Yi Xu
Pretraining with Token-Level Adaptive Latent Chain-of-Thought
Feb 09, 2026Abstract:Scaling large language models by increasing parameters and training data is increasingly constrained by limited high-quality corpora and rising communication costs. This work explores an alternative axis: increasing per-token computation without expanding parameters, by internalizing latent Chain-of-Thought (CoT) into pretraining. We propose Pretraining with Token-Level Adaptive Latent CoT (adaptive latent CoT), where the model generates a variable-length latent CoT trajectory before emitting each token -- allocating longer trajectories to difficult tokens and shorter (or even zero) trajectories to easy ones. Importantly, this behavior emerges naturally from one-stage pretraining on general text and reduces computation in both training and inference via token-wise adaptive halting. Experiments with Llama architectures show that adaptive latent CoT consistently improves language modeling perplexity and broad downstream accuracy, even with fewer training FLOPs than prior recurrent baselines.
Thinking in Frames: How Visual Context and Test-Time Scaling Empower Video Reasoning
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Vision-Language Models have excelled at textual reasoning, but they often struggle with fine-grained spatial understanding and continuous action planning, failing to simulate the dynamics required for complex visual reasoning. In this work, we formulate visual reasoning by means of video generation models, positing that generated frames can act as intermediate reasoning steps between initial states and solutions. We evaluate their capacity in two distinct regimes: Maze Navigation for sequential discrete planning with low visual change and Tangram Puzzle for continuous manipulation with high visual change. Our experiments reveal three critical insights: (1) Robust Zero-Shot Generalization: In both tasks, the model demonstrates strong performance on unseen data distributions without specific finetuning. (2) Visual Context: The model effectively uses visual context as explicit control, such as agent icons and tangram shapes, enabling it to maintain high visual consistency and adapt its planning capability robustly to unseen patterns. (3) Visual Test-Time Scaling: We observe a test-time scaling law in sequential planning; increasing the generated video length (visual inference budget) empowers better zero-shot generalization to spatially and temporally complex paths. These findings suggest that video generation is not merely a media tool, but a scalable, generalizable paradigm for visual reasoning.
NeRF-MIR: Towards High-Quality Restoration of Masked Images with Neural Radiance Fields
Jan 24, 2026Abstract:Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) have demonstrated remarkable performance in novel view synthesis. However, there is much improvement room on restoring 3D scenes based on NeRF from corrupted images, which are common in natural scene captures and can significantly impact the effectiveness of NeRF. This paper introduces NeRF-MIR, a novel neural rendering approach specifically proposed for the restoration of masked images, demonstrating the potential of NeRF in this domain. Recognizing that randomly emitting rays to pixels in NeRF may not effectively learn intricate image textures, we propose a \textbf{P}atch-based \textbf{E}ntropy for \textbf{R}ay \textbf{E}mitting (\textbf{PERE}) strategy to distribute emitted rays properly. This enables NeRF-MIR to fuse comprehensive information from images of different views. Additionally, we introduce a \textbf{P}rogressively \textbf{I}terative \textbf{RE}storation (\textbf{PIRE}) mechanism to restore the masked regions in a self-training process. Furthermore, we design a dynamically-weighted loss function that automatically recalibrates the loss weights for masked regions. As existing datasets do not support NeRF-based masked image restoration, we construct three masked datasets to simulate corrupted scenarios. Extensive experiments on real data and constructed datasets demonstrate the superiority of NeRF-MIR over its counterparts in masked image restoration.
Adaptive Speaker Embedding Self-Augmentation for Personal Voice Activity Detection with Short Enrollment Speech
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:Personal Voice Activity Detection (PVAD) is crucial for identifying target speaker segments in the mixture, yet its performance heavily depends on the quality of speaker embeddings. A key practical limitation is the short enrollment speech--such as a wake-up word--which provides limited cues. This paper proposes a novel adaptive speaker embedding self-augmentation strategy that enhances PVAD performance by augmenting the original enrollment embeddings through additive fusion of keyframe embeddings extracted from mixed speech. Furthermore, we introduce a long-term adaptation strategy to iteratively refine embeddings during detection, mitigating speaker temporal variability. Experiments show significant gains in recall, precision, and F1-score under short enrollment conditions, matching full-length enrollment performance after five iterative updates. The source code is available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/ASE-PVAD-E5D6 .
Controlled Self-Evolution for Algorithmic Code Optimization
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Self-evolution methods enhance code generation through iterative "generate-verify-refine" cycles, yet existing approaches suffer from low exploration efficiency, failing to discover solutions with superior complexity within limited budgets. This inefficiency stems from initialization bias trapping evolution in poor solution regions, uncontrolled stochastic operations lacking feedback guidance, and insufficient experience utilization across tasks. To address these bottlenecks, we propose Controlled Self-Evolution (CSE), which consists of three key components. Diversified Planning Initialization generates structurally distinct algorithmic strategies for broad solution space coverage. Genetic Evolution replaces stochastic operations with feedback-guided mechanisms, enabling targeted mutation and compositional crossover. Hierarchical Evolution Memory captures both successful and failed experiences at inter-task and intra-task levels. Experiments on EffiBench-X demonstrate that CSE consistently outperforms all baselines across various LLM backbones. Furthermore, CSE achieves higher efficiency from early generations and maintains continuous improvement throughout evolution. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/QuantaAlpha/EvoControl.
Inference-Time Alignment for Diffusion Models via Doob's Matching
Jan 10, 2026Abstract:Inference-time alignment for diffusion models aims to adapt a pre-trained diffusion model toward a target distribution without retraining the base score network, thereby preserving the generative capacity of the base model while enforcing desired properties at the inference time. A central mechanism for achieving such alignment is guidance, which modifies the sampling dynamics through an additional drift term. In this work, we introduce Doob's matching, a novel framework for guidance estimation grounded in Doob's $h$-transform. Our approach formulates guidance as the gradient of logarithm of an underlying Doob's $h$-function and employs gradient-penalized regression to simultaneously estimate both the $h$-function and its gradient, resulting in a consistent estimator of the guidance. Theoretically, we establish non-asymptotic convergence rates for the estimated guidance. Moreover, we analyze the resulting controllable diffusion processes and prove non-asymptotic convergence guarantees for the generated distributions in the 2-Wasserstein distance.
G3Splat: Geometrically Consistent Generalizable Gaussian Splatting
Dec 19, 2025Abstract:3D Gaussians have recently emerged as an effective scene representation for real-time splatting and accurate novel-view synthesis, motivating several works to adapt multi-view structure prediction networks to regress per-pixel 3D Gaussians from images. However, most prior work extends these networks to predict additional Gaussian parameters -- orientation, scale, opacity, and appearance -- while relying almost exclusively on view-synthesis supervision. We show that a view-synthesis loss alone is insufficient to recover geometrically meaningful splats in this setting. We analyze and address the ambiguities of learning 3D Gaussian splats under self-supervision for pose-free generalizable splatting, and introduce G3Splat, which enforces geometric priors to obtain geometrically consistent 3D scene representations. Trained on RE10K, our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance in (i) geometrically consistent reconstruction, (ii) relative pose estimation, and (iii) novel-view synthesis. We further demonstrate strong zero-shot generalization on ScanNet, substantially outperforming prior work in both geometry recovery and relative pose estimation. Code and pretrained models are released on our project page (https://m80hz.github.io/g3splat/).
Distillation-Guided Structural Transfer for Continual Learning Beyond Sparse Distributed Memory
Dec 17, 2025Abstract:Sparse neural systems are gaining traction for efficient continual learning due to their modularity and low interference. Architectures such as Sparse Distributed Memory Multi-Layer Perceptrons (SDMLP) construct task-specific subnetworks via Top-K activation and have shown resilience against catastrophic forgetting. However, their rigid modularity limits cross-task knowledge reuse and leads to performance degradation under high sparsity. We propose Selective Subnetwork Distillation (SSD), a structurally guided continual learning framework that treats distillation not as a regularizer but as a topology-aligned information conduit. SSD identifies neurons with high activation frequency and selectively distills knowledge within previous Top-K subnetworks and output logits, without requiring replay or task labels. This enables structural realignment while preserving sparse modularity. Experiments on Split CIFAR-10, CIFAR-100, and MNIST demonstrate that SSD improves accuracy, retention, and representation coverage, offering a structurally grounded solution for sparse continual learning.
FaultDiffusion: Few-Shot Fault Time Series Generation with Diffusion Model
Nov 19, 2025Abstract:In industrial equipment monitoring, fault diagnosis is critical for ensuring system reliability and enabling predictive maintenance. However, the scarcity of fault data, due to the rarity of fault events and the high cost of data annotation, significantly hinders data-driven approaches. Existing time-series generation models, optimized for abundant normal data, struggle to capture fault distributions in few-shot scenarios, producing samples that lack authenticity and diversity due to the large domain gap and high intra-class variability of faults. To address this, we propose a novel few-shot fault time-series generation framework based on diffusion models. Our approach employs a positive-negative difference adapter, leveraging pre-trained normal data distributions to model the discrepancies between normal and fault domains for accurate fault synthesis. Additionally, a diversity loss is introduced to prevent mode collapse, encouraging the generation of diverse fault samples through inter-sample difference regularization. Experimental results demonstrate that our model significantly outperforms traditional methods in authenticity and diversity, achieving state-of-the-art performance on key benchmarks.
Towards High-Consistency Embodied World Model with Multi-View Trajectory Videos
Nov 19, 2025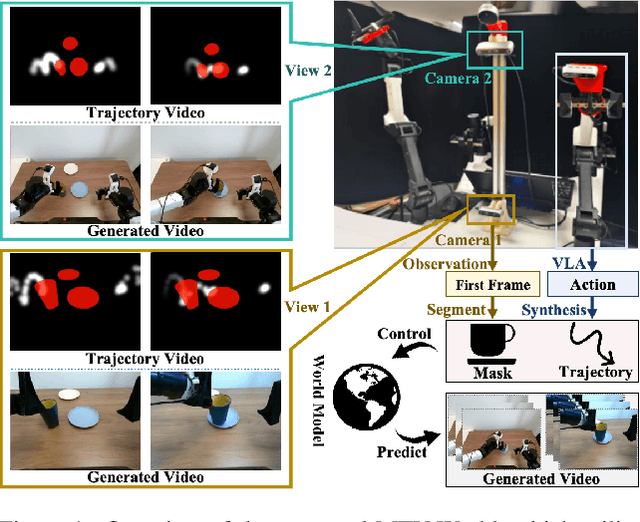
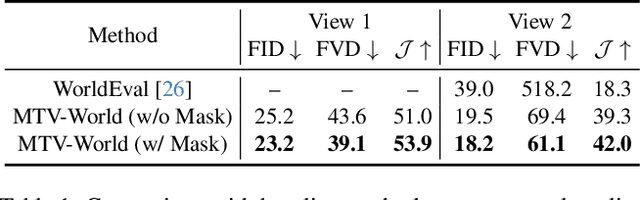
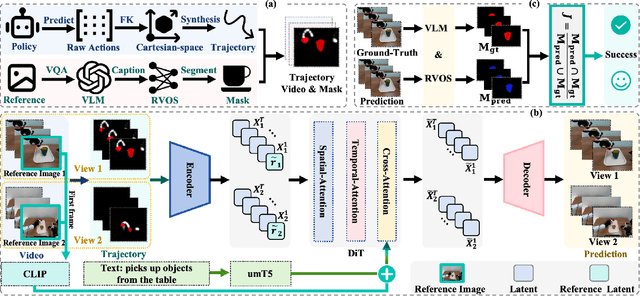
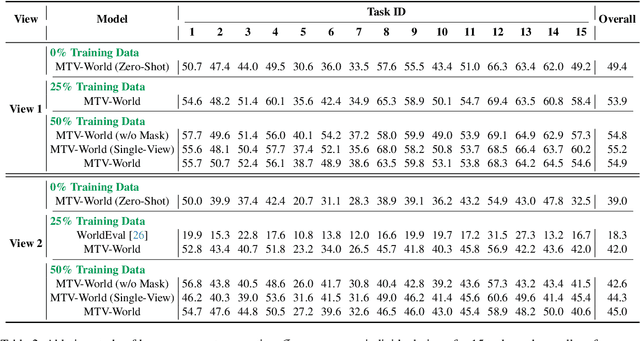
Abstract:Embodied world models aim to predict and interact with the physical world through visual observations and actions. However, existing models struggle to accurately translate low-level actions (e.g., joint positions) into precise robotic movements in predicted frames, leading to inconsistencies with real-world physical interactions. To address these limitations, we propose MTV-World, an embodied world model that introduces Multi-view Trajectory-Video control for precise visuomotor prediction. Specifically, instead of directly using low-level actions for control, we employ trajectory videos obtained through camera intrinsic and extrinsic parameters and Cartesian-space transformation as control signals. However, projecting 3D raw actions onto 2D images inevitably causes a loss of spatial information, making a single view insufficient for accurate interaction modeling. To overcome this, we introduce a multi-view framework that compensates for spatial information loss and ensures high-consistency with physical world. MTV-World forecasts future frames based on multi-view trajectory videos as input and conditioning on an initial frame per view. Furthermore, to systematically evaluate both robotic motion precision and object interaction accuracy, we develop an auto-evaluation pipeline leveraging multimodal large models and referring video object segmentation models. To measure spatial consistency, we formulate it as an object location matching problem and adopt the Jaccard Index as the evaluation metric. Extensive experiments demonstrate that MTV-World achieves precise control execution and accurate physical interaction modeling in complex dual-arm scenarios.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge