Kangrui Wang
SkillCraft: Can LLM Agents Learn to Use Tools Skillfully?
Feb 28, 2026Abstract:Real-world tool-using agents operate over long-horizon workflows with recurring structure and diverse demands, where effective behavior requires not only invoking atomic tools but also abstracting, and reusing higher-level tool compositions. However, existing benchmarks mainly measure instance-level success under static tool sets, offering limited insight into agents' ability to acquire such reusable skills. We address this gap by introducing SkillCraft, a benchmark explicitly stress-test agent ability to form and reuse higher-level tool compositions, where we call Skills. SkillCraft features realistic, highly compositional tool-use scenarios with difficulty scaled along both quantitative and structural dimensions, designed to elicit skill abstraction and cross-task reuse. We further propose a lightweight evaluation protocol that enables agents to auto-compose atomic tools into executable Skills, cache and reuse them inside and across tasks, thereby improving efficiency while accumulating a persistent library of reusable skills. Evaluating state-of-the-art agents on SkillCraft, we observe substantial efficiency gains, with token usage reduced by up to 80% by skill saving and reuse. Moreover, success rate strongly correlates with tool composition ability at test time, underscoring compositional skill acquisition as a core capability.
ERA: Transforming VLMs into Embodied Agents via Embodied Prior Learning and Online Reinforcement Learning
Oct 14, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in embodied AI highlight the potential of vision language models (VLMs) as agents capable of perception, reasoning, and interaction in complex environments. However, top-performing systems rely on large-scale models that are costly to deploy, while smaller VLMs lack the necessary knowledge and skills to succeed. To bridge this gap, we present \textit{Embodied Reasoning Agent (ERA)}, a two-stage framework that integrates prior knowledge learning and online reinforcement learning (RL). The first stage, \textit{Embodied Prior Learning}, distills foundational knowledge from three types of data: (1) Trajectory-Augmented Priors, which enrich existing trajectory data with structured reasoning generated by stronger models; (2) Environment-Anchored Priors, which provide in-environment knowledge and grounding supervision; and (3) External Knowledge Priors, which transfer general knowledge from out-of-environment datasets. In the second stage, we develop an online RL pipeline that builds on these priors to further enhance agent performance. To overcome the inherent challenges in agent RL, including long horizons, sparse rewards, and training instability, we introduce three key designs: self-summarization for context management, dense reward shaping, and turn-level policy optimization. Extensive experiments on both high-level planning (EB-ALFRED) and low-level control (EB-Manipulation) tasks demonstrate that ERA-3B surpasses both prompting-based large models and previous training-based baselines. Specifically, it achieves overall improvements of 8.4\% on EB-ALFRED and 19.4\% on EB-Manipulation over GPT-4o, and exhibits strong generalization to unseen tasks. Overall, ERA offers a practical path toward scalable embodied intelligence, providing methodological insights for future embodied AI systems.
Spatial Mental Modeling from Limited Views
Jun 26, 2025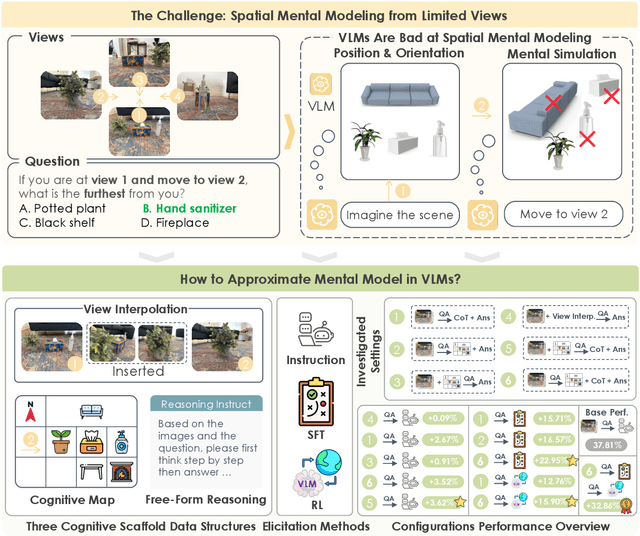
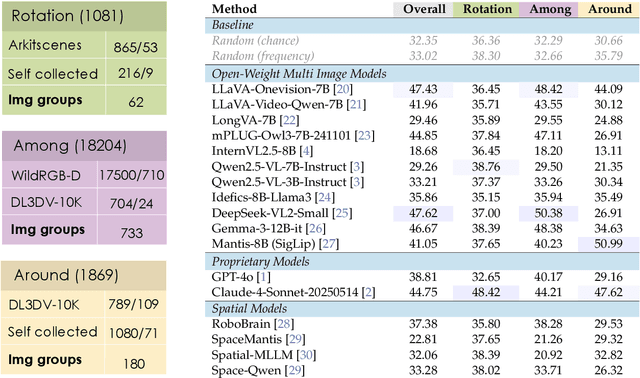
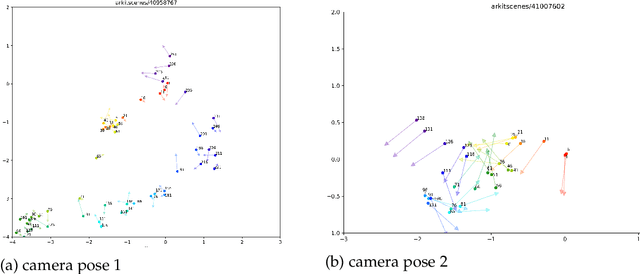
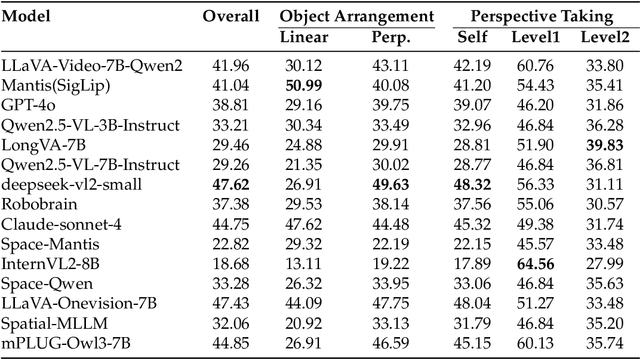
Abstract:Can Vision Language Models (VLMs) imagine the full scene from just a few views, like humans do? Humans form spatial mental models, internal representations of unseen space, to reason about layout, perspective, and motion. Our new MindCube benchmark with 21,154 questions across 3,268 images exposes this critical gap, where existing VLMs exhibit near-random performance. Using MindCube, we systematically evaluate how well VLMs build robust spatial mental models through representing positions (cognitive mapping), orientations (perspective-taking), and dynamics (mental simulation for "what-if" movements). We then explore three approaches to help VLMs approximate spatial mental models, including unseen intermediate views, natural language reasoning chains, and cognitive maps. The significant improvement comes from a synergistic approach, "map-then-reason", that jointly trains the model to first generate a cognitive map and then reason upon it. By training models to reason over these internal maps, we boosted accuracy from 37.8% to 60.8% (+23.0%). Adding reinforcement learning pushed performance even further to 70.7% (+32.9%). Our key insight is that such scaffolding of spatial mental models, actively constructing and utilizing internal structured spatial representations with flexible reasoning processes, significantly improves understanding of unobservable space.
RAGEN: Understanding Self-Evolution in LLM Agents via Multi-Turn Reinforcement Learning
Apr 24, 2025Abstract:Training large language models (LLMs) as interactive agents presents unique challenges including long-horizon decision making and interacting with stochastic environment feedback. While reinforcement learning (RL) has enabled progress in static tasks, multi-turn agent RL training remains underexplored. We propose StarPO (State-Thinking-Actions-Reward Policy Optimization), a general framework for trajectory-level agent RL, and introduce RAGEN, a modular system for training and evaluating LLM agents. Our study on three stylized environments reveals three core findings. First, our agent RL training shows a recurring mode of Echo Trap where reward variance cliffs and gradient spikes; we address this with StarPO-S, a stabilized variant with trajectory filtering, critic incorporation, and decoupled clipping. Second, we find the shaping of RL rollouts would benefit from diverse initial states, medium interaction granularity and more frequent sampling. Third, we show that without fine-grained, reasoning-aware reward signals, agent reasoning hardly emerge through multi-turn RL and they may show shallow strategies or hallucinated thoughts. Code and environments are available at https://github.com/RAGEN-AI/RAGEN.
EmbodiedBench: Comprehensive Benchmarking Multi-modal Large Language Models for Vision-Driven Embodied Agents
Feb 13, 2025



Abstract:Leveraging Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs) to create embodied agents offers a promising avenue for tackling real-world tasks. While language-centric embodied agents have garnered substantial attention, MLLM-based embodied agents remain underexplored due to the lack of comprehensive evaluation frameworks. To bridge this gap, we introduce EmbodiedBench, an extensive benchmark designed to evaluate vision-driven embodied agents. EmbodiedBench features: (1) a diverse set of 1,128 testing tasks across four environments, ranging from high-level semantic tasks (e.g., household) to low-level tasks involving atomic actions (e.g., navigation and manipulation); and (2) six meticulously curated subsets evaluating essential agent capabilities like commonsense reasoning, complex instruction understanding, spatial awareness, visual perception, and long-term planning. Through extensive experiments, we evaluated 13 leading proprietary and open-source MLLMs within EmbodiedBench. Our findings reveal that: MLLMs excel at high-level tasks but struggle with low-level manipulation, with the best model, GPT-4o, scoring only 28.9% on average. EmbodiedBench provides a multifaceted standardized evaluation platform that not only highlights existing challenges but also offers valuable insights to advance MLLM-based embodied agents. Our code is available at https://embodiedbench.github.io.
Embodied Agent Interface: Benchmarking LLMs for Embodied Decision Making
Oct 09, 2024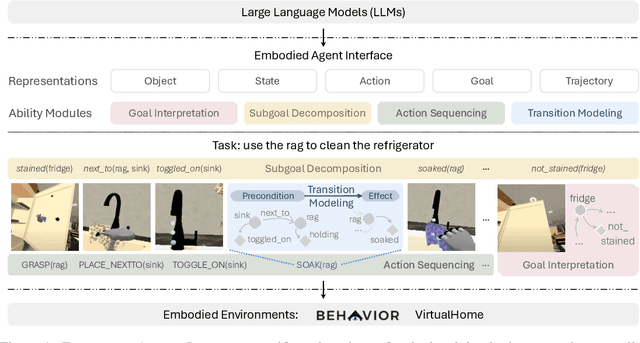
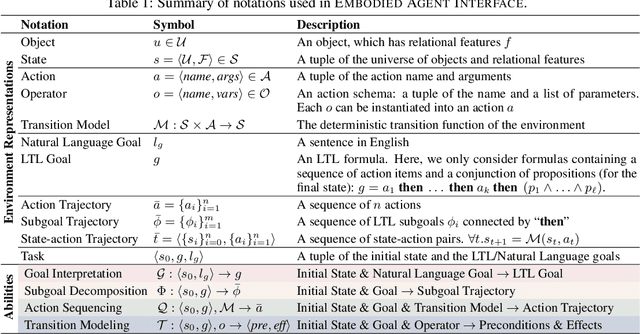
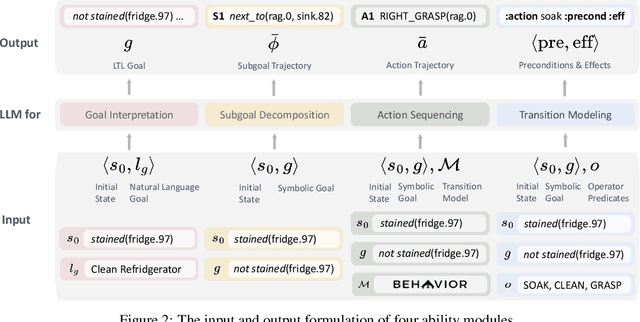
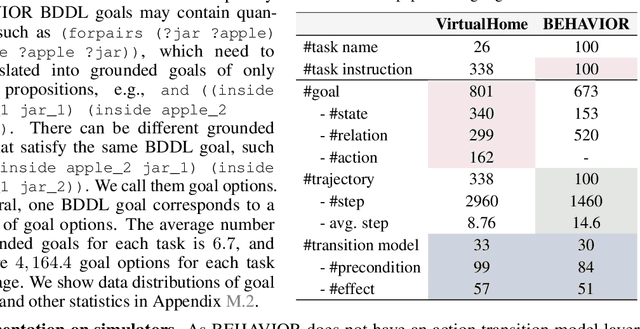
Abstract:We aim to evaluate Large Language Models (LLMs) for embodied decision making. While a significant body of work has been leveraging LLMs for decision making in embodied environments, we still lack a systematic understanding of their performance because they are usually applied in different domains, for different purposes, and built based on different inputs and outputs. Furthermore, existing evaluations tend to rely solely on a final success rate, making it difficult to pinpoint what ability is missing in LLMs and where the problem lies, which in turn blocks embodied agents from leveraging LLMs effectively and selectively. To address these limitations, we propose a generalized interface (Embodied Agent Interface) that supports the formalization of various types of tasks and input-output specifications of LLM-based modules. Specifically, it allows us to unify 1) a broad set of embodied decision-making tasks involving both state and temporally extended goals, 2) four commonly-used LLM-based modules for decision making: goal interpretation, subgoal decomposition, action sequencing, and transition modeling, and 3) a collection of fine-grained metrics which break down evaluation into various types of errors, such as hallucination errors, affordance errors, various types of planning errors, etc. Overall, our benchmark offers a comprehensive assessment of LLMs' performance for different subtasks, pinpointing the strengths and weaknesses in LLM-powered embodied AI systems, and providing insights for effective and selective use of LLMs in embodied decision making.
MANGO: A Benchmark for Evaluating Mapping and Navigation Abilities of Large Language Models
Mar 29, 2024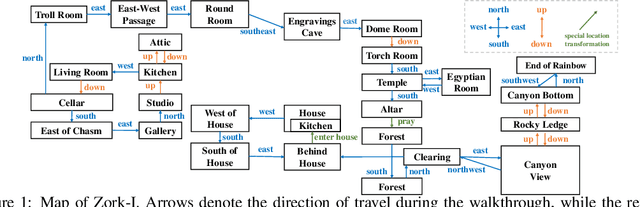
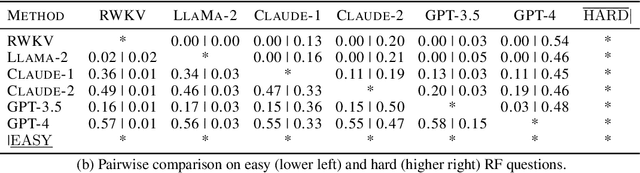
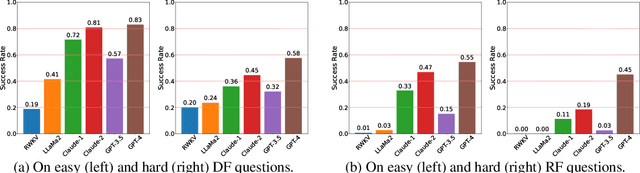
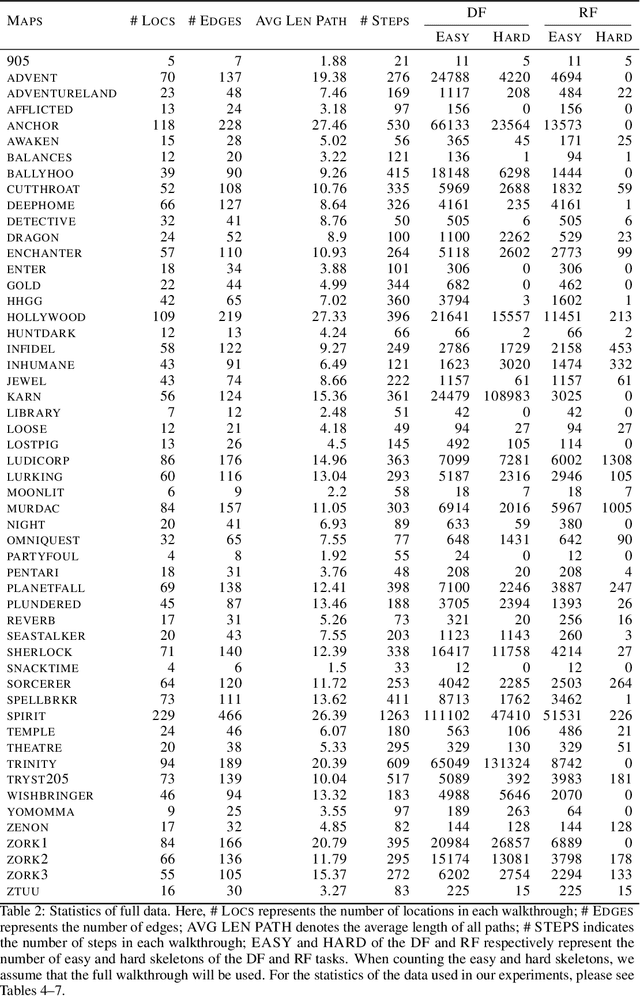
Abstract:Large language models such as ChatGPT and GPT-4 have recently achieved astonishing performance on a variety of natural language processing tasks. In this paper, we propose MANGO, a benchmark to evaluate their capabilities to perform text-based mapping and navigation. Our benchmark includes 53 mazes taken from a suite of textgames: each maze is paired with a walkthrough that visits every location but does not cover all possible paths. The task is question-answering: for each maze, a large language model reads the walkthrough and answers hundreds of mapping and navigation questions such as "How should you go to Attic from West of House?" and "Where are we if we go north and east from Cellar?". Although these questions are easy to humans, it turns out that even GPT-4, the best-to-date language model, performs poorly at answering them. Further, our experiments suggest that a strong mapping and navigation ability would benefit large language models in performing relevant downstream tasks, such as playing textgames. Our MANGO benchmark will facilitate future research on methods that improve the mapping and navigation capabilities of language models. We host our leaderboard, data, code, and evaluation program at https://mango.ttic.edu and https://github.com/oaklight/mango/.
Language Models Can Improve Event Prediction by Few-Shot Abductive Reasoning
May 26, 2023Abstract:Large language models have shown astonishing performance on a wide range of reasoning tasks. In this paper, we investigate whether they could reason about real-world events and help improve the prediction accuracy of event sequence models. We design a modeling and prediction framework where a large language model performs abductive reasoning to assist an event sequence model: the event model proposes predictions on future events given the past; instructed by a few expert-annotated demonstrations, the language model learns to suggest possible causes for each proposal; a search module finds out the previous events that match the causes; a scoring function learns to examine whether the retrieved events could actually cause the proposal. Through extensive experiments on two challenging real-world datasets (Amazon Review and GDELT), we demonstrate that our framework -- thanks to the reasoning ability of language models -- could significantly outperform the state-of-the-art event sequence models.
Explicit Planning Helps Language Models in Logical Reasoning
Mar 28, 2023

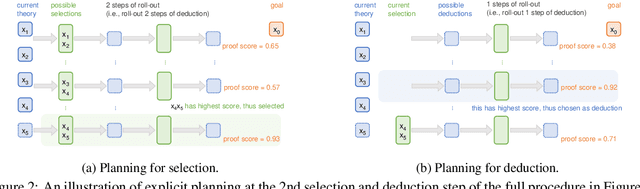

Abstract:Language models have been shown to perform remarkably well on a wide range of natural language processing tasks. In this paper, we propose a novel system that uses language models to perform multi-step logical reasoning. Our system incorporates explicit planning into its inference procedure, thus able to make more informed reasoning decisions at each step by looking ahead into their future effects. In our experiments, our full system significantly outperforms other competing systems. On a multiple-choice question answering task, our system performs competitively compared to GPT-3-davinci despite having only around 1.5B parameters. We conduct several ablation studies to demonstrate that explicit planning plays a crucial role in the system's performance.
Trap of Feature Diversity in the Learning of MLPs
Dec 02, 2021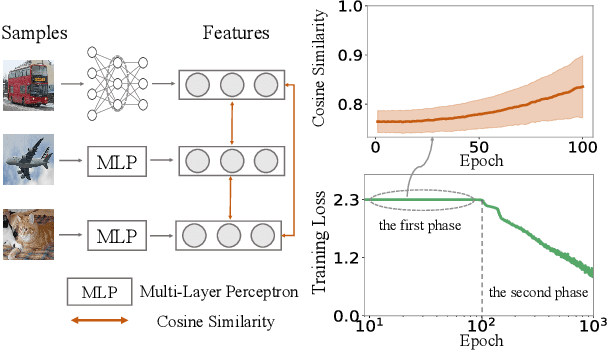
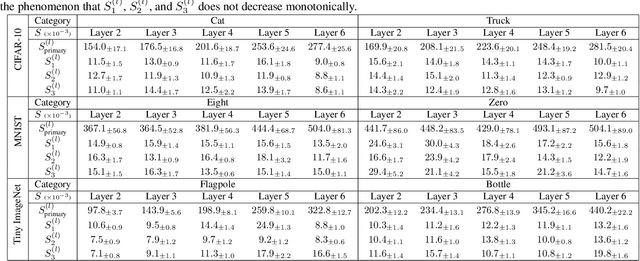
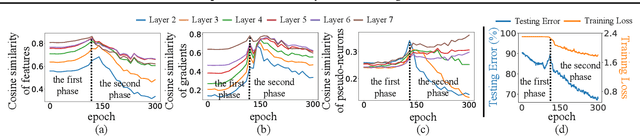
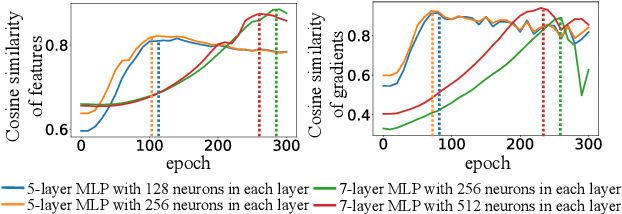
Abstract:In this paper, we discover a two-phase phenomenon in the learning of multi-layer perceptrons (MLPs). I.e., in the first phase, the training loss does not decrease significantly, but the similarity of features between different samples keeps increasing, which hurts the feature diversity. We explain such a two-phase phenomenon in terms of the learning dynamics of the MLP. Furthermore, we propose two normalization operations to eliminate the two-phase phenomenon, which avoids the decrease of the feature diversity and speeds up the training process.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge