Ke Yang
Equal contributions, University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign
Tail-Aware Post-Training Quantization for 3D Geometry Models
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:The burgeoning complexity and scale of 3D geometry models pose significant challenges for deployment on resource-constrained platforms. While Post-Training Quantization (PTQ) enables efficient inference without retraining, conventional methods, primarily optimized for 2D Vision Transformers, fail to transfer effectively to 3D models due to intricate feature distributions and prohibitive calibration overhead. To address these challenges, we propose TAPTQ, a Tail-Aware Post-Training Quantization pipeline specifically engineered for 3D geometric learning. Our contribution is threefold: (1) To overcome the data-scale bottleneck in 3D datasets, we develop a progressive coarse-to-fine calibration construction strategy that constructs a highly compact subset to achieve both statistical purity and geometric representativeness. (2) We reformulate the quantization interval search as an optimization problem and introduce a ternary-search-based solver, reducing the computational complexity from $\mathcal{O}(N)$ to $\mathcal{O}(\log N)$ for accelerated deployment. (3) To mitigate quantization error accumulation, we propose TRE-Guided Module-wise Compensation, which utilizes a Tail Relative Error (TRE) metric to adaptively identify and rectify distortions in modules sensitive to long-tailed activation outliers. Extensive experiments on the VGGT and Pi3 benchmarks demonstrate that TAPTQ consistently outperforms state-of-the-art PTQ methods in accuracy while significantly reducing calibration time. The code will be released soon.
Deep GraphRAG: A Balanced Approach to Hierarchical Retrieval and Adaptive Integration
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:Graph-based Retrieval-Augmented Generation (GraphRAG) frameworks face a trade-off between the comprehensiveness of global search and the efficiency of local search. Existing methods are often challenged by navigating large-scale hierarchical graphs, optimizing retrieval paths, and balancing exploration-exploitation dynamics, frequently lacking robust multi-stage re-ranking. To overcome these deficits, we propose Deep GraphRAG, a framework designed for a balanced approach to hierarchical retrieval and adaptive integration. It introduces a hierarchical global-to-local retrieval strategy that integrates macroscopic inter-community and microscopic intra-community contextual relations. This strategy employs a three-stage process: (1) inter-community filtering, which prunes the search space using local context; (2) community-level refinement, which prioritizes relevant subgraphs via entity-interaction analysis; and (3) entity-level fine-grained search within target communities. A beam search-optimized dynamic re-ranking module guides this process, continuously filtering candidates to balance efficiency and global comprehensiveness. Deep GraphRAG also features a Knowledge Integration Module leveraging a compact LLM, trained with Dynamic Weighting Reward GRPO (DW-GRPO). This novel reinforcement learning approach dynamically adjusts reward weights to balance three key objectives: relevance, faithfulness, and conciseness. This training enables compact models (1.5B) to approach the performance of large models (70B) in the integration task. Evaluations on Natural Questions and HotpotQA demonstrate that Deep GraphRAG significantly outperforms baseline graph retrieval methods in both accuracy and efficiency.
ERA: Transforming VLMs into Embodied Agents via Embodied Prior Learning and Online Reinforcement Learning
Oct 14, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in embodied AI highlight the potential of vision language models (VLMs) as agents capable of perception, reasoning, and interaction in complex environments. However, top-performing systems rely on large-scale models that are costly to deploy, while smaller VLMs lack the necessary knowledge and skills to succeed. To bridge this gap, we present \textit{Embodied Reasoning Agent (ERA)}, a two-stage framework that integrates prior knowledge learning and online reinforcement learning (RL). The first stage, \textit{Embodied Prior Learning}, distills foundational knowledge from three types of data: (1) Trajectory-Augmented Priors, which enrich existing trajectory data with structured reasoning generated by stronger models; (2) Environment-Anchored Priors, which provide in-environment knowledge and grounding supervision; and (3) External Knowledge Priors, which transfer general knowledge from out-of-environment datasets. In the second stage, we develop an online RL pipeline that builds on these priors to further enhance agent performance. To overcome the inherent challenges in agent RL, including long horizons, sparse rewards, and training instability, we introduce three key designs: self-summarization for context management, dense reward shaping, and turn-level policy optimization. Extensive experiments on both high-level planning (EB-ALFRED) and low-level control (EB-Manipulation) tasks demonstrate that ERA-3B surpasses both prompting-based large models and previous training-based baselines. Specifically, it achieves overall improvements of 8.4\% on EB-ALFRED and 19.4\% on EB-Manipulation over GPT-4o, and exhibits strong generalization to unseen tasks. Overall, ERA offers a practical path toward scalable embodied intelligence, providing methodological insights for future embodied AI systems.
RLinf: Flexible and Efficient Large-scale Reinforcement Learning via Macro-to-Micro Flow Transformation
Sep 19, 2025



Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) has demonstrated immense potential in advancing artificial general intelligence, agentic intelligence, and embodied intelligence. However, the inherent heterogeneity and dynamicity of RL workflows often lead to low hardware utilization and slow training on existing systems. In this paper, we present RLinf, a high-performance RL training system based on our key observation that the major roadblock to efficient RL training lies in system flexibility. To maximize flexibility and efficiency, RLinf is built atop a novel RL system design paradigm called macro-to-micro flow transformation (M2Flow), which automatically breaks down high-level, easy-to-compose RL workflows at both the temporal and spatial dimensions, and recomposes them into optimized execution flows. Supported by RLinf worker's adaptive communication capability, we devise context switching and elastic pipelining to realize M2Flow transformation, and a profiling-guided scheduling policy to generate optimal execution plans. Extensive evaluations on both reasoning RL and embodied RL tasks demonstrate that RLinf consistently outperforms state-of-the-art systems, achieving 1.1x-2.13x speedup in end-to-end training throughput.
MiniMax-M1: Scaling Test-Time Compute Efficiently with Lightning Attention
Jun 16, 2025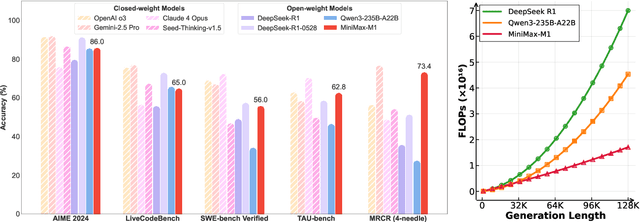
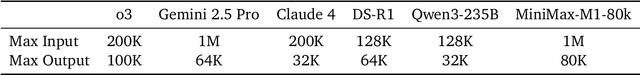
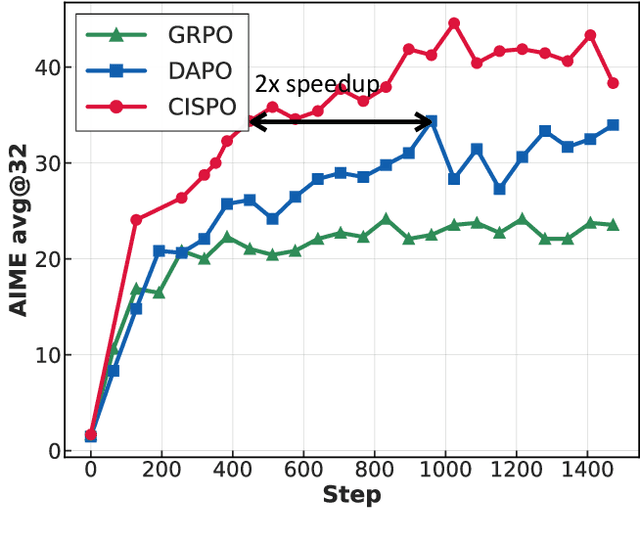
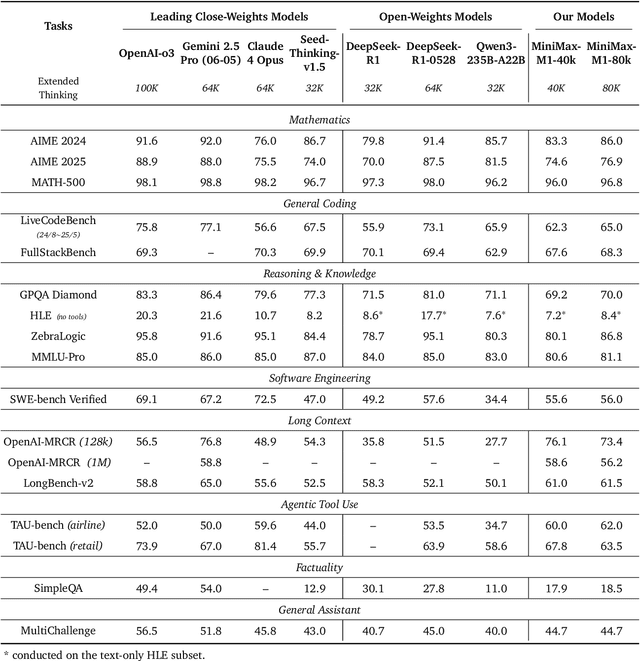
Abstract:We introduce MiniMax-M1, the world's first open-weight, large-scale hybrid-attention reasoning model. MiniMax-M1 is powered by a hybrid Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture combined with a lightning attention mechanism. The model is developed based on our previous MiniMax-Text-01 model, which contains a total of 456 billion parameters with 45.9 billion parameters activated per token. The M1 model natively supports a context length of 1 million tokens, 8x the context size of DeepSeek R1. Furthermore, the lightning attention mechanism in MiniMax-M1 enables efficient scaling of test-time compute. These properties make M1 particularly suitable for complex tasks that require processing long inputs and thinking extensively. MiniMax-M1 is trained using large-scale reinforcement learning (RL) on diverse problems including sandbox-based, real-world software engineering environments. In addition to M1's inherent efficiency advantage for RL training, we propose CISPO, a novel RL algorithm to further enhance RL efficiency. CISPO clips importance sampling weights rather than token updates, outperforming other competitive RL variants. Combining hybrid-attention and CISPO enables MiniMax-M1's full RL training on 512 H800 GPUs to complete in only three weeks, with a rental cost of just $534,700. We release two versions of MiniMax-M1 models with 40K and 80K thinking budgets respectively, where the 40K model represents an intermediate phase of the 80K training. Experiments on standard benchmarks show that our models are comparable or superior to strong open-weight models such as the original DeepSeek-R1 and Qwen3-235B, with particular strengths in complex software engineering, tool utilization, and long-context tasks. We publicly release MiniMax-M1 at https://github.com/MiniMax-AI/MiniMax-M1.
Ten Principles of AI Agent Economics
May 26, 2025Abstract:The rapid rise of AI-based autonomous agents is transforming human society and economic systems, as these entities increasingly exhibit human-like or superhuman intelligence. From excelling at complex games like Go to tackling diverse general-purpose tasks with large language and multimodal models, AI agents are evolving from specialized tools into dynamic participants in social and economic ecosystems. Their autonomy and decision-making capabilities are poised to impact industries, professions, and human lives profoundly, raising critical questions about their integration into economic activities, potential ethical concerns, and the balance between their utility and safety. To address these challenges, this paper presents ten principles of AI agent economics, offering a framework to understand how AI agents make decisions, influence social interactions, and participate in the broader economy. Drawing on economics, decision theory, and ethics, we explore fundamental questions, such as whether AI agents might evolve from tools into independent entities, their impact on labor markets, and the ethical safeguards needed to align them with human values. These principles build on existing economic theories while accounting for the unique traits of AI agents, providing a roadmap for their responsible integration into human systems. Beyond theoretical insights, this paper highlights the urgency of future research into AI trustworthiness, ethical guidelines, and regulatory oversight. As we enter a transformative era, this work serves as both a guide and a call to action, ensuring AI agents contribute positively to human progress while addressing risks tied to their unprecedented capabilities.
DexCtrl: Towards Sim-to-Real Dexterity with Adaptive Controller Learning
May 02, 2025


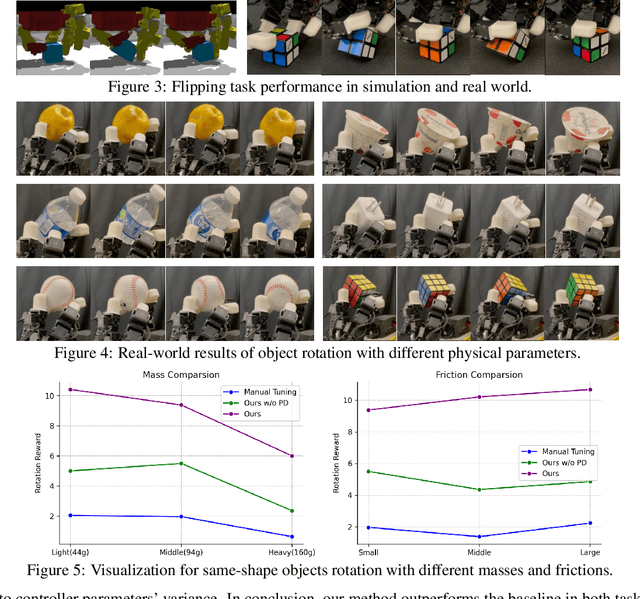
Abstract:Dexterous manipulation has seen remarkable progress in recent years, with policies capable of executing many complex and contact-rich tasks in simulation. However, transferring these policies from simulation to real world remains a significant challenge. One important issue is the mismatch in low-level controller dynamics, where identical trajectories can lead to vastly different contact forces and behaviors when control parameters vary. Existing approaches often rely on manual tuning or controller randomization, which can be labor-intensive, task-specific, and introduce significant training difficulty. In this work, we propose a framework that jointly learns actions and controller parameters based on the historical information of both trajectory and controller. This adaptive controller adjustment mechanism allows the policy to automatically tune control parameters during execution, thereby mitigating the sim-to-real gap without extensive manual tuning or excessive randomization. Moreover, by explicitly providing controller parameters as part of the observation, our approach facilitates better reasoning over force interactions and improves robustness in real-world scenarios. Experimental results demonstrate that our method achieves improved transfer performance across a variety of dexterous tasks involving variable force conditions.
TinyHelen's First Curriculum: Training and Evaluating Tiny Language Models in a Simpler Language Environment
Dec 31, 2024



Abstract:Training language models (LMs) and their application agents is increasingly costly due to large datasets and models, making test failures difficult to bear. Simplified language environments serve as primordial training and testing grounds, retaining essential commonsense and communication skills but in a more digestible form, potentially enhancing the learning efficiency of LMs, and thus reducing the required model size and data volume for effective training and evaluation. In these simplified language environments, workable strategies for small models, datasets, and agents may be adaptable to larger models, datasets, and agents in complex language environments. To create such environments, we focus on two aspects: i) minimizing language dataset noise and complexity, and ii) preserving the essential text distribution characteristics. Unlike previous methods, we propose a pipeline to refine text data by eliminating noise, minimizing vocabulary, and maintaining genre-specific patterns (e.g., for books, conversation, code, etc.). Implementing this pipeline with large LMs, we have created a leaner suite of LM training and evaluation datasets: 71M Leaner-Pretrain, 7M Leaner-Instruct, Leaner-Glue for assessing linguistic proficiency, and Leaner-Eval for testing instruction-following ability. Our experiments show that leaner pre-training boosts LM learning efficiency. Tiny LMs trained on these datasets outperform those trained on original datasets in instruction-following across different language granularity levels. Moreover, the Leaner-Pretrain dataset's alignment with conventional large LM training sets enables resource-optimized analysis of how learning objectives, model architectures, and training techniques impact performance on language modeling and downstream tasks. Our code and datasets are available at https://github.com/EmpathYang/TinyHelen.git.
ORBIT: Cost-Effective Dataset Curation for Large Language Model Domain Adaptation with an Astronomy Case Study
Dec 19, 2024



Abstract:Recent advances in language modeling demonstrate the need for high-quality domain-specific training data, especially for tasks that require specialized knowledge. General-purpose models, while versatile, often lack the depth needed for expert-level tasks because of limited domain-specific information. Domain adaptation training can enhance these models, but it demands substantial, high-quality data. To address this, we propose ORBIT, a cost-efficient methodology for curating massive, high-quality domain-specific datasets from noisy web sources, tailored for training specialist large language models. Using astronomy as a primary case study, we refined the 1.3T-token FineWeb-Edu dataset into a high-quality, 10B-token subset focused on astronomy. Fine-tuning \textsc{LLaMA-3-8B} on a 1B-token astronomy subset improved performance on the MMLU astronomy benchmark from 69\% to 76\% and achieved top results on AstroBench, an astronomy-specific benchmark. Moreover, our model (Orbit-LLaMA) outperformed \textsc{LLaMA-3-8B-base}, with GPT-4o evaluations preferring it in 73\% of cases across 1000 astronomy-specific questions. Additionally, we validated ORBIT's generalizability by applying it to law and medicine, achieving a significant improvement of data quality compared to an unfiltered baseline. We open-source the ORBIT methodology, including the curated datasets, the codebase, and the resulting model at \href{https://github.com/ModeEric/ORBIT-Llama}{https://github.com/ModeEric/ORBIT-Llama}.
Which Channel in 6G, Low-rank or Full-rank, more needs RIS?
Dec 04, 2024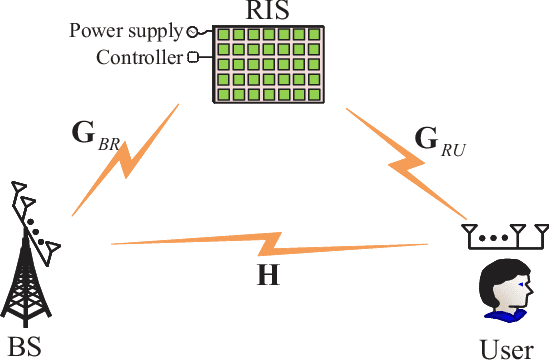



Abstract:Reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS), as an efficient tool to improve receive signal-to-noise ratio, extend coverage and create more spatial diversity, is viewed as a most promising technique for the future wireless networks like 6G. As you know, RIS is very suitable for a special wireless scenario with wireless link between BS and users being completely blocked, i.e., no link. In this paper, we extend its applications to a general scenario, i.e., rank-deficient channel, particularly some extremely low-rank ones such as no link, and line-of-sight (LoS, rank-one). Actually, there are several potential important low-rank applications like low-altitude, satellite, UAV, marine, and deep-space communications. In such a situation, it is found that RIS may make a dramatic degrees of freedom (DoF) enhancement over no RIS. By using a distributed RISs placement, the DoF of channel from BS to user in LoS channel may be even boosted from a low-rank like 0/1 to full-rank. This will achieve an extremely rate improvement via spatial parallel multiple-stream transmission from BS to user. In this paper, we present a complete review of making an in-depth discussion on DoF effect of RIS.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge