Ali Maatouk
Multi-Modal Time Series Prediction via Mixture of Modulated Experts
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Real-world time series exhibit complex and evolving dynamics, making accurate forecasting extremely challenging. Recent multi-modal forecasting methods leverage textual information such as news reports to improve prediction, but most rely on token-level fusion that mixes temporal patches with language tokens in a shared embedding space. However, such fusion can be ill-suited when high-quality time-text pairs are scarce and when time series exhibit substantial variation in scale and characteristics, thus complicating cross-modal alignment. In parallel, Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architectures have proven effective for both time series modeling and multi-modal learning, yet many existing MoE-based modality integration methods still depend on token-level fusion. To address this, we propose Expert Modulation, a new paradigm for multi-modal time series prediction that conditions both routing and expert computation on textual signals, enabling direct and efficient cross-modal control over expert behavior. Through comprehensive theoretical analysis and experiments, our proposed method demonstrates substantial improvements in multi-modal time series prediction. The current code is available at https://github.com/BruceZhangReve/MoME
TRACE: Grounding Time Series in Context for Multimodal Embedding and Retrieval
Jun 10, 2025Abstract:The ubiquity of dynamic data in domains such as weather, healthcare, and energy underscores a growing need for effective interpretation and retrieval of time-series data. These data are inherently tied to domain-specific contexts, such as clinical notes or weather narratives, making cross-modal retrieval essential not only for downstream tasks but also for developing robust time-series foundation models by retrieval-augmented generation (RAG). Despite the increasing demand, time-series retrieval remains largely underexplored. Existing methods often lack semantic grounding, struggle to align heterogeneous modalities, and have limited capacity for handling multi-channel signals. To address this gap, we propose TRACE, a generic multimodal retriever that grounds time-series embeddings in aligned textual context. TRACE enables fine-grained channel-level alignment and employs hard negative mining to facilitate semantically meaningful retrieval. It supports flexible cross-modal retrieval modes, including Text-to-Timeseries and Timeseries-to-Text, effectively linking linguistic descriptions with complex temporal patterns. By retrieving semantically relevant pairs, TRACE enriches downstream models with informative context, leading to improved predictive accuracy and interpretability. Beyond a static retrieval engine, TRACE also serves as a powerful standalone encoder, with lightweight task-specific tuning that refines context-aware representations while maintaining strong cross-modal alignment. These representations achieve state-of-the-art performance on downstream forecasting and classification tasks. Extensive experiments across multiple domains highlight its dual utility, as both an effective encoder for downstream applications and a general-purpose retriever to enhance time-series models.
HELM: Hyperbolic Large Language Models via Mixture-of-Curvature Experts
May 30, 2025



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have shown great success in text modeling tasks across domains. However, natural language exhibits inherent semantic hierarchies and nuanced geometric structure, which current LLMs do not capture completely owing to their reliance on Euclidean operations. Recent studies have also shown that not respecting the geometry of token embeddings leads to training instabilities and degradation of generative capabilities. These findings suggest that shifting to non-Euclidean geometries can better align language models with the underlying geometry of text. We thus propose to operate fully in Hyperbolic space, known for its expansive, scale-free, and low-distortion properties. We thus introduce HELM, a family of HypErbolic Large Language Models, offering a geometric rethinking of the Transformer-based LLM that addresses the representational inflexibility, missing set of necessary operations, and poor scalability of existing hyperbolic LMs. We additionally introduce a Mixture-of-Curvature Experts model, HELM-MICE, where each expert operates in a distinct curvature space to encode more fine-grained geometric structure from text, as well as a dense model, HELM-D. For HELM-MICE, we further develop hyperbolic Multi-Head Latent Attention (HMLA) for efficient, reduced-KV-cache training and inference. For both models, we develop essential hyperbolic equivalents of rotary positional encodings and RMS normalization. We are the first to train fully hyperbolic LLMs at billion-parameter scale, and evaluate them on well-known benchmarks such as MMLU and ARC, spanning STEM problem-solving, general knowledge, and commonsense reasoning. Our results show consistent gains from our HELM architectures -- up to 4% -- over popular Euclidean architectures used in LLaMA and DeepSeek, highlighting the efficacy and enhanced reasoning afforded by hyperbolic geometry in large-scale LM pretraining.
Telco-oRAG: Optimizing Retrieval-augmented Generation for Telecom Queries via Hybrid Retrieval and Neural Routing
May 17, 2025Abstract:Artificial intelligence will be one of the key pillars of the next generation of mobile networks (6G), as it is expected to provide novel added-value services and improve network performance. In this context, large language models have the potential to revolutionize the telecom landscape through intent comprehension, intelligent knowledge retrieval, coding proficiency, and cross-domain orchestration capabilities. This paper presents Telco-oRAG, an open-source Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) framework optimized for answering technical questions in the telecommunications domain, with a particular focus on 3GPP standards. Telco-oRAG introduces a hybrid retrieval strategy that combines 3GPP domain-specific retrieval with web search, supported by glossary-enhanced query refinement and a neural router for memory-efficient retrieval. Our results show that Telco-oRAG improves the accuracy in answering 3GPP-related questions by up to 17.6% and achieves a 10.6% improvement in lexicon queries compared to baselines. Furthermore, Telco-oRAG reduces memory usage by 45% through targeted retrieval of relevant 3GPP series compared to baseline RAG, and enables open-source LLMs to reach GPT-4-level accuracy on telecom benchmarks.
Position: Beyond Euclidean -- Foundation Models Should Embrace Non-Euclidean Geometries
Apr 11, 2025Abstract:In the era of foundation models and Large Language Models (LLMs), Euclidean space has been the de facto geometric setting for machine learning architectures. However, recent literature has demonstrated that this choice comes with fundamental limitations. At a large scale, real-world data often exhibit inherently non-Euclidean structures, such as multi-way relationships, hierarchies, symmetries, and non-isotropic scaling, in a variety of domains, such as languages, vision, and the natural sciences. It is challenging to effectively capture these structures within the constraints of Euclidean spaces. This position paper argues that moving beyond Euclidean geometry is not merely an optional enhancement but a necessity to maintain the scaling law for the next-generation of foundation models. By adopting these geometries, foundation models could more efficiently leverage the aforementioned structures. Task-aware adaptability that dynamically reconfigures embeddings to match the geometry of downstream applications could further enhance efficiency and expressivity. Our position is supported by a series of theoretical and empirical investigations of prevalent foundation models.Finally, we outline a roadmap for integrating non-Euclidean geometries into foundation models, including strategies for building geometric foundation models via fine-tuning, training from scratch, and hybrid approaches.
MTBench: A Multimodal Time Series Benchmark for Temporal Reasoning and Question Answering
Mar 21, 2025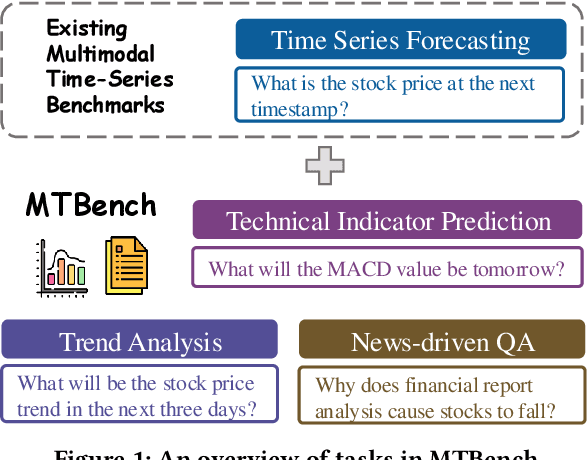

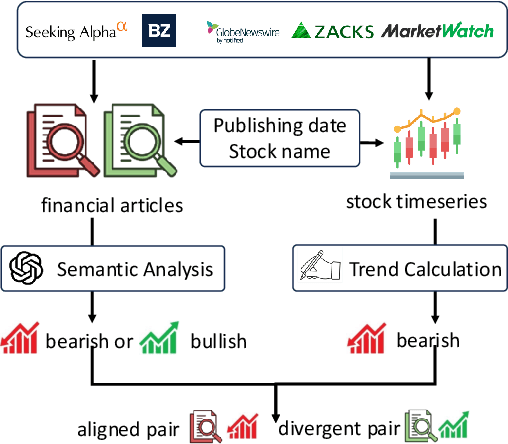

Abstract:Understanding the relationship between textual news and time-series evolution is a critical yet under-explored challenge in applied data science. While multimodal learning has gained traction, existing multimodal time-series datasets fall short in evaluating cross-modal reasoning and complex question answering, which are essential for capturing complex interactions between narrative information and temporal patterns. To bridge this gap, we introduce Multimodal Time Series Benchmark (MTBench), a large-scale benchmark designed to evaluate large language models (LLMs) on time series and text understanding across financial and weather domains. MTbench comprises paired time series and textual data, including financial news with corresponding stock price movements and weather reports aligned with historical temperature records. Unlike existing benchmarks that focus on isolated modalities, MTbench provides a comprehensive testbed for models to jointly reason over structured numerical trends and unstructured textual narratives. The richness of MTbench enables formulation of diverse tasks that require a deep understanding of both text and time-series data, including time-series forecasting, semantic and technical trend analysis, and news-driven question answering (QA). These tasks target the model's ability to capture temporal dependencies, extract key insights from textual context, and integrate cross-modal information. We evaluate state-of-the-art LLMs on MTbench, analyzing their effectiveness in modeling the complex relationships between news narratives and temporal patterns. Our findings reveal significant challenges in current models, including difficulties in capturing long-term dependencies, interpreting causality in financial and weather trends, and effectively fusing multimodal information.
Large-Scale AI in Telecom: Charting the Roadmap for Innovation, Scalability, and Enhanced Digital Experiences
Mar 06, 2025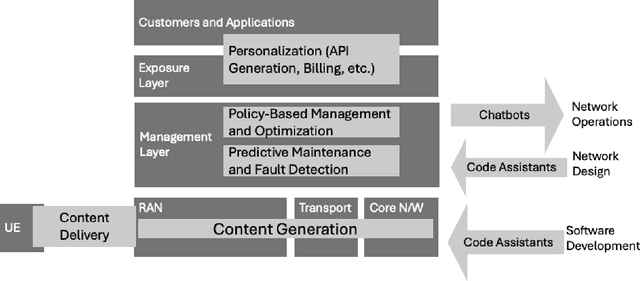
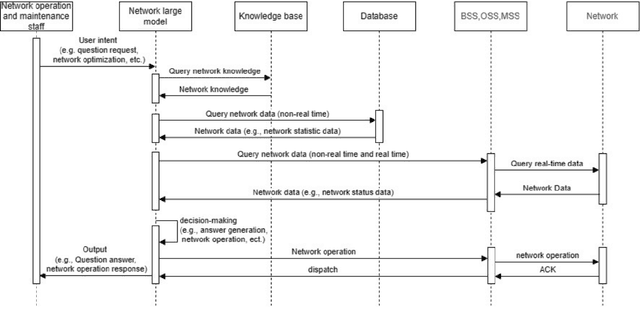
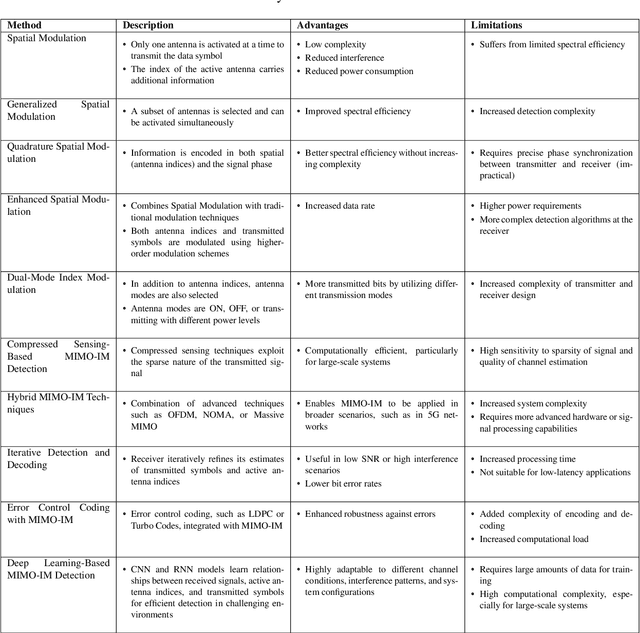
Abstract:This white paper discusses the role of large-scale AI in the telecommunications industry, with a specific focus on the potential of generative AI to revolutionize network functions and user experiences, especially in the context of 6G systems. It highlights the development and deployment of Large Telecom Models (LTMs), which are tailored AI models designed to address the complex challenges faced by modern telecom networks. The paper covers a wide range of topics, from the architecture and deployment strategies of LTMs to their applications in network management, resource allocation, and optimization. It also explores the regulatory, ethical, and standardization considerations for LTMs, offering insights into their future integration into telecom infrastructure. The goal is to provide a comprehensive roadmap for the adoption of LTMs to enhance scalability, performance, and user-centric innovation in telecom networks.
SANDWICH: Towards an Offline, Differentiable, Fully-Trainable Wireless Neural Ray-Tracing Surrogate
Nov 13, 2024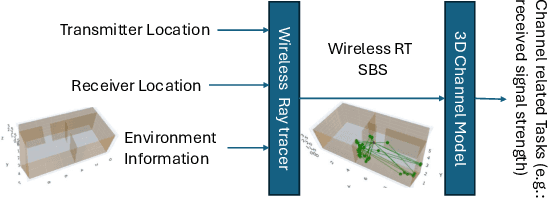
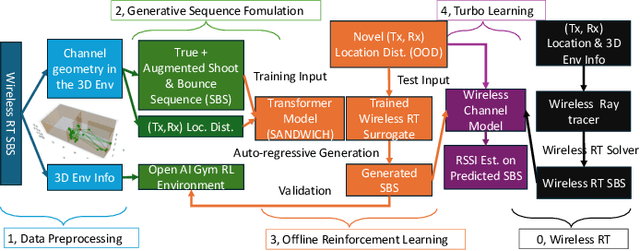
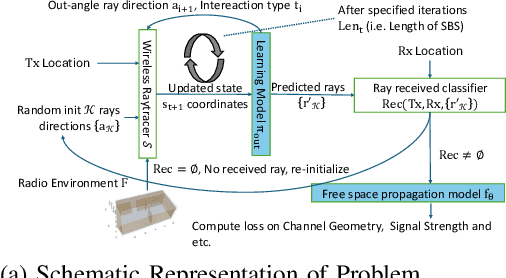
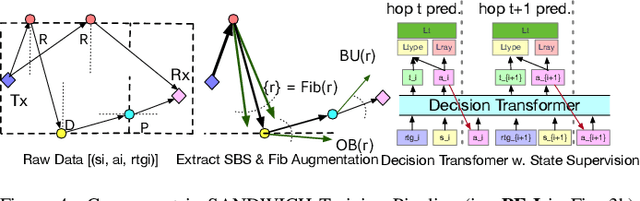
Abstract:Wireless ray-tracing (RT) is emerging as a key tool for three-dimensional (3D) wireless channel modeling, driven by advances in graphical rendering. Current approaches struggle to accurately model beyond 5G (B5G) network signaling, which often operates at higher frequencies and is more susceptible to environmental conditions and changes. Existing online learning solutions require real-time environmental supervision during training, which is both costly and incompatible with GPU-based processing. In response, we propose a novel approach that redefines ray trajectory generation as a sequential decision-making problem, leveraging generative models to jointly learn the optical, physical, and signal properties within each designated environment. Our work introduces the Scene-Aware Neural Decision Wireless Channel Raytracing Hierarchy (SANDWICH), an innovative offline, fully differentiable approach that can be trained entirely on GPUs. SANDWICH offers superior performance compared to existing online learning methods, outperforms the baseline by 4e^-2 radian in RT accuracy, and only fades 0.5 dB away from toplined channel gain estimation.
Hermes: A Large Language Model Framework on the Journey to Autonomous Networks
Nov 10, 2024



Abstract:The drive toward automating cellular network operations has grown with the increasing complexity of these systems. Despite advancements, full autonomy currently remains out of reach due to reliance on human intervention for modeling network behaviors and defining policies to meet target requirements. Network Digital Twins (NDTs) have shown promise in enhancing network intelligence, but the successful implementation of this technology is constrained by use case-specific architectures, limiting its role in advancing network autonomy. A more capable network intelligence, or "telecommunications brain", is needed to enable seamless, autonomous management of cellular network. Large Language Models (LLMs) have emerged as potential enablers for this vision but face challenges in network modeling, especially in reasoning and handling diverse data types. To address these gaps, we introduce Hermes, a chain of LLM agents that uses "blueprints" for constructing NDT instances through structured and explainable logical steps. Hermes allows automatic, reliable, and accurate network modeling of diverse use cases and configurations, thus marking progress toward fully autonomous network operations.
Tele-LLMs: A Series of Specialized Large Language Models for Telecommunications
Sep 09, 2024



Abstract:The emergence of large language models (LLMs) has significantly impacted various fields, from natural language processing to sectors like medicine and finance. However, despite their rapid proliferation, the applications of LLMs in telecommunications remain limited, often relying on general-purpose models that lack domain-specific specialization. This lack of specialization results in underperformance, particularly when dealing with telecommunications-specific technical terminology and their associated mathematical representations. This paper addresses this gap by first creating and disseminating Tele-Data, a comprehensive dataset of telecommunications material curated from relevant sources, and Tele-Eval, a large-scale question-and-answer dataset tailored to the domain. Through extensive experiments, we explore the most effective training techniques for adapting LLMs to the telecommunications domain, ranging from examining the division of expertise across various telecommunications aspects to employing parameter-efficient techniques. We also investigate how models of different sizes behave during adaptation and analyze the impact of their training data on this behavior. Leveraging these findings, we develop and open-source Tele-LLMs, the first series of language models ranging from 1B to 8B parameters, specifically tailored for telecommunications. Our evaluations demonstrate that these models outperform their general-purpose counterparts on Tele-Eval while retaining their previously acquired capabilities, thus avoiding the catastrophic forgetting phenomenon.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge