Guoying Zhao
Steering Vision-Language Pre-trained Models for Incremental Face Presentation Attack Detection
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:Face Presentation Attack Detection (PAD) demands incremental learning (IL) to combat evolving spoofing tactics and domains. Privacy regulations, however, forbid retaining past data, necessitating rehearsal-free IL (RF-IL). Vision-Language Pre-trained (VLP) models, with their prompt-tunable cross-modal representations, enable efficient adaptation to new spoofing styles and domains. Capitalizing on this strength, we propose \textbf{SVLP-IL}, a VLP-based RF-IL framework that balances stability and plasticity via \textit{Multi-Aspect Prompting} (MAP) and \textit{Selective Elastic Weight Consolidation} (SEWC). MAP isolates domain dependencies, enhances distribution-shift sensitivity, and mitigates forgetting by jointly exploiting universal and domain-specific cues. SEWC selectively preserves critical weights from previous tasks, retaining essential knowledge while allowing flexibility for new adaptations. Comprehensive experiments across multiple PAD benchmarks show that SVLP-IL significantly reduces catastrophic forgetting and enhances performance on unseen domains. SVLP-IL offers a privacy-compliant, practical solution for robust lifelong PAD deployment in RF-IL settings.
Semantic Mismatch and Perceptual Degradation: A New Perspective on Image Editing Immunity
Dec 16, 2025



Abstract:Text-guided image editing via diffusion models, while powerful, raises significant concerns about misuse, motivating efforts to immunize images against unauthorized edits using imperceptible perturbations. Prevailing metrics for evaluating immunization success typically rely on measuring the visual dissimilarity between the output generated from a protected image and a reference output generated from the unprotected original. This approach fundamentally overlooks the core requirement of image immunization, which is to disrupt semantic alignment with attacker intent, regardless of deviation from any specific output. We argue that immunization success should instead be defined by the edited output either semantically mismatching the prompt or suffering substantial perceptual degradations, both of which thwart malicious intent. To operationalize this principle, we propose Synergistic Intermediate Feature Manipulation (SIFM), a method that strategically perturbs intermediate diffusion features through dual synergistic objectives: (1) maximizing feature divergence from the original edit trajectory to disrupt semantic alignment with the expected edit, and (2) minimizing feature norms to induce perceptual degradations. Furthermore, we introduce the Immunization Success Rate (ISR), a novel metric designed to rigorously quantify true immunization efficacy for the first time. ISR quantifies the proportion of edits where immunization induces either semantic failure relative to the prompt or significant perceptual degradations, assessed via Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs). Extensive experiments show our SIFM achieves the state-of-the-art performance for safeguarding visual content against malicious diffusion-based manipulation.
Controllable Localized Face Anonymization Via Diffusion Inpainting
Sep 18, 2025



Abstract:The growing use of portrait images in computer vision highlights the need to protect personal identities. At the same time, anonymized images must remain useful for downstream computer vision tasks. In this work, we propose a unified framework that leverages the inpainting ability of latent diffusion models to generate realistic anonymized images. Unlike prior approaches, we have complete control over the anonymization process by designing an adaptive attribute-guidance module that applies gradient correction during the reverse denoising process, aligning the facial attributes of the generated image with those of the synthesized target image. Our framework also supports localized anonymization, allowing users to specify which facial regions are left unchanged. Extensive experiments conducted on the public CelebA-HQ and FFHQ datasets show that our method outperforms state-of-the-art approaches while requiring no additional model training. The source code is available on our page.
Learning Transferable Facial Emotion Representations from Large-Scale Semantically Rich Captions
Jul 28, 2025Abstract:Current facial emotion recognition systems are predominately trained to predict a fixed set of predefined categories or abstract dimensional values. This constrained form of supervision hinders generalization and applicability, as it reduces the rich and nuanced spectrum of emotions into oversimplified labels or scales. In contrast, natural language provides a more flexible, expressive, and interpretable way to represent emotions, offering a much broader source of supervision. Yet, leveraging semantically rich natural language captions as supervisory signals for facial emotion representation learning remains relatively underexplored, primarily due to two key challenges: 1) the lack of large-scale caption datasets with rich emotional semantics, and 2) the absence of effective frameworks tailored to harness such rich supervision. To this end, we introduce EmoCap100K, a large-scale facial emotion caption dataset comprising over 100,000 samples, featuring rich and structured semantic descriptions that capture both global affective states and fine-grained local facial behaviors. Building upon this dataset, we further propose EmoCapCLIP, which incorporates a joint global-local contrastive learning framework enhanced by a cross-modal guided positive mining module. This design facilitates the comprehensive exploitation of multi-level caption information while accommodating semantic similarities between closely related expressions. Extensive evaluations on over 20 benchmarks covering five tasks demonstrate the superior performance of our method, highlighting the promise of learning facial emotion representations from large-scale semantically rich captions. The code and data will be available at https://github.com/sunlicai/EmoCapCLIP.
EmotionHallucer: Evaluating Emotion Hallucinations in Multimodal Large Language Models
May 16, 2025Abstract:Emotion understanding is a critical yet challenging task. Recent advances in Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have significantly enhanced their capabilities in this area. However, MLLMs often suffer from hallucinations, generating irrelevant or nonsensical content. To the best of our knowledge, despite the importance of this issue, there has been no dedicated effort to evaluate emotion-related hallucinations in MLLMs. In this work, we introduce EmotionHallucer, the first benchmark for detecting and analyzing emotion hallucinations in MLLMs. Unlike humans, whose emotion understanding stems from the interplay of biology and social learning, MLLMs rely solely on data-driven learning and lack innate emotional instincts. Fortunately, emotion psychology provides a solid foundation of knowledge about human emotions. Building on this, we assess emotion hallucinations from two dimensions: emotion psychology knowledge and real-world multimodal perception. To support robust evaluation, we utilize an adversarial binary question-answer (QA) framework, which employs carefully crafted basic and hallucinated pairs to assess the emotion hallucination tendencies of MLLMs. By evaluating 38 LLMs and MLLMs on EmotionHallucer, we reveal that: i) most current models exhibit substantial issues with emotion hallucinations; ii) closed-source models outperform open-source ones in detecting emotion hallucinations, and reasoning capability provides additional advantages; iii) existing models perform better in emotion psychology knowledge than in multimodal emotion perception. As a byproduct, these findings inspire us to propose the PEP-MEK framework, which yields an average improvement of 9.90% in emotion hallucination detection across selected models. Resources will be available at https://github.com/xxtars/EmotionHallucer.
MagicPortrait: Temporally Consistent Face Reenactment with 3D Geometric Guidance
Apr 30, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we propose a method for video face reenactment that integrates a 3D face parametric model into a latent diffusion framework, aiming to improve shape consistency and motion control in existing video-based face generation approaches. Our approach employs the FLAME (Faces Learned with an Articulated Model and Expressions) model as the 3D face parametric representation, providing a unified framework for modeling face expressions and head pose. This enables precise extraction of detailed face geometry and motion features from driving videos. Specifically, we enhance the latent diffusion model with rich 3D expression and detailed pose information by incorporating depth maps, normal maps, and rendering maps derived from FLAME sequences. A multi-layer face movements fusion module with integrated self-attention mechanisms is used to combine identity and motion latent features within the spatial domain. By utilizing the 3D face parametric model as motion guidance, our method enables parametric alignment of face identity between the reference image and the motion captured from the driving video. Experimental results on benchmark datasets show that our method excels at generating high-quality face animations with precise expression and head pose variation modeling. In addition, it demonstrates strong generalization performance on out-of-domain images. Code is publicly available at https://github.com/weimengting/MagicPortrait.
Contrastive Language-Image Learning with Augmented Textual Prompts for 3D/4D FER Using Vision-Language Model
Apr 28, 2025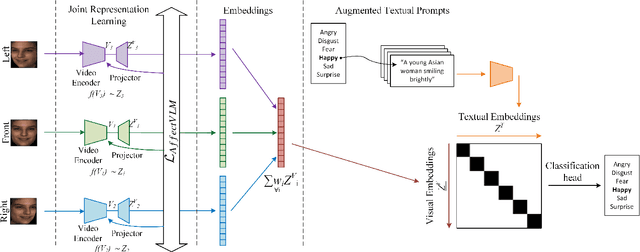
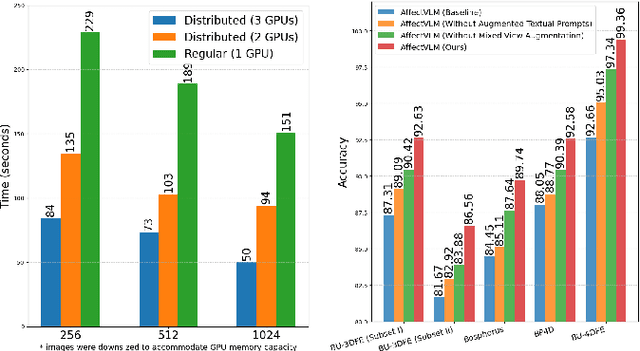

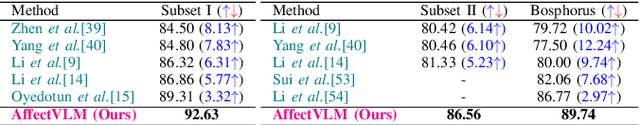
Abstract:In this paper, we introduce AffectVLM, a vision-language model designed to integrate multiviews for a semantically rich and visually comprehensive understanding of facial emotions from 3D/4D data. To effectively capture visual features, we propose a joint representation learning framework paired with a novel gradient-friendly loss function that accelerates model convergence towards optimal feature representation. Additionally, we introduce augmented textual prompts to enhance the model's linguistic capabilities and employ mixed view augmentation to expand the visual dataset. We also develop a Streamlit app for a real-time interactive inference and enable the model for distributed learning. Extensive experiments validate the superior performance of AffectVLM across multiple benchmarks.
Infused Suppression Of Magnification Artefacts For Micro-AU Detection
Apr 12, 2025Abstract:Facial micro-expressions are spontaneous, brief and subtle facial motions that unveil the underlying, suppressed emotions. Detecting Action Units (AUs) in micro-expressions is crucial because it yields a finer representation of facial motions than categorical emotions, effectively resolving the ambiguity among different expressions. One of the difficulties in micro-expression analysis is that facial motions are subtle and brief, thereby increasing the difficulty in correlating facial motion features to AU occurrence. To bridge the subtlety issue, flow-related features and motion magnification are a few common approaches as they can yield descriptive motion changes and increased motion amplitude respectively. While motion magnification can amplify the motion changes, it also accounts for illumination changes and projection errors during the amplification process, thereby creating motion artefacts that confuse the model to learn inauthentic magnified motion features. The problem is further aggravated in the context of a more complicated task where more AU classes are analyzed in cross-database settings. To address this issue, we propose InfuseNet, a layer-wise unitary feature infusion framework that leverages motion context to constrain the Action Unit (AU) learning within an informative facial movement region, thereby alleviating the influence of magnification artefacts. On top of that, we propose leveraging magnified latent features instead of reconstructing magnified samples to limit the distortion and artefacts caused by the projection inaccuracy in the motion reconstruction process. Via alleviating the magnification artefacts, InfuseNet has surpassed the state-of-the-art results in the CD6ME protocol. Further quantitative studies have also demonstrated the efficacy of motion artefacts alleviation.
From Laboratory to Real World: A New Benchmark Towards Privacy-Preserved Visible-Infrared Person Re-Identification
Mar 15, 2025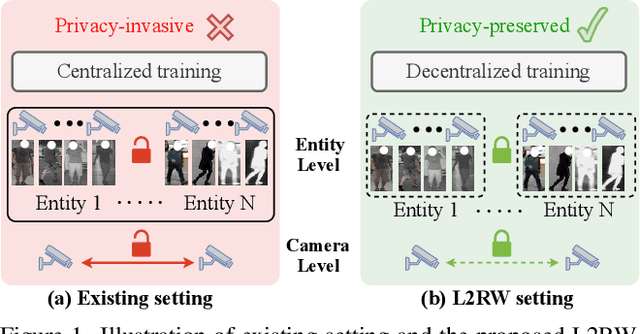
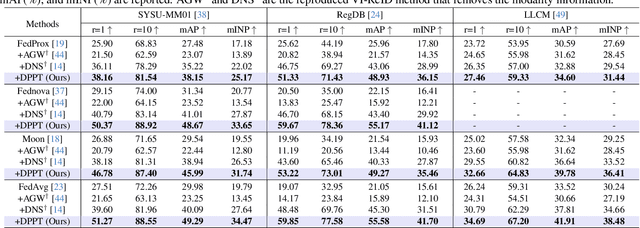
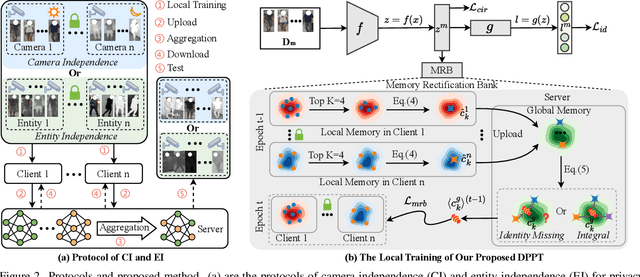
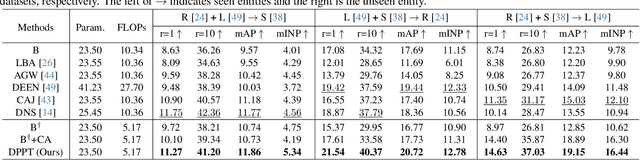
Abstract:Aiming to match pedestrian images captured under varying lighting conditions, visible-infrared person re-identification (VI-ReID) has drawn intensive research attention and achieved promising results. However, in real-world surveillance contexts, data is distributed across multiple devices/entities, raising privacy and ownership concerns that make existing centralized training impractical for VI-ReID. To tackle these challenges, we propose L2RW, a benchmark that brings VI-ReID closer to real-world applications. The rationale of L2RW is that integrating decentralized training into VI-ReID can address privacy concerns in scenarios with limited data-sharing regulation. Specifically, we design protocols and corresponding algorithms for different privacy sensitivity levels. In our new benchmark, we ensure the model training is done in the conditions that: 1) data from each camera remains completely isolated, or 2) different data entities (e.g., data controllers of a certain region) can selectively share the data. In this way, we simulate scenarios with strict privacy constraints which is closer to real-world conditions. Intensive experiments with various server-side federated algorithms are conducted, showing the feasibility of decentralized VI-ReID training. Notably, when evaluated in unseen domains (i.e., new data entities), our L2RW, trained with isolated data (privacy-preserved), achieves performance comparable to SOTAs trained with shared data (privacy-unrestricted). We hope this work offers a novel research entry for deploying VI-ReID that fits real-world scenarios and can benefit the community.
Enhancing Facial Privacy Protection via Weakening Diffusion Purification
Mar 13, 2025Abstract:The rapid growth of social media has led to the widespread sharing of individual portrait images, which pose serious privacy risks due to the capabilities of automatic face recognition (AFR) systems for mass surveillance. Hence, protecting facial privacy against unauthorized AFR systems is essential. Inspired by the generation capability of the emerging diffusion models, recent methods employ diffusion models to generate adversarial face images for privacy protection. However, they suffer from the diffusion purification effect, leading to a low protection success rate (PSR). In this paper, we first propose learning unconditional embeddings to increase the learning capacity for adversarial modifications and then use them to guide the modification of the adversarial latent code to weaken the diffusion purification effect. Moreover, we integrate an identity-preserving structure to maintain structural consistency between the original and generated images, allowing human observers to recognize the generated image as having the same identity as the original. Extensive experiments conducted on two public datasets, i.e., CelebA-HQ and LADN, demonstrate the superiority of our approach. The protected faces generated by our method outperform those produced by existing facial privacy protection approaches in terms of transferability and natural appearance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge