Xingyu Zhou
Guiding a Diffusion Transformer with the Internal Dynamics of Itself
Dec 30, 2025Abstract:The diffusion model presents a powerful ability to capture the entire (conditional) data distribution. However, due to the lack of sufficient training and data to learn to cover low-probability areas, the model will be penalized for failing to generate high-quality images corresponding to these areas. To achieve better generation quality, guidance strategies such as classifier free guidance (CFG) can guide the samples to the high-probability areas during the sampling stage. However, the standard CFG often leads to over-simplified or distorted samples. On the other hand, the alternative line of guiding diffusion model with its bad version is limited by carefully designed degradation strategies, extra training and additional sampling steps. In this paper, we proposed a simple yet effective strategy Internal Guidance (IG), which introduces an auxiliary supervision on the intermediate layer during training process and extrapolates the intermediate and deep layer's outputs to obtain generative results during sampling process. This simple strategy yields significant improvements in both training efficiency and generation quality on various baselines. On ImageNet 256x256, SiT-XL/2+IG achieves FID=5.31 and FID=1.75 at 80 and 800 epochs. More impressively, LightningDiT-XL/1+IG achieves FID=1.34 which achieves a large margin between all of these methods. Combined with CFG, LightningDiT-XL/1+IG achieves the current state-of-the-art FID of 1.19.
Improved Bounds for Private and Robust Alignment
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we study the private and robust alignment of language models from a theoretical perspective by establishing upper bounds on the suboptimality gap in both offline and online settings. We consider preference labels subject to privacy constraints and/or adversarial corruption, and analyze two distinct interplays between them: privacy-first and corruption-first. For the privacy-only setting, we show that log loss with an MLE-style algorithm achieves near-optimal rates, in contrast to conventional wisdom. For the joint privacy-and-corruption setting, we first demonstrate that existing offline algorithms in fact provide stronger guarantees -- simultaneously in terms of corruption level and privacy parameters -- than previously known, which further yields improved bounds in the corruption-only regime. In addition, we also present the first set of results for private and robust online alignment. Our results are enabled by new uniform convergence guarantees for log loss and square loss under privacy and corruption, which we believe have broad applicability across learning theory and statistics.
Reducing Pilots in Channel Estimation With Predictive Foundation Models
Dec 17, 2025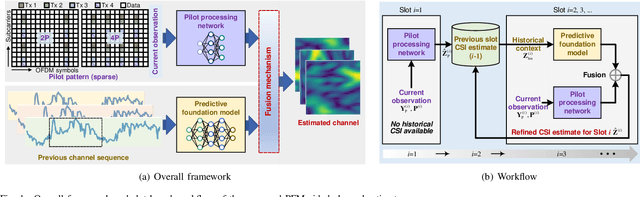
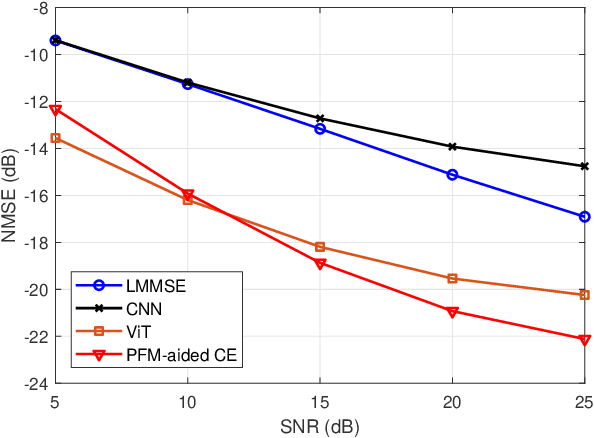
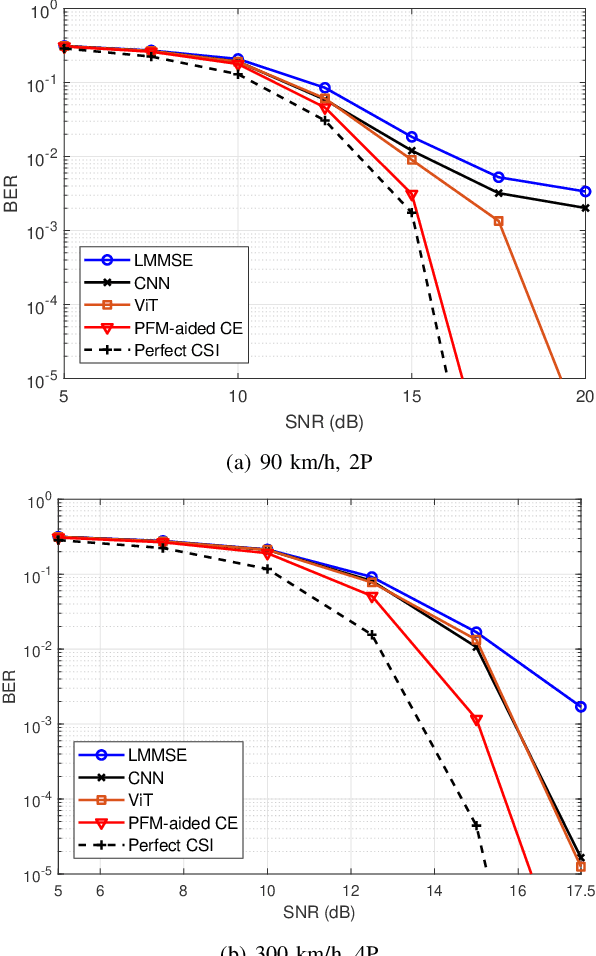
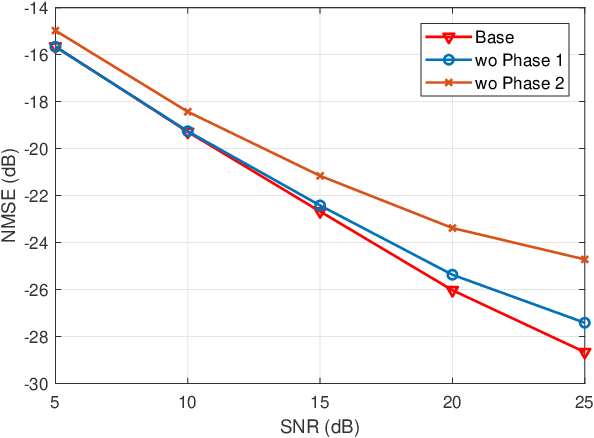
Abstract:Accurate channel state information (CSI) acquisition is essential for modern wireless systems, which becomes increasingly difficult under large antenna arrays, strict pilot overhead constraints, and diverse deployment environments. Existing artificial intelligence-based solutions often lack robustness and fail to generalize across scenarios. To address this limitation, this paper introduces a predictive-foundation-model-based channel estimation framework that enables accurate, low-overhead, and generalizable CSI acquisition. The proposed framework employs a predictive foundation model trained on large-scale cross-domain CSI data to extract universal channel representations and provide predictive priors with strong cross-scenario transferability. A pilot processing network based on a vision transformer architecture is further designed to capture spatial, temporal, and frequency correlations from pilot observations. An efficient fusion mechanism integrates predictive priors with real-time measurements, enabling reliable CSI reconstruction even under sparse or noisy conditions. Extensive evaluations across diverse configurations demonstrate that the proposed estimator significantly outperforms both classical and data-driven baselines in accuracy, robustness, and generalization capability.
Next-Generation AI-Native Wireless Communications: MCMC-Based Receiver Architectures for Unified Processing
Oct 02, 2025Abstract:The multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) receiver processing is a key technology for current and next-generation wireless communications. However, it faces significant challenges related to complexity and scalability as the number of antennas increases. Artificial intelligence (AI), a cornerstone of next-generation wireless networks, offers considerable potential for addressing these challenges. This paper proposes an AI-driven, universal MIMO receiver architecture based on Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) techniques. Unlike existing AI-based methods that treat receiver processing as a black box, our MCMC-based approach functions as a generic Bayesian computing engine applicable to various processing tasks, including channel estimation, symbol detection, and channel decoding. This method enhances the interpretability, scalability, and flexibility of receivers in diverse scenarios. Furthermore, the proposed approach integrates these tasks into a unified probabilistic framework, thereby enabling overall performance optimization. This unified framework can also be seamlessly combined with data-driven learning methods to facilitate the development of fully intelligent communication receivers.
Square$χ$PO: Differentially Private and Robust $χ^2$-Preference Optimization in Offline Direct Alignment
May 27, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we theoretically study the offline alignment of language models with human preference feedback, under both preference label corruption and privacy protections. To this end, we propose Square$\chi$PO, a simple one-line change to $\chi$PO where the standard log-loss is replaced by a new square loss over probability. Thanks to the inherent properties of this new loss, we have advanced the state-of-the-art of differentially private and robust offline direct alignment. Specifically, for the local model of label privacy, Square$\chi$PO is the first algorithm that attains an optimal rate based on single-policy concentrability even with general function approximations. It also gives the first result under the central model of privacy protection over both prompts (responses) and labels. On the robustness side against Huber label corruption, Square$\chi$PO is the first alignment method that has a meaningful theoretical guarantee under general function approximations. More importantly, Square$\chi$PO can address privacy protection and corruption simultaneously, where an interesting separation is observed, implying that the order of privacy and corruption matters. Furthermore, we show that Square$\chi$PO can also be easily extended to handle the scenario of the general preference model with state-of-the-art guarantees under corruption and privacy. Last but not least, all of our theoretical guarantees enjoy a unified analysis, building upon a new result on the generalization error bounds of least-square regression under corruption and privacy constraints, which we believe is of independent interest to the community.
A Unified Theoretical Analysis of Private and Robust Offline Alignment: from RLHF to DPO
May 21, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we theoretically investigate the effects of noisy labels in offline alignment, with a focus on the interplay between privacy and robustness against adversarial corruption. Specifically, under linear modeling assumptions, we present a unified analysis covering both reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) and direct preference optimization (DPO) under different privacy-corruption scenarios, such as Local differential privacy-then-Corruption (LTC), where human preference labels are privatized before being corrupted by an adversary, and Corruption-then-Local differential privacy (CTL), where labels are corrupted before privacy protection. Our analysis leverages a reduction framework that reduces the offline alignment problem under linear modeling assumptions to parameter estimation in logistic regression. This framework allows us to establish an interesting separation result between LTC and CTL, demonstrating that LTC presents a greater challenge than CTL in offline alignment, even under linear models. As important by-products, our findings also advance the state-of-the-art theoretical results in offline alignment under privacy-only or corruption-only scenarios.
Small Clips, Big Gains: Learning Long-Range Refocused Temporal Information for Video Super-Resolution
May 04, 2025Abstract:Video super-resolution (VSR) can achieve better performance compared to single image super-resolution by additionally leveraging temporal information. In particular, the recurrent-based VSR model exploits long-range temporal information during inference and achieves superior detail restoration. However, effectively learning these long-term dependencies within long videos remains a key challenge. To address this, we propose LRTI-VSR, a novel training framework for recurrent VSR that efficiently leverages Long-Range Refocused Temporal Information. Our framework includes a generic training strategy that utilizes temporal propagation features from long video clips while training on shorter video clips. Additionally, we introduce a refocused intra&inter-frame transformer block which allows the VSR model to selectively prioritize useful temporal information through its attention module while further improving inter-frame information utilization in the FFN module. We evaluate LRTI-VSR on both CNN and transformer-based VSR architectures, conducting extensive ablation studies to validate the contribution of each component. Experiments on long-video test sets demonstrate that LRTI-VSR achieves state-of-the-art performance while maintaining training and computational efficiency.
Neural Stereo Video Compression with Hybrid Disparity Compensation
Apr 29, 2025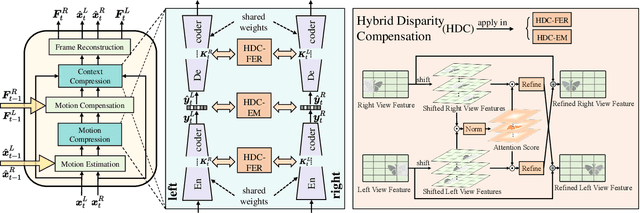
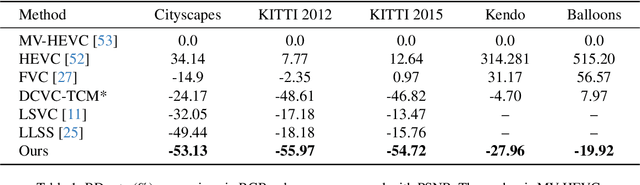
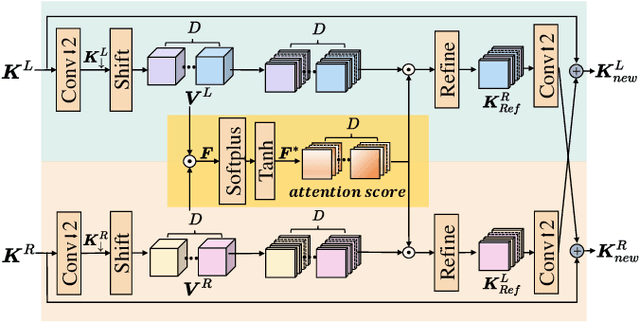
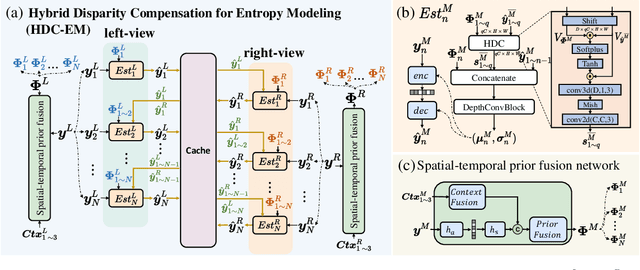
Abstract:Disparity compensation represents the primary strategy in stereo video compression (SVC) for exploiting cross-view redundancy. These mechanisms can be broadly categorized into two types: one that employs explicit horizontal shifting, and another that utilizes an implicit cross-attention mechanism to reduce cross-view disparity redundancy. In this work, we propose a hybrid disparity compensation (HDC) strategy that leverages explicit pixel displacement as a robust prior feature to simplify optimization and perform implicit cross-attention mechanisms for subsequent warping operations, thereby capturing a broader range of disparity information. Specifically, HDC first computes a similarity map by fusing the horizontally shifted cross-view features to capture pixel displacement information. This similarity map is then normalized into an "explicit pixel-wise attention score" to perform the cross-attention mechanism, implicitly aligning features from one view to another. Building upon HDC, we introduce a novel end-to-end optimized neural stereo video compression framework, which integrates HDC-based modules into key coding operations, including cross-view feature extraction and reconstruction (HDC-FER) and cross-view entropy modeling (HDC-EM). Extensive experiments on SVC benchmarks, including KITTI 2012, KITTI 2015, and Nagoya, which cover both autonomous driving and general scenes, demonstrate that our framework outperforms both neural and traditional SVC methodologies.
Joint Channel Estimation and Signal Detection for MIMO-OFDM: A Novel Data-Aided Approach with Reduced Computational Overhead
Apr 20, 2025



Abstract:The acquisition of channel state information (CSI) is essential in MIMO-OFDM communication systems. Data-aided enhanced receivers, by incorporating domain knowledge, effectively mitigate performance degradation caused by imperfect CSI, particularly in dynamic wireless environments. However, existing methodologies face notable challenges: they either refine channel estimates within MIMO subsystems separately, which proves ineffective due to deviations from assumptions regarding the time-varying nature of channels, or fully exploit the time-frequency characteristics but incur significantly high computational overhead due to dimensional concatenation. To address these issues, this study introduces a novel data-aided method aimed at reducing complexity, particularly suited for fast-fading scenarios in fifth-generation (5G) and beyond networks. We derive a general form of a data-aided linear minimum mean-square error (LMMSE)-based algorithm, optimized for iterative joint channel estimation and signal detection. Additionally, we propose a computationally efficient alternative to this algorithm, which achieves comparable performance with significantly reduced complexity. Empirical evaluations reveal that our proposed algorithms outperform several state-of-the-art approaches across various MIMO-OFDM configurations, pilot sequence lengths, and in the presence of time variability. Comparative analysis with basis expansion model-based iterative receivers highlights the superiority of our algorithms in achieving an effective trade-off between accuracy and computational complexity.
Learned Image Compression with Dictionary-based Entropy Model
Apr 01, 2025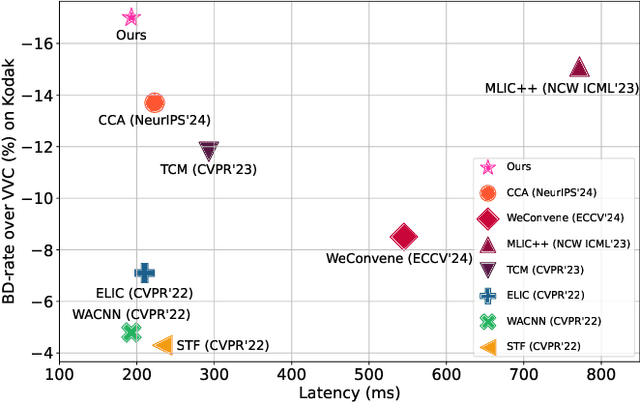
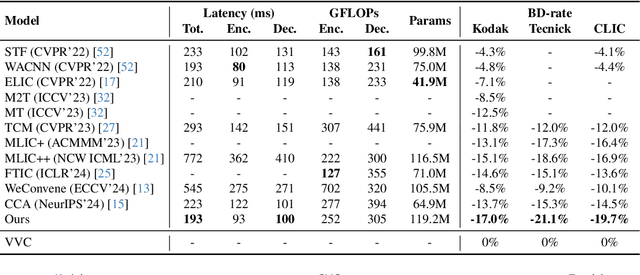
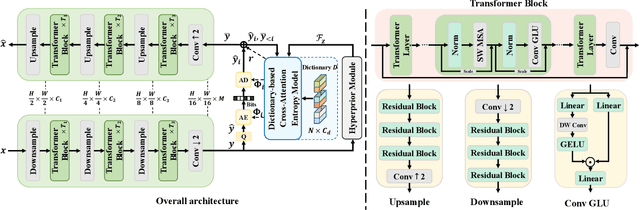
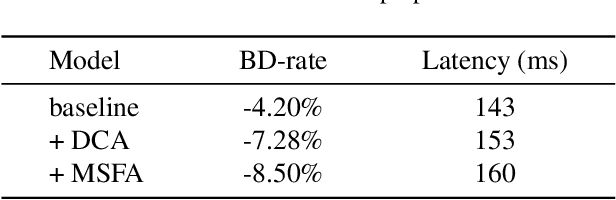
Abstract:Learned image compression methods have attracted great research interest and exhibited superior rate-distortion performance to the best classical image compression standards of the present. The entropy model plays a key role in learned image compression, which estimates the probability distribution of the latent representation for further entropy coding. Most existing methods employed hyper-prior and auto-regressive architectures to form their entropy models. However, they only aimed to explore the internal dependencies of latent representation while neglecting the importance of extracting prior from training data. In this work, we propose a novel entropy model named Dictionary-based Cross Attention Entropy model, which introduces a learnable dictionary to summarize the typical structures occurring in the training dataset to enhance the entropy model. Extensive experimental results have demonstrated that the proposed model strikes a better balance between performance and latency, achieving state-of-the-art results on various benchmark datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge