Srishti Gupta
Out-of-Distribution Detection for Continual Learning: Design Principles and Benchmarking
Dec 16, 2025



Abstract:Recent years have witnessed significant progress in the development of machine learning models across a wide range of fields, fueled by increased computational resources, large-scale datasets, and the rise of deep learning architectures. From malware detection to enabling autonomous navigation, modern machine learning systems have demonstrated remarkable capabilities. However, as these models are deployed in ever-changing real-world scenarios, their ability to remain reliable and adaptive over time becomes increasingly important. For example, in the real world, new malware families are continuously developed, whereas autonomous driving cars are employed in many different cities and weather conditions. Models trained in fixed settings can not respond effectively to novel conditions encountered post-deployment. In fact, most machine learning models are still developed under the assumption that training and test data are independent and identically distributed (i.i.d.), i.e., sampled from the same underlying (unknown) distribution. While this assumption simplifies model development and evaluation, it does not hold in many real-world applications, where data changes over time and unexpected inputs frequently occur. Retraining models from scratch whenever new data appears is computationally expensive, time-consuming, and impractical in resource-constrained environments. These limitations underscore the need for Continual Learning (CL), which enables models to incrementally learn from evolving data streams without forgetting past knowledge, and Out-of-Distribution (OOD) detection, which allows systems to identify and respond to novel or anomalous inputs. Jointly addressing both challenges is critical to developing robust, efficient, and adaptive AI systems.
Buffer-free Class-Incremental Learning with Out-of-Distribution Detection
May 29, 2025Abstract:Class-incremental learning (CIL) poses significant challenges in open-world scenarios, where models must not only learn new classes over time without forgetting previous ones but also handle inputs from unknown classes that a closed-set model would misclassify. Recent works address both issues by (i)~training multi-head models using the task-incremental learning framework, and (ii) predicting the task identity employing out-of-distribution (OOD) detectors. While effective, the latter mainly relies on joint training with a memory buffer of past data, raising concerns around privacy, scalability, and increased training time. In this paper, we present an in-depth analysis of post-hoc OOD detection methods and investigate their potential to eliminate the need for a memory buffer. We uncover that these methods, when applied appropriately at inference time, can serve as a strong substitute for buffer-based OOD detection. We show that this buffer-free approach achieves comparable or superior performance to buffer-based methods both in terms of class-incremental learning and the rejection of unknown samples. Experimental results on CIFAR-10, CIFAR-100 and Tiny ImageNet datasets support our findings, offering new insights into the design of efficient and privacy-preserving CIL systems for open-world settings.
Over-parameterization and Adversarial Robustness in Neural Networks: An Overview and Empirical Analysis
Jun 14, 2024



Abstract:Thanks to their extensive capacity, over-parameterized neural networks exhibit superior predictive capabilities and generalization. However, having a large parameter space is considered one of the main suspects of the neural networks' vulnerability to adversarial example -- input samples crafted ad-hoc to induce a desired misclassification. Relevant literature has claimed contradictory remarks in support of and against the robustness of over-parameterized networks. These contradictory findings might be due to the failure of the attack employed to evaluate the networks' robustness. Previous research has demonstrated that depending on the considered model, the algorithm employed to generate adversarial examples may not function properly, leading to overestimating the model's robustness. In this work, we empirically study the robustness of over-parameterized networks against adversarial examples. However, unlike the previous works, we also evaluate the considered attack's reliability to support the results' veracity. Our results show that over-parameterized networks are robust against adversarial attacks as opposed to their under-parameterized counterparts.
TONE: A 3-Tiered ONtology for Emotion analysis
Jan 11, 2024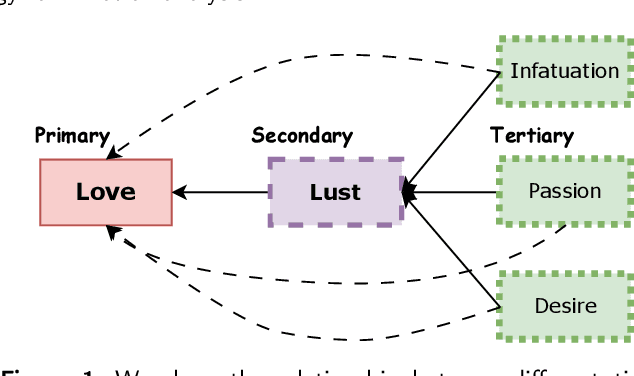
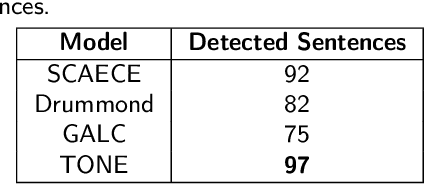
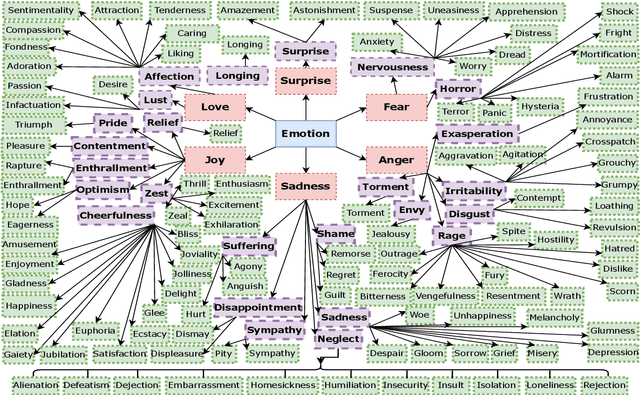
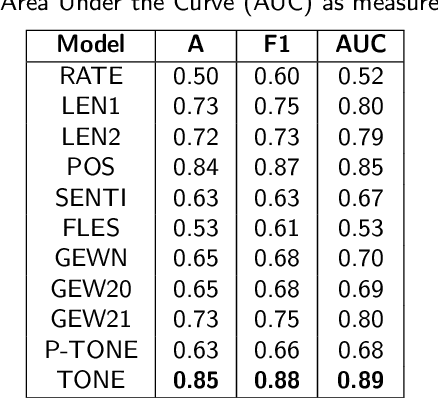
Abstract:Emotions have played an important part in many sectors, including psychology, medicine, mental health, computer science, and so on, and categorizing them has proven extremely useful in separating one emotion from another. Emotions can be classified using the following two methods: (1) The supervised method's efficiency is strongly dependent on the size and domain of the data collected. A categorization established using relevant data from one domain may not work well in another. (2) An unsupervised method that uses either domain expertise or a knowledge base of emotion types already exists. Though this second approach provides a suitable and generic categorization of emotions and is cost-effective, the literature doesn't possess a publicly available knowledge base that can be directly applied to any emotion categorization-related task. This pushes us to create a knowledge base that can be used for emotion classification across domains, and ontology is often used for this purpose. In this study, we provide TONE, an emotion-based ontology that effectively creates an emotional hierarchy based on Dr. Gerrod Parrot's group of emotions. In addition to ontology development, we introduce a semi-automated vocabulary construction process to generate a detailed collection of terms for emotions at each tier of the hierarchy. We also demonstrate automated methods for establishing three sorts of dependencies in order to develop linkages between different emotions. Our human and automatic evaluation results show the ontology's quality. Furthermore, we describe three distinct use cases that demonstrate the applicability of our ontology.
IKDSumm: Incorporating Key-phrases into BERT for extractive Disaster Tweet Summarization
May 19, 2023Abstract:Online social media platforms, such as Twitter, are one of the most valuable sources of information during disaster events. Therefore, humanitarian organizations, government agencies, and volunteers rely on a summary of this information, i.e., tweets, for effective disaster management. Although there are several existing supervised and unsupervised approaches for automated tweet summary approaches, these approaches either require extensive labeled information or do not incorporate specific domain knowledge of disasters. Additionally, the most recent approaches to disaster summarization have proposed BERT-based models to enhance the summary quality. However, for further improved performance, we introduce the utilization of domain-specific knowledge without any human efforts to understand the importance (salience) of a tweet which further aids in summary creation and improves summary quality. In this paper, we propose a disaster-specific tweet summarization framework, IKDSumm, which initially identifies the crucial and important information from each tweet related to a disaster through key-phrases of that tweet. We identify these key-phrases by utilizing the domain knowledge (using existing ontology) of disasters without any human intervention. Further, we utilize these key-phrases to automatically generate a summary of the tweets. Therefore, given tweets related to a disaster, IKDSumm ensures fulfillment of the summarization key objectives, such as information coverage, relevance, and diversity in summary without any human intervention. We evaluate the performance of IKDSumm with 8 state-of-the-art techniques on 12 disaster datasets. The evaluation results show that IKDSumm outperforms existing techniques by approximately 2-79% in terms of ROUGE-N F1-score.
Heterogeneous Edge Embeddings for Friend Recommendation
Feb 07, 2019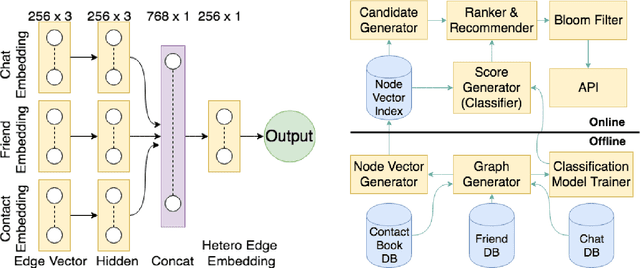
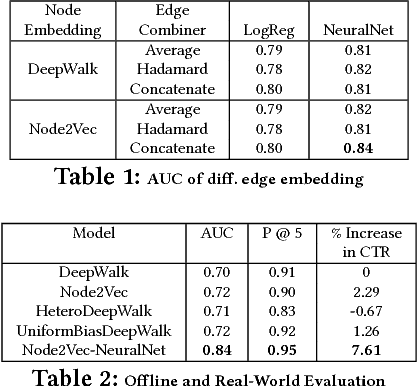
Abstract:We propose a friend recommendation system (an application of link prediction) using edge embeddings on social networks. Most real-world social networks are multi-graphs, where different kinds of relationships (e.g. chat, friendship) are possible between a pair of users. Existing network embedding techniques do not leverage signals from different edge types and thus perform inadequately on link prediction in such networks. We propose a method to mine network representation that effectively exploits heterogeneity in multi-graphs. We evaluate our model on a real-world, active social network where this system is deployed for friend recommendation for millions of users. Our method outperforms various state-of-the-art baselines on Hike's social network in terms of accuracy as well as user satisfaction.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge