Bihan Wen
School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Nanyang Technological University
RSGround-R1: Rethinking Remote Sensing Visual Grounding through Spatial Reasoning
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Remote Sensing Visual Grounding (RSVG) aims to localize target objects in large-scale aerial imagery based on natural language descriptions. Owing to the vast spatial scale and high semantic ambiguity of remote sensing scenes, these descriptions often rely heavily on positional cues, posing unique challenges for Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) in spatial reasoning. To leverage this unique feature, we propose a reasoning-guided, position-aware post-training framework, dubbed \textbf{RSGround-R1}, to progressively enhance spatial understanding. Specifically, we first introduce Chain-of-Thought Supervised Fine-Tuning (CoT-SFT) using synthetically generated RSVG reasoning data to establish explicit position awareness. Reinforcement Fine-Tuning (RFT) is then applied, augmented by our newly designed positional reward that provides continuous and distance-aware guidance toward accurate localization. Moreover, to mitigate incoherent localization behaviors across rollouts, we introduce a spatial consistency guided optimization scheme that dynamically adjusts policy updates based on their spatial coherence, ensuring stable and robust convergence. Extensive experiments on RSVG benchmarks demonstrate superior performance and generalization of our model.
Improving Flexible Image Tokenizers for Autoregressive Image Generation
Jan 04, 2026Abstract:Flexible image tokenizers aim to represent an image using an ordered 1D variable-length token sequence. This flexible tokenization is typically achieved through nested dropout, where a portion of trailing tokens is randomly truncated during training, and the image is reconstructed using the remaining preceding sequence. However, this tail-truncation strategy inherently concentrates the image information in the early tokens, limiting the effectiveness of downstream AutoRegressive (AR) image generation as the token length increases. To overcome these limitations, we propose \textbf{ReToK}, a flexible tokenizer with \underline{Re}dundant \underline{Tok}en Padding and Hierarchical Semantic Regularization, designed to fully exploit all tokens for enhanced latent modeling. Specifically, we introduce \textbf{Redundant Token Padding} to activate tail tokens more frequently, thereby alleviating information over-concentration in the early tokens. In addition, we apply \textbf{Hierarchical Semantic Regularization} to align the decoding features of earlier tokens with those from a pre-trained vision foundation model, while progressively reducing the regularization strength toward the tail to allow finer low-level detail reconstruction. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of ReTok: on ImageNet 256$\times$256, our method achieves superior generation performance compared with both flexible and fixed-length tokenizers. Code will be available at: \href{https://github.com/zfu006/ReTok}{https://github.com/zfu006/ReTok}
Learning Through Little Eyes: Attribute Discrimination Beyond Objects
Dec 22, 2025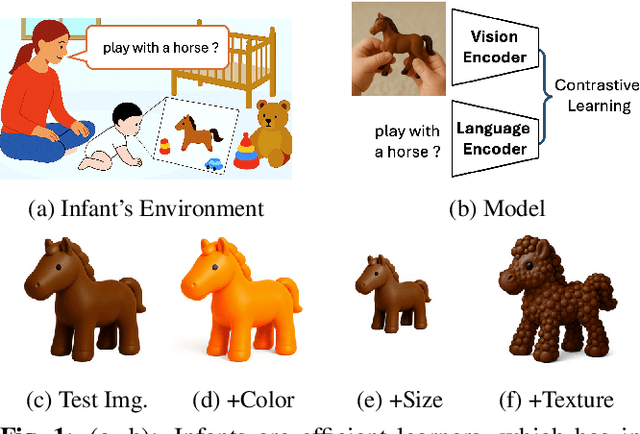

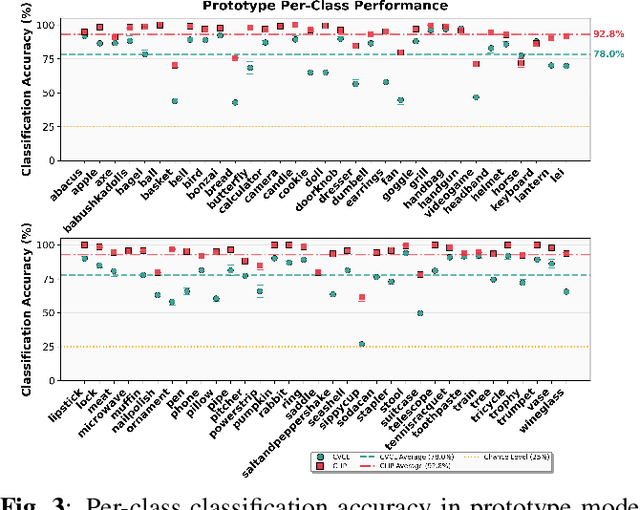
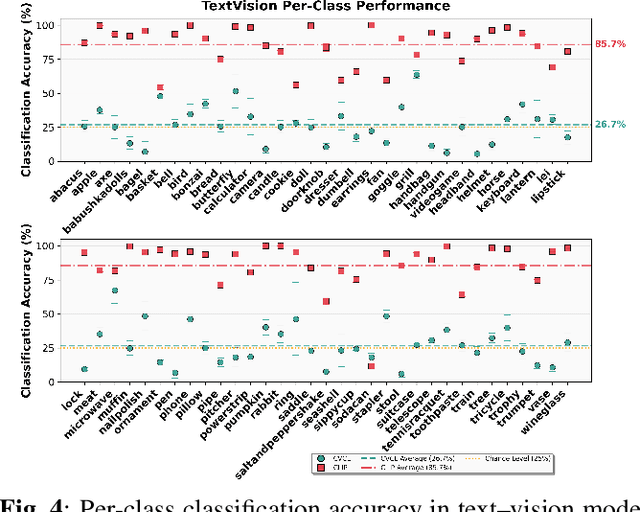
Abstract:Infants learn to recognize not only object categories but also fine grained attributes such as color, size, and texture within their first two years of life. Prior work explores Childs View for Contrastive Learning (CVCL), a CLIP style model trained on infant egocentric video as a computational model of early infant learning, but it focuses only on class level recognition. This leaves it unclear whether infant scale learning also supports attribute discrimination. To address this, we introduce a benchmark that systematically varies color, size, and texture, allowing controlled tests of within class attribute recognition. Comparing CVCL with CLIP shows clear differences. CVCL is better at size discrimination, while CLIP achieves higher accuracy on color discrimination. Both models represent texture in image embeddings but fail to ground texture linguistically, suggesting a gap between visual and language spaces.
RealisticDreamer: Guidance Score Distillation for Few-shot Gaussian Splatting
Nov 14, 2025Abstract:3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has recently gained great attention in the 3D scene representation for its high-quality real-time rendering capabilities. However, when the input comprises sparse training views, 3DGS is prone to overfitting, primarily due to the lack of intermediate-view supervision. Inspired by the recent success of Video Diffusion Models (VDM), we propose a framework called Guidance Score Distillation (GSD) to extract the rich multi-view consistency priors from pretrained VDMs. Building on the insights from Score Distillation Sampling (SDS), GSD supervises rendered images from multiple neighboring views, guiding the Gaussian splatting representation towards the generative direction of VDM. However, the generative direction often involves object motion and random camera trajectories, making it challenging for direct supervision in the optimization process. To address this problem, we introduce an unified guidance form to correct the noise prediction result of VDM. Specifically, we incorporate both a depth warp guidance based on real depth maps and a guidance based on semantic image features, ensuring that the score update direction from VDM aligns with the correct camera pose and accurate geometry. Experimental results show that our method outperforms existing approaches across multiple datasets.
Conformal Prediction for Multi-Source Detection on a Network
Nov 12, 2025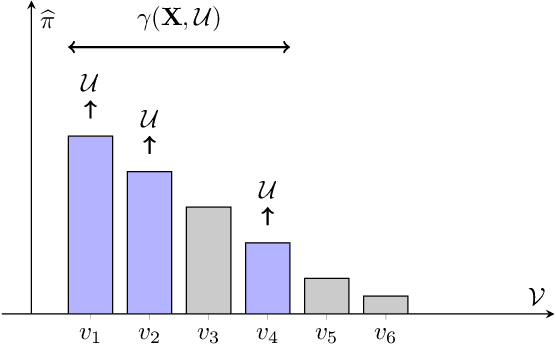
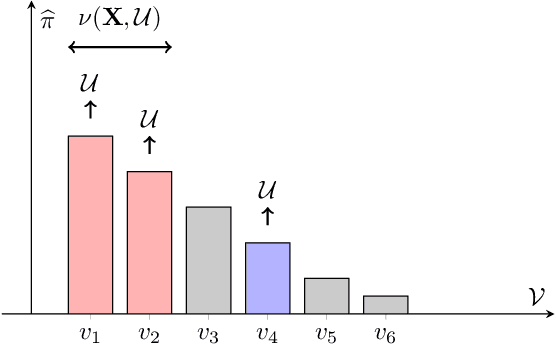
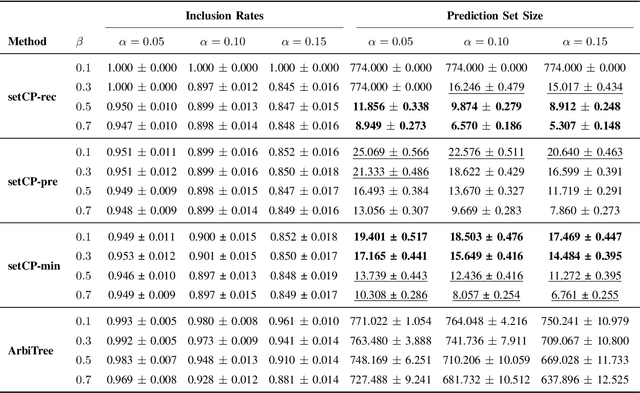
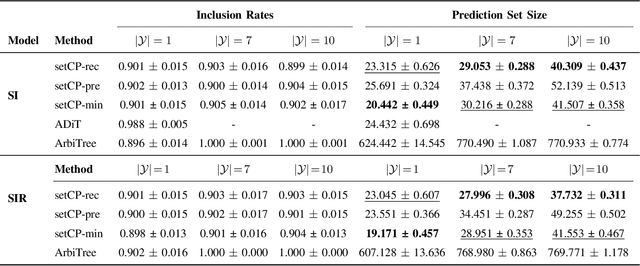
Abstract:Detecting the origin of information or infection spread in networks is a fundamental challenge with applications in misinformation tracking, epidemiology, and beyond. We study the multi-source detection problem: given snapshot observations of node infection status on a graph, estimate the set of source nodes that initiated the propagation. Existing methods either lack statistical guarantees or are limited to specific diffusion models and assumptions. We propose a novel conformal prediction framework that provides statistically valid recall guarantees for source set detection, independent of the underlying diffusion process or data distribution. Our approach introduces principled score functions to quantify the alignment between predicted probabilities and true sources, and leverages a calibration set to construct prediction sets with user-specified recall and coverage levels. The method is applicable to both single- and multi-source scenarios, supports general network diffusion dynamics, and is computationally efficient for large graphs. Empirical results demonstrate that our method achieves rigorous coverage with competitive accuracy, outperforming existing baselines in both reliability and scalability.The code is available online.
FailSafe: Reasoning and Recovery from Failures in Vision-Language-Action Models
Oct 02, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in robotic manipulation have integrated low-level robotic control into Vision-Language Models (VLMs), extending them into Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models. Although state-of-the-art VLAs achieve strong performance in downstream robotic applications, supported by large-scale crowd-sourced robot training data, they still inevitably encounter failures during execution. Enabling robots to reason about and recover from unpredictable and abrupt failures remains a critical challenge. Existing robotic manipulation datasets, collected in either simulation or the real world, primarily provide only ground-truth trajectories, leaving robots unable to recover once failures occur. Moreover, the few datasets that address failure detection typically offer only textual explanations, which are difficult to utilize directly in VLA models. To address this gap, we introduce FailSafe, a novel failure generation and recovery system that automatically produces diverse failure cases paired with executable recovery actions. FailSafe can be seamlessly applied to any manipulation task in any simulator, enabling scalable creation of failure-action data. To demonstrate its effectiveness, we fine-tune LLaVa-OneVision-7B (LLaVa-OV-7B) to build FailSafe-VLM. Experimental results show that FailSafe-VLM successfully helps robotic arm detect and recover from potential failures, improving the performance of three state-of-the-art VLA models pi0-FAST, OpenVLA, OpenVLA-OFT) by up to 22.6% on average across several tasks in Maniskill. Furthermore, FailSafe-VLM could generalize across different spatial configurations, camera viewpoints, and robotic embodiments. We plan to release the FailSafe code to the community.
RF4D:Neural Radar Fields for Novel View Synthesis in Outdoor Dynamic Scenes
May 27, 2025Abstract:Neural fields (NFs) have demonstrated remarkable performance in scene reconstruction, powering various tasks such as novel view synthesis. However, existing NF methods relying on RGB or LiDAR inputs often exhibit severe fragility to adverse weather, particularly when applied in outdoor scenarios like autonomous driving. In contrast, millimeter-wave radar is inherently robust to environmental changes, while unfortunately, its integration with NFs remains largely underexplored. Besides, as outdoor driving scenarios frequently involve moving objects, making spatiotemporal modeling essential for temporally consistent novel view synthesis. To this end, we introduce RF4D, a radar-based neural field framework specifically designed for novel view synthesis in outdoor dynamic scenes. RF4D explicitly incorporates temporal information into its representation, significantly enhancing its capability to model moving objects. We further introduce a feature-level flow module that predicts latent temporal offsets between adjacent frames, enforcing temporal coherence in dynamic scene modeling. Moreover, we propose a radar-specific power rendering formulation closely aligned with radar sensing physics, improving synthesis accuracy and interoperability. Extensive experiments on public radar datasets demonstrate the superior performance of RF4D in terms of radar measurement synthesis quality and occupancy estimation accuracy, achieving especially pronounced improvements in dynamic outdoor scenarios.
Sparc3D: Sparse Representation and Construction for High-Resolution 3D Shapes Modeling
May 21, 2025Abstract:High-fidelity 3D object synthesis remains significantly more challenging than 2D image generation due to the unstructured nature of mesh data and the cubic complexity of dense volumetric grids. Existing two-stage pipelines-compressing meshes with a VAE (using either 2D or 3D supervision), followed by latent diffusion sampling-often suffer from severe detail loss caused by inefficient representations and modality mismatches introduced in VAE. We introduce Sparc3D, a unified framework that combines a sparse deformable marching cubes representation Sparcubes with a novel encoder Sparconv-VAE. Sparcubes converts raw meshes into high-resolution ($1024^3$) surfaces with arbitrary topology by scattering signed distance and deformation fields onto a sparse cube, allowing differentiable optimization. Sparconv-VAE is the first modality-consistent variational autoencoder built entirely upon sparse convolutional networks, enabling efficient and near-lossless 3D reconstruction suitable for high-resolution generative modeling through latent diffusion. Sparc3D achieves state-of-the-art reconstruction fidelity on challenging inputs, including open surfaces, disconnected components, and intricate geometry. It preserves fine-grained shape details, reduces training and inference cost, and integrates naturally with latent diffusion models for scalable, high-resolution 3D generation.
DEEMO: De-identity Multimodal Emotion Recognition and Reasoning
Apr 28, 2025Abstract:Emotion understanding is a critical yet challenging task. Most existing approaches rely heavily on identity-sensitive information, such as facial expressions and speech, which raises concerns about personal privacy. To address this, we introduce the De-identity Multimodal Emotion Recognition and Reasoning (DEEMO), a novel task designed to enable emotion understanding using de-identified video and audio inputs. The DEEMO dataset consists of two subsets: DEEMO-NFBL, which includes rich annotations of Non-Facial Body Language (NFBL), and DEEMO-MER, an instruction dataset for Multimodal Emotion Recognition and Reasoning using identity-free cues. This design supports emotion understanding without compromising identity privacy. In addition, we propose DEEMO-LLaMA, a Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM) that integrates de-identified audio, video, and textual information to enhance both emotion recognition and reasoning. Extensive experiments show that DEEMO-LLaMA achieves state-of-the-art performance on both tasks, outperforming existing MLLMs by a significant margin, achieving 74.49% accuracy and 74.45% F1-score in de-identity emotion recognition, and 6.20 clue overlap and 7.66 label overlap in de-identity emotion reasoning. Our work contributes to ethical AI by advancing privacy-preserving emotion understanding and promoting responsible affective computing.
PAD: Phase-Amplitude Decoupling Fusion for Multi-Modal Land Cover Classification
Apr 27, 2025Abstract:The fusion of Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) and RGB imagery for land cover classification remains challenging due to modality heterogeneity and the underutilization of spectral complementarity. Existing methods often fail to decouple shared structural features from modality-specific radiometric attributes, leading to feature conflicts and information loss. To address this issue, we propose Phase-Amplitude Decoupling (PAD), a frequency-aware framework that separates phase (modality-shared) and amplitude (modality-specific) components in the Fourier domain. Specifically, PAD consists of two key components: 1) Phase Spectrum Correction (PSC), which aligns cross-modal phase features through convolution-guided scaling to enhance geometric consistency, and 2) Amplitude Spectrum Fusion (ASF), which dynamically integrates high-frequency details and low-frequency structures using frequency-adaptive multilayer perceptrons. This approach leverages SAR's sensitivity to morphological features and RGB's spectral richness. Extensive experiments on WHU-OPT-SAR and DDHR-SK datasets demonstrate state-of-the-art performance. Our work establishes a new paradigm for physics-aware multi-modal fusion in remote sensing. The code will be available at https://github.com/RanFeng2/PAD.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge