine. Building on these core strengths of Gemini, we introduce Med-Gemini, a family of highly capable multimodal models that are specialized in medicine with the ability to seamlessly use web search, and that can be efficiently tailored to novel modalities using custom encoders. We evaluate Med-Gemini on 14 medical benchmarks, establishing new state-of-the-art (SoTA) performance on 10 of them, and surpass the GPT-4 model family on every benchmark where a direct comparison is viable, often by a wide margin. On the popular MedQA (USMLE) benchmark, our best-performing Med-Gemini model achieves SoTA performance of 91.1% accuracy, using a novel uncertainty-guided search strategy. On 7 multimodal benchmarks including NEJM Image Challenges and MMMU (health & medicine), Med-Gemini improves over GPT-4V by an average relative margin of 44.5%. We demonstrate the effectiveness of Med-Gemini's long-context capabilities through SoTA performance on a needle-in-a-haystack retrieval task from long de-identified health records and medical video question answering, surpassing prior bespoke methods using only in-context learning. Finally, Med-Gemini's performance suggests real-world utility by surpassing human experts on tasks such as medical text summarization, alongside demonstrations of promising potential for multimodal medical dialogue, medical research and education. Taken together, our results offer compelling evidence for Med-Gemini's potential, although further rigorous evaluation will be crucial before real-world deployment in this safety-critical domain.
Towards Conversational Diagnostic AI
Jan 11, 2024Abstract:At the heart of medicine lies the physician-patient dialogue, where skillful history-taking paves the way for accurate diagnosis, effective management, and enduring trust. Artificial Intelligence (AI) systems capable of diagnostic dialogue could increase accessibility, consistency, and quality of care. However, approximating clinicians' expertise is an outstanding grand challenge. Here, we introduce AMIE (Articulate Medical Intelligence Explorer), a Large Language Model (LLM) based AI system optimized for diagnostic dialogue. AMIE uses a novel self-play based simulated environment with automated feedback mechanisms for scaling learning across diverse disease conditions, specialties, and contexts. We designed a framework for evaluating clinically-meaningful axes of performance including history-taking, diagnostic accuracy, management reasoning, communication skills, and empathy. We compared AMIE's performance to that of primary care physicians (PCPs) in a randomized, double-blind crossover study of text-based consultations with validated patient actors in the style of an Objective Structured Clinical Examination (OSCE). The study included 149 case scenarios from clinical providers in Canada, the UK, and India, 20 PCPs for comparison with AMIE, and evaluations by specialist physicians and patient actors. AMIE demonstrated greater diagnostic accuracy and superior performance on 28 of 32 axes according to specialist physicians and 24 of 26 axes according to patient actors. Our research has several limitations and should be interpreted with appropriate caution. Clinicians were limited to unfamiliar synchronous text-chat which permits large-scale LLM-patient interactions but is not representative of usual clinical practice. While further research is required before AMIE could be translated to real-world settings, the results represent a milestone towards conversational diagnostic AI.
Bad Students Make Great Teachers: Active Learning Accelerates Large-Scale Visual Understanding
Dec 12, 2023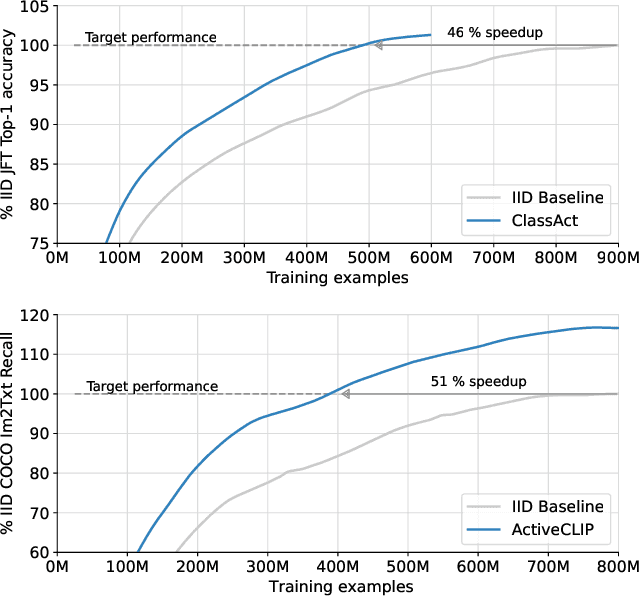

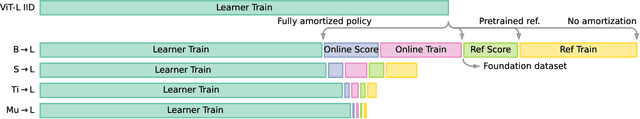

Abstract:We propose a method for accelerating large-scale pre-training with online data selection policies. For the first time, we demonstrate that model-based data selection can reduce the total computation needed to reach the performance of models trained with uniform sampling. The key insight which enables this "compute-positive" regime is that small models provide good proxies for the loss of much larger models, such that computation spent on scoring data can be drastically scaled down but still significantly accelerate training of the learner.. These data selection policies also strongly generalize across datasets and tasks, opening an avenue for further amortizing the overhead of data scoring by re-using off-the-shelf models and training sequences. Our methods, ClassAct and ActiveCLIP, require 46% and 51% fewer training updates and up to 25% less total computation when training visual classifiers on JFT and multimodal models on ALIGN, respectively. Finally, our paradigm seamlessly applies to the curation of large-scale image-text datasets, yielding a new state-of-the-art in several multimodal transfer tasks and pre-training regimes.
Consensus, dissensus and synergy between clinicians and specialist foundation models in radiology report generation
Dec 06, 2023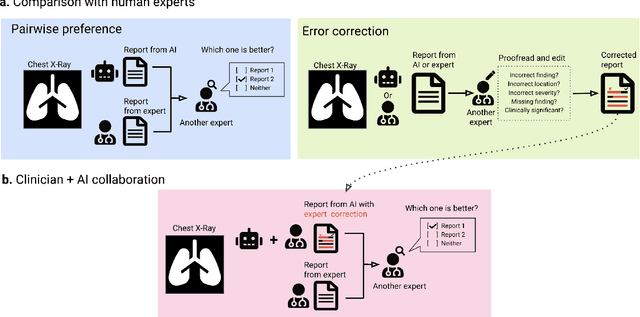
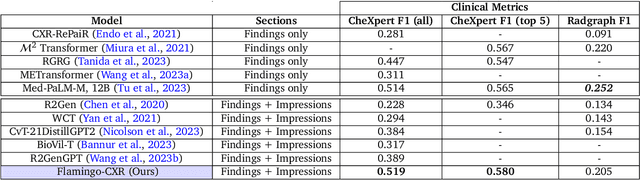
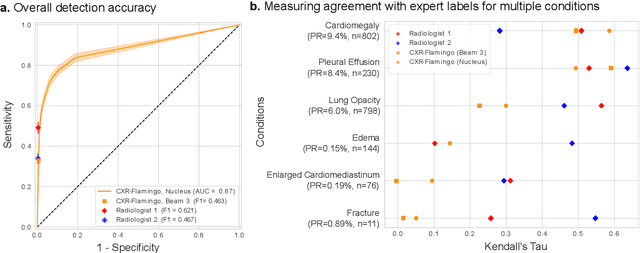
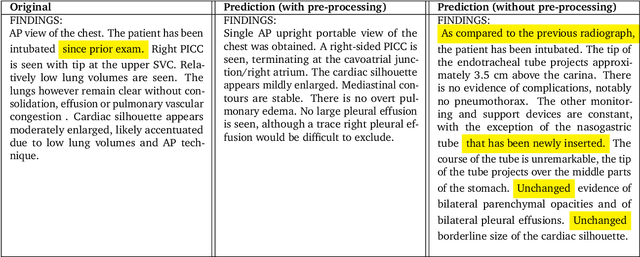
Abstract:Radiology reports are an instrumental part of modern medicine, informing key clinical decisions such as diagnosis and treatment. The worldwide shortage of radiologists, however, restricts access to expert care and imposes heavy workloads, contributing to avoidable errors and delays in report delivery. While recent progress in automated report generation with vision-language models offer clear potential in ameliorating the situation, the path to real-world adoption has been stymied by the challenge of evaluating the clinical quality of AI-generated reports. In this study, we build a state-of-the-art report generation system for chest radiographs, \textit{Flamingo-CXR}, by fine-tuning a well-known vision-language foundation model on radiology data. To evaluate the quality of the AI-generated reports, a group of 16 certified radiologists provide detailed evaluations of AI-generated and human written reports for chest X-rays from an intensive care setting in the United States and an inpatient setting in India. At least one radiologist (out of two per case) preferred the AI report to the ground truth report in over 60$\%$ of cases for both datasets. Amongst the subset of AI-generated reports that contain errors, the most frequently cited reasons were related to the location and finding, whereas for human written reports, most mistakes were related to severity and finding. This disparity suggested potential complementarity between our AI system and human experts, prompting us to develop an assistive scenario in which \textit{Flamingo-CXR} generates a first-draft report, which is subsequently revised by a clinician. This is the first demonstration of clinician-AI collaboration for report writing, and the resultant reports are assessed to be equivalent or preferred by at least one radiologist to reports written by experts alone in 80$\%$ of in-patient cases and 60$\%$ of intensive care cases.
An Image is Worth Multiple Words: Learning Object Level Concepts using Multi-Concept Prompt Learning
Oct 18, 2023Abstract:Textural Inversion, a prompt learning method, learns a singular embedding for a new "word" to represent image style and appearance, allowing it to be integrated into natural language sentences to generate novel synthesised images. However, identifying and integrating multiple object-level concepts within one scene poses significant challenges even when embeddings for individual concepts are attainable. This is further confirmed by our empirical tests. To address this challenge, we introduce a framework for Multi-Concept Prompt Learning (MCPL), where multiple new "words" are simultaneously learned from a single sentence-image pair. To enhance the accuracy of word-concept correlation, we propose three regularisation techniques: Attention Masking (AttnMask) to concentrate learning on relevant areas; Prompts Contrastive Loss (PromptCL) to separate the embeddings of different concepts; and Bind adjective (Bind adj.) to associate new "words" with known words. We evaluate via image generation, editing, and attention visualisation with diverse images. Extensive quantitative comparisons demonstrate that our method can learn more semantically disentangled concepts with enhanced word-concept correlation. Additionally, we introduce a novel dataset and evaluation protocol tailored for this new task of learning object-level concepts.
Towards Generalist Biomedical AI
Jul 26, 2023



Abstract:Medicine is inherently multimodal, with rich data modalities spanning text, imaging, genomics, and more. Generalist biomedical artificial intelligence (AI) systems that flexibly encode, integrate, and interpret this data at scale can potentially enable impactful applications ranging from scientific discovery to care delivery. To enable the development of these models, we first curate MultiMedBench, a new multimodal biomedical benchmark. MultiMedBench encompasses 14 diverse tasks such as medical question answering, mammography and dermatology image interpretation, radiology report generation and summarization, and genomic variant calling. We then introduce Med-PaLM Multimodal (Med-PaLM M), our proof of concept for a generalist biomedical AI system. Med-PaLM M is a large multimodal generative model that flexibly encodes and interprets biomedical data including clinical language, imaging, and genomics with the same set of model weights. Med-PaLM M reaches performance competitive with or exceeding the state of the art on all MultiMedBench tasks, often surpassing specialist models by a wide margin. We also report examples of zero-shot generalization to novel medical concepts and tasks, positive transfer learning across tasks, and emergent zero-shot medical reasoning. To further probe the capabilities and limitations of Med-PaLM M, we conduct a radiologist evaluation of model-generated (and human) chest X-ray reports and observe encouraging performance across model scales. In a side-by-side ranking on 246 retrospective chest X-rays, clinicians express a pairwise preference for Med-PaLM M reports over those produced by radiologists in up to 40.50% of cases, suggesting potential clinical utility. While considerable work is needed to validate these models in real-world use cases, our results represent a milestone towards the development of generalist biomedical AI systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge