Ranjay Krishna
VLS: Steering Pretrained Robot Policies via Vision-Language Models
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Why do pretrained diffusion or flow-matching policies fail when the same task is performed near an obstacle, on a shifted support surface, or amid mild clutter? Such failures rarely reflect missing motor skills; instead, they expose a limitation of imitation learning under train-test shifts, where action generation is tightly coupled to training-specific spatial configurations and task specifications. Retraining or fine-tuning to address these failures is costly and conceptually misaligned, as the required behaviors already exist but cannot be selectively adapted at test time. We propose Vision-Language Steering (VLS), a training-free framework for inference-time adaptation of frozen generative robot policies. VLS treats adaptation as an inference-time control problem, steering the sampling process of a pretrained diffusion or flow-matching policy in response to out-of-distribution observation-language inputs without modifying policy parameters. By leveraging vision-language models to synthesize trajectory-differentiable reward functions, VLS guides denoising toward action trajectories that satisfy test-time spatial and task requirements. Across simulation and real-world evaluations, VLS consistently outperforms prior steering methods, achieving a 31% improvement on CALVIN and a 13% gain on LIBERO-PRO. Real-world deployment on a Franka robot further demonstrates robust inference-time adaptation under test-time spatial and semantic shifts. Project page: https://vision-language-steering.github.io/webpage/
AdaReasoner: Dynamic Tool Orchestration for Iterative Visual Reasoning
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:When humans face problems beyond their immediate capabilities, they rely on tools, providing a promising paradigm for improving visual reasoning in multimodal large language models (MLLMs). Effective reasoning, therefore, hinges on knowing which tools to use, when to invoke them, and how to compose them over multiple steps, even when faced with new tools or new tasks. We introduce \textbf{AdaReasoner}, a family of multimodal models that learn tool use as a general reasoning skill rather than as tool-specific or explicitly supervised behavior. AdaReasoner is enabled by (i) a scalable data curation pipeline exposing models to long-horizon, multi-step tool interactions; (ii) Tool-GRPO, a reinforcement learning algorithm that optimizes tool selection and sequencing based on end-task success; and (iii) an adaptive learning mechanism that dynamically regulates tool usage. Together, these components allow models to infer tool utility from task context and intermediate outcomes, enabling coordination of multiple tools and generalization to unseen tools. Empirically, AdaReasoner exhibits strong tool-adaptive and generalization behaviors: it autonomously adopts beneficial tools, suppresses irrelevant ones, and adjusts tool usage frequency based on task demands, despite never being explicitly trained to do so. These capabilities translate into state-of-the-art performance across challenging benchmarks, improving the 7B base model by +24.9\% on average and surpassing strong proprietary systems such as GPT-5 on multiple tasks, including VSP and Jigsaw.
Molmo2: Open Weights and Data for Vision-Language Models with Video Understanding and Grounding
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Today's strongest video-language models (VLMs) remain proprietary. The strongest open-weight models either rely on synthetic data from proprietary VLMs, effectively distilling from them, or do not disclose their training data or recipe. As a result, the open-source community lacks the foundations needed to improve on the state-of-the-art video (and image) language models. Crucially, many downstream applications require more than just high-level video understanding; they require grounding -- either by pointing or by tracking in pixels. Even proprietary models lack this capability. We present Molmo2, a new family of VLMs that are state-of-the-art among open-source models and demonstrate exceptional new capabilities in point-driven grounding in single image, multi-image, and video tasks. Our key contribution is a collection of 7 new video datasets and 2 multi-image datasets, including a dataset of highly detailed video captions for pre-training, a free-form video Q&A dataset for fine-tuning, a new object tracking dataset with complex queries, and an innovative new video pointing dataset, all collected without the use of closed VLMs. We also present a training recipe for this data utilizing an efficient packing and message-tree encoding scheme, and show bi-directional attention on vision tokens and a novel token-weight strategy improves performance. Our best-in-class 8B model outperforms others in the class of open weight and data models on short videos, counting, and captioning, and is competitive on long-videos. On video-grounding Molmo2 significantly outperforms existing open-weight models like Qwen3-VL (35.5 vs 29.6 accuracy on video counting) and surpasses proprietary models like Gemini 3 Pro on some tasks (38.4 vs 20.0 F1 on video pointing and 56.2 vs 41.1 J&F on video tracking).
GenEval 2: Addressing Benchmark Drift in Text-to-Image Evaluation
Dec 18, 2025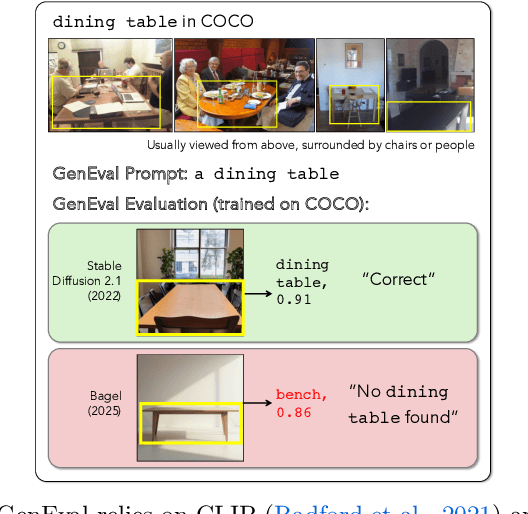
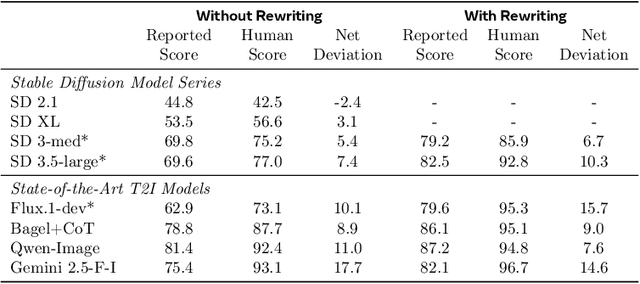
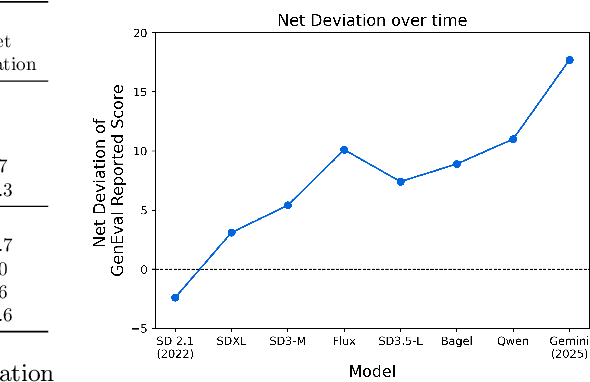
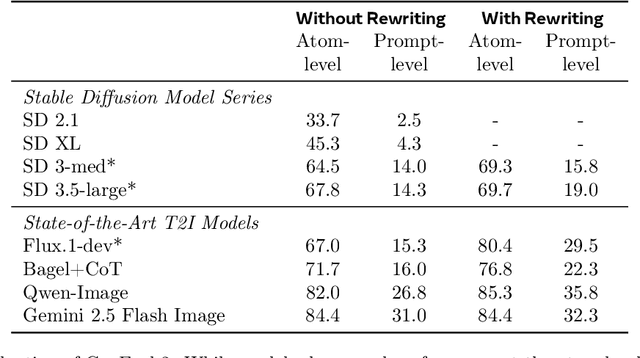
Abstract:Automating Text-to-Image (T2I) model evaluation is challenging; a judge model must be used to score correctness, and test prompts must be selected to be challenging for current T2I models but not the judge. We argue that satisfying these constraints can lead to benchmark drift over time, where the static benchmark judges fail to keep up with newer model capabilities. We show that benchmark drift is a significant problem for GenEval, one of the most popular T2I benchmarks. Although GenEval was well-aligned with human judgment at the time of its release, it has drifted far from human judgment over time -- resulting in an absolute error of as much as 17.7% for current models. This level of drift strongly suggests that GenEval has been saturated for some time, as we verify via a large-scale human study. To help fill this benchmarking gap, we introduce a new benchmark, GenEval 2, with improved coverage of primitive visual concepts and higher degrees of compositionality, which we show is more challenging for current models. We also introduce Soft-TIFA, an evaluation method for GenEval 2 that combines judgments for visual primitives, which we show is more well-aligned with human judgment and argue is less likely to drift from human-alignment over time (as compared to more holistic judges such as VQAScore). Although we hope GenEval 2 will provide a strong benchmark for many years, avoiding benchmark drift is far from guaranteed and our work, more generally, highlights the importance of continual audits and improvement for T2I and related automated model evaluation benchmarks.
Structure From Tracking: Distilling Structure-Preserving Motion for Video Generation
Dec 12, 2025
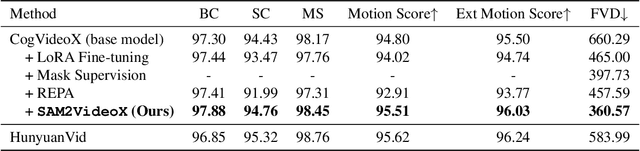
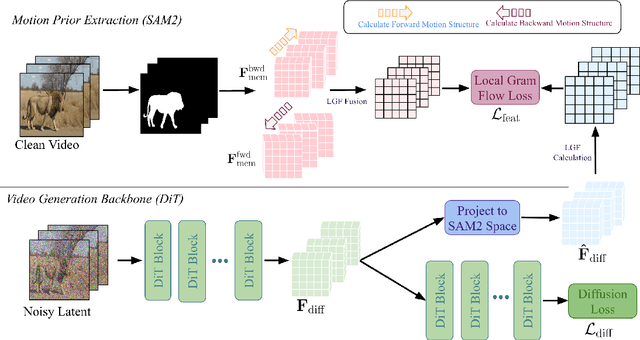
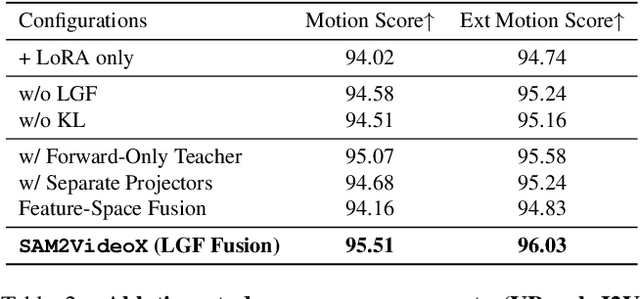
Abstract:Reality is a dance between rigid constraints and deformable structures. For video models, that means generating motion that preserves fidelity as well as structure. Despite progress in diffusion models, producing realistic structure-preserving motion remains challenging, especially for articulated and deformable objects such as humans and animals. Scaling training data alone, so far, has failed to resolve physically implausible transitions. Existing approaches rely on conditioning with noisy motion representations, such as optical flow or skeletons extracted using an external imperfect model. To address these challenges, we introduce an algorithm to distill structure-preserving motion priors from an autoregressive video tracking model (SAM2) into a bidirectional video diffusion model (CogVideoX). With our method, we train SAM2VideoX, which contains two innovations: (1) a bidirectional feature fusion module that extracts global structure-preserving motion priors from a recurrent model like SAM2; (2) a Local Gram Flow loss that aligns how local features move together. Experiments on VBench and in human studies show that SAM2VideoX delivers consistent gains (+2.60\% on VBench, 21-22\% lower FVD, and 71.4\% human preference) over prior baselines. Specifically, on VBench, we achieve 95.51\%, surpassing REPA (92.91\%) by 2.60\%, and reduce FVD to 360.57, a 21.20\% and 22.46\% improvement over REPA- and LoRA-finetuning, respectively. The project website can be found at https://sam2videox.github.io/ .
Agile Deliberation: Concept Deliberation for Subjective Visual Classification
Dec 11, 2025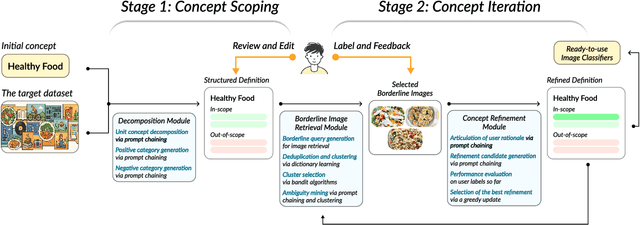
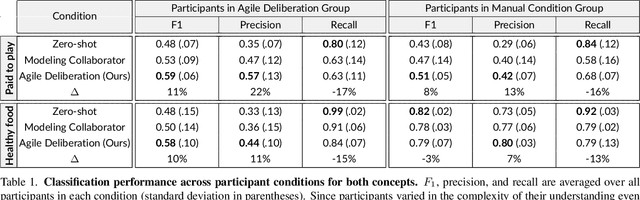
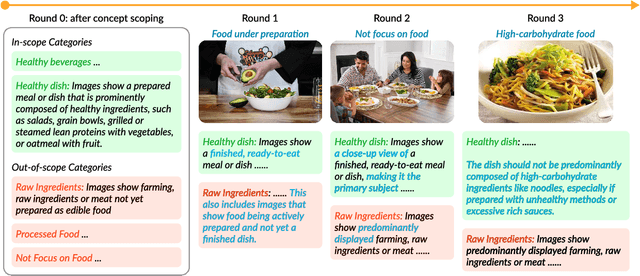
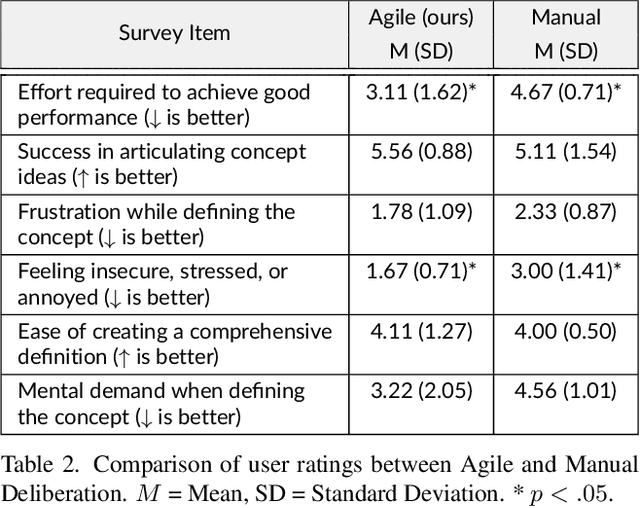
Abstract:From content moderation to content curation, applications requiring vision classifiers for visual concepts are rapidly expanding. Existing human-in-the-loop approaches typically assume users begin with a clear, stable concept understanding to be able to provide high-quality supervision. In reality, users often start with a vague idea and must iteratively refine it through "concept deliberation", a practice we uncovered through structured interviews with content moderation experts. We operationalize the common strategies in deliberation used by real content moderators into a human-in-the-loop framework called "Agile Deliberation" that explicitly supports evolving and subjective concepts. The system supports users in defining the concept for themselves by exposing them to borderline cases. The system does this with two deliberation stages: (1) concept scoping, which decomposes the initial concept into a structured hierarchy of sub-concepts, and (2) concept iteration, which surfaces semantically borderline examples for user reflection and feedback to iteratively align an image classifier with the user's evolving intent. Since concept deliberation is inherently subjective and interactive, we painstakingly evaluate the framework through 18 user sessions, each 1.5h long, rather than standard benchmarking datasets. We find that Agile Deliberation achieves 7.5% higher F1 scores than automated decomposition baselines and more than 3% higher than manual deliberation, while participants reported clearer conceptual understanding and lower cognitive effort.
OmniView: An All-Seeing Diffusion Model for 3D and 4D View Synthesis
Dec 11, 2025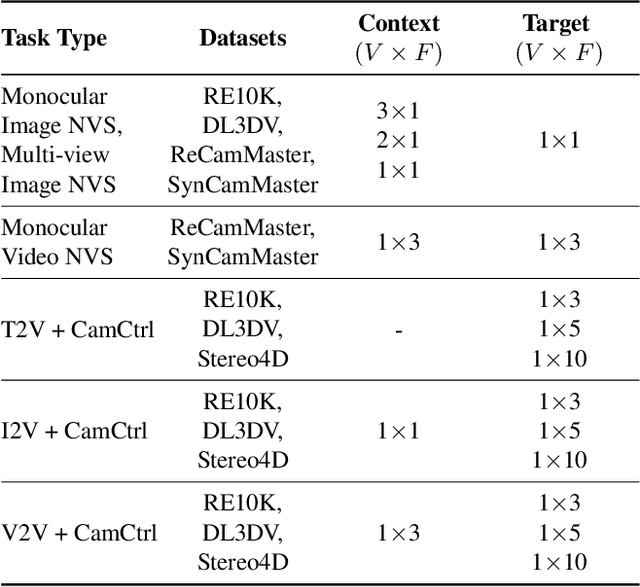
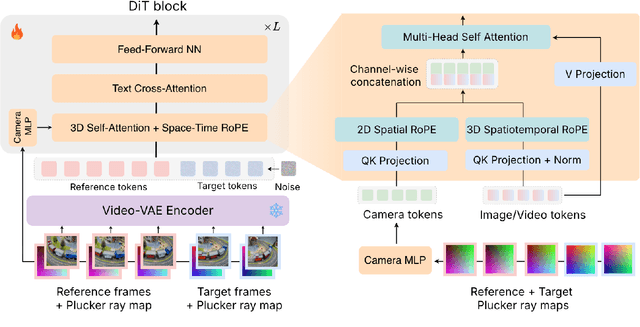
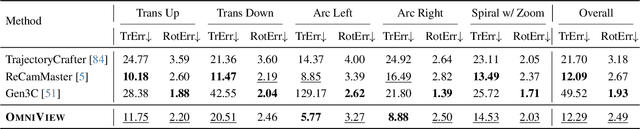

Abstract:Prior approaches injecting camera control into diffusion models have focused on specific subsets of 4D consistency tasks: novel view synthesis, text-to-video with camera control, image-to-video, amongst others. Therefore, these fragmented approaches are trained on disjoint slices of available 3D/4D data. We introduce OmniView, a unified framework that generalizes across a wide range of 4D consistency tasks. Our method separately represents space, time, and view conditions, enabling flexible combinations of these inputs. For example, OmniView can synthesize novel views from static, dynamic, and multiview inputs, extrapolate trajectories forward and backward in time, and create videos from text or image prompts with full camera control. OmniView is competitive with task-specific models across diverse benchmarks and metrics, improving image quality scores among camera-conditioned diffusion models by up to 33\% in multiview NVS LLFF dataset, 60\% in dynamic NVS Neural 3D Video benchmark, 20\% in static camera control on RE-10K, and reducing camera trajectory errors by 4x in text-conditioned video generation. With strong generalizability in one model, OmniView demonstrates the feasibility of a generalist 4D video model. Project page is available at https://snap-research.github.io/OmniView/
Mull-Tokens: Modality-Agnostic Latent Thinking
Dec 11, 2025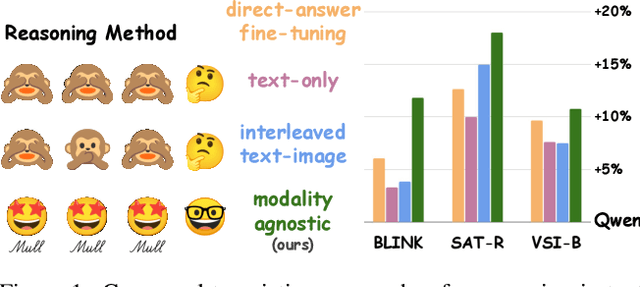
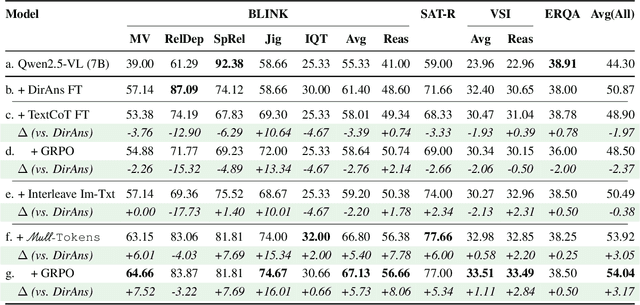
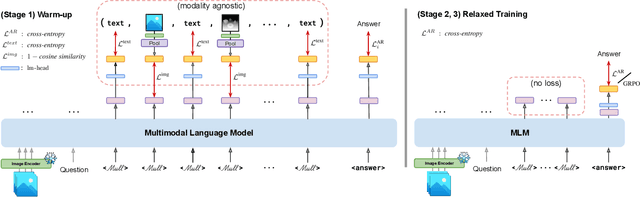
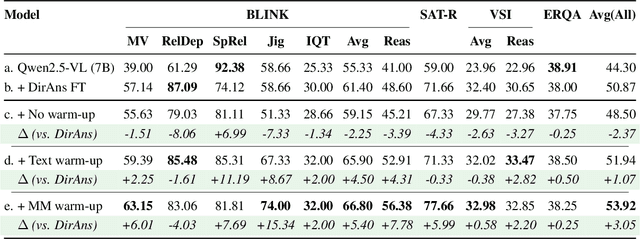
Abstract:Reasoning goes beyond language; the real world requires reasoning about space, time, affordances, and much more that words alone cannot convey. Existing multimodal models exploring the potential of reasoning with images are brittle and do not scale. They rely on calling specialist tools, costly generation of images, or handcrafted reasoning data to switch between text and image thoughts. Instead, we offer a simpler alternative -- Mull-Tokens -- modality-agnostic latent tokens pre-trained to hold intermediate information in either image or text modalities to let the model think free-form towards the correct answer. We investigate best practices to train Mull-Tokens inspired by latent reasoning frameworks. We first train Mull-Tokens using supervision from interleaved text-image traces, and then fine-tune without any supervision by only using the final answers. Across four challenging spatial reasoning benchmarks involving tasks such as solving puzzles and taking different perspectives, we demonstrate that Mull-Tokens improve upon several baselines utilizing text-only reasoning or interleaved image-text reasoning, achieving a +3% average improvement and up to +16% on a puzzle solving reasoning-heavy split compared to our strongest baseline. Adding to conversations around challenges in grounding textual and visual reasoning, Mull-Tokens offers a simple solution to abstractly think in multiple modalities.
OlmoEarth: Stable Latent Image Modeling for Multimodal Earth Observation
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:Earth observation data presents a unique challenge: it is spatial like images, sequential like video or text, and highly multimodal. We present OlmoEarth: a multimodal, spatio-temporal foundation model that employs a novel self-supervised learning formulation, masking strategy, and loss all designed for the Earth observation domain. OlmoEarth achieves state-of-the-art performance compared to 12 other foundation models across a variety of research benchmarks and real-world tasks from external partners. When evaluating embeddings OlmoEarth achieves the best performance on 15 out of 24 tasks, and with full fine-tuning it is the best on 19 of 29 tasks. We deploy OlmoEarth as the backbone of an end-to-end platform for data collection, labeling, training, and inference of Earth observation models. The OlmoEarth Platform puts frontier foundation models and powerful data management tools into the hands of non-profits and NGOs working to solve the world's biggest problems. OlmoEarth source code, training data, and pre-trained weights are available at $\href{https://github.com/allenai/olmoearth_pretrain}{\text{https://github.com/allenai/olmoearth_pretrain}}$.
SIMS-V: Simulated Instruction-Tuning for Spatial Video Understanding
Nov 06, 2025Abstract:Despite impressive high-level video comprehension, multimodal language models struggle with spatial reasoning across time and space. While current spatial training approaches rely on real-world video data, obtaining diverse footage with precise spatial annotations remains a bottleneck. To alleviate this bottleneck, we present SIMS-V -- a systematic data-generation framework that leverages the privileged information of 3D simulators to create spatially-rich video training data for multimodal language models. Using this framework, we investigate which properties of simulated data drive effective real-world transfer through systematic ablations of question types, mixes, and scales. We identify a minimal set of three question categories (metric measurement, perspective-dependent reasoning, and temporal tracking) that prove most effective for developing transferable spatial intelligence, outperforming comprehensive coverage despite using fewer question types. These insights enable highly efficient training: our 7B-parameter video LLM fine-tuned on just 25K simulated examples outperforms the larger 72B baseline and achieves competitive performance with proprietary models on rigorous real-world spatial reasoning benchmarks. Our approach demonstrates robust generalization, maintaining performance on general video understanding while showing substantial improvements on embodied and real-world spatial tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge