Yang Zhao
Frank
ShardMemo: Masked MoE Routing for Sharded Agentic LLM Memory
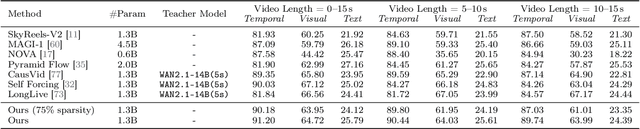
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Agentic large language model (LLM) systems rely on external memory for long-horizon state and concurrent multi-agent execution, but centralized indexes and heuristic partitions become bottlenecks as memory volume and parallel access grow. We present ShardMemo, a budgeted tiered memory service with Tier A per-agent working state, Tier B sharded evidence with shard-local approximate nearest neighbor (ANN) indexes, and Tier C, a versioned skill library. Tier B enforces scope-before-routing: structured eligibility constraints mask ineligible shards before routing or ANN search. We cast shard probing as masked mixture-of-experts (MoE) routing over eligible shards, probing up to $B_{\mathrm{probe}}$ shards via Top-$B_{\mathrm{probe}}$ or adaptive Top-$P$, and use cost-aware gating over profile/observation/session shard families; the router is trained from evidence-to-shard supervision. On LoCoMo, ShardMemo improves over the strongest baseline (GAM) by +5.11 to +6.82 F1 across question categories. Under a fixed-budget routing setting ($B_{\mathrm{probe}}=3$), ShardMemo improves over cosine-to-prototype shard routing by +6.87 F1 while reducing retrieval work (VecScan 521->414, -20.5%) and p95 latency (95->76 ms). On long-context HotpotQA, ShardMemo achieves 63.41/61.88/57.95 F1 at 56K/224K/448K tokens. On ToolBench, Tier C reaches 0.97 Precision@3 and 1.94 StepRed (+10.2% and +7.2% over embedding-similarity retrieval).
SKANet: A Cognitive Dual-Stream Framework with Adaptive Modality Fusion for Robust Compound GNSS Interference Classification
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:As the electromagnetic environment becomes increasingly complex, Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) face growing threats from sophisticated jamming interference. Although Deep Learning (DL) effectively identifies basic interference, classifying compound interference remains difficult due to the superposition of diverse jamming sources. Existing single-domain approaches often suffer from performance degradation because transient burst signals and continuous global signals require conflicting feature extraction scales. We propose the Selective Kernel and Asymmetric convolution Network(SKANet), a cognitive deep learning framework built upon a dual-stream architecture that integrates Time-Frequency Images (TFIs) and Power Spectral Density (PSD). Distinct from conventional fusion methods that rely on static receptive fields, the proposed architecture incorporates a Multi-Branch Selective Kernel (SK) module combined with Asymmetric Convolution Blocks (ACBs). This mechanism enables the network to dynamically adjust its receptive fields, acting as an adaptive filter that simultaneously captures micro-scale transient features and macro-scale spectral trends within entangled compound signals. To complement this spatial-temporal adaptation, a Squeeze-and-Excitation (SE) mechanism is integrated at the fusion stage to adaptively recalibrate the contribution of heterogeneous features from each modality. Evaluations on a dataset of 405,000 samples demonstrate that SKANet achieves an overall accuracy of 96.99\%, exhibiting superior robustness for compound jamming classification, particularly under low Jamming-to-Noise Ratio (JNR) regimes.
PhyG-MoE: A Physics-Guided Mixture-of-Experts Framework for Energy-Efficient GNSS Interference Recognition
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:Complex electromagnetic interference increasingly compromises Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS), threatening the reliability of Space-Air-Ground Integrated Networks (SAGIN). Although deep learning has advanced interference recognition, current static models suffer from a \textbf{fundamental limitation}: they impose a fixed computational topology regardless of the input's physical entropy. This rigidity leads to severe resource mismatch, where simple primitives consume the same processing cost as chaotic, saturated mixtures. To resolve this, this paper introduces PhyG-MoE (Physics-Guided Mixture-of-Experts), a framework designed to \textbf{dynamically align model capacity with signal complexity}. Unlike static architectures, the proposed system employs a spectrum-based gating mechanism that routes signals based on their spectral feature entanglement. A high-capacity TransNeXt expert is activated on-demand to disentangle complex features in saturated scenarios, while lightweight experts handle fundamental signals to minimize latency. Evaluations on 21 jamming categories demonstrate that PhyG-MoE achieves an overall accuracy of 97.58\%. By resolving the intrinsic conflict between static computing and dynamic electromagnetic environments, the proposed framework significantly reduces computational overhead without performance degradation, offering a viable solution for resource-constrained cognitive receivers.
Consolidation or Adaptation? PRISM: Disentangling SFT and RL Data via Gradient Concentration
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:While Hybrid Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) followed by Reinforcement Learning (RL) has become the standard paradigm for training LLM agents, effective mechanisms for data allocation between these stages remain largely underexplored. Current data arbitration strategies often rely on surface-level heuristics that fail to diagnose intrinsic learning needs. Since SFT targets pattern consolidation through imitation while RL drives structural adaptation via exploration, misaligning data with these functional roles causes severe optimization interference. We propose PRISM, a dynamics-aware framework grounded in Schema Theory that arbitrates data based on its degree of cognitive conflict with the model's existing knowledge. By analyzing the spatial geometric structure of gradients, PRISM identifies data triggering high spatial concentration as high-conflict signals that require RL for structural restructuring. In contrast, data yielding diffuse updates is routed to SFT for efficient consolidation. Extensive experiments on WebShop and ALFWorld demonstrate that PRISM achieves a Pareto improvement, outperforming state-of-the-art hybrid methods while reducing computational costs by up to 3.22$\times$. Our findings suggest that disentangling data based on internal optimization regimes is crucial for scalable and robust agent alignment.
MAESTRO: Meta-learning Adaptive Estimation of Scalarization Trade-offs for Reward Optimization
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Group-Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) has emerged as an efficient paradigm for aligning Large Language Models (LLMs), yet its efficacy is primarily confined to domains with verifiable ground truths. Extending GRPO to open-domain settings remains a critical challenge, as unconstrained generation entails multi-faceted and often conflicting objectives - such as creativity versus factuality - where rigid, static reward scalarization is inherently suboptimal. To address this, we propose MAESTRO (Meta-learning Adaptive Estimation of Scalarization Trade-offs for Reward Optimization), which introduces a meta-cognitive orchestration layer that treats reward scalarization as a dynamic latent policy, leveraging the model's terminal hidden states as a semantic bottleneck to perceive task-specific priorities. We formulate this as a contextual bandit problem within a bi-level optimization framework, where a lightweight Conductor network co-evolves with the policy by utilizing group-relative advantages as a meta-reward signal. Across seven benchmarks, MAESTRO consistently outperforms single-reward and static multi-objective baselines, while preserving the efficiency advantages of GRPO, and in some settings even reducing redundant generation.
HiSciBench: A Hierarchical Multi-disciplinary Benchmark for Scientific Intelligence from Reading to Discovery
Dec 28, 2025Abstract:The rapid advancement of large language models (LLMs) and multimodal foundation models has sparked growing interest in their potential for scientific research. However, scientific intelligence encompasses a broad spectrum of abilities ranging from understanding fundamental knowledge to conducting creative discovery, and existing benchmarks remain fragmented. Most focus on narrow tasks and fail to reflect the hierarchical and multi-disciplinary nature of real scientific inquiry. We introduce \textbf{HiSciBench}, a hierarchical benchmark designed to evaluate foundation models across five levels that mirror the complete scientific workflow: \textit{Scientific Literacy} (L1), \textit{Literature Parsing} (L2), \textit{Literature-based Question Answering} (L3), \textit{Literature Review Generation} (L4), and \textit{Scientific Discovery} (L5). HiSciBench contains 8,735 carefully curated instances spanning six major scientific disciplines, including mathematics, physics, chemistry, biology, geography, and astronomy, and supports multimodal inputs including text, equations, figures, and tables, as well as cross-lingual evaluation. Unlike prior benchmarks that assess isolated abilities, HiSciBench provides an integrated, dependency-aware framework that enables detailed diagnosis of model capabilities across different stages of scientific reasoning. Comprehensive evaluations of leading models, including GPT-5, DeepSeek-R1, and several multimodal systems, reveal substantial performance gaps: while models achieve up to 69\% accuracy on basic literacy tasks, performance declines sharply to 25\% on discovery-level challenges. HiSciBench establishes a new standard for evaluating scientific Intelligence and offers actionable insights for developing models that are not only more capable but also more reliable. The benchmark will be publicly released to facilitate future research.
Seedance 1.5 pro: A Native Audio-Visual Joint Generation Foundation Model
Dec 23, 2025Abstract:Recent strides in video generation have paved the way for unified audio-visual generation. In this work, we present Seedance 1.5 pro, a foundational model engineered specifically for native, joint audio-video generation. Leveraging a dual-branch Diffusion Transformer architecture, the model integrates a cross-modal joint module with a specialized multi-stage data pipeline, achieving exceptional audio-visual synchronization and superior generation quality. To ensure practical utility, we implement meticulous post-training optimizations, including Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) on high-quality datasets and Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) with multi-dimensional reward models. Furthermore, we introduce an acceleration framework that boosts inference speed by over 10X. Seedance 1.5 pro distinguishes itself through precise multilingual and dialect lip-syncing, dynamic cinematic camera control, and enhanced narrative coherence, positioning it as a robust engine for professional-grade content creation. Seedance 1.5 pro is now accessible on Volcano Engine at https://console.volcengine.com/ark/region:ark+cn-beijing/experience/vision?type=GenVideo.
End-to-End Training for Autoregressive Video Diffusion via Self-Resampling
Dec 17, 2025
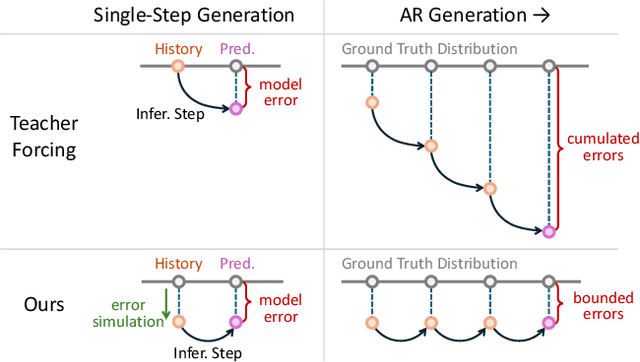

Abstract:Autoregressive video diffusion models hold promise for world simulation but are vulnerable to exposure bias arising from the train-test mismatch. While recent works address this via post-training, they typically rely on a bidirectional teacher model or online discriminator. To achieve an end-to-end solution, we introduce Resampling Forcing, a teacher-free framework that enables training autoregressive video models from scratch and at scale. Central to our approach is a self-resampling scheme that simulates inference-time model errors on history frames during training. Conditioned on these degraded histories, a sparse causal mask enforces temporal causality while enabling parallel training with frame-level diffusion loss. To facilitate efficient long-horizon generation, we further introduce history routing, a parameter-free mechanism that dynamically retrieves the top-k most relevant history frames for each query. Experiments demonstrate that our approach achieves performance comparable to distillation-based baselines while exhibiting superior temporal consistency on longer videos owing to native-length training.
VaseVQA-3D: Benchmarking 3D VLMs on Ancient Greek Pottery
Oct 06, 2025



Abstract:Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have achieved significant progress in multimodal understanding tasks, demonstrating strong capabilities particularly in general tasks such as image captioning and visual reasoning. However, when dealing with specialized cultural heritage domains like 3D vase artifacts, existing models face severe data scarcity issues and insufficient domain knowledge limitations. Due to the lack of targeted training data, current VLMs struggle to effectively handle such culturally significant specialized tasks. To address these challenges, we propose the VaseVQA-3D dataset, which serves as the first 3D visual question answering dataset for ancient Greek pottery analysis, collecting 664 ancient Greek vase 3D models with corresponding question-answer data and establishing a complete data construction pipeline. We further develop the VaseVLM model, enhancing model performance in vase artifact analysis through domain-adaptive training. Experimental results validate the effectiveness of our approach, where we improve by 12.8% on R@1 metrics and by 6.6% on lexical similarity compared with previous state-of-the-art on the VaseVQA-3D dataset, significantly improving the recognition and understanding of 3D vase artifacts, providing new technical pathways for digital heritage preservation research.
MANZANO: A Simple and Scalable Unified Multimodal Model with a Hybrid Vision Tokenizer
Sep 19, 2025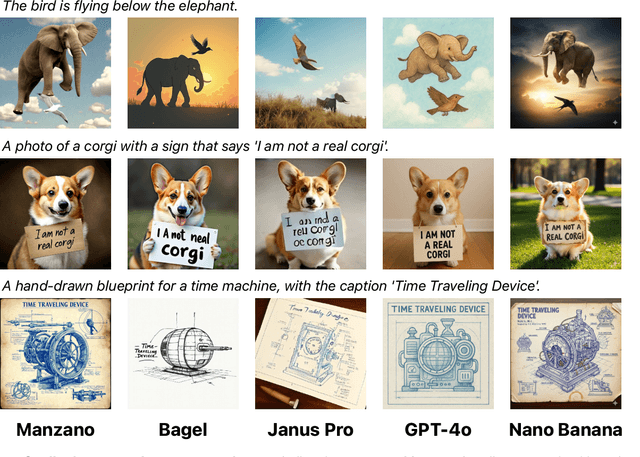
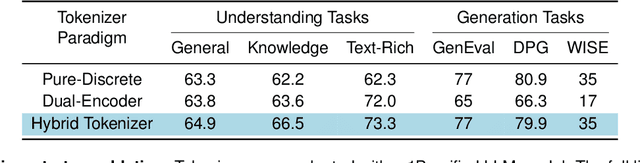
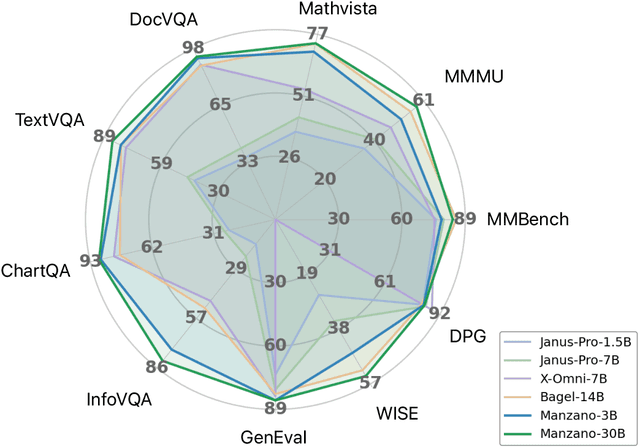
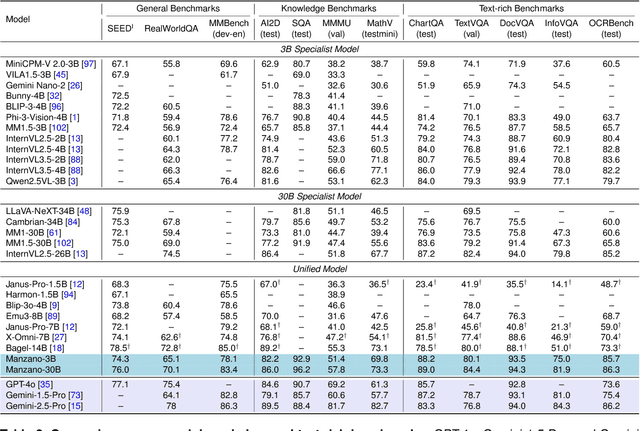
Abstract:Unified multimodal Large Language Models (LLMs) that can both understand and generate visual content hold immense potential. However, existing open-source models often suffer from a performance trade-off between these capabilities. We present Manzano, a simple and scalable unified framework that substantially reduces this tension by coupling a hybrid image tokenizer with a well-curated training recipe. A single shared vision encoder feeds two lightweight adapters that produce continuous embeddings for image-to-text understanding and discrete tokens for text-to-image generation within a common semantic space. A unified autoregressive LLM predicts high-level semantics in the form of text and image tokens, with an auxiliary diffusion decoder subsequently translating the image tokens into pixels. The architecture, together with a unified training recipe over understanding and generation data, enables scalable joint learning of both capabilities. Manzano achieves state-of-the-art results among unified models, and is competitive with specialist models, particularly on text-rich evaluation. Our studies show minimal task conflicts and consistent gains from scaling model size, validating our design choice of a hybrid tokenizer.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge