Maura Pintor
SAGE-5GC: Security-Aware Guidelines for Evaluating Anomaly Detection in the 5G Core Network
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Machine learning-based anomaly detection systems are increasingly being adopted in 5G Core networks to monitor complex, high-volume traffic. However, most existing approaches are evaluated under strong assumptions that rarely hold in operational environments, notably the availability of independent and identically distributed (IID) data and the absence of adaptive attackers.In this work, we study the problem of detecting 5G attacks \textit{in the wild}, focusing on realistic deployment settings. We propose a set of Security-Aware Guidelines for Evaluating anomaly detectors in 5G Core Network (SAGE-5GC), driven by domain knowledge and consideration of potential adversarial threats. Using a realistic 5G Core dataset, we first train several anomaly detectors and assess their baseline performance against standard 5GC control-plane cyberattacks targeting PFCP-based network services.We then extend the evaluation to adversarial settings, where an attacker tries to manipulate the observable features of the network traffic to evade detection, under the constraint that the intended functionality of the malicious traffic is preserved. Starting from a selected set of controllable features, we analyze model sensitivity and adversarial robustness through randomized perturbations. Finally, we introduce a practical optimization strategy based on genetic algorithms that operates exclusively on attacker-controllable features and does not require prior knowledge of the underlying detection model. Our experimental results show that adversarially crafted attacks can substantially degrade detection performance, underscoring the need for robust, security-aware evaluation methodologies for anomaly detection in 5G networks deployed in the wild.
Out-of-Distribution Detection for Continual Learning: Design Principles and Benchmarking
Dec 16, 2025



Abstract:Recent years have witnessed significant progress in the development of machine learning models across a wide range of fields, fueled by increased computational resources, large-scale datasets, and the rise of deep learning architectures. From malware detection to enabling autonomous navigation, modern machine learning systems have demonstrated remarkable capabilities. However, as these models are deployed in ever-changing real-world scenarios, their ability to remain reliable and adaptive over time becomes increasingly important. For example, in the real world, new malware families are continuously developed, whereas autonomous driving cars are employed in many different cities and weather conditions. Models trained in fixed settings can not respond effectively to novel conditions encountered post-deployment. In fact, most machine learning models are still developed under the assumption that training and test data are independent and identically distributed (i.i.d.), i.e., sampled from the same underlying (unknown) distribution. While this assumption simplifies model development and evaluation, it does not hold in many real-world applications, where data changes over time and unexpected inputs frequently occur. Retraining models from scratch whenever new data appears is computationally expensive, time-consuming, and impractical in resource-constrained environments. These limitations underscore the need for Continual Learning (CL), which enables models to incrementally learn from evolving data streams without forgetting past knowledge, and Out-of-Distribution (OOD) detection, which allows systems to identify and respond to novel or anomalous inputs. Jointly addressing both challenges is critical to developing robust, efficient, and adaptive AI systems.
RAID: A Dataset for Testing the Adversarial Robustness of AI-Generated Image Detectors
Jun 09, 2025Abstract:AI-generated images have reached a quality level at which humans are incapable of reliably distinguishing them from real images. To counteract the inherent risk of fraud and disinformation, the detection of AI-generated images is a pressing challenge and an active research topic. While many of the presented methods claim to achieve high detection accuracy, they are usually evaluated under idealized conditions. In particular, the adversarial robustness is often neglected, potentially due to a lack of awareness or the substantial effort required to conduct a comprehensive robustness analysis. In this work, we tackle this problem by providing a simpler means to assess the robustness of AI-generated image detectors. We present RAID (Robust evaluation of AI-generated image Detectors), a dataset of 72k diverse and highly transferable adversarial examples. The dataset is created by running attacks against an ensemble of seven state-of-the-art detectors and images generated by four different text-to-image models. Extensive experiments show that our methodology generates adversarial images that transfer with a high success rate to unseen detectors, which can be used to quickly provide an approximate yet still reliable estimate of a detector's adversarial robustness. Our findings indicate that current state-of-the-art AI-generated image detectors can be easily deceived by adversarial examples, highlighting the critical need for the development of more robust methods. We release our dataset at https://huggingface.co/datasets/aimagelab/RAID and evaluation code at https://github.com/pralab/RAID.
Buffer-free Class-Incremental Learning with Out-of-Distribution Detection
May 29, 2025Abstract:Class-incremental learning (CIL) poses significant challenges in open-world scenarios, where models must not only learn new classes over time without forgetting previous ones but also handle inputs from unknown classes that a closed-set model would misclassify. Recent works address both issues by (i)~training multi-head models using the task-incremental learning framework, and (ii) predicting the task identity employing out-of-distribution (OOD) detectors. While effective, the latter mainly relies on joint training with a memory buffer of past data, raising concerns around privacy, scalability, and increased training time. In this paper, we present an in-depth analysis of post-hoc OOD detection methods and investigate their potential to eliminate the need for a memory buffer. We uncover that these methods, when applied appropriately at inference time, can serve as a strong substitute for buffer-based OOD detection. We show that this buffer-free approach achieves comparable or superior performance to buffer-based methods both in terms of class-incremental learning and the rejection of unknown samples. Experimental results on CIFAR-10, CIFAR-100 and Tiny ImageNet datasets support our findings, offering new insights into the design of efficient and privacy-preserving CIL systems for open-world settings.
Adversarial Pruning: A Survey and Benchmark of Pruning Methods for Adversarial Robustness
Sep 02, 2024Abstract:Recent work has proposed neural network pruning techniques to reduce the size of a network while preserving robustness against adversarial examples, i.e., well-crafted inputs inducing a misclassification. These methods, which we refer to as adversarial pruning methods, involve complex and articulated designs, making it difficult to analyze the differences and establish a fair and accurate comparison. In this work, we overcome these issues by surveying current adversarial pruning methods and proposing a novel taxonomy to categorize them based on two main dimensions: the pipeline, defining when to prune; and the specifics, defining how to prune. We then highlight the limitations of current empirical analyses and propose a novel, fair evaluation benchmark to address them. We finally conduct an empirical re-evaluation of current adversarial pruning methods and discuss the results, highlighting the shared traits of top-performing adversarial pruning methods, as well as common issues. We welcome contributions in our publicly-available benchmark at https://github.com/pralab/AdversarialPruningBenchmark
HO-FMN: Hyperparameter Optimization for Fast Minimum-Norm Attacks
Jul 11, 2024



Abstract:Gradient-based attacks are a primary tool to evaluate robustness of machine-learning models. However, many attacks tend to provide overly-optimistic evaluations as they use fixed loss functions, optimizers, step-size schedulers, and default hyperparameters. In this work, we tackle these limitations by proposing a parametric variation of the well-known fast minimum-norm attack algorithm, whose loss, optimizer, step-size scheduler, and hyperparameters can be dynamically adjusted. We re-evaluate 12 robust models, showing that our attack finds smaller adversarial perturbations without requiring any additional tuning. This also enables reporting adversarial robustness as a function of the perturbation budget, providing a more complete evaluation than that offered by fixed-budget attacks, while remaining efficient. We release our open-source code at https://github.com/pralab/HO-FMN.
Over-parameterization and Adversarial Robustness in Neural Networks: An Overview and Empirical Analysis
Jun 14, 2024



Abstract:Thanks to their extensive capacity, over-parameterized neural networks exhibit superior predictive capabilities and generalization. However, having a large parameter space is considered one of the main suspects of the neural networks' vulnerability to adversarial example -- input samples crafted ad-hoc to induce a desired misclassification. Relevant literature has claimed contradictory remarks in support of and against the robustness of over-parameterized networks. These contradictory findings might be due to the failure of the attack employed to evaluate the networks' robustness. Previous research has demonstrated that depending on the considered model, the algorithm employed to generate adversarial examples may not function properly, leading to overestimating the model's robustness. In this work, we empirically study the robustness of over-parameterized networks against adversarial examples. However, unlike the previous works, we also evaluate the considered attack's reliability to support the results' veracity. Our results show that over-parameterized networks are robust against adversarial attacks as opposed to their under-parameterized counterparts.
AttackBench: Evaluating Gradient-based Attacks for Adversarial Examples
Apr 30, 2024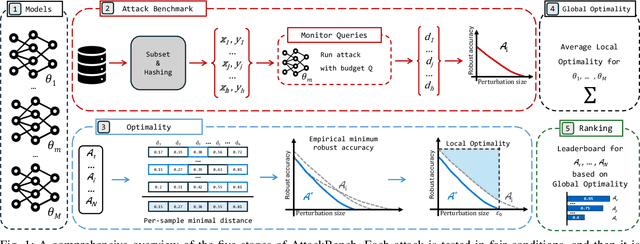
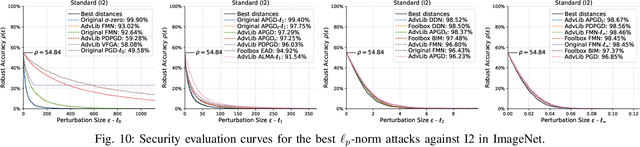
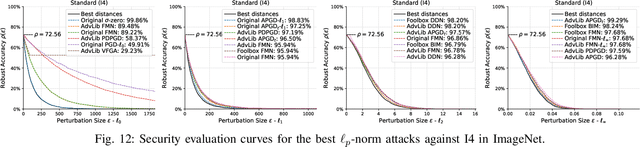
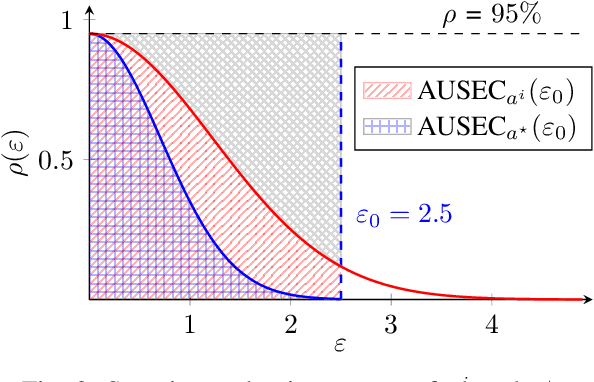
Abstract:Adversarial examples are typically optimized with gradient-based attacks. While novel attacks are continuously proposed, each is shown to outperform its predecessors using different experimental setups, hyperparameter settings, and number of forward and backward calls to the target models. This provides overly-optimistic and even biased evaluations that may unfairly favor one particular attack over the others. In this work, we aim to overcome these limitations by proposing AttackBench, i.e., the first evaluation framework that enables a fair comparison among different attacks. To this end, we first propose a categorization of gradient-based attacks, identifying their main components and differences. We then introduce our framework, which evaluates their effectiveness and efficiency. We measure these characteristics by (i) defining an optimality metric that quantifies how close an attack is to the optimal solution, and (ii) limiting the number of forward and backward queries to the model, such that all attacks are compared within a given maximum query budget. Our extensive experimental analysis compares more than 100 attack implementations with a total of over 800 different configurations against CIFAR-10 and ImageNet models, highlighting that only very few attacks outperform all the competing approaches. Within this analysis, we shed light on several implementation issues that prevent many attacks from finding better solutions or running at all. We release AttackBench as a publicly available benchmark, aiming to continuously update it to include and evaluate novel gradient-based attacks for optimizing adversarial examples.
Robustness-Congruent Adversarial Training for Secure Machine Learning Model Updates
Feb 27, 2024



Abstract:Machine-learning models demand for periodic updates to improve their average accuracy, exploiting novel architectures and additional data. However, a newly-updated model may commit mistakes that the previous model did not make. Such misclassifications are referred to as negative flips, and experienced by users as a regression of performance. In this work, we show that this problem also affects robustness to adversarial examples, thereby hindering the development of secure model update practices. In particular, when updating a model to improve its adversarial robustness, some previously-ineffective adversarial examples may become misclassified, causing a regression in the perceived security of the system. We propose a novel technique, named robustness-congruent adversarial training, to address this issue. It amounts to fine-tuning a model with adversarial training, while constraining it to retain higher robustness on the adversarial examples that were correctly classified before the update. We show that our algorithm and, more generally, learning with non-regression constraints, provides a theoretically-grounded framework to train consistent estimators. Our experiments on robust models for computer vision confirm that (i) both accuracy and robustness, even if improved after model update, can be affected by negative flips, and (ii) our robustness-congruent adversarial training can mitigate the problem, outperforming competing baseline methods.
$σ$-zero: Gradient-based Optimization of $\ell_0$-norm Adversarial Examples
Feb 02, 2024Abstract:Evaluating the adversarial robustness of deep networks to gradient-based attacks is challenging. While most attacks consider $\ell_2$- and $\ell_\infty$-norm constraints to craft input perturbations, only a few investigate sparse $\ell_1$- and $\ell_0$-norm attacks. In particular, $\ell_0$-norm attacks remain the least studied due to the inherent complexity of optimizing over a non-convex and non-differentiable constraint. However, evaluating adversarial robustness under these attacks could reveal weaknesses otherwise left untested with more conventional $\ell_2$- and $\ell_\infty$-norm attacks. In this work, we propose a novel $\ell_0$-norm attack, called $\sigma$-zero, which leverages an ad hoc differentiable approximation of the $\ell_0$ norm to facilitate gradient-based optimization, and an adaptive projection operator to dynamically adjust the trade-off between loss minimization and perturbation sparsity. Extensive evaluations using MNIST, CIFAR10, and ImageNet datasets, involving robust and non-robust models, show that $\sigma$-zero finds minimum $\ell_0$-norm adversarial examples without requiring any time-consuming hyperparameter tuning, and that it outperforms all competing sparse attacks in terms of success rate, perturbation size, and scalability.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge