Shuhang Gu
School of Electrical and Information Engineering, The University of Sydney, Australia
From Local Windows to Adaptive Candidates via Individualized Exploratory: Rethinking Attention for Image Super-Resolution
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Single Image Super-Resolution (SISR) is a fundamental computer vision task that aims to reconstruct a high-resolution (HR) image from a low-resolution (LR) input. Transformer-based methods have achieved remarkable performance by modeling long-range dependencies in degraded images. However, their feature-intensive attention computation incurs high computational cost. To improve efficiency, most existing approaches partition images into fixed groups and restrict attention within each group. Such group-wise attention overlooks the inherent asymmetry in token similarities, thereby failing to enable flexible and token-adaptive attention computation. To address this limitation, we propose the Individualized Exploratory Transformer (IET), which introduces a novel Individualized Exploratory Attention (IEA) mechanism that allows each token to adaptively select its own content-aware and independent attention candidates. This token-adaptive and asymmetric design enables more precise information aggregation while maintaining computational efficiency. Extensive experiments on standard SR benchmarks demonstrate that IET achieves state-of-the-art performance under comparable computational complexity.
IDESplat: Iterative Depth Probability Estimation for Generalizable 3D Gaussian Splatting
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Generalizable 3D Gaussian Splatting aims to directly predict Gaussian parameters using a feed-forward network for scene reconstruction. Among these parameters, Gaussian means are particularly difficult to predict, so depth is usually estimated first and then unprojected to obtain the Gaussian sphere centers. Existing methods typically rely solely on a single warp to estimate depth probability, which hinders their ability to fully leverage cross-view geometric cues, resulting in unstable and coarse depth maps. To address this limitation, we propose IDESplat, which iteratively applies warp operations to boost depth probability estimation for accurate Gaussian mean prediction. First, to eliminate the inherent instability of a single warp, we introduce a Depth Probability Boosting Unit (DPBU) that integrates epipolar attention maps produced by cascading warp operations in a multiplicative manner. Next, we construct an iterative depth estimation process by stacking multiple DPBUs, progressively identifying potential depth candidates with high likelihood. As IDESplat iteratively boosts depth probability estimates and updates the depth candidates, the depth map is gradually refined, resulting in accurate Gaussian means. We conduct experiments on RealEstate10K, ACID, and DL3DV. IDESplat achieves outstanding reconstruction quality and state-of-the-art performance with real-time efficiency. On RE10K, it outperforms DepthSplat by 0.33 dB in PSNR, using only 10.7% of the parameters and 70% of the memory. Additionally, our IDESplat improves PSNR by 2.95 dB over DepthSplat on the DTU dataset in cross-dataset experiments, demonstrating its strong generalization ability.
Guiding a Diffusion Transformer with the Internal Dynamics of Itself
Dec 30, 2025Abstract:The diffusion model presents a powerful ability to capture the entire (conditional) data distribution. However, due to the lack of sufficient training and data to learn to cover low-probability areas, the model will be penalized for failing to generate high-quality images corresponding to these areas. To achieve better generation quality, guidance strategies such as classifier free guidance (CFG) can guide the samples to the high-probability areas during the sampling stage. However, the standard CFG often leads to over-simplified or distorted samples. On the other hand, the alternative line of guiding diffusion model with its bad version is limited by carefully designed degradation strategies, extra training and additional sampling steps. In this paper, we proposed a simple yet effective strategy Internal Guidance (IG), which introduces an auxiliary supervision on the intermediate layer during training process and extrapolates the intermediate and deep layer's outputs to obtain generative results during sampling process. This simple strategy yields significant improvements in both training efficiency and generation quality on various baselines. On ImageNet 256x256, SiT-XL/2+IG achieves FID=5.31 and FID=1.75 at 80 and 800 epochs. More impressively, LightningDiT-XL/1+IG achieves FID=1.34 which achieves a large margin between all of these methods. Combined with CFG, LightningDiT-XL/1+IG achieves the current state-of-the-art FID of 1.19.
BasicAVSR: Arbitrary-Scale Video Super-Resolution via Image Priors and Enhanced Motion Compensation
Oct 30, 2025Abstract:Arbitrary-scale video super-resolution (AVSR) aims to enhance the resolution of video frames, potentially at various scaling factors, which presents several challenges regarding spatial detail reproduction, temporal consistency, and computational complexity. In this paper, we propose a strong baseline BasicAVSR for AVSR by integrating four key components: 1) adaptive multi-scale frequency priors generated from image Laplacian pyramids, 2) a flow-guided propagation unit to aggregate spatiotemporal information from adjacent frames, 3) a second-order motion compensation unit for more accurate spatial alignment of adjacent frames, and 4) a hyper-upsampling unit to generate scale-aware and content-independent upsampling kernels. To meet diverse application demands, we instantiate three propagation variants: (i) a unidirectional RNN unit for strictly online inference, (ii) a unidirectional RNN unit empowered with a limited lookahead that tolerates a small output delay, and (iii) a bidirectional RNN unit designed for offline tasks where computational resources are less constrained. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness and adaptability of our model across these different scenarios. Through extensive experiments, we show that BasicAVSR significantly outperforms existing methods in terms of super-resolution quality, generalization ability, and inference speed. Our work not only advances the state-of-the-art in AVSR but also extends its core components to multiple frameworks for diverse scenarios. The code is available at https://github.com/shangwei5/BasicAVSR.
Learning Pixel-adaptive Multi-layer Perceptrons for Real-time Image Enhancement
Jul 16, 2025Abstract:Deep learning-based bilateral grid processing has emerged as a promising solution for image enhancement, inherently encoding spatial and intensity information while enabling efficient full-resolution processing through slicing operations. However, existing approaches are limited to linear affine transformations, hindering their ability to model complex color relationships. Meanwhile, while multi-layer perceptrons (MLPs) excel at non-linear mappings, traditional MLP-based methods employ globally shared parameters, which is hard to deal with localized variations. To overcome these dual challenges, we propose a Bilateral Grid-based Pixel-Adaptive Multi-layer Perceptron (BPAM) framework. Our approach synergizes the spatial modeling of bilateral grids with the non-linear capabilities of MLPs. Specifically, we generate bilateral grids containing MLP parameters, where each pixel dynamically retrieves its unique transformation parameters and obtain a distinct MLP for color mapping based on spatial coordinates and intensity values. In addition, we propose a novel grid decomposition strategy that categorizes MLP parameters into distinct types stored in separate subgrids. Multi-channel guidance maps are used to extract category-specific parameters from corresponding subgrids, ensuring effective utilization of color information during slicing while guiding precise parameter generation. Extensive experiments on public datasets demonstrate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art methods in performance while maintaining real-time processing capabilities.
Learning Unpaired Image Dehazing with Physics-based Rehazy Generation
Jun 15, 2025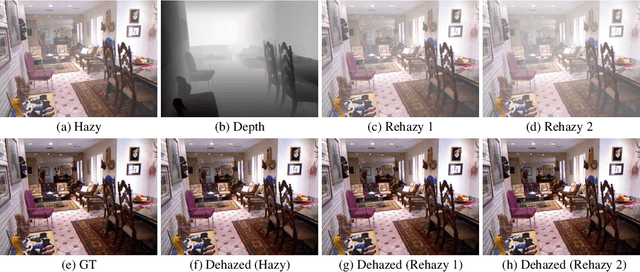
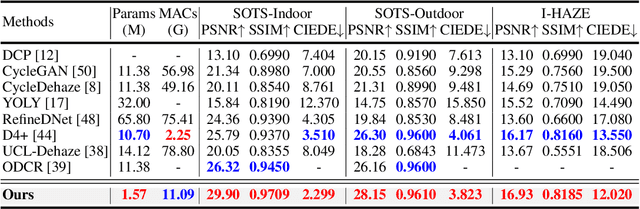
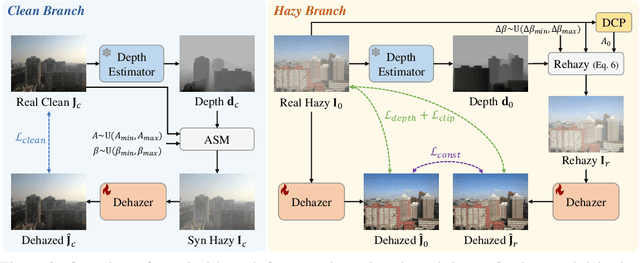
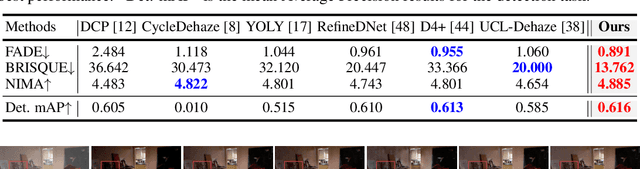
Abstract:Overfitting to synthetic training pairs remains a critical challenge in image dehazing, leading to poor generalization capability to real-world scenarios. To address this issue, existing approaches utilize unpaired realistic data for training, employing CycleGAN or contrastive learning frameworks. Despite their progress, these methods often suffer from training instability, resulting in limited dehazing performance. In this paper, we propose a novel training strategy for unpaired image dehazing, termed Rehazy, to improve both dehazing performance and training stability. This strategy explores the consistency of the underlying clean images across hazy images and utilizes hazy-rehazy pairs for effective learning of real haze characteristics. To favorably construct hazy-rehazy pairs, we develop a physics-based rehazy generation pipeline, which is theoretically validated to reliably produce high-quality rehazy images. Additionally, leveraging the rehazy strategy, we introduce a dual-branch framework for dehazing network training, where a clean branch provides a basic dehazing capability in a synthetic manner, and a hazy branch enhances the generalization ability with hazy-rehazy pairs. Moreover, we design a new dehazing network within these branches to improve the efficiency, which progressively restores clean scenes from coarse to fine. Extensive experiments on four benchmarks demonstrate the superior performance of our approach, exceeding the previous state-of-the-art methods by 3.58 dB on the SOTS-Indoor dataset and by 1.85 dB on the SOTS-Outdoor dataset in PSNR. Our code will be publicly available.
Generative Image Compression by Estimating Gradients of the Rate-variable Feature Distribution
May 27, 2025Abstract:While learned image compression (LIC) focuses on efficient data transmission, generative image compression (GIC) extends this framework by integrating generative modeling to produce photo-realistic reconstructed images. In this paper, we propose a novel diffusion-based generative modeling framework tailored for generative image compression. Unlike prior diffusion-based approaches that indirectly exploit diffusion modeling, we reinterpret the compression process itself as a forward diffusion path governed by stochastic differential equations (SDEs). A reverse neural network is trained to reconstruct images by reversing the compression process directly, without requiring Gaussian noise initialization. This approach achieves smooth rate adjustment and photo-realistic reconstructions with only a minimal number of sampling steps. Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate that our method outperforms existing generative image compression approaches across a range of metrics, including perceptual distortion, statistical fidelity, and no-reference quality assessments.
MVAR: Visual Autoregressive Modeling with Scale and Spatial Markovian Conditioning
May 19, 2025Abstract:Essential to visual generation is efficient modeling of visual data priors. Conventional next-token prediction methods define the process as learning the conditional probability distribution of successive tokens. Recently, next-scale prediction methods redefine the process to learn the distribution over multi-scale representations, significantly reducing generation latency. However, these methods condition each scale on all previous scales and require each token to consider all preceding tokens, exhibiting scale and spatial redundancy. To better model the distribution by mitigating redundancy, we propose Markovian Visual AutoRegressive modeling (MVAR), a novel autoregressive framework that introduces scale and spatial Markov assumptions to reduce the complexity of conditional probability modeling. Specifically, we introduce a scale-Markov trajectory that only takes as input the features of adjacent preceding scale for next-scale prediction, enabling the adoption of a parallel training strategy that significantly reduces GPU memory consumption. Furthermore, we propose spatial-Markov attention, which restricts the attention of each token to a localized neighborhood of size k at corresponding positions on adjacent scales, rather than attending to every token across these scales, for the pursuit of reduced modeling complexity. Building on these improvements, we reduce the computational complexity of attention calculation from O(N^2) to O(Nk), enabling training with just eight NVIDIA RTX 4090 GPUs and eliminating the need for KV cache during inference. Extensive experiments on ImageNet demonstrate that MVAR achieves comparable or superior performance with both small model trained from scratch and large fine-tuned models, while reducing the average GPU memory footprint by 3.0x.
Small Clips, Big Gains: Learning Long-Range Refocused Temporal Information for Video Super-Resolution
May 04, 2025Abstract:Video super-resolution (VSR) can achieve better performance compared to single image super-resolution by additionally leveraging temporal information. In particular, the recurrent-based VSR model exploits long-range temporal information during inference and achieves superior detail restoration. However, effectively learning these long-term dependencies within long videos remains a key challenge. To address this, we propose LRTI-VSR, a novel training framework for recurrent VSR that efficiently leverages Long-Range Refocused Temporal Information. Our framework includes a generic training strategy that utilizes temporal propagation features from long video clips while training on shorter video clips. Additionally, we introduce a refocused intra&inter-frame transformer block which allows the VSR model to selectively prioritize useful temporal information through its attention module while further improving inter-frame information utilization in the FFN module. We evaluate LRTI-VSR on both CNN and transformer-based VSR architectures, conducting extensive ablation studies to validate the contribution of each component. Experiments on long-video test sets demonstrate that LRTI-VSR achieves state-of-the-art performance while maintaining training and computational efficiency.
HiLLIE: Human-in-the-Loop Training for Low-Light Image Enhancement
May 04, 2025Abstract:Developing effective approaches to generate enhanced results that align well with human visual preferences for high-quality well-lit images remains a challenge in low-light image enhancement (LLIE). In this paper, we propose a human-in-the-loop LLIE training framework that improves the visual quality of unsupervised LLIE model outputs through iterative training stages, named HiLLIE. At each stage, we introduce human guidance into the training process through efficient visual quality annotations of enhanced outputs. Subsequently, we employ a tailored image quality assessment (IQA) model to learn human visual preferences encoded in the acquired labels, which is then utilized to guide the training process of an enhancement model. With only a small amount of pairwise ranking annotations required at each stage, our approach continually improves the IQA model's capability to simulate human visual assessment of enhanced outputs, thus leading to visually appealing LLIE results. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach significantly improves unsupervised LLIE model performance in terms of both quantitative and qualitative performance. The code and collected ranking dataset will be available at https://github.com/LabShuHangGU/HiLLIE.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge