Andrew Sellergren
CoCa-CXR: Contrastive Captioners Learn Strong Temporal Structures for Chest X-Ray Vision-Language Understanding
Feb 27, 2025Abstract:Vision-language models have proven to be of great benefit for medical image analysis since they learn rich semantics from both images and reports. Prior efforts have focused on better alignment of image and text representations to enhance image understanding. However, though explicit reference to a prior image is common in Chest X-Ray (CXR) reports, aligning progression descriptions with the semantics differences in image pairs remains under-explored. In this work, we propose two components to address this issue. (1) A CXR report processing pipeline to extract temporal structure. It processes reports with a large language model (LLM) to separate the description and comparison contexts, and extracts fine-grained annotations from reports. (2) A contrastive captioner model for CXR, namely CoCa-CXR, to learn how to both describe images and their temporal progressions. CoCa-CXR incorporates a novel regional cross-attention module to identify local differences between paired CXR images. Extensive experiments show the superiority of CoCa-CXR on both progression analysis and report generation compared to previous methods. Notably, on MS-CXR-T progression classification, CoCa-CXR obtains 65.0% average testing accuracy on five pulmonary conditions, outperforming the previous state-of-the-art (SOTA) model BioViL-T by 4.8%. It also achieves a RadGraph F1 of 24.2% on MIMIC-CXR, which is comparable to the Med-Gemini foundation model.
Health AI Developer Foundations
Nov 26, 2024



Abstract:Robust medical Machine Learning (ML) models have the potential to revolutionize healthcare by accelerating clinical research, improving workflows and outcomes, and producing novel insights or capabilities. Developing such ML models from scratch is cost prohibitive and requires substantial compute, data, and time (e.g., expert labeling). To address these challenges, we introduce Health AI Developer Foundations (HAI-DEF), a suite of pre-trained, domain-specific foundation models, tools, and recipes to accelerate building ML for health applications. The models cover various modalities and domains, including radiology (X-rays and computed tomography), histopathology, dermatological imaging, and audio. These models provide domain specific embeddings that facilitate AI development with less labeled data, shorter training times, and reduced computational costs compared to traditional approaches. In addition, we utilize a common interface and style across these models, and prioritize usability to enable developers to integrate HAI-DEF efficiently. We present model evaluations across various tasks and conclude with a discussion of their application and evaluation, covering the importance of ensuring efficacy, fairness, and equity. Finally, while HAI-DEF and specifically the foundation models lower the barrier to entry for ML in healthcare, we emphasize the importance of validation with problem- and population-specific data for each desired usage setting. This technical report will be updated over time as more modalities and features are added.
PathAlign: A vision-language model for whole slide images in histopathology
Jun 27, 2024Abstract:Microscopic interpretation of histopathology images underlies many important diagnostic and treatment decisions. While advances in vision-language modeling raise new opportunities for analysis of such images, the gigapixel-scale size of whole slide images (WSIs) introduces unique challenges. Additionally, pathology reports simultaneously highlight key findings from small regions while also aggregating interpretation across multiple slides, often making it difficult to create robust image-text pairs. As such, pathology reports remain a largely untapped source of supervision in computational pathology, with most efforts relying on region-of-interest annotations or self-supervision at the patch-level. In this work, we develop a vision-language model based on the BLIP-2 framework using WSIs paired with curated text from pathology reports. This enables applications utilizing a shared image-text embedding space, such as text or image retrieval for finding cases of interest, as well as integration of the WSI encoder with a frozen large language model (LLM) for WSI-based generative text capabilities such as report generation or AI-in-the-loop interactions. We utilize a de-identified dataset of over 350,000 WSIs and diagnostic text pairs, spanning a wide range of diagnoses, procedure types, and tissue types. We present pathologist evaluation of text generation and text retrieval using WSI embeddings, as well as results for WSI classification and workflow prioritization (slide-level triaging). Model-generated text for WSIs was rated by pathologists as accurate, without clinically significant error or omission, for 78% of WSIs on average. This work demonstrates exciting potential capabilities for language-aligned WSI embeddings.
Advancing Multimodal Medical Capabilities of Gemini
May 06, 2024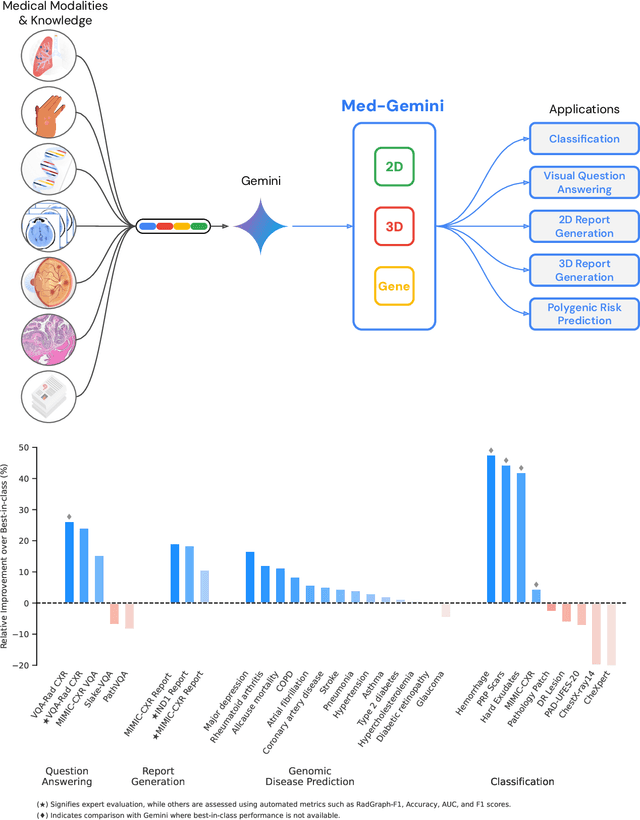
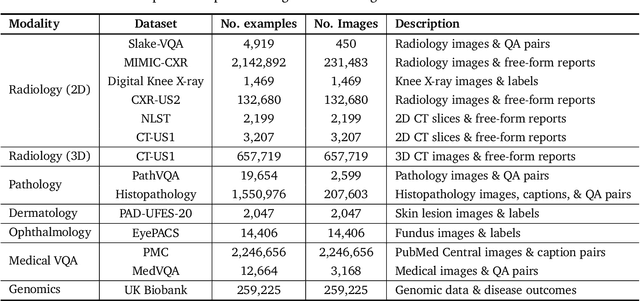

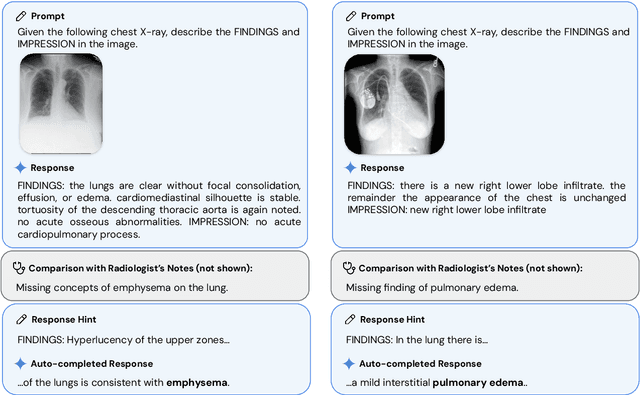
Abstract:Many clinical tasks require an understanding of specialized data, such as medical images and genomics, which is not typically found in general-purpose large multimodal models. Building upon Gemini's multimodal models, we develop several models within the new Med-Gemini family that inherit core capabilities of Gemini and are optimized for medical use via fine-tuning with 2D and 3D radiology, histopathology, ophthalmology, dermatology and genomic data. Med-Gemini-2D sets a new standard for AI-based chest X-ray (CXR) report generation based on expert evaluation, exceeding previous best results across two separate datasets by an absolute margin of 1% and 12%, where 57% and 96% of AI reports on normal cases, and 43% and 65% on abnormal cases, are evaluated as "equivalent or better" than the original radiologists' reports. We demonstrate the first ever large multimodal model-based report generation for 3D computed tomography (CT) volumes using Med-Gemini-3D, with 53% of AI reports considered clinically acceptable, although additional research is needed to meet expert radiologist reporting quality. Beyond report generation, Med-Gemini-2D surpasses the previous best performance in CXR visual question answering (VQA) and performs well in CXR classification and radiology VQA, exceeding SoTA or baselines on 17 of 20 tasks. In histopathology, ophthalmology, and dermatology image classification, Med-Gemini-2D surpasses baselines across 18 out of 20 tasks and approaches task-specific model performance. Beyond imaging, Med-Gemini-Polygenic outperforms the standard linear polygenic risk score-based approach for disease risk prediction and generalizes to genetically correlated diseases for which it has never been trained. Although further development and evaluation are necessary in the safety-critical medical domain, our results highlight the potential of Med-Gemini across a wide range of medical tasks.
Consensus, dissensus and synergy between clinicians and specialist foundation models in radiology report generation
Dec 06, 2023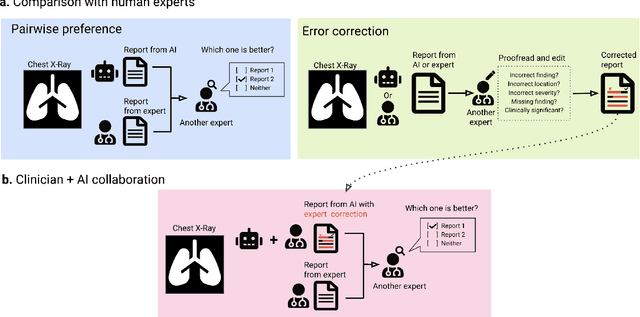
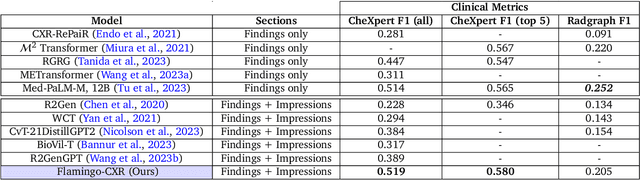
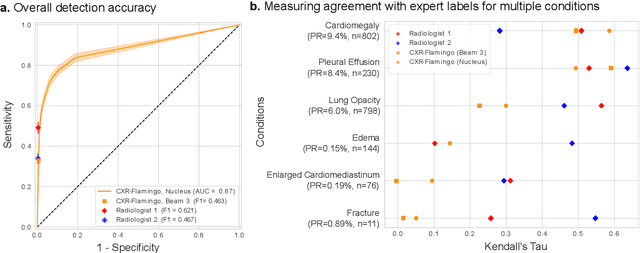
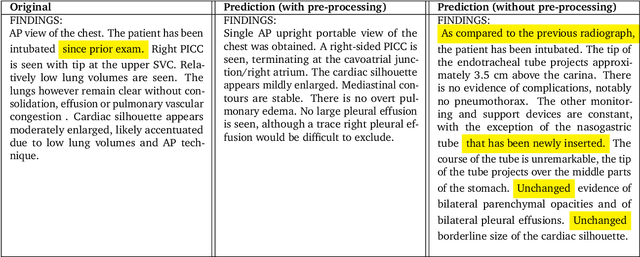
Abstract:Radiology reports are an instrumental part of modern medicine, informing key clinical decisions such as diagnosis and treatment. The worldwide shortage of radiologists, however, restricts access to expert care and imposes heavy workloads, contributing to avoidable errors and delays in report delivery. While recent progress in automated report generation with vision-language models offer clear potential in ameliorating the situation, the path to real-world adoption has been stymied by the challenge of evaluating the clinical quality of AI-generated reports. In this study, we build a state-of-the-art report generation system for chest radiographs, \textit{Flamingo-CXR}, by fine-tuning a well-known vision-language foundation model on radiology data. To evaluate the quality of the AI-generated reports, a group of 16 certified radiologists provide detailed evaluations of AI-generated and human written reports for chest X-rays from an intensive care setting in the United States and an inpatient setting in India. At least one radiologist (out of two per case) preferred the AI report to the ground truth report in over 60$\%$ of cases for both datasets. Amongst the subset of AI-generated reports that contain errors, the most frequently cited reasons were related to the location and finding, whereas for human written reports, most mistakes were related to severity and finding. This disparity suggested potential complementarity between our AI system and human experts, prompting us to develop an assistive scenario in which \textit{Flamingo-CXR} generates a first-draft report, which is subsequently revised by a clinician. This is the first demonstration of clinician-AI collaboration for report writing, and the resultant reports are assessed to be equivalent or preferred by at least one radiologist to reports written by experts alone in 80$\%$ of in-patient cases and 60$\%$ of intensive care cases.
ELIXR: Towards a general purpose X-ray artificial intelligence system through alignment of large language models and radiology vision encoders
Aug 02, 2023Abstract:Our approach, which we call Embeddings for Language/Image-aligned X-Rays, or ELIXR, leverages a language-aligned image encoder combined or grafted onto a fixed LLM, PaLM 2, to perform a broad range of tasks. We train this lightweight adapter architecture using images paired with corresponding free-text radiology reports from the MIMIC-CXR dataset. ELIXR achieved state-of-the-art performance on zero-shot chest X-ray (CXR) classification (mean AUC of 0.850 across 13 findings), data-efficient CXR classification (mean AUCs of 0.893 and 0.898 across five findings (atelectasis, cardiomegaly, consolidation, pleural effusion, and pulmonary edema) for 1% (~2,200 images) and 10% (~22,000 images) training data), and semantic search (0.76 normalized discounted cumulative gain (NDCG) across nineteen queries, including perfect retrieval on twelve of them). Compared to existing data-efficient methods including supervised contrastive learning (SupCon), ELIXR required two orders of magnitude less data to reach similar performance. ELIXR also showed promise on CXR vision-language tasks, demonstrating overall accuracies of 58.7% and 62.5% on visual question answering and report quality assurance tasks, respectively. These results suggest that ELIXR is a robust and versatile approach to CXR AI.
Deep Learning for Distinguishing Normal versus Abnormal Chest Radiographs and Generalization to Unseen Diseases
Oct 22, 2020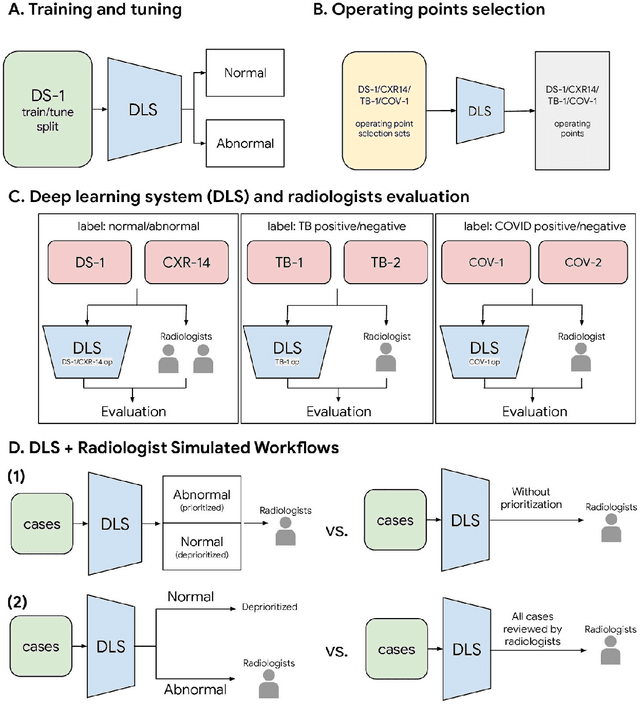
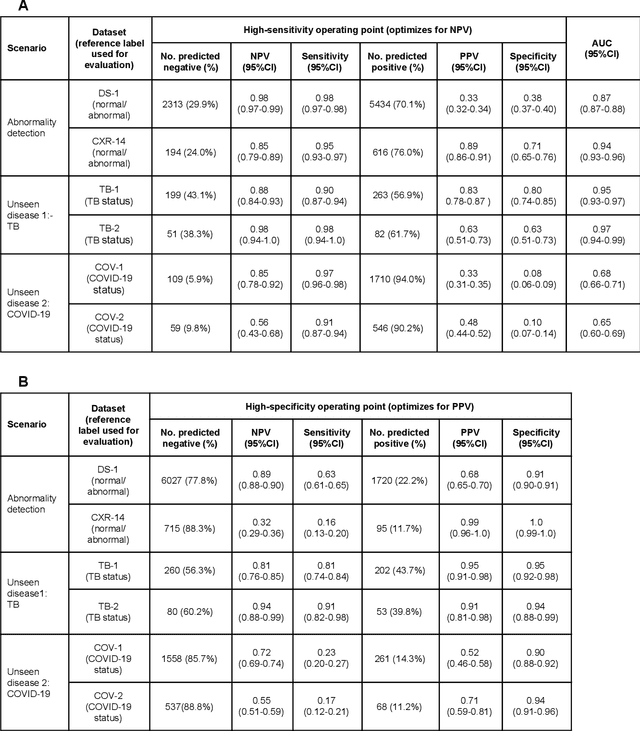
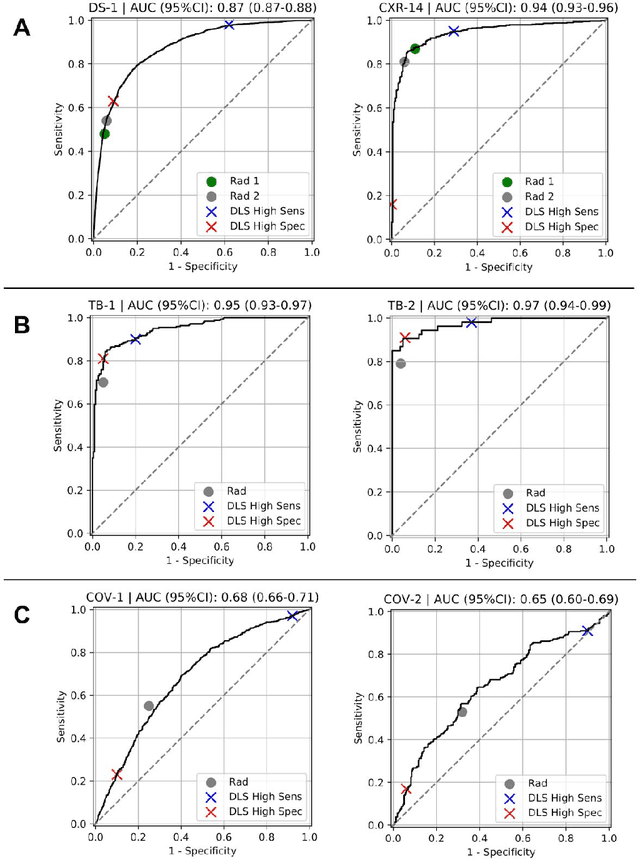
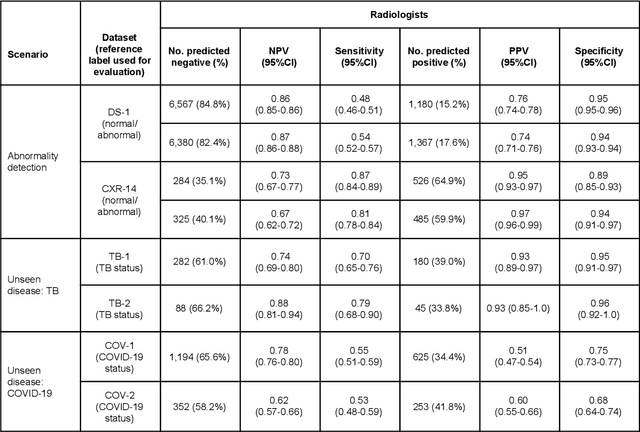
Abstract:Chest radiography (CXR) is the most widely-used thoracic clinical imaging modality and is crucial for guiding the management of cardiothoracic conditions. The detection of specific CXR findings has been the main focus of several artificial intelligence (AI) systems. However, the wide range of possible CXR abnormalities makes it impractical to build specific systems to detect every possible condition. In this work, we developed and evaluated an AI system to classify CXRs as normal or abnormal. For development, we used a de-identified dataset of 248,445 patients from a multi-city hospital network in India. To assess generalizability, we evaluated our system using 6 international datasets from India, China, and the United States. Of these datasets, 4 focused on diseases that the AI was not trained to detect: 2 datasets with tuberculosis and 2 datasets with coronavirus disease 2019. Our results suggest that the AI system generalizes to new patient populations and abnormalities. In a simulated workflow where the AI system prioritized abnormal cases, the turnaround time for abnormal cases reduced by 7-28%. These results represent an important step towards evaluating whether AI can be safely used to flag cases in a general setting where previously unseen abnormalities exist.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge