Bo Yang
Department of Automation, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China, Key Laboratory of System Control and Information Processing, Ministry of Education of China, Shanghai, China, Shanghai Engineering Research Center of Intelligent Control and Management, Shanghai, China
HySparse: A Hybrid Sparse Attention Architecture with Oracle Token Selection and KV Cache Sharing
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:This work introduces Hybrid Sparse Attention (HySparse), a new architecture that interleaves each full attention layer with several sparse attention layers. While conceptually simple, HySparse strategically derives each sparse layer's token selection and KV caches directly from the preceding full attention layer. This architecture resolves two fundamental limitations of prior sparse attention methods. First, conventional approaches typically rely on additional proxies to predict token importance, introducing extra complexity and potentially suboptimal performance. In contrast, HySparse uses the full attention layer as a precise oracle to identify important tokens. Second, existing sparse attention designs often reduce computation without saving KV cache. HySparse enables sparse attention layers to reuse the full attention KV cache, thereby reducing both computation and memory. We evaluate HySparse on both 7B dense and 80B MoE models. Across all settings, HySparse consistently outperforms both full attention and hybrid SWA baselines. Notably, in the 80B MoE model with 49 total layers, only 5 layers employ full attention, yet HySparse achieves substantial performance gains while reducing KV cache storage by nearly 10x.
Empowering LLMs for Structure-Based Drug Design via Exploration-Augmented Latent Inference
Jan 25, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) possess strong representation and reasoning capabilities, but their application to structure-based drug design (SBDD) is limited by insufficient understanding of protein structures and unpredictable molecular generation. To address these challenges, we propose Exploration-Augmented Latent Inference for LLMs (ELILLM), a framework that reinterprets the LLM generation process as an encoding, latent space exploration, and decoding workflow. ELILLM explicitly explores portions of the design problem beyond the model's current knowledge while using a decoding module to handle familiar regions, generating chemically valid and synthetically reasonable molecules. In our implementation, Bayesian optimization guides the systematic exploration of latent embeddings, and a position-aware surrogate model efficiently predicts binding affinity distributions to inform the search. Knowledge-guided decoding further reduces randomness and effectively imposes chemical validity constraints. We demonstrate ELILLM on the CrossDocked2020 benchmark, showing strong controlled exploration and high binding affinity scores compared with seven baseline methods. These results demonstrate that ELILLM can effectively enhance LLMs capabilities for SBDD.
ZPD Detector: Data Selection via Capability-Difficulty Alignment for Large Language Models
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:As the cost of training large language models continues to increase and high-quality training data become increasingly scarce, selecting high-value samples or synthesizing effective training data under limited data budgets has emerged as a critical research problem. Most existing data selection methods rely on static criteria, such as difficulty, uncertainty, or heuristics, and fail to model the evolving relationship between the model and the data. Inspired by the educational theory of the Zone of Proximal Development (ZPD), we propose ZPD Detector, a data selection framework that adopts a bidirectional perspective between models and data by explicitly modeling the alignment between sample difficulty and the model's current capability. ZPD Detector integrates difficulty calibration, model capability estimation based on Item Response Theory (IRT), and a capability-difficulty matching score to dynamically identify the most informative samples at each learning stage, improving data utilization efficiency; moreover, this dynamic matching strategy provides new insights into training strategy design. All code and data will be released after our work be accepted to support reproducible researc
MCGA: A Multi-task Classical Chinese Literary Genre Audio Corpus
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:With the rapid advancement of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs), their potential has garnered significant attention in Chinese Classical Studies (CCS). While existing research has primarily focused on text and visual modalities, the audio corpus within this domain remains largely underexplored. To bridge this gap, we propose the Multi-task Classical Chinese Literary Genre Audio Corpus (MCGA). It encompasses a diverse range of literary genres across six tasks: Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR), Speech-to-Text Translation (S2TT), Speech Emotion Captioning (SEC), Spoken Question Answering (SQA), Speech Understanding (SU), and Speech Reasoning (SR). Through the evaluation of ten MLLMs, our experimental results demonstrate that current models still face substantial challenges when processed on the MCGA test set. Furthermore, we introduce an evaluation metric for SEC and a metric to measure the consistency between the speech and text capabilities of MLLMs. We release MCGA and our code to the public to facilitate the development of MLLMs with more robust multidimensional audio capabilities in CCS. MCGA Corpus: https://github.com/yxduir/MCGA
AgriAgent: Contract-Driven Planning and Capability-Aware Tool Orchestration in Real-World Agriculture
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Intelligent agent systems in real-world agricultural scenarios must handle diverse tasks under multimodal inputs, ranging from lightweight information understanding to complex multi-step execution. However, most existing approaches rely on a unified execution paradigm, which struggles to accommodate large variations in task complexity and incomplete tool availability commonly observed in agricultural environments. To address this challenge, we propose AgriAgent, a two-level agent framework for real-world agriculture. AgriAgent adopts a hierarchical execution strategy based on task complexity: simple tasks are handled through direct reasoning by modality-specific agents, while complex tasks trigger a contract-driven planning mechanism that formulates tasks as capability requirements and performs capability-aware tool orchestration and dynamic tool generation, enabling multi-step and verifiable execution with failure recovery. Experimental results show that AgriAgent achieves higher execution success rates and robustness on complex tasks compared to existing tool-centric agent baselines that rely on unified execution paradigms. All code, data will be released at after our work be accepted to promote reproducible research.
MiMo-V2-Flash Technical Report
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:We present MiMo-V2-Flash, a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) model with 309B total parameters and 15B active parameters, designed for fast, strong reasoning and agentic capabilities. MiMo-V2-Flash adopts a hybrid attention architecture that interleaves Sliding Window Attention (SWA) with global attention, with a 128-token sliding window under a 5:1 hybrid ratio. The model is pre-trained on 27 trillion tokens with Multi-Token Prediction (MTP), employing a native 32k context length and subsequently extended to 256k. To efficiently scale post-training compute, MiMo-V2-Flash introduces a novel Multi-Teacher On-Policy Distillation (MOPD) paradigm. In this framework, domain-specialized teachers (e.g., trained via large-scale reinforcement learning) provide dense and token-level reward, enabling the student model to perfectly master teacher expertise. MiMo-V2-Flash rivals top-tier open-weight models such as DeepSeek-V3.2 and Kimi-K2, despite using only 1/2 and 1/3 of their total parameters, respectively. During inference, by repurposing MTP as a draft model for speculative decoding, MiMo-V2-Flash achieves up to 3.6 acceptance length and 2.6x decoding speedup with three MTP layers. We open-source both the model weights and the three-layer MTP weights to foster open research and community collaboration.
AgriGPT-Omni: A Unified Speech-Vision-Text Framework for Multilingual Agricultural Intelligence
Dec 11, 2025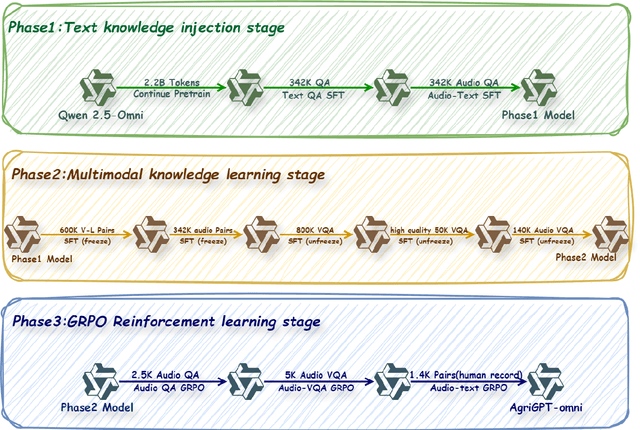
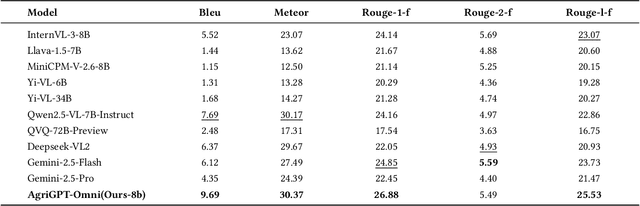
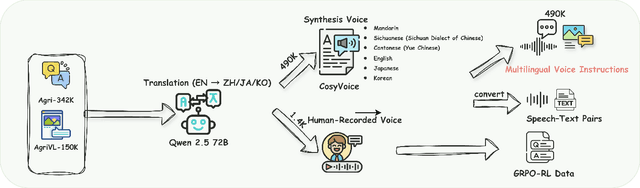
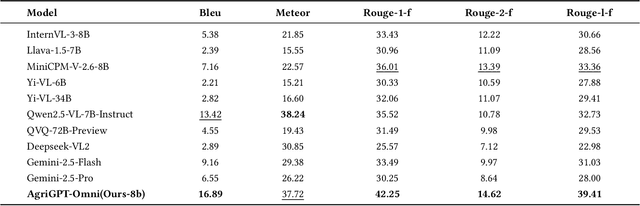
Abstract:Despite rapid advances in multimodal large language models, agricultural applications remain constrained by the lack of multilingual speech data, unified multimodal architectures, and comprehensive evaluation benchmarks. To address these challenges, we present AgriGPT-Omni, an agricultural omni-framework that integrates speech, vision, and text in a unified framework. First, we construct a scalable data synthesis and collection pipeline that converts agricultural texts and images into training data, resulting in the largest agricultural speech dataset to date, including 492K synthetic and 1.4K real speech samples across six languages. Second, based on this, we train the first agricultural omni-model via a three-stage paradigm: textual knowledge injection, progressive multimodal alignment, and GRPO-based reinforcement learning, enabling unified reasoning across languages and modalities. Third, we propose AgriBench-Omni-2K, the first tri-modal benchmark for agriculture, covering diverse speech-vision-text tasks and multilingual slices, with standardized protocols and reproducible tools. Experiments show that AgriGPT-Omni significantly outperforms general-purpose baselines on multilingual and multimodal reasoning as well as real-world speech understanding. All models, data, benchmarks, and code will be released to promote reproducible research, inclusive agricultural intelligence, and sustainable AI development for low-resource regions.
Air-Chamber Based Soft Six-Axis Force/Torque Sensor for Human-Robot Interaction
Nov 17, 2025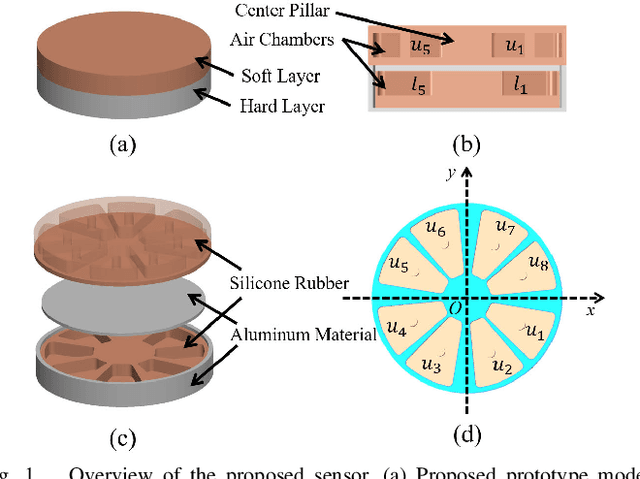
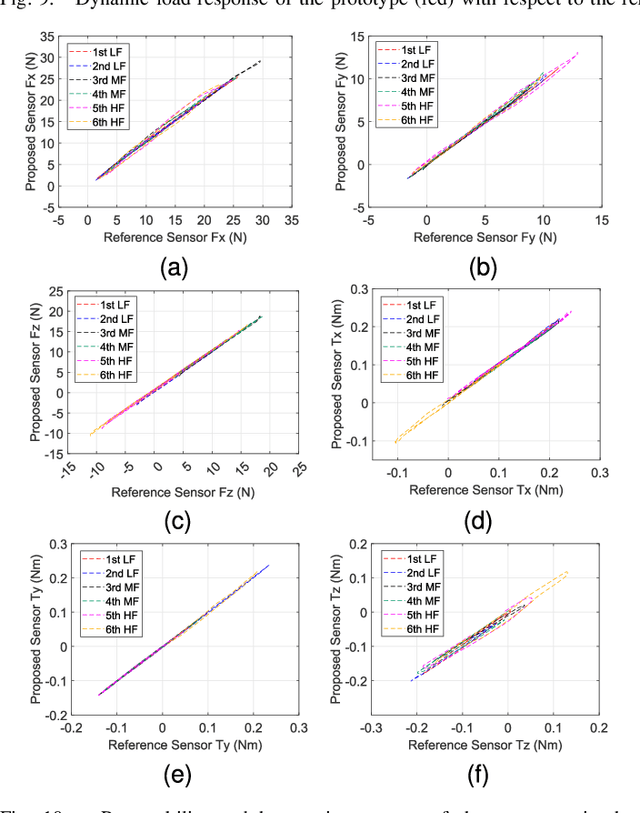
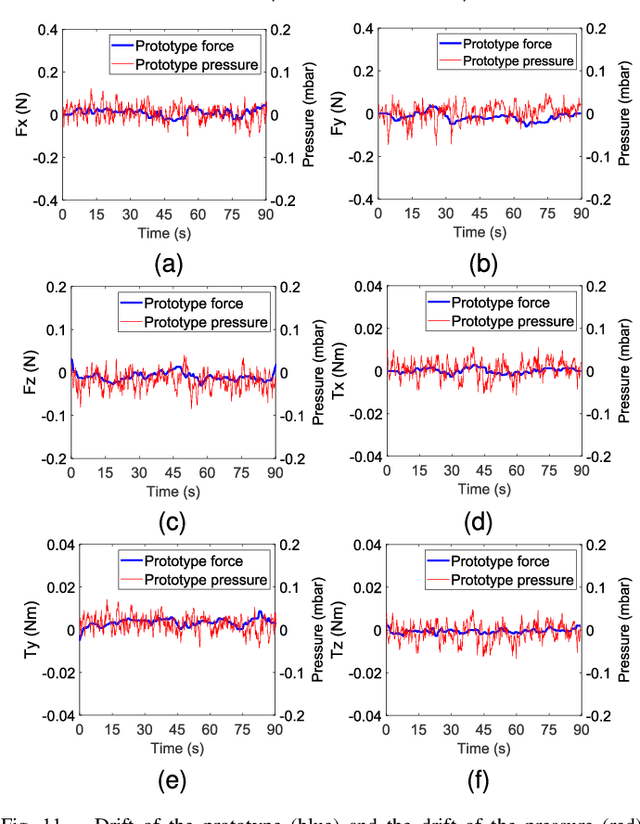
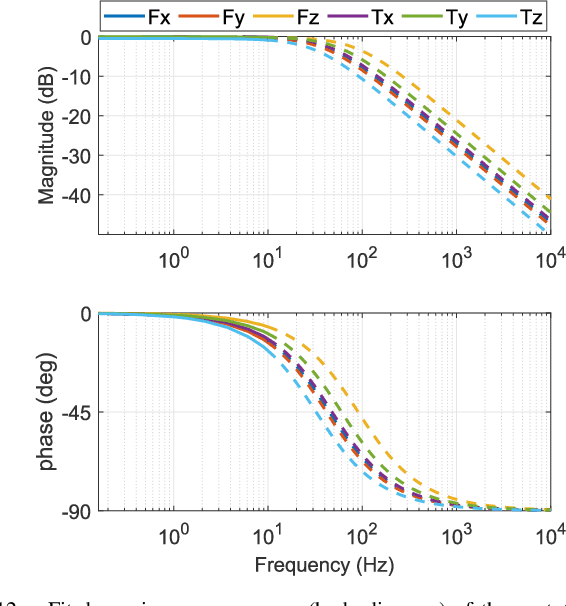
Abstract:Soft multi-axis force/torque sensors provide safe and precise force interaction. Capturing the complete degree-of-freedom of force is imperative for accurate force measurement with six-axis force/torque sensors. However, cross-axis coupling can lead to calibration issues and decreased accuracy. In this instance, developing a soft and accurate six-axis sensor is a challenging task. In this paper, a soft air-chamber type six-axis force/torque sensor with 16-channel barometers is introduced, which housed in hyper-elastic air chambers made of silicone rubber. Additionally, an effective decoupling method is proposed, based on a rigid-soft hierarchical structure, which reduces the six-axis decoupling problem to two three-axis decoupling problems. Finite element model simulation and experiments demonstrate the compatibility of the proposed approach with reality. The prototype's sensing performance is quantitatively measured in terms of static load response, dynamic load response and dynamic response characteristic. It possesses a measuring range of 50 N force and 1 Nm torque, and the average deviation, repeatability, non-linearity and hysteresis are 4.9$\%$, 2.7$\%$, 5.8$\%$ and 6.7$\%$, respectively. The results indicate that the prototype exhibits satisfactory sensing performance while maintaining its softness due to the presence of soft air chambers.
Innovative Design of Multi-functional Supernumerary Robotic Limbs with Ellipsoid Workspace Optimization
Nov 15, 2025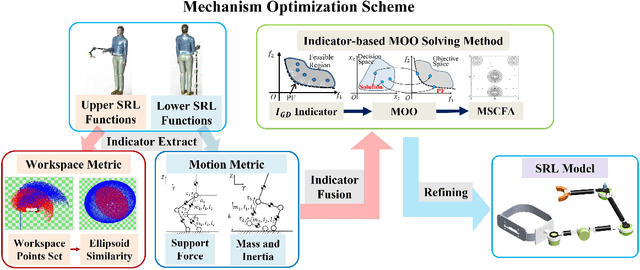
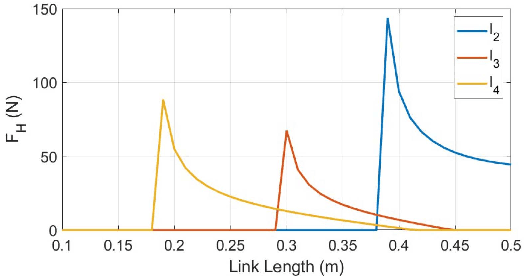
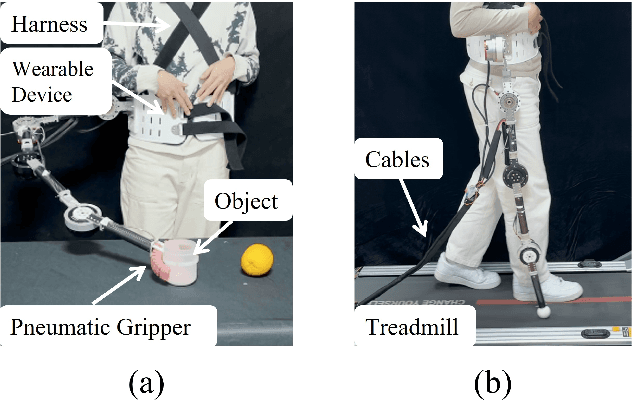
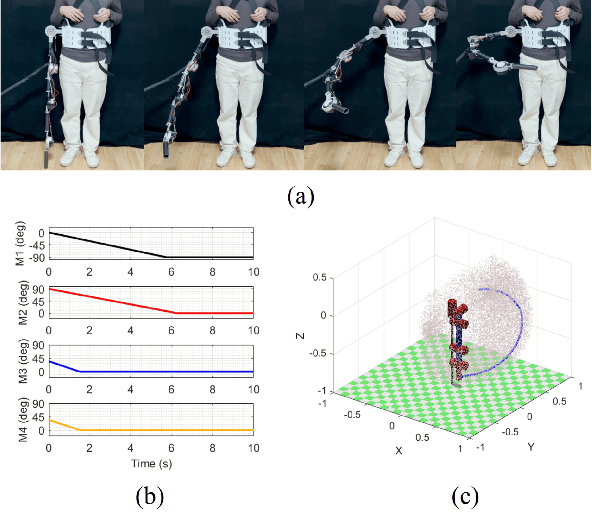
Abstract:Supernumerary robotic limbs (SRLs) offer substantial potential in both the rehabilitation of hemiplegic patients and the enhancement of functional capabilities for healthy individuals. Designing a general-purpose SRL device is inherently challenging, particularly when developing a unified theoretical framework that meets the diverse functional requirements of both upper and lower limbs. In this paper, we propose a multi-objective optimization (MOO) design theory that integrates grasping workspace similarity, walking workspace similarity, braced force for sit-to-stand (STS) movements, and overall mass and inertia. A geometric vector quantification method is developed using an ellipsoid to represent the workspace, aiming to reduce computational complexity and address quantification challenges. The ellipsoid envelope transforms workspace points into ellipsoid attributes, providing a parametric description of the workspace. Furthermore, the STS static braced force assesses the effectiveness of force transmission. The overall mass and inertia restricts excessive link length. To facilitate rapid and stable convergence of the model to high-dimensional irregular Pareto fronts, we introduce a multi-subpopulation correction firefly algorithm. This algorithm incorporates a strategy involving attractive and repulsive domains to effectively handle the MOO task. The optimized solution is utilized to redesign the prototype for experimentation to meet specified requirements. Six healthy participants and two hemiplegia patients participated in real experiments. Compared to the pre-optimization results, the average grasp success rate improved by 7.2%, while the muscle activity during walking and STS tasks decreased by an average of 12.7% and 25.1%, respectively. The proposed design theory offers an efficient option for the design of multi-functional SRL mechanisms.
TimeEmb: A Lightweight Static-Dynamic Disentanglement Framework for Time Series Forecasting
Oct 01, 2025Abstract:Temporal non-stationarity, the phenomenon that time series distributions change over time, poses fundamental challenges to reliable time series forecasting. Intuitively, the complex time series can be decomposed into two factors, \ie time-invariant and time-varying components, which indicate static and dynamic patterns, respectively. Nonetheless, existing methods often conflate the time-varying and time-invariant components, and jointly learn the combined long-term patterns and short-term fluctuations, leading to suboptimal performance facing distribution shifts. To address this issue, we initiatively propose a lightweight static-dynamic decomposition framework, TimeEmb, for time series forecasting. TimeEmb innovatively separates time series into two complementary components: (1) time-invariant component, captured by a novel global embedding module that learns persistent representations across time series, and (2) time-varying component, processed by an efficient frequency-domain filtering mechanism inspired by full-spectrum analysis in signal processing. Experiments on real-world datasets demonstrate that TimeEmb outperforms state-of-the-art baselines and requires fewer computational resources. We conduct comprehensive quantitative and qualitative analyses to verify the efficacy of static-dynamic disentanglement. This lightweight framework can also improve existing time-series forecasting methods with simple integration. To ease reproducibility, the code is available at https://github.com/showmeon/TimeEmb.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge