From Laboratory to Real World: A New Benchmark Towards Privacy-Preserved Visible-Infrared Person Re-Identification
Paper and Code
Mar 15, 2025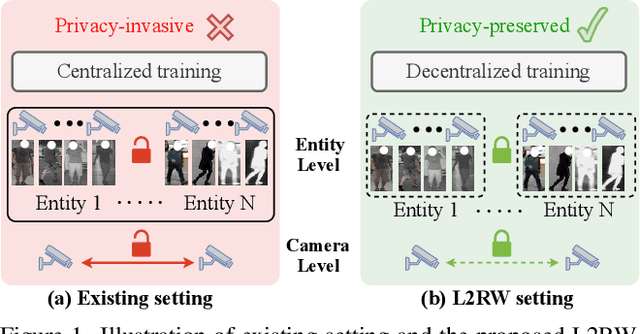
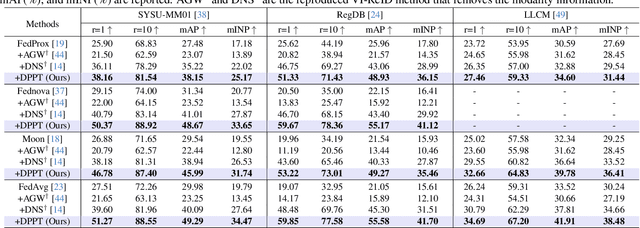
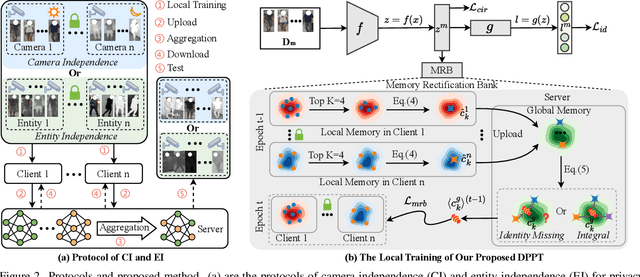
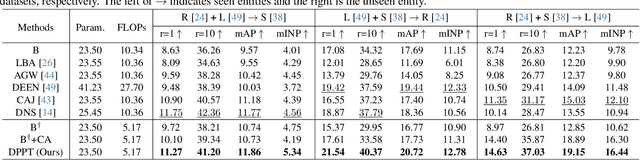
Aiming to match pedestrian images captured under varying lighting conditions, visible-infrared person re-identification (VI-ReID) has drawn intensive research attention and achieved promising results. However, in real-world surveillance contexts, data is distributed across multiple devices/entities, raising privacy and ownership concerns that make existing centralized training impractical for VI-ReID. To tackle these challenges, we propose L2RW, a benchmark that brings VI-ReID closer to real-world applications. The rationale of L2RW is that integrating decentralized training into VI-ReID can address privacy concerns in scenarios with limited data-sharing regulation. Specifically, we design protocols and corresponding algorithms for different privacy sensitivity levels. In our new benchmark, we ensure the model training is done in the conditions that: 1) data from each camera remains completely isolated, or 2) different data entities (e.g., data controllers of a certain region) can selectively share the data. In this way, we simulate scenarios with strict privacy constraints which is closer to real-world conditions. Intensive experiments with various server-side federated algorithms are conducted, showing the feasibility of decentralized VI-ReID training. Notably, when evaluated in unseen domains (i.e., new data entities), our L2RW, trained with isolated data (privacy-preserved), achieves performance comparable to SOTAs trained with shared data (privacy-unrestricted). We hope this work offers a novel research entry for deploying VI-ReID that fits real-world scenarios and can benefit the community.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge