Zhang Chen
MS-ISSM: Objective Quality Assessment of Point Clouds Using Multi-scale Implicit Structural Similarity
Jan 03, 2026Abstract:The unstructured and irregular nature of point clouds poses a significant challenge for objective quality assessment (PCQA), particularly in establishing accurate perceptual feature correspondence. To tackle this, we propose the Multi-scale Implicit Structural Similarity Measurement (MS-ISSM). Unlike traditional point-to-point matching, MS-ISSM utilizes Radial Basis Functions (RBF) to represent local features continuously, transforming distortion measurement into a comparison of implicit function coefficients. This approach effectively circumvents matching errors inherent in irregular data. Additionally, we propose a ResGrouped-MLP quality assessment network, which robustly maps multi-scale feature differences to perceptual scores. The network architecture departs from traditional flat MLPs by adopting a grouped encoding strategy integrated with Residual Blocks and Channel-wise Attention mechanisms. This hierarchical design allows the model to preserve the distinct physical semantics of luma, chroma, and geometry while adaptively focusing on the most salient distortion features across High, Medium, and Low scales. Experimental results on multiple benchmarks demonstrate that MS-ISSM outperforms state-of-the-art metrics in both reliability and generalization. The source code is available at: https://github.com/ZhangChen2022/MS-ISSM.
DualMat: PBR Material Estimation via Coherent Dual-Path Diffusion
Aug 07, 2025Abstract:We present DualMat, a novel dual-path diffusion framework for estimating Physically Based Rendering (PBR) materials from single images under complex lighting conditions. Our approach operates in two distinct latent spaces: an albedo-optimized path leveraging pretrained visual knowledge through RGB latent space, and a material-specialized path operating in a compact latent space designed for precise metallic and roughness estimation. To ensure coherent predictions between the albedo-optimized and material-specialized paths, we introduce feature distillation during training. We employ rectified flow to enhance efficiency by reducing inference steps while maintaining quality. Our framework extends to high-resolution and multi-view inputs through patch-based estimation and cross-view attention, enabling seamless integration into image-to-3D pipelines. DualMat achieves state-of-the-art performance on both Objaverse and real-world data, significantly outperforming existing methods with up to 28% improvement in albedo estimation and 39% reduction in metallic-roughness prediction errors.
A Survey on Vision-Language-Action Models: An Action Tokenization Perspective
Jul 02, 2025Abstract:The remarkable advancements of vision and language foundation models in multimodal understanding, reasoning, and generation has sparked growing efforts to extend such intelligence to the physical world, fueling the flourishing of vision-language-action (VLA) models. Despite seemingly diverse approaches, we observe that current VLA models can be unified under a single framework: vision and language inputs are processed by a series of VLA modules, producing a chain of \textit{action tokens} that progressively encode more grounded and actionable information, ultimately generating executable actions. We further determine that the primary design choice distinguishing VLA models lies in how action tokens are formulated, which can be categorized into language description, code, affordance, trajectory, goal state, latent representation, raw action, and reasoning. However, there remains a lack of comprehensive understanding regarding action tokens, significantly impeding effective VLA development and obscuring future directions. Therefore, this survey aims to categorize and interpret existing VLA research through the lens of action tokenization, distill the strengths and limitations of each token type, and identify areas for improvement. Through this systematic review and analysis, we offer a synthesized outlook on the broader evolution of VLA models, highlight underexplored yet promising directions, and contribute guidance for future research, hoping to bring the field closer to general-purpose intelligence.
Confidence in Large Language Model Evaluation: A Bayesian Approach to Limited-Sample Challenges
Apr 30, 2025


Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) exhibit probabilistic output characteristics, yet conventional evaluation frameworks rely on deterministic scalar metrics. This study introduces a Bayesian approach for LLM capability assessment that integrates prior knowledge through probabilistic inference, addressing limitations under limited-sample regimes. By treating model capabilities as latent variables and leveraging a curated query set to induce discriminative responses, we formalize model ranking as a Bayesian hypothesis testing problem over mutually exclusive capability intervals. Experimental evaluations with GPT-series models demonstrate that the proposed method achieves superior discrimination compared to conventional evaluation methods. Results indicate that even with reduced sample sizes, the approach maintains statistical robustness while providing actionable insights, such as probabilistic statements about a model's likelihood of surpassing specific baselines. This work advances LLM evaluation methodologies by bridging Bayesian inference with practical constraints in real-world deployment scenarios.
Steady-State Drifting Equilibrium Analysis of Single-Track Two-Wheeled Robots for Controller Design
Apr 12, 2025Abstract:Drifting is an advanced driving technique where the wheeled robot's tire-ground interaction breaks the common non-holonomic pure rolling constraint. This allows high-maneuverability tasks like quick cornering, and steady-state drifting control enhances motion stability under lateral slip conditions. While drifting has been successfully achieved in four-wheeled robot systems, its application to single-track two-wheeled (STTW) robots, such as unmanned motorcycles or bicycles, has not been thoroughly studied. To bridge this gap, this paper extends the drifting equilibrium theory to STTW robots and reveals the mechanism behind the steady-state drifting maneuver. Notably, the counter-steering drifting technique used by skilled motorcyclists is explained through this theory. In addition, an analytical algorithm based on intrinsic geometry and kinematics relationships is proposed, reducing the computation time by four orders of magnitude while maintaining less than 6% error compared to numerical methods. Based on equilibrium analysis, a model predictive controller (MPC) is designed to achieve steady-state drifting and equilibrium points transition, with its effectiveness and robustness validated through simulations.
PanoDreamer: Consistent Text to 360-Degree Scene Generation
Apr 07, 2025



Abstract:Automatically generating a complete 3D scene from a text description, a reference image, or both has significant applications in fields like virtual reality and gaming. However, current methods often generate low-quality textures and inconsistent 3D structures. This is especially true when extrapolating significantly beyond the field of view of the reference image. To address these challenges, we propose PanoDreamer, a novel framework for consistent, 3D scene generation with flexible text and image control. Our approach employs a large language model and a warp-refine pipeline, first generating an initial set of images and then compositing them into a 360-degree panorama. This panorama is then lifted into 3D to form an initial point cloud. We then use several approaches to generate additional images, from different viewpoints, that are consistent with the initial point cloud and expand/refine the initial point cloud. Given the resulting set of images, we utilize 3D Gaussian Splatting to create the final 3D scene, which can then be rendered from different viewpoints. Experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of PanoDreamer in generating high-quality, geometrically consistent 3D scenes.
RBFIM: Perceptual Quality Assessment for Compressed Point Clouds Using Radial Basis Function Interpolation
Mar 18, 2025Abstract:One of the main challenges in point cloud compression (PCC) is how to evaluate the perceived distortion so that the codec can be optimized for perceptual quality. Current standard practices in PCC highlight a primary issue: while single-feature metrics are widely used to assess compression distortion, the classic method of searching point-to-point nearest neighbors frequently fails to adequately build precise correspondences between point clouds, resulting in an ineffective capture of human perceptual features. To overcome the related limitations, we propose a novel assessment method called RBFIM, utilizing radial basis function (RBF) interpolation to convert discrete point features into a continuous feature function for the distorted point cloud. By substituting the geometry coordinates of the original point cloud into the feature function, we obtain the bijective sets of point features. This enables an establishment of precise corresponding features between distorted and original point clouds and significantly improves the accuracy of quality assessments. Moreover, this method avoids the complexity caused by bidirectional searches. Extensive experiments on multiple subjective quality datasets of compressed point clouds demonstrate that our RBFIM excels in addressing human perception tasks, thereby providing robust support for PCC optimization efforts.
InfinitePOD: Building Datacenter-Scale High-Bandwidth Domain for LLM with Optical Circuit Switching Transceivers
Feb 07, 2025



Abstract:Scaling Large Language Model (LLM) training relies on multi-dimensional parallelism, where High-Bandwidth Domains (HBDs) are critical for communication-intensive parallelism like Tensor Parallelism (TP) and Expert Parallelism (EP). However, existing HBD architectures face fundamental limitations in scalability, cost, and fault resiliency: switch-centric HBDs (e.g., NVL-72) incur prohibitive scaling costs, while GPU-centric HBDs (e.g., TPUv3/Dojo) suffer from severe fault propagation. Switch-GPU hybrid HBDs such as TPUv4 takes a middle-ground approach by leveraging Optical Circuit Switches, but the fault explosion radius remains large at the cube level (e.g., 64 TPUs). We propose InfinitePOD, a novel transceiver-centric HBD architecture that unifies connectivity and dynamic switching at the transceiver level using Optical Circuit Switching (OCS). By embedding OCS within each transceiver, InfinitePOD achieves reconfigurable point-to-multipoint connectivity, allowing the topology to adapt into variable-size rings. This design provides: i) datacenter-wide scalability without cost explosion; ii) fault resilience by isolating failures to a single node, and iii) full bandwidth utilization for fault-free GPUs. Key innovations include a Silicon Photonic (SiPh) based low-cost OCS transceiver (OCSTrx), a reconfigurable k-hop ring topology co-designed with intra-/inter-node communication, and an HBD-DCN orchestration algorithm maximizing GPU utilization while minimizing cross-ToR datacenter network traffic. The evaluation demonstrates that InfinitePOD achieves 31% of the cost of NVL-72, near-zero GPU waste ratio (over one order of magnitude lower than NVL-72 and TPUv4), near-zero cross-ToR traffic when node fault ratios under 7%, and improves Model FLOPs Utilization by 3.37x compared to NVIDIA DGX (8 GPUs per Node).
SolidGS: Consolidating Gaussian Surfel Splatting for Sparse-View Surface Reconstruction
Dec 19, 2024



Abstract:Gaussian splatting has achieved impressive improvements for both novel-view synthesis and surface reconstruction from multi-view images. However, current methods still struggle to reconstruct high-quality surfaces from only sparse view input images using Gaussian splatting. In this paper, we propose a novel method called SolidGS to address this problem. We observed that the reconstructed geometry can be severely inconsistent across multi-views, due to the property of Gaussian function in geometry rendering. This motivates us to consolidate all Gaussians by adopting a more solid kernel function, which effectively improves the surface reconstruction quality. With the additional help of geometrical regularization and monocular normal estimation, our method achieves superior performance on the sparse view surface reconstruction than all the Gaussian splatting methods and neural field methods on the widely used DTU, Tanks-and-Temples, and LLFF datasets.
SparseLGS: Sparse View Language Embedded Gaussian Splatting
Dec 03, 2024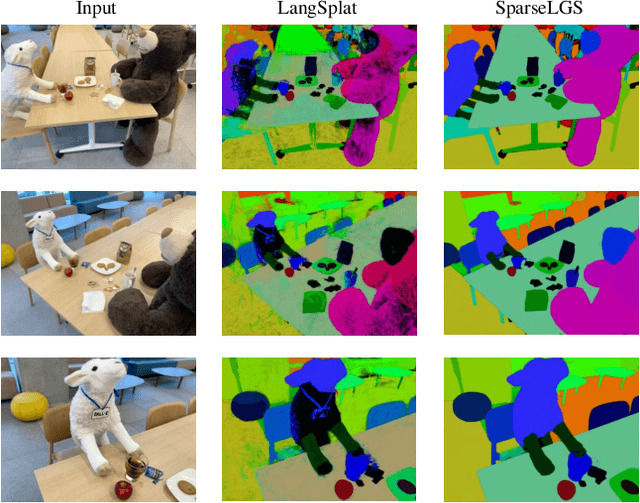
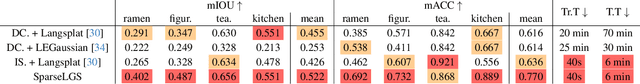
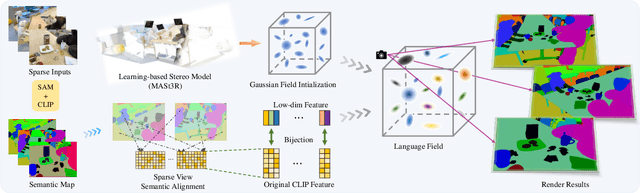
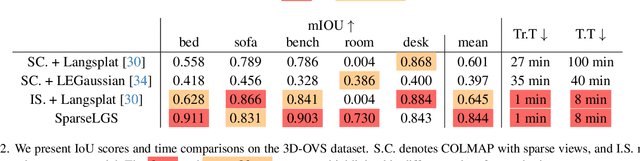
Abstract:Recently, several studies have combined Gaussian Splatting to obtain scene representations with language embeddings for open-vocabulary 3D scene understanding. While these methods perform well, they essentially require very dense multi-view inputs, limiting their applicability in real-world scenarios. In this work, we propose SparseLGS to address the challenge of 3D scene understanding with pose-free and sparse view input images. Our method leverages a learning-based dense stereo model to handle pose-free and sparse inputs, and a three-step region matching approach to address the multi-view semantic inconsistency problem, which is especially important for sparse inputs. Different from directly learning high-dimensional CLIP features, we extract low-dimensional information and build bijections to avoid excessive learning and storage costs. We introduce a reconstruction loss during semantic training to improve Gaussian positions and shapes. To the best of our knowledge, we are the first to address the 3D semantic field problem with sparse pose-free inputs. Experimental results show that SparseLGS achieves comparable quality when reconstructing semantic fields with fewer inputs (3-4 views) compared to previous SOTA methods with dense input. Besides, when using the same sparse input, SparseLGS leads significantly in quality and heavily improves the computation speed (5$\times$ speedup). Project page: {\tt\small \url{https://ustc3dv.github.io/SparseLGS}}
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge