Chao-Kai Wen
Lawrence
AI-Driven Subcarrier-Level CQI Feedback
Dec 22, 2025Abstract:The Channel Quality Indicator (CQI) is a fundamental component of channel state information (CSI) that enables adaptive modulation and coding by selecting the optimal modulation and coding scheme to meet a target block error rate. While AI-enabled CSI feedback has achieved significant advances, especially in precoding matrix index feedback, AI-based CQI feedback remains underexplored. Conventional subband-based CQI approaches, due to coarse granularity, often fail to capture fine frequency-selective variations and thus lead to suboptimal resource allocation. In this paper, we propose an AI-driven subcarrier-level CQI feedback framework tailored for 6G and NextG systems. First, we introduce CQInet, an autoencoder-based scheme that compresses per-subcarrier CQI at the user equipment and reconstructs it at the base station, significantly reducing feedback overhead without compromising CQI accuracy. Simulation results show that CQInet increases the effective data rate by 7.6% relative to traditional subband CQI under equivalent feedback overhead. Building on this, we develop SR-CQInet, which leverages super-resolution to infer fine-grained subcarrier CQI from sparsely reported CSI reference signals (CSI-RS). SR-CQInet reduces CSI-RS overhead to 3.5% of CQInet's requirements while maintaining comparable throughput. These results demonstrate that AI-driven subcarrier-level CQI feedback can substantially enhance spectral efficiency and reliability in future wireless networks.
Reducing Pilots in Channel Estimation With Predictive Foundation Models
Dec 17, 2025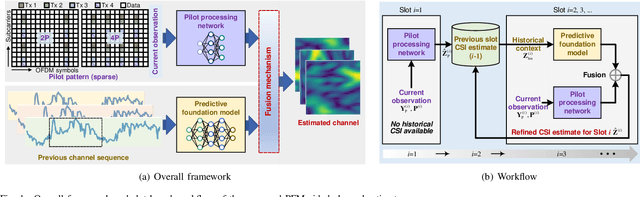
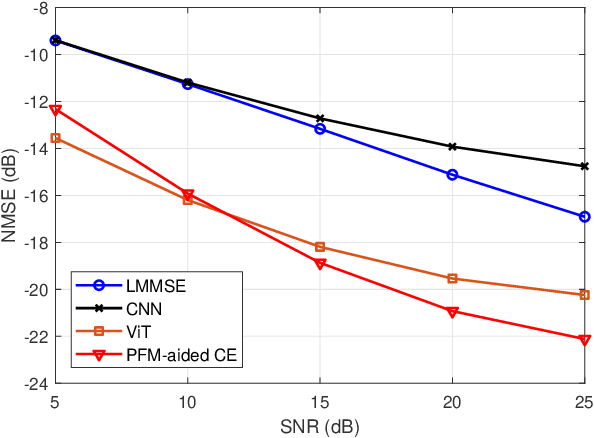
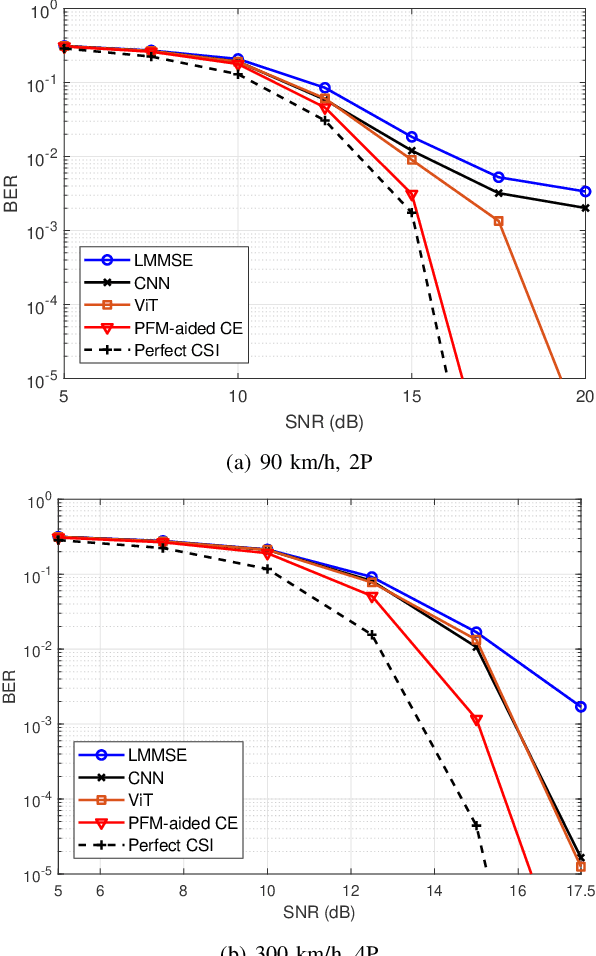
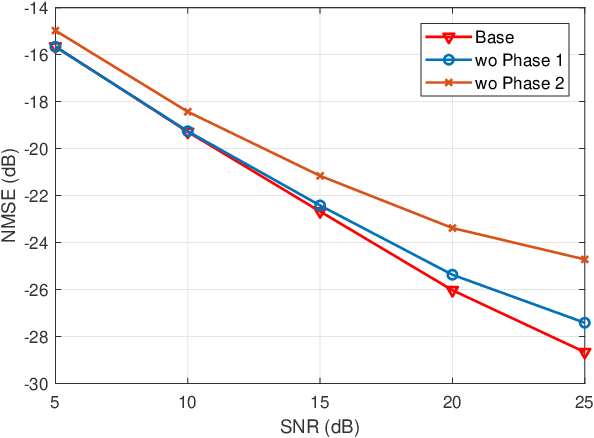
Abstract:Accurate channel state information (CSI) acquisition is essential for modern wireless systems, which becomes increasingly difficult under large antenna arrays, strict pilot overhead constraints, and diverse deployment environments. Existing artificial intelligence-based solutions often lack robustness and fail to generalize across scenarios. To address this limitation, this paper introduces a predictive-foundation-model-based channel estimation framework that enables accurate, low-overhead, and generalizable CSI acquisition. The proposed framework employs a predictive foundation model trained on large-scale cross-domain CSI data to extract universal channel representations and provide predictive priors with strong cross-scenario transferability. A pilot processing network based on a vision transformer architecture is further designed to capture spatial, temporal, and frequency correlations from pilot observations. An efficient fusion mechanism integrates predictive priors with real-time measurements, enabling reliable CSI reconstruction even under sparse or noisy conditions. Extensive evaluations across diverse configurations demonstrate that the proposed estimator significantly outperforms both classical and data-driven baselines in accuracy, robustness, and generalization capability.
Power Consumption and Energy Efficiency of Mid-Band XL-MIMO: Modeling, Scaling Laws, and Performance Insights
Dec 14, 2025Abstract:Mid-band extra-large-scale multiple-input multiple-output (XL-MIMO), emerging as a critical enabler for future communication systems, is expected to deliver significantly higher throughput by leveraging the extended bandwidth and enlarged antenna aperture. However, power consumption remains a significant concern due to the enlarged system dimension, underscoring the need for thorough investigations into efficient system design and deployment. To this end, an in-depth study is conducted on mid-band XL-MIMO systems. Specifically, a comprehensive power consumption model is proposed, encompassing the power consumption of major hardware components and signal processing procedures, while capturing the influence of key system parameters. Considering typical near-field propagation characteristics, closed-form approximations of throughput are derived, providing an analytical framework for assessing energy efficiency (EE). Based on the proposed framework, the scaling law of EE with respect to key system configurations is derived, offering valuable insights for system design. Subsequently, extensions and comparisons are conducted among representative multi-antenna technologies, demonstrating the superiority of mid-band XL-MIMO in EE. Extensive numerical results not only verify the tightness of the throughput analysis but also validate the EE evaluations, unveiling the potential of energy-efficient mid-band XL-MIMO systems.
Next-Generation AI-Native Wireless Communications: MCMC-Based Receiver Architectures for Unified Processing
Oct 02, 2025Abstract:The multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) receiver processing is a key technology for current and next-generation wireless communications. However, it faces significant challenges related to complexity and scalability as the number of antennas increases. Artificial intelligence (AI), a cornerstone of next-generation wireless networks, offers considerable potential for addressing these challenges. This paper proposes an AI-driven, universal MIMO receiver architecture based on Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) techniques. Unlike existing AI-based methods that treat receiver processing as a black box, our MCMC-based approach functions as a generic Bayesian computing engine applicable to various processing tasks, including channel estimation, symbol detection, and channel decoding. This method enhances the interpretability, scalability, and flexibility of receivers in diverse scenarios. Furthermore, the proposed approach integrates these tasks into a unified probabilistic framework, thereby enabling overall performance optimization. This unified framework can also be seamlessly combined with data-driven learning methods to facilitate the development of fully intelligent communication receivers.
Deep Learning-based Position-domain Channel Extrapolation for Cell-Free Massive MIMO
Jul 23, 2025Abstract:To reduce channel acquisition overhead, spatial, time, and frequency-domain channel extrapolation techniques have been widely studied. In this paper, we propose a novel deep learning-based Position-domain Channel Extrapolation framework (named PCEnet) for cell-free massive multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) systems. The user's position, which contains significant channel characteristic information, can greatly enhance the efficiency of channel acquisition. In cell-free massive MIMO, while the propagation environments between different base stations and a specific user vary and their respective channels are uncorrelated, the user's position remains constant and unique across all channels. Building on this, the proposed PCEnet framework leverages the position as a bridge between channels to establish a mapping between the characteristics of different channels, thereby using one acquired channel to assist in the estimation and feedback of others. Specifically, this approach first utilizes neural networks (NNs) to infer the user's position from the obtained channel. {The estimated position, shared among BSs through a central processing unit (CPU)}, is then fed into an NN to design pilot symbols and concatenated with the feedback information to the channel reconstruction NN to reconstruct other channels, thereby significantly enhancing channel acquisition performance. Additionally, we propose a simplified strategy where only the estimated position is used in the reconstruction process without modifying the pilot design, thereby reducing latency. Furthermore, we introduce a position label-free approach that infers the relative user position instead of the absolute position, eliminating the need for ground truth position labels during the localization NN training. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed PCEnet framework reduces pilot and feedback overheads by up to 50%.
RIS-Aided Cooperative ISAC Networks for Structural Health Monitoring
Jul 03, 2025



Abstract:Integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) is a key feature of future cellular systems, enabling applications such as intruder detection, monitoring, and tracking using the same infrastructure. However, its potential for structural health monitoring (SHM), which requires the detection of slow and subtle structural changes, remains largely unexplored due to challenges such as multipath interference and the need for ultra-high sensing precision. This study introduces a novel theoretical framework for SHM via ISAC by leveraging reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RIS) as reference points in collaboration with base stations and users. By dynamically adjusting RIS phases to generate distinct radio signals that suppress background multipath interference, measurement accuracy at these reference points is enhanced. We theoretically analyze RIS-aided collaborative sensing in three-dimensional cellular networks using Fisher information theory, demonstrating how increasing observation time, incorporating additional receivers (even with self-positioning errors), optimizing RIS phases, and refining collaborative node selection can reduce the position error bound to meet SHM's stringent accuracy requirements. Furthermore, we develop a Bayesian inference model to identify structural states and validate damage detection probabilities. Both theoretical and numerical analyses confirm ISAC's capability for millimeter-level deformation detection, highlighting its potential for high-precision SHM applications.
Joint Spatial Division and Multiplexing with Customized Orthogonal Group Channels in Multi-RIS-Assisted Systems
Jul 03, 2025



Abstract:Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RISs) offer the unique capability to reshape the radio environment, thereby simplifying transmission schemes traditionally contingent on channel conditions. Joint spatial division and multiplexing (JSDM) emerges as a low-overhead transmission scheme for multi-user equipment (UE) scenarios, typically requiring complex matrix decomposition to achieve block-diagonalization of the effective channel matrix. In this study, we introduce an innovative JSDM design that leverages RISs to customize channels, thereby streamlining the overall procedures. By strategically positioning RISs at the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) directions of the base station (BS), we establish orthogonal line-of-sight links within the BS-RIS channel, enabling a straightforward pre-beamforming design. Based on UE grouping, we devise reflected beams of the RIS with optimized directions to mitigate inter-group interference in the RISs-UEs channel. An approximation of the channel cross-correlation coefficient is derived and serves as a foundation for the RISs-UEs association, further diminishing inter-group interference. Numerical results substantiate the efficacy of our RIS-customized JSDM in not only achieving effective channel block-diagonalization but also in significantly enhancing the sum spectral efficiency for multi-UE transmissions.
Experimental Evaluation of Multiple Active RISs for 5G MIMO Commercial Networks
May 21, 2025Abstract:While numerous experimental studies have demonstrated the feasibility of reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS) technology, most have primarily focused on extending coverage. In contrast, this paper presents an experimental evaluation of multiple active RISs deployed in a 5G multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) commercial network, emphasizing enhancements in channel rank and throughput. We propose a low-complexity, codebook-based beamforming algorithm specifically tailored for multi-RIS configurations, which diversifies directional channels and reduces reliance on explicit channel state information. Field tests using a commercial base station and user equipment reveal that the multi-RIS system can improve channel rank and throughput by up to 14% compared to single-RIS deployments, while maintaining low computational complexity. These findings underscore the practical benefits of active multi-RIS systems for next-generation networks.
Cooperative ISAC Network for Off-Grid Imaging-based Low-Altitude Surveillance
May 05, 2025



Abstract:The low-altitude economy has emerged as a critical focus for future economic development, emphasizing the urgent need for flight activity surveillance utilizing the existing sensing capabilities of mobile cellular networks. Traditional monostatic or localization-based sensing methods, however, encounter challenges in fusing sensing results and matching channel parameters. To address these challenges, we propose an innovative approach that directly draws the radio images of the low-altitude space, leveraging its inherent sparsity with compressed sensing (CS)-based algorithms and the cooperation of multiple base stations. Furthermore, recognizing that unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) are randomly distributed in space, we introduce a physics-embedded learning method to overcome off-grid issues inherent in CS-based models. Additionally, an online hard example mining method is incorporated into the design of the loss function, enabling the network to adaptively concentrate on the samples bearing significant discrepancy with the ground truth, thereby enhancing its ability to detect the rare UAVs within the expansive low-altitude space. Simulation results demonstrate the effectiveness of the imaging-based low-altitude surveillance approach, with the proposed physics-embedded learning algorithm significantly outperforming traditional CS-based methods under off-grid conditions.
Learned Intelligent Recognizer with Adaptively Customized RIS Phases in Communication Systems
May 05, 2025Abstract:This study presents an advanced wireless system that embeds target recognition within reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS)-aided communication systems, powered by cuttingedge deep learning innovations. Such a system faces the challenge of fine-tuning both the RIS phase shifts and neural network (NN) parameters, since they intricately interdepend on each other to accomplish the recognition task. To address these challenges, we propose an intelligent recognizer that strategically harnesses every piece of prior action responses, thereby ingeniously multiplexing downlink signals to facilitate environment sensing. Specifically, we design a novel NN based on the long short-term memory (LSTM) architecture and the physical channel model. The NN iteratively captures and fuses information from previous measurements and adaptively customizes RIS configurations to acquire the most relevant information for the recognition task in subsequent moments. Tailored dynamically, these configurations adapt to the scene, task, and target specifics. Simulation results reveal that our proposed method significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art method, while resulting in minimal impacts on communication performance, even as sensing is performed simultaneously.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge