Heikki Kälviäinen
Unsupervised Pelage Pattern Unwrapping for Animal Re-identification
Jun 18, 2025Abstract:Existing individual re-identification methods often struggle with the deformable nature of animal fur or skin patterns which undergo geometric distortions due to body movement and posture changes. In this paper, we propose a geometry-aware texture mapping approach that unwarps pelage patterns, the unique markings found on an animal's skin or fur, into a canonical UV space, enabling more robust feature matching. Our method uses surface normal estimation to guide the unwrapping process while preserving the geometric consistency between the 3D surface and the 2D texture space. We focus on two challenging species: Saimaa ringed seals (Pusa hispida saimensis) and leopards (Panthera pardus). Both species have distinctive yet highly deformable fur patterns. By integrating our pattern-preserving UV mapping with existing re-identification techniques, we demonstrate improved accuracy across diverse poses and viewing angles. Our framework does not require ground truth UV annotations and can be trained in a self-supervised manner. Experiments on seal and leopard datasets show up to a 5.4% improvement in re-identification accuracy.
EmotionHallucer: Evaluating Emotion Hallucinations in Multimodal Large Language Models
May 16, 2025Abstract:Emotion understanding is a critical yet challenging task. Recent advances in Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have significantly enhanced their capabilities in this area. However, MLLMs often suffer from hallucinations, generating irrelevant or nonsensical content. To the best of our knowledge, despite the importance of this issue, there has been no dedicated effort to evaluate emotion-related hallucinations in MLLMs. In this work, we introduce EmotionHallucer, the first benchmark for detecting and analyzing emotion hallucinations in MLLMs. Unlike humans, whose emotion understanding stems from the interplay of biology and social learning, MLLMs rely solely on data-driven learning and lack innate emotional instincts. Fortunately, emotion psychology provides a solid foundation of knowledge about human emotions. Building on this, we assess emotion hallucinations from two dimensions: emotion psychology knowledge and real-world multimodal perception. To support robust evaluation, we utilize an adversarial binary question-answer (QA) framework, which employs carefully crafted basic and hallucinated pairs to assess the emotion hallucination tendencies of MLLMs. By evaluating 38 LLMs and MLLMs on EmotionHallucer, we reveal that: i) most current models exhibit substantial issues with emotion hallucinations; ii) closed-source models outperform open-source ones in detecting emotion hallucinations, and reasoning capability provides additional advantages; iii) existing models perform better in emotion psychology knowledge than in multimodal emotion perception. As a byproduct, these findings inspire us to propose the PEP-MEK framework, which yields an average improvement of 9.90% in emotion hallucination detection across selected models. Resources will be available at https://github.com/xxtars/EmotionHallucer.
FSBench: A Figure Skating Benchmark for Advancing Artistic Sports Understanding
Apr 28, 2025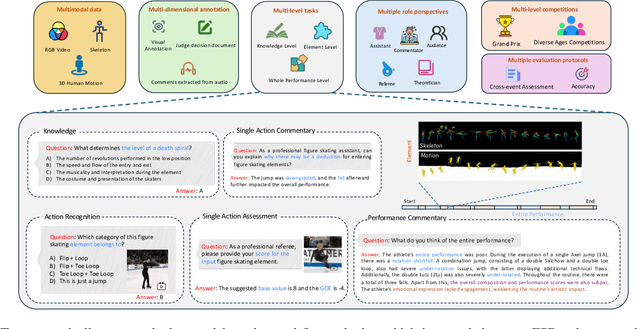
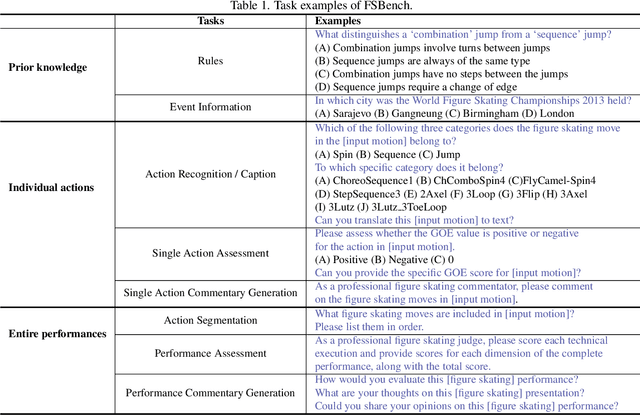
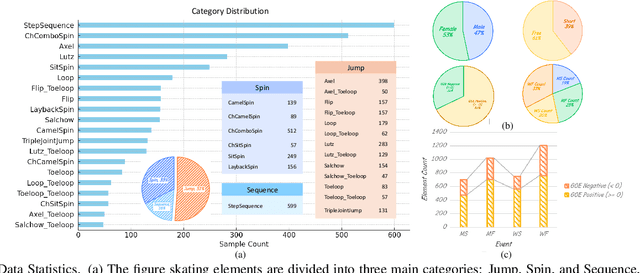
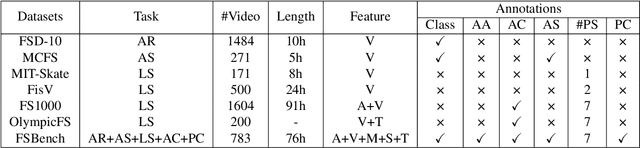
Abstract:Figure skating, known as the "Art on Ice," is among the most artistic sports, challenging to understand due to its blend of technical elements (like jumps and spins) and overall artistic expression. Existing figure skating datasets mainly focus on single tasks, such as action recognition or scoring, lacking comprehensive annotations for both technical and artistic evaluation. Current sports research is largely centered on ball games, with limited relevance to artistic sports like figure skating. To address this, we introduce FSAnno, a large-scale dataset advancing artistic sports understanding through figure skating. FSAnno includes an open-access training and test dataset, alongside a benchmark dataset, FSBench, for fair model evaluation. FSBench consists of FSBench-Text, with multiple-choice questions and explanations, and FSBench-Motion, containing multimodal data and Question and Answer (QA) pairs, supporting tasks from technical analysis to performance commentary. Initial tests on FSBench reveal significant limitations in existing models' understanding of artistic sports. We hope FSBench will become a key tool for evaluating and enhancing model comprehension of figure skating.
DEEMO: De-identity Multimodal Emotion Recognition and Reasoning
Apr 28, 2025Abstract:Emotion understanding is a critical yet challenging task. Most existing approaches rely heavily on identity-sensitive information, such as facial expressions and speech, which raises concerns about personal privacy. To address this, we introduce the De-identity Multimodal Emotion Recognition and Reasoning (DEEMO), a novel task designed to enable emotion understanding using de-identified video and audio inputs. The DEEMO dataset consists of two subsets: DEEMO-NFBL, which includes rich annotations of Non-Facial Body Language (NFBL), and DEEMO-MER, an instruction dataset for Multimodal Emotion Recognition and Reasoning using identity-free cues. This design supports emotion understanding without compromising identity privacy. In addition, we propose DEEMO-LLaMA, a Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM) that integrates de-identified audio, video, and textual information to enhance both emotion recognition and reasoning. Extensive experiments show that DEEMO-LLaMA achieves state-of-the-art performance on both tasks, outperforming existing MLLMs by a significant margin, achieving 74.49% accuracy and 74.45% F1-score in de-identity emotion recognition, and 6.20 clue overlap and 7.66 label overlap in de-identity emotion reasoning. Our work contributes to ethical AI by advancing privacy-preserving emotion understanding and promoting responsible affective computing.
AU-TTT: Vision Test-Time Training model for Facial Action Unit Detection
Mar 30, 2025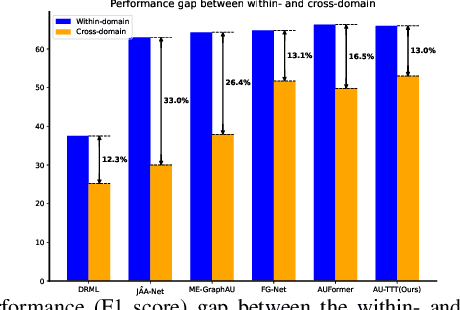
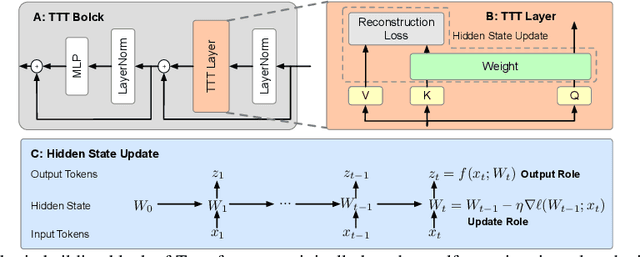
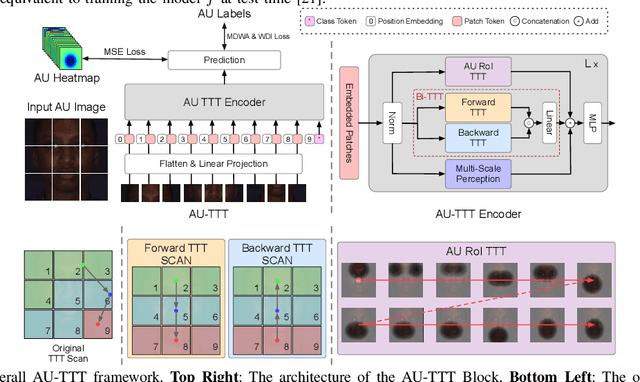
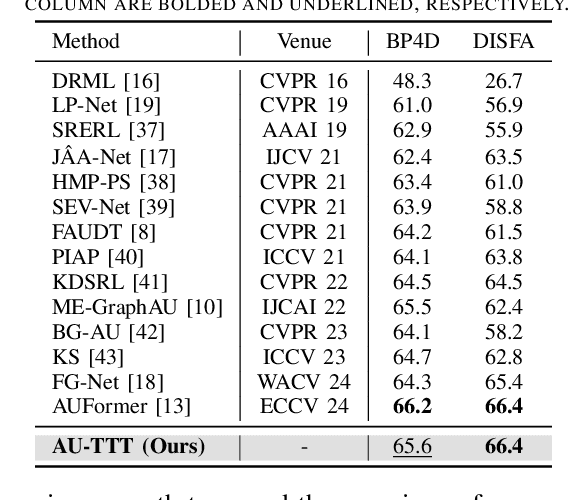
Abstract:Facial Action Units (AUs) detection is a cornerstone of objective facial expression analysis and a critical focus in affective computing. Despite its importance, AU detection faces significant challenges, such as the high cost of AU annotation and the limited availability of datasets. These constraints often lead to overfitting in existing methods, resulting in substantial performance degradation when applied across diverse datasets. Addressing these issues is essential for improving the reliability and generalizability of AU detection methods. Moreover, many current approaches leverage Transformers for their effectiveness in long-context modeling, but they are hindered by the quadratic complexity of self-attention. Recently, Test-Time Training (TTT) layers have emerged as a promising solution for long-sequence modeling. Additionally, TTT applies self-supervised learning for iterative updates during both training and inference, offering a potential pathway to mitigate the generalization challenges inherent in AU detection tasks. In this paper, we propose a novel vision backbone tailored for AU detection, incorporating bidirectional TTT blocks, named AU-TTT. Our approach introduces TTT Linear to the AU detection task and optimizes image scanning mechanisms for enhanced performance. Additionally, we design an AU-specific Region of Interest (RoI) scanning mechanism to capture fine-grained facial features critical for AU detection. Experimental results demonstrate that our method achieves competitive performance in both within-domain and cross-domain scenarios.
Self-Supervised Pretraining for Fine-Grained Plankton Recognition
Mar 14, 2025Abstract:Plankton recognition is an important computer vision problem due to plankton's essential role in ocean food webs and carbon capture, highlighting the need for species-level monitoring. However, this task is challenging due to its fine-grained nature and dataset shifts caused by different imaging instruments and varying species distributions. As new plankton image datasets are collected at an increasing pace, there is a need for general plankton recognition models that require minimal expert effort for data labeling. In this work, we study large-scale self-supervised pretraining for fine-grained plankton recognition. We first employ masked autoencoding and a large volume of diverse plankton image data to pretrain a general-purpose plankton image encoder. Then we utilize fine-tuning to obtain accurate plankton recognition models for new datasets with a very limited number of labeled training images. Our experiments show that self-supervised pretraining with diverse plankton data clearly increases plankton recognition accuracy compared to standard ImageNet pretraining when the amount of training data is limited. Moreover, the accuracy can be further improved when unlabeled target data is available and utilized during the pretraining.
Open-Set Plankton Recognition
Mar 14, 2025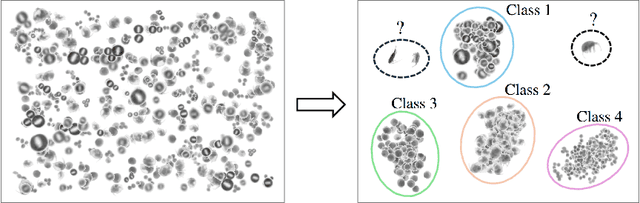
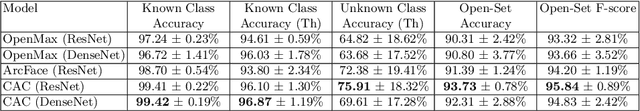
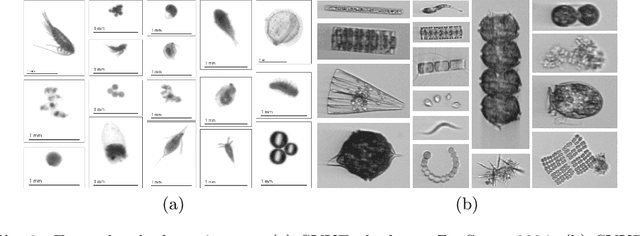
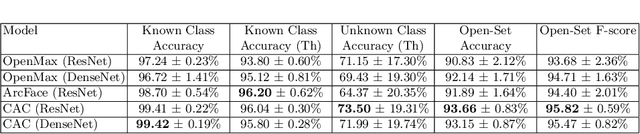
Abstract:This paper considers open-set recognition (OSR) of plankton images. Plankton include a diverse range of microscopic aquatic organisms that have an important role in marine ecosystems as primary producers and as a base of food webs. Given their sensitivity to environmental changes, fluctuations in plankton populations offer valuable information about oceans' health and climate change motivating their monitoring. Modern automatic plankton imaging devices enable the collection of large-scale plankton image datasets, facilitating species-level analysis. Plankton species recognition can be seen as an image classification task and is typically solved using deep learning-based image recognition models. However, data collection in real aquatic environments results in imaging devices capturing a variety of non-plankton particles and plankton species not present in the training set. This creates a challenging fine-grained OSR problem, characterized by subtle differences between taxonomically close plankton species. We address this challenge by conducting extensive experiments on three OSR approaches using both phyto- and zooplankton images analyzing also on the effect of the rejection thresholds for OSR. The results demonstrate that high OSR accuracy can be obtained promoting the use of these methods in operational plankton research. We have made the data publicly available to the research community.
DiffFAS: Face Anti-Spoofing via Generative Diffusion Models
Sep 13, 2024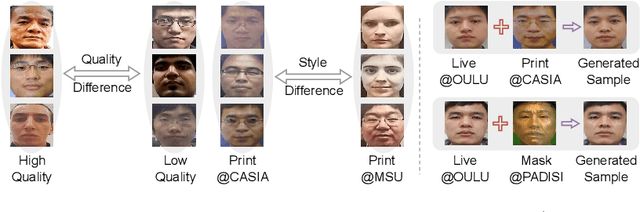
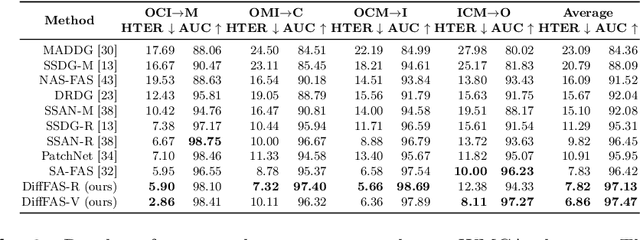
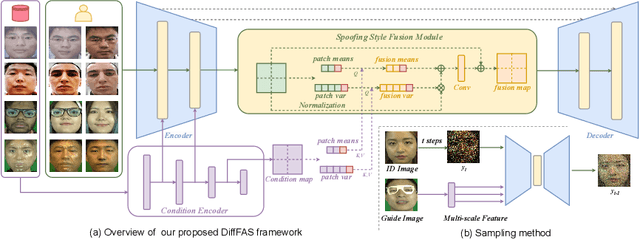
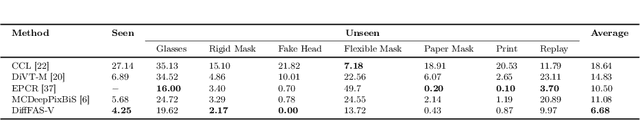
Abstract:Face anti-spoofing (FAS) plays a vital role in preventing face recognition (FR) systems from presentation attacks. Nowadays, FAS systems face the challenge of domain shift, impacting the generalization performance of existing FAS methods. In this paper, we rethink about the inherence of domain shift and deconstruct it into two factors: image style and image quality. Quality influences the purity of the presentation of spoof information, while style affects the manner in which spoof information is presented. Based on our analysis, we propose DiffFAS framework, which quantifies quality as prior information input into the network to counter image quality shift, and performs diffusion-based high-fidelity cross-domain and cross-attack types generation to counter image style shift. DiffFAS transforms easily collectible live faces into high-fidelity attack faces with precise labels while maintaining consistency between live and spoof face identities, which can also alleviate the scarcity of labeled data with novel type attacks faced by nowadays FAS system. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our framework on challenging cross-domain and cross-attack FAS datasets, achieving the state-of-the-art performance. Available at https://github.com/murphytju/DiffFAS.
EMO-LLaMA: Enhancing Facial Emotion Understanding with Instruction Tuning
Aug 21, 2024



Abstract:Facial expression recognition (FER) is an important research topic in emotional artificial intelligence. In recent decades, researchers have made remarkable progress. However, current FER paradigms face challenges in generalization, lack semantic information aligned with natural language, and struggle to process both images and videos within a unified framework, making their application in multimodal emotion understanding and human-computer interaction difficult. Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have recently achieved success, offering advantages in addressing these issues and potentially overcoming the limitations of current FER paradigms. However, directly applying pre-trained MLLMs to FER still faces several challenges. Our zero-shot evaluations of existing open-source MLLMs on FER indicate a significant performance gap compared to GPT-4V and current supervised state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods. In this paper, we aim to enhance MLLMs' capabilities in understanding facial expressions. We first generate instruction data for five FER datasets with Gemini. We then propose a novel MLLM, named EMO-LLaMA, which incorporates facial priors from a pretrained facial analysis network to enhance human facial information. Specifically, we design a Face Info Mining module to extract both global and local facial information. Additionally, we utilize a handcrafted prompt to introduce age-gender-race attributes, considering the emotional differences across different human groups. Extensive experiments show that EMO-LLaMA achieves SOTA-comparable or competitive results across both static and dynamic FER datasets. The instruction dataset and code are available at https://github.com/xxtars/EMO-LLaMA.
Understanding the Impact of Training Set Size on Animal Re-identification
May 24, 2024Abstract:Recent advancements in the automatic re-identification of animal individuals from images have opened up new possibilities for studying wildlife through camera traps and citizen science projects. Existing methods leverage distinct and permanent visual body markings, such as fur patterns or scars, and typically employ one of two strategies: local features or end-to-end learning. In this study, we delve into the impact of training set size by conducting comprehensive experiments across six different methods and five animal species. While it is well known that end-to-end learning-based methods surpass local feature-based methods given a sufficient amount of good-quality training data, the challenge of gathering such datasets for wildlife animals means that local feature-based methods remain a more practical approach for many species. We demonstrate the benefits of both local feature and end-to-end learning-based approaches and show that species-specific characteristics, particularly intra-individual variance, have a notable effect on training data requirements.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge