Hanyang Chen
Visual Backdoor Attacks on MLLM Embodied Decision Making via Contrastive Trigger Learning
Oct 31, 2025Abstract:Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have advanced embodied agents by enabling direct perception, reasoning, and planning task-oriented actions from visual inputs. However, such vision driven embodied agents open a new attack surface: visual backdoor attacks, where the agent behaves normally until a visual trigger appears in the scene, then persistently executes an attacker-specified multi-step policy. We introduce BEAT, the first framework to inject such visual backdoors into MLLM-based embodied agents using objects in the environments as triggers. Unlike textual triggers, object triggers exhibit wide variation across viewpoints and lighting, making them difficult to implant reliably. BEAT addresses this challenge by (1) constructing a training set that spans diverse scenes, tasks, and trigger placements to expose agents to trigger variability, and (2) introducing a two-stage training scheme that first applies supervised fine-tuning (SFT) and then our novel Contrastive Trigger Learning (CTL). CTL formulates trigger discrimination as preference learning between trigger-present and trigger-free inputs, explicitly sharpening the decision boundaries to ensure precise backdoor activation. Across various embodied agent benchmarks and MLLMs, BEAT achieves attack success rates up to 80%, while maintaining strong benign task performance, and generalizes reliably to out-of-distribution trigger placements. Notably, compared to naive SFT, CTL boosts backdoor activation accuracy up to 39% under limited backdoor data. These findings expose a critical yet unexplored security risk in MLLM-based embodied agents, underscoring the need for robust defenses before real-world deployment.
ERA: Transforming VLMs into Embodied Agents via Embodied Prior Learning and Online Reinforcement Learning
Oct 14, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in embodied AI highlight the potential of vision language models (VLMs) as agents capable of perception, reasoning, and interaction in complex environments. However, top-performing systems rely on large-scale models that are costly to deploy, while smaller VLMs lack the necessary knowledge and skills to succeed. To bridge this gap, we present \textit{Embodied Reasoning Agent (ERA)}, a two-stage framework that integrates prior knowledge learning and online reinforcement learning (RL). The first stage, \textit{Embodied Prior Learning}, distills foundational knowledge from three types of data: (1) Trajectory-Augmented Priors, which enrich existing trajectory data with structured reasoning generated by stronger models; (2) Environment-Anchored Priors, which provide in-environment knowledge and grounding supervision; and (3) External Knowledge Priors, which transfer general knowledge from out-of-environment datasets. In the second stage, we develop an online RL pipeline that builds on these priors to further enhance agent performance. To overcome the inherent challenges in agent RL, including long horizons, sparse rewards, and training instability, we introduce three key designs: self-summarization for context management, dense reward shaping, and turn-level policy optimization. Extensive experiments on both high-level planning (EB-ALFRED) and low-level control (EB-Manipulation) tasks demonstrate that ERA-3B surpasses both prompting-based large models and previous training-based baselines. Specifically, it achieves overall improvements of 8.4\% on EB-ALFRED and 19.4\% on EB-Manipulation over GPT-4o, and exhibits strong generalization to unseen tasks. Overall, ERA offers a practical path toward scalable embodied intelligence, providing methodological insights for future embodied AI systems.
EmbodiedBench: Comprehensive Benchmarking Multi-modal Large Language Models for Vision-Driven Embodied Agents
Feb 13, 2025



Abstract:Leveraging Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs) to create embodied agents offers a promising avenue for tackling real-world tasks. While language-centric embodied agents have garnered substantial attention, MLLM-based embodied agents remain underexplored due to the lack of comprehensive evaluation frameworks. To bridge this gap, we introduce EmbodiedBench, an extensive benchmark designed to evaluate vision-driven embodied agents. EmbodiedBench features: (1) a diverse set of 1,128 testing tasks across four environments, ranging from high-level semantic tasks (e.g., household) to low-level tasks involving atomic actions (e.g., navigation and manipulation); and (2) six meticulously curated subsets evaluating essential agent capabilities like commonsense reasoning, complex instruction understanding, spatial awareness, visual perception, and long-term planning. Through extensive experiments, we evaluated 13 leading proprietary and open-source MLLMs within EmbodiedBench. Our findings reveal that: MLLMs excel at high-level tasks but struggle with low-level manipulation, with the best model, GPT-4o, scoring only 28.9% on average. EmbodiedBench provides a multifaceted standardized evaluation platform that not only highlights existing challenges but also offers valuable insights to advance MLLM-based embodied agents. Our code is available at https://embodiedbench.github.io.
DiffLight: A Partial Rewards Conditioned Diffusion Model for Traffic Signal Control with Missing Data
Oct 31, 2024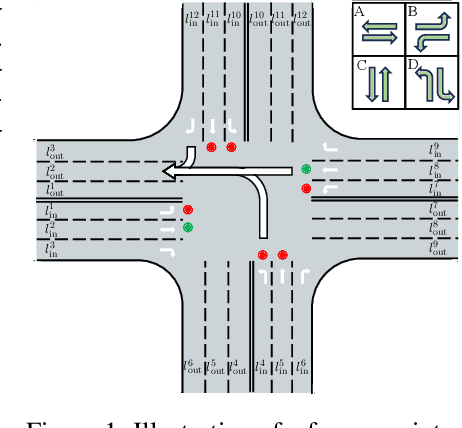
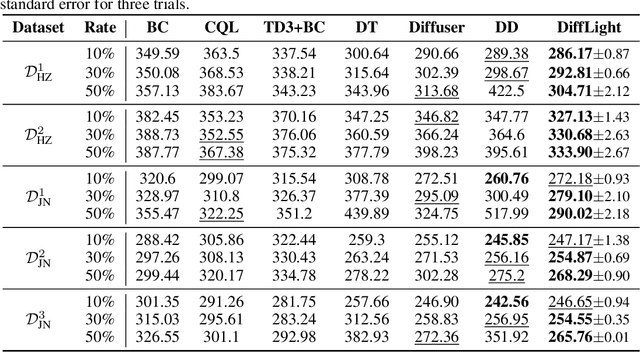
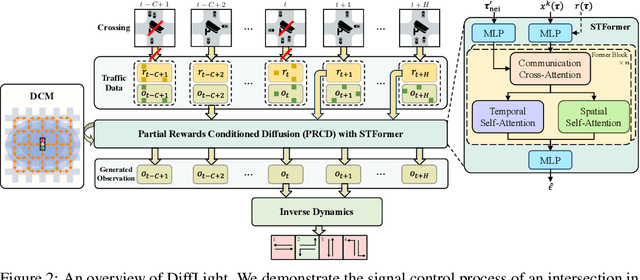
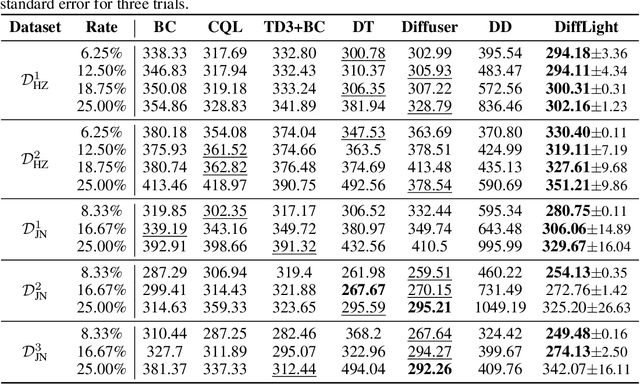
Abstract:The application of reinforcement learning in traffic signal control (TSC) has been extensively researched and yielded notable achievements. However, most existing works for TSC assume that traffic data from all surrounding intersections is fully and continuously available through sensors. In real-world applications, this assumption often fails due to sensor malfunctions or data loss, making TSC with missing data a critical challenge. To meet the needs of practical applications, we introduce DiffLight, a novel conditional diffusion model for TSC under data-missing scenarios in the offline setting. Specifically, we integrate two essential sub-tasks, i.e., traffic data imputation and decision-making, by leveraging a Partial Rewards Conditioned Diffusion (PRCD) model to prevent missing rewards from interfering with the learning process. Meanwhile, to effectively capture the spatial-temporal dependencies among intersections, we design a Spatial-Temporal transFormer (STFormer) architecture. In addition, we propose a Diffusion Communication Mechanism (DCM) to promote better communication and control performance under data-missing scenarios. Extensive experiments on five datasets with various data-missing scenarios demonstrate that DiffLight is an effective controller to address TSC with missing data. The code of DiffLight is released at https://github.com/lokol5579/DiffLight-release.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge