Zhaoqiang Xia
Over-parameterization and Adversarial Robustness in Neural Networks: An Overview and Empirical Analysis
Jun 14, 2024



Abstract:Thanks to their extensive capacity, over-parameterized neural networks exhibit superior predictive capabilities and generalization. However, having a large parameter space is considered one of the main suspects of the neural networks' vulnerability to adversarial example -- input samples crafted ad-hoc to induce a desired misclassification. Relevant literature has claimed contradictory remarks in support of and against the robustness of over-parameterized networks. These contradictory findings might be due to the failure of the attack employed to evaluate the networks' robustness. Previous research has demonstrated that depending on the considered model, the algorithm employed to generate adversarial examples may not function properly, leading to overestimating the model's robustness. In this work, we empirically study the robustness of over-parameterized networks against adversarial examples. However, unlike the previous works, we also evaluate the considered attack's reliability to support the results' veracity. Our results show that over-parameterized networks are robust against adversarial attacks as opposed to their under-parameterized counterparts.
HandS3C: 3D Hand Mesh Reconstruction with State Space Spatial Channel Attention from RGB images
May 14, 2024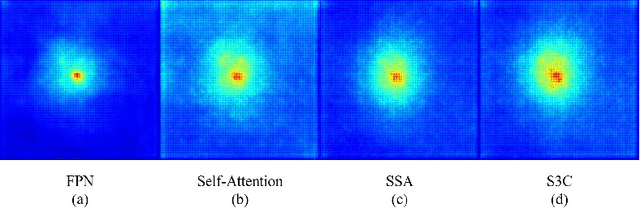
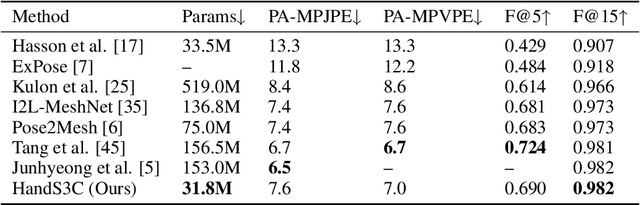
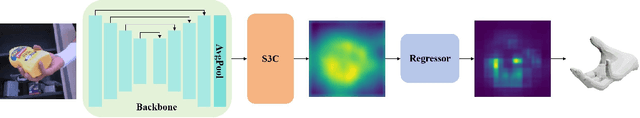

Abstract:Reconstructing the hand mesh from one single RGB image is a challenging task because hands are often occluded by other objects. Most previous works attempt to explore more additional information and adopt attention mechanisms for improving 3D reconstruction performance, while it would increase computational complexity simultaneously. To achieve a performance-reserving architecture with high computational efficiency, in this work, we propose a simple but effective 3D hand mesh reconstruction network (i.e., HandS3C), which is the first time to incorporate state space model into the task of hand mesh reconstruction. In the network, we design a novel state-space spatial-channel attention module that extends the effective receptive field, extracts hand features in the spatial dimension, and enhances regional features of hands in the channel dimension. This helps to reconstruct a complete and detailed hand mesh. Extensive experiments conducted on well-known datasets facing heavy occlusions (such as FREIHAND, DEXYCB, and HO3D) demonstrate that our proposed HandS3C achieves state-of-the-art performance while maintaining a minimal parameters.
Hardening RGB-D Object Recognition Systems against Adversarial Patch Attacks
Sep 13, 2023



Abstract:RGB-D object recognition systems improve their predictive performances by fusing color and depth information, outperforming neural network architectures that rely solely on colors. While RGB-D systems are expected to be more robust to adversarial examples than RGB-only systems, they have also been proven to be highly vulnerable. Their robustness is similar even when the adversarial examples are generated by altering only the original images' colors. Different works highlighted the vulnerability of RGB-D systems; however, there is a lacking of technical explanations for this weakness. Hence, in our work, we bridge this gap by investigating the learned deep representation of RGB-D systems, discovering that color features make the function learned by the network more complex and, thus, more sensitive to small perturbations. To mitigate this problem, we propose a defense based on a detection mechanism that makes RGB-D systems more robust against adversarial examples. We empirically show that this defense improves the performances of RGB-D systems against adversarial examples even when they are computed ad-hoc to circumvent this detection mechanism, and that is also more effective than adversarial training.
Why Adversarial Reprogramming Works, When It Fails, and How to Tell the Difference
Aug 31, 2021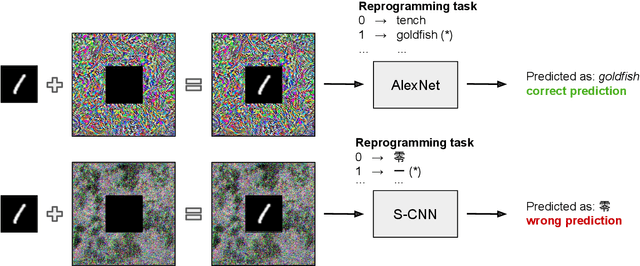

Abstract:Adversarial reprogramming allows repurposing a machine-learning model to perform a different task. For example, a model trained to recognize animals can be reprogrammed to recognize digits by embedding an adversarial program in the digit images provided as input. Recent work has shown that adversarial reprogramming may not only be used to abuse machine-learning models provided as a service, but also beneficially, to improve transfer learning when training data is scarce. However, the factors affecting its success are still largely unexplained. In this work, we develop a first-order linear model of adversarial reprogramming to show that its success inherently depends on the size of the average input gradient, which grows when input gradients are more aligned, and when inputs have higher dimensionality. The results of our experimental analysis, involving fourteen distinct reprogramming tasks, show that the above factors are correlated with the success and the failure of adversarial reprogramming.
Revisiting Pixel-Wise Supervision for Face Anti-Spoofing
Nov 24, 2020



Abstract:Face anti-spoofing (FAS) plays a vital role in securing face recognition systems from the presentation attacks (PAs). As more and more realistic PAs with novel types spring up, it is necessary to develop robust algorithms for detecting unknown attacks even in unseen scenarios. However, deep models supervised by traditional binary loss (e.g., `0' for bonafide vs. `1' for PAs) are weak in describing intrinsic and discriminative spoofing patterns. Recently, pixel-wise supervision has been proposed for the FAS task, intending to provide more fine-grained pixel/patch-level cues. In this paper, we firstly give a comprehensive review and analysis about the existing pixel-wise supervision methods for FAS. Then we propose a novel pyramid supervision, which guides deep models to learn both local details and global semantics from multi-scale spatial context. Extensive experiments are performed on five FAS benchmark datasets to show that, without bells and whistles, the proposed pyramid supervision could not only improve the performance beyond existing pixel-wise supervision frameworks, but also enhance the model's interpretability (i.e., locating the patch-level positions of PAs more reasonably). Furthermore, elaborate studies are conducted for exploring the efficacy of different architecture configurations with two kinds of pixel-wise supervisions (binary mask and depth map supervisions), which provides inspirable insights for future architecture/supervision design.
Mix Dimension in Poincaré Geometry for 3D Skeleton-based Action Recognition
Aug 03, 2020



Abstract:Graph Convolutional Networks (GCNs) have already demonstrated their powerful ability to model the irregular data, e.g., skeletal data in human action recognition, providing an exciting new way to fuse rich structural information for nodes residing in different parts of a graph. In human action recognition, current works introduce a dynamic graph generation mechanism to better capture the underlying semantic skeleton connections and thus improves the performance. In this paper, we provide an orthogonal way to explore the underlying connections. Instead of introducing an expensive dynamic graph generation paradigm, we build a more efficient GCN on a Riemann manifold, which we think is a more suitable space to model the graph data, to make the extracted representations fit the embedding matrix. Specifically, we present a novel spatial-temporal GCN (ST-GCN) architecture which is defined via the Poincar\'e geometry such that it is able to better model the latent anatomy of the structure data. To further explore the optimal projection dimension in the Riemann space, we mix different dimensions on the manifold and provide an efficient way to explore the dimension for each ST-GCN layer. With the final resulted architecture, we evaluate our method on two current largest scale 3D datasets, i.e., NTU RGB+D and NTU RGB+D 120. The comparison results show that the model could achieve a superior performance under any given evaluation metrics with only 40\% model size when compared with the previous best GCN method, which proves the effectiveness of our model.
Revealing the Invisible with Model and Data Shrinking for Composite-database Micro-expression Recognition
Jun 17, 2020



Abstract:Composite-database micro-expression recognition is attracting increasing attention as it is more practical to real-world applications. Though the composite database provides more sample diversity for learning good representation models, the important subtle dynamics are prone to disappearing in the domain shift such that the models greatly degrade their performance, especially for deep models. In this paper, we analyze the influence of learning complexity, including the input complexity and model complexity, and discover that the lower-resolution input data and shallower-architecture model are helpful to ease the degradation of deep models in composite-database task. Based on this, we propose a recurrent convolutional network (RCN) to explore the shallower-architecture and lower-resolution input data, shrinking model and input complexities simultaneously. Furthermore, we develop three parameter-free modules (i.e., wide expansion, shortcut connection and attention unit) to integrate with RCN without increasing any learnable parameters. These three modules can enhance the representation ability in various perspectives while preserving not-very-deep architecture for lower-resolution data. Besides, three modules can further be combined by an automatic strategy (a neural architecture search strategy) and the searched architecture becomes more robust. Extensive experiments on MEGC2019 dataset (composited of existing SMIC, CASME II and SAMM datasets) have verified the influence of learning complexity and shown that RCNs with three modules and the searched combination outperform the state-of-the-art approaches.
3D Face Mask Presentation Attack Detection Based on Intrinsic Image Analysis
Mar 27, 2019
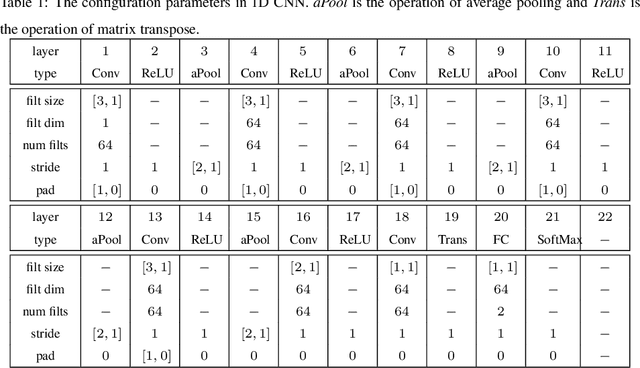
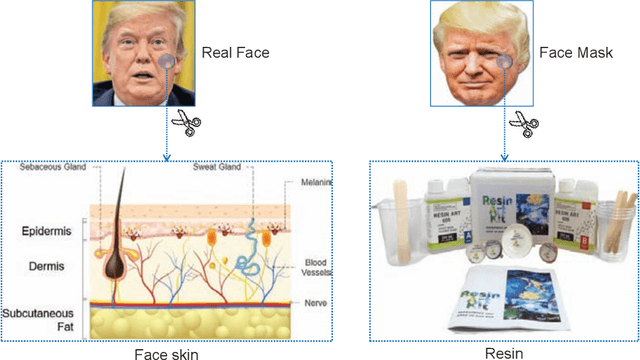
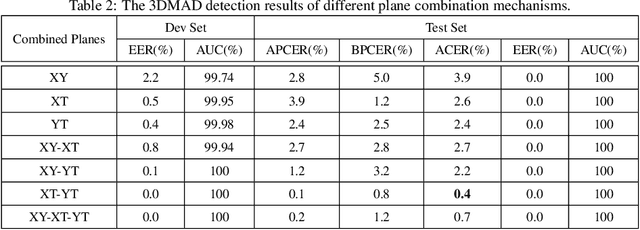
Abstract:Face presentation attacks have become a major threat to face recognition systems and many countermeasures have been proposed in the past decade. However, most of them are devoted to 2D face presentation attacks, rather than 3D face masks. Unlike the real face, the 3D face mask is usually made of resin materials and has a smooth surface, resulting in reflectance differences. So, we propose a novel detection method for 3D face mask presentation attack by modeling reflectance differences based on intrinsic image analysis. In the proposed method, the face image is first processed with intrinsic image decomposition to compute its reflectance image. Then, the intensity distribution histograms are extracted from three orthogonal planes to represent the intensity differences of reflectance images between the real face and 3D face mask. After that, the 1D convolutional network is further used to capture the information for describing different materials or surfaces react differently to changes in illumination. Extensive experiments on the 3DMAD database demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed method in distinguishing a face mask from the real one and show that the detection performance outperforms other state-of-the-art methods.
Spatiotemporal Recurrent Convolutional Networks for Recognizing Spontaneous Micro-expressions
Jan 15, 2019



Abstract:Recently, the recognition task of spontaneous facial micro-expressions has attracted much attention with its various real-world applications. Plenty of handcrafted or learned features have been employed for a variety of classifiers and achieved promising performances for recognizing micro-expressions. However, the micro-expression recognition is still challenging due to the subtle spatiotemporal changes of micro-expressions. To exploit the merits of deep learning, we propose a novel deep recurrent convolutional networks based micro-expression recognition approach, capturing the spatial-temporal deformations of micro-expression sequence. Specifically, the proposed deep model is constituted of several recurrent convolutional layers for extracting visual features and a classificatory layer for recognition. It is optimized by an end-to-end manner and obviates manual feature design. To handle sequential data, we exploit two types of extending the connectivity of convolutional networks across temporal domain, in which the spatiotemporal deformations are modeled in views of facial appearance and geometry separately. Besides, to overcome the shortcomings of limited and imbalanced training samples, temporal data augmentation strategies as well as a balanced loss are jointly used for our deep network. By performing the experiments on three spontaneous micro-expression datasets, we verify the effectiveness of our proposed micro-expression recognition approach compared to the state-of-the-art methods.
Face Presentation Attack Detection in Learned Color-liked Space
Oct 31, 2018


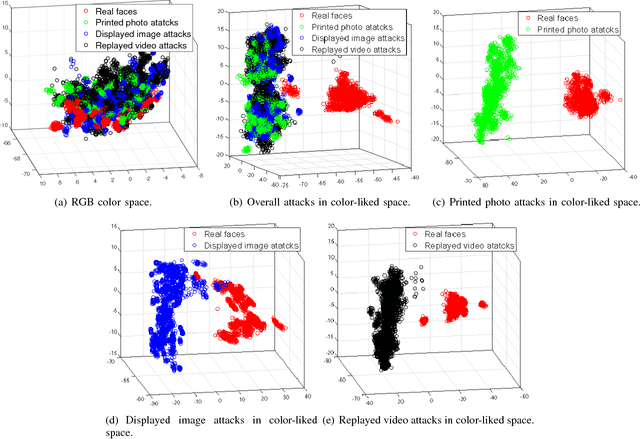
Abstract:Face presentation attack detection (PAD) has become a thorny problem for biometric systems and numerous countermeasures have been proposed to address it. However, majority of them directly extract feature descriptors and distinguish fake faces from the real ones in existing color spaces (e.g. RGB, HSV and YCbCr). Unfortunately, it is unknown for us which color space is the best or how to combine different spaces together. To make matters worse, the real and fake faces are overlapped in existing color spaces. So, in this paper, a learned distinguishable color-liked space is generated to deal with the problem of face PAD. More specifically, we present an end-to-end deep learning network that can map existing color spaces to a new learned color-liked space. Inspired by the generator of generative adversarial network (GAN), the proposed network consists of a space generator and a feature extractor. When training the color-liked space, a new triplet combination mechanism of points-to-center is explored to maximize interclass distance and minimize intraclass distance, and also keep a safe margin between the real and presented fake faces. Extensive experiments on two standard face PAD databases, i.e., Relay-Attack and OULU-NPU, indicate that our proposed color-liked space analysis based countermeasure significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art methods and show excellent generalization capability.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge