Jie Yang
RE-MCDF: Closed-Loop Multi-Expert LLM Reasoning for Knowledge-Grounded Clinical Diagnosis
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Electronic medical records (EMRs), particularly in neurology, are inherently heterogeneous, sparse, and noisy, which poses significant challenges for large language models (LLMs) in clinical diagnosis. In such settings, single-agent systems are vulnerable to self-reinforcing errors, as their predictions lack independent validation and can drift toward spurious conclusions. Although recent multi-agent frameworks attempt to mitigate this issue through collaborative reasoning, their interactions are often shallow and loosely structured, failing to reflect the rigorous, evidence-driven processes used by clinical experts. More fundamentally, existing approaches largely ignore the rich logical dependencies among diseases, such as mutual exclusivity, pathological compatibility, and diagnostic confusion. This limitation prevents them from ruling out clinically implausible hypotheses, even when sufficient evidence is available. To overcome these, we propose RE-MCDF, a relation-enhanced multi-expert clinical diagnosis framework. RE-MCDF introduces a generation--verification--revision closed-loop architecture that integrates three complementary components: (i) a primary expert that generates candidate diagnoses and supporting evidence, (ii) a laboratory expert that dynamically prioritizes heterogeneous clinical indicators, and (iii) a multi-relation awareness and evaluation expert group that explicitly enforces inter-disease logical constraints. Guided by a medical knowledge graph (MKG), the first two experts adaptively reweight EMR evidence, while the expert group validates and corrects candidate diagnoses to ensure logical consistency. Extensive experiments on the neurology subset of CMEMR (NEEMRs) and on our curated dataset (XMEMRs) demonstrate that RE-MCDF consistently outperforms state-of-the-art baselines in complex diagnostic scenarios.
From Observations to States: Latent Time Series Forecasting
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Deep learning has achieved strong performance in Time Series Forecasting (TSF). However, we identify a critical representation paradox, termed Latent Chaos: models with accurate predictions often learn latent representations that are temporally disordered and lack continuity. We attribute this phenomenon to the dominant observation-space forecasting paradigm. Most TSF models minimize point-wise errors on noisy and partially observed data, which encourages shortcut solutions instead of the recovery of underlying system dynamics. To address this issue, we propose Latent Time Series Forecasting (LatentTSF), a novel paradigm that shifts TSF from observation regression to latent state prediction. Specifically, LatentTSF employs an AutoEncoder to project observations at each time step into a higher-dimensional latent state space. This expanded representation aims to capture underlying system variables and impose a smoother temporal structure. Forecasting is then performed entirely in the latent space, allowing the model to focus on learning structured temporal dynamics. Theoretical analysis demonstrates that our proposed latent objectives implicitly maximize mutual information between predicted latent states and ground-truth states and observations. Extensive experiments on widely-used benchmarks confirm that LatentTSF effectively mitigates latent chaos, achieving superior performance. Our code is available in https://github.com/Muyiiiii/LatentTSF.
ABC-Bench: Benchmarking Agentic Backend Coding in Real-World Development
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:The evolution of Large Language Models (LLMs) into autonomous agents has expanded the scope of AI coding from localized code generation to complex, repository-level, and execution-driven problem solving. However, current benchmarks predominantly evaluate code logic in static contexts, neglecting the dynamic, full-process requirements of real-world engineering, particularly in backend development which demands rigorous environment configuration and service deployment. To address this gap, we introduce ABC-Bench, a benchmark explicitly designed to evaluate agentic backend coding within a realistic, executable workflow. Using a scalable automated pipeline, we curated 224 practical tasks spanning 8 languages and 19 frameworks from open-source repositories. Distinct from previous evaluations, ABC-Bench require the agents to manage the entire development lifecycle from repository exploration to instantiating containerized services and pass the external end-to-end API tests. Our extensive evaluation reveals that even state-of-the-art models struggle to deliver reliable performance on these holistic tasks, highlighting a substantial disparity between current model capabilities and the demands of practical backend engineering. Our code is available at https://github.com/OpenMOSS/ABC-Bench.
EmbeddingRWKV: State-Centric Retrieval with Reusable States
Jan 10, 2026Abstract:Current Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems typically employ a traditional two-stage pipeline: an embedding model for initial retrieval followed by a reranker for refinement. However, this paradigm suffers from significant inefficiency due to the lack of shared information between stages, leading to substantial redundant computation. To address this limitation, we propose \textbf{State-Centric Retrieval}, a unified retrieval paradigm that utilizes "states" as a bridge to connect embedding models and rerankers. First, we perform state representation learning by fine-tuning an RWKV-based LLM, transforming it into \textbf{EmbeddingRWKV}, a unified model that serves as both an embedding model and a state backbone for extracting compact, reusable states. Building upon these reusable states, we further design a state-based reranker to fully leverage precomputed information. During reranking, the model processes only query tokens, decoupling inference cost from document length and yielding a 5.4$\times$--44.8$\times$ speedup. Furthermore, we observe that retaining all intermediate layer states is unnecessary; with a uniform layer selection strategy, our model maintains 98.62\% of full-model performance using only 25\% of the layers. Extensive experiments demonstrate that State-Centric Retrieval achieves high-quality retrieval and reranking results while significantly enhancing overall system efficiency. Code is available at \href{https://github.com/howard-hou/EmbeddingRWKV}{our GitHub repository}.
Integrating Low-Altitude SAR Imaging into UAV Data Backhaul
Dec 26, 2025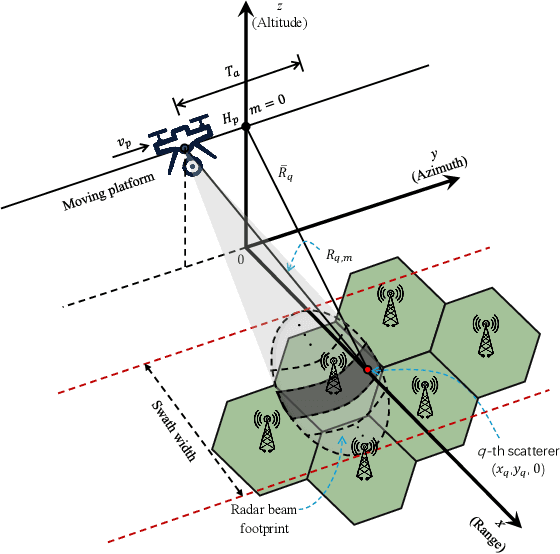
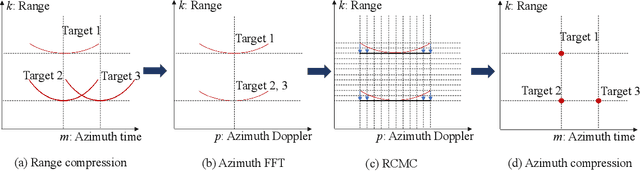
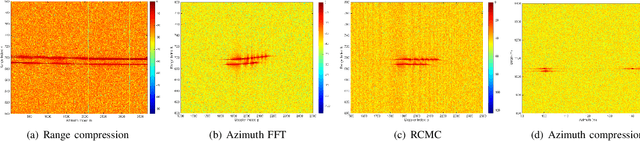
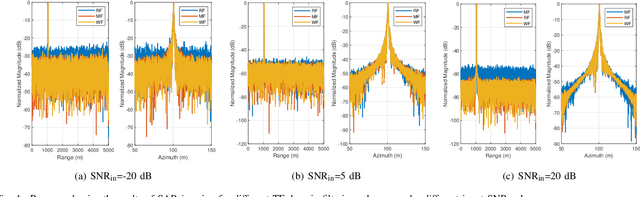
Abstract:Synthetic aperture radar (SAR) deployed on unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) is expected to provide burgeoning imaging services for low-altitude wireless networks (LAWNs), thereby enabling large-scale environmental sensing and timely situational awareness. Conventional SAR systems typically leverages a deterministic radar waveform, while it conflicts with the integrated sensing and communications (ISAC) paradigm by discarding signaling randomness, in whole or in part. In fact, this approach reduces to the uplink pilot sensing in 5G New Radio (NR) with sounding reference signals (SRS), underutilizing data symbols. To explore the potential of data-aided imaging, we develop a low-altitude SAR imaging framework that sufficiently leverages data symbols carried by the native orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) communication waveform. The randomness of modulated data in the temporal-frequency (TF) domain, introduced by non-constant modulus constellations such as quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM), may however severely degrade the imaging quality. To mitigate this effect, we incorporate several TF-domain filtering schemes within a rangeDoppler (RD) imaging framework and evaluate their impact. We further propose using the normalized mean square error (NMSE) of a reference point target's profile as an imaging performance metric. Simulation results with 5G NR parameters demonstrate that data-aided imaging substantially outperforms pilot-only counterpart, accordingly validating the effectiveness of the proposed OFDM-SAR imaging approach in LAWNs.
Grad: Guided Relation Diffusion Generation for Graph Augmentation in Graph Fraud Detection
Dec 19, 2025



Abstract:Nowadays, Graph Fraud Detection (GFD) in financial scenarios has become an urgent research topic to protect online payment security. However, as organized crime groups are becoming more professional in real-world scenarios, fraudsters are employing more sophisticated camouflage strategies. Specifically, fraudsters disguise themselves by mimicking the behavioral data collected by platforms, ensuring that their key characteristics are consistent with those of benign users to a high degree, which we call Adaptive Camouflage. Consequently, this narrows the differences in behavioral traits between them and benign users within the platform's database, thereby making current GFD models lose efficiency. To address this problem, we propose a relation diffusion-based graph augmentation model Grad. In detail, Grad leverages a supervised graph contrastive learning module to enhance the fraud-benign difference and employs a guided relation diffusion generator to generate auxiliary homophilic relations from scratch. Based on these, weak fraudulent signals would be enhanced during the aggregation process, thus being obvious enough to be captured. Extensive experiments have been conducted on two real-world datasets provided by WeChat Pay, one of the largest online payment platforms with billions of users, and three public datasets. The results show that our proposed model Grad outperforms SOTA methods in both various scenarios, achieving at most 11.10% and 43.95% increases in AUC and AP, respectively. Our code is released at https://github.com/AI4Risk/antifraud and https://github.com/Muyiiiii/WWW25-Grad.
* Accepted by The Web Conference 2025 (WWW'25). 12 pages, includes implementation details. Code: https://github.com/AI4Risk/antifraud and https://github.com/Muyiiiiii/WWW25-Grad
Insight Miner: A Time Series Analysis Dataset for Cross-Domain Alignment with Natural Language
Dec 12, 2025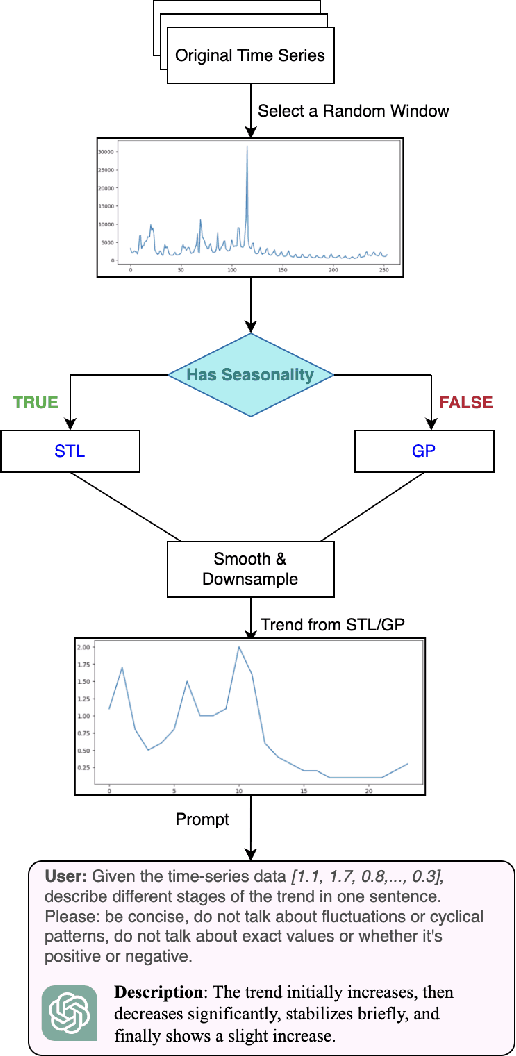
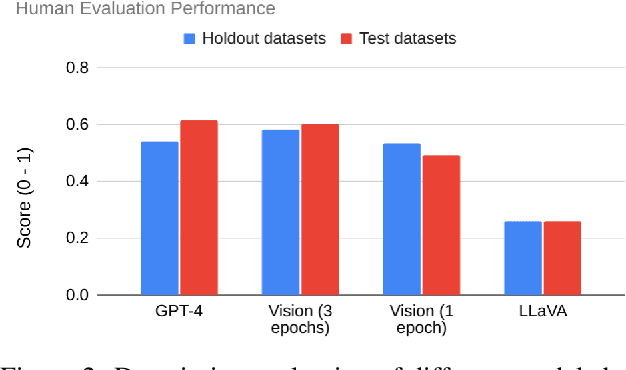
Abstract:Time-series data is critical across many scientific and industrial domains, including environmental analysis, agriculture, transportation, and finance. However, mining insights from this data typically requires deep domain expertise, a process that is both time-consuming and labor-intensive. In this paper, we propose \textbf{Insight Miner}, a large-scale multimodal model (LMM) designed to generate high-quality, comprehensive time-series descriptions enriched with domain-specific knowledge. To facilitate this, we introduce \textbf{TS-Insights}\footnote{Available at \href{https://huggingface.co/datasets/zhykoties/time-series-language-alignment}{https://huggingface.co/datasets/zhykoties/time-series-language-alignment}.}, the first general-domain dataset for time series and language alignment. TS-Insights contains 100k time-series windows sampled from 20 forecasting datasets. We construct this dataset using a novel \textbf{agentic workflow}, where we use statistical tools to extract features from raw time series before synthesizing them into coherent trend descriptions with GPT-4. Following instruction tuning on TS-Insights, Insight Miner outperforms state-of-the-art multimodal models, such as LLaVA \citep{liu2023llava} and GPT-4, in generating time-series descriptions and insights. Our findings suggest a promising direction for leveraging LMMs in time series analysis, and serve as a foundational step toward enabling LLMs to interpret time series as a native input modality.
SMoFi: Step-wise Momentum Fusion for Split Federated Learning on Heterogeneous Data
Nov 16, 2025



Abstract:Split Federated Learning is a system-efficient federated learning paradigm that leverages the rich computing resources at a central server to train model partitions. Data heterogeneity across silos, however, presents a major challenge undermining the convergence speed and accuracy of the global model. This paper introduces Step-wise Momentum Fusion (SMoFi), an effective and lightweight framework that counteracts gradient divergence arising from data heterogeneity by synchronizing the momentum buffers across server-side optimizers. To control gradient divergence over the training process, we design a staleness-aware alignment mechanism that imposes constraints on gradient updates of the server-side submodel at each optimization step. Extensive validations on multiple real-world datasets show that SMoFi consistently improves global model accuracy (up to 7.1%) and convergence speed (up to 10.25$\times$). Furthermore, SMoFi has a greater impact with more clients involved and deeper learning models, making it particularly suitable for model training in resource-constrained contexts.
Causal Inspired Multi Modal Recommendation
Oct 14, 2025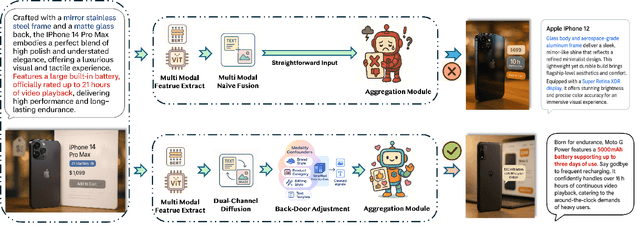
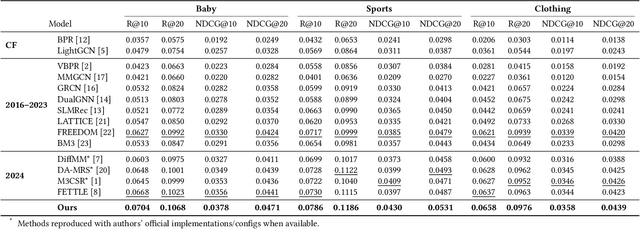
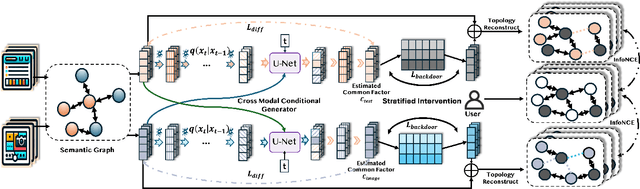
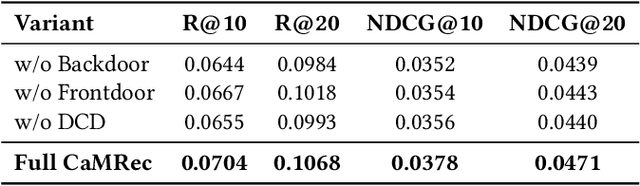
Abstract:Multimodal recommender systems enhance personalized recommendations in e-commerce and online advertising by integrating visual, textual, and user-item interaction data. However, existing methods often overlook two critical biases: (i) modal confounding, where latent factors (e.g., brand style or product category) simultaneously drive multiple modalities and influence user preference, leading to spurious feature-preference associations; (ii) interaction bias, where genuine user preferences are mixed with noise from exposure effects and accidental clicks. To address these challenges, we propose a Causal-inspired multimodal Recommendation framework. Specifically, we introduce a dual-channel cross-modal diffusion module to identify hidden modal confounders, utilize back-door adjustment with hierarchical matching and vector-quantized codebooks to block confounding paths, and apply front-door adjustment combined with causal topology reconstruction to build a deconfounded causal subgraph. Extensive experiments on three real-world e-commerce datasets demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms state-of-the-art baselines while maintaining strong interpretability.
Glocal Information Bottleneck for Time Series Imputation
Oct 06, 2025



Abstract:Time Series Imputation (TSI), which aims to recover missing values in temporal data, remains a fundamental challenge due to the complex and often high-rate missingness in real-world scenarios. Existing models typically optimize the point-wise reconstruction loss, focusing on recovering numerical values (local information). However, we observe that under high missing rates, these models still perform well in the training phase yet produce poor imputations and distorted latent representation distributions (global information) in the inference phase. This reveals a critical optimization dilemma: current objectives lack global guidance, leading models to overfit local noise and fail to capture global information of the data. To address this issue, we propose a new training paradigm, Glocal Information Bottleneck (Glocal-IB). Glocal-IB is model-agnostic and extends the standard IB framework by introducing a Global Alignment loss, derived from a tractable mutual information approximation. This loss aligns the latent representations of masked inputs with those of their originally observed counterparts. It helps the model retain global structure and local details while suppressing noise caused by missing values, giving rise to better generalization under high missingness. Extensive experiments on nine datasets confirm that Glocal-IB leads to consistently improved performance and aligned latent representations under missingness. Our code implementation is available in https://github.com/Muyiiiii/NeurIPS-25-Glocal-IB.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge