Rex Ying
Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning of LLMs with Mixture of Space Experts
Feb 16, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have achieved remarkable progress, with Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT) emerging as a key technique for downstream task adaptation. However, existing PEFT methods mainly operate in Euclidean space, fundamentally limiting their capacity to capture complex geometric structures inherent in language data. While alternative geometric spaces, like hyperbolic geometries for hierarchical data and spherical manifolds for circular patterns, offer theoretical advantages, forcing representations into a single manifold type ultimately limits expressiveness, even when curvature parameters are learnable. To address this, we propose Mixture of Space (MoS), a unified framework that leverages multiple geometric spaces simultaneously to learn richer, curvature-aware representations. Building on this scheme, we develop MoSLoRA, which extends Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) with heterogeneous geometric experts, enabling models to dynamically select or combine appropriate geometric spaces based on input context. Furthermore, to address the computational overhead of frequent manifold switching, we develop a lightweight routing mechanism. Moreover, we provide empirical insights into how curvature optimization impacts training stability and model performance. Our experiments across diverse benchmarks demonstrate that MoSLoRA consistently outperforms strong baselines, achieving up to 5.6% improvement on MATH500 and 15.9% on MAWPS.
HypRAG: Hyperbolic Dense Retrieval for Retrieval Augmented Generation
Feb 08, 2026Abstract:Embedding geometry plays a fundamental role in retrieval quality, yet dense retrievers for retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) remain largely confined to Euclidean space. However, natural language exhibits hierarchical structure from broad topics to specific entities that Euclidean embeddings fail to preserve, causing semantically distant documents to appear spuriously similar and increasing hallucination risk. To address these limitations, we introduce hyperbolic dense retrieval, developing two model variants in the Lorentz model of hyperbolic space: HyTE-FH, a fully hyperbolic transformer, and HyTE-H, a hybrid architecture projecting pre-trained Euclidean embeddings into hyperbolic space. To prevent representational collapse during sequence aggregation, we introduce the Outward Einstein Midpoint, a geometry-aware pooling operator that provably preserves hierarchical structure. On MTEB, HyTE-FH outperforms equivalent Euclidean baselines, while on RAGBench, HyTE-H achieves up to 29% gains over Euclidean baselines in context relevance and answer relevance using substantially smaller models than current state-of-the-art retrievers. Our analysis also reveals that hyperbolic representations encode document specificity through norm-based separation, with over 20% radial increase from general to specific concepts, a property absent in Euclidean embeddings, underscoring the critical role of geometric inductive bias in faithful RAG systems.
Fin-RATE: A Real-world Financial Analytics and Tracking Evaluation Benchmark for LLMs on SEC Filings
Feb 07, 2026Abstract:With increasing deployment of Large Language Models (LLMs) in the finance domain, LLMs are increasingly expected to parse complex regulatory disclosures. However, existing benchmarks often focus on isolated details, failing to reflect the complexity of professional analysis that requires synthesizing information across multiple documents, reporting periods, and corporate entities. They do not distinguish whether errors stem from retrieval failures, generation flaws, finance-specific reasoning mistakes, or misunderstanding of the query or context. This makes it difficult to pinpoint performance bottlenecks. To bridge these gaps, we introduce Fin-RATE, a benchmark built on U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) filings and mirror financial analyst workflows through three pathways: detail-oriented reasoning within individual disclosures, cross-entity comparison under shared topics, and longitudinal tracking of the same firm across reporting periods. We benchmark 17 leading LLMs, spanning open-source, closed-source, and finance-specialized models, under both ground-truth context and retrieval-augmented settings. Results show substantial performance degradation, with accuracy dropping by 18.60% and 14.35% as tasks shift from single-document reasoning to longitudinal and cross-entity analysis. This is driven by rising comparison hallucinations, time and entity mismatches, and mirrored by declines in reasoning and factuality--limitations that prior benchmarks have yet to formally categorize or quantify.
Efficient Long-Horizon Vision-Language-Action Models via Static-Dynamic Disentanglement
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models have recently emerged as a promising paradigm for generalist robotic control. Built upon vision-language model (VLM) architectures, VLAs predict actions conditioned on visual observations and language instructions, achieving strong performance and generalization across tasks. However, VLAs face two major challenges: limited long-horizon context and inefficient inference due to the quadratic attention complexity and large parameter counts. Our work is motivated by the observation that much of the visual information in a trajectory remains static across timesteps (e.g., the background). Leveraging this property, we propose SD-VLA, a framework that disentangles visual inputs into multi-level static and dynamic tokens, which enables (1) retaining a single copy of static tokens across frames to significantly reduce context length, and (2) reusing the key-value (KV) cache of static tokens through a lightweight recache gate that updates only when necessary. This design enables efficient multi-frame integration and efficient inference. In addition, we introduce a new benchmark that more effectively evaluates the long-horizon temporal dependency modeling ability of VLAs. Experimental results show that our approach outperforms baselines on this benchmark by 39.8% absolute improvement in success rate, and achieves a 3.9% gain on the SimplerEnv benchmark. Moreover, SD-VLA delivers a 2.26x inference speedup over the base VLA model on the same benchmark, enabling faster and more practical real-world deployment.
Multi-Modal Time Series Prediction via Mixture of Modulated Experts
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Real-world time series exhibit complex and evolving dynamics, making accurate forecasting extremely challenging. Recent multi-modal forecasting methods leverage textual information such as news reports to improve prediction, but most rely on token-level fusion that mixes temporal patches with language tokens in a shared embedding space. However, such fusion can be ill-suited when high-quality time-text pairs are scarce and when time series exhibit substantial variation in scale and characteristics, thus complicating cross-modal alignment. In parallel, Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architectures have proven effective for both time series modeling and multi-modal learning, yet many existing MoE-based modality integration methods still depend on token-level fusion. To address this, we propose Expert Modulation, a new paradigm for multi-modal time series prediction that conditions both routing and expert computation on textual signals, enabling direct and efficient cross-modal control over expert behavior. Through comprehensive theoretical analysis and experiments, our proposed method demonstrates substantial improvements in multi-modal time series prediction. The current code is available at https://github.com/BruceZhangReve/MoME
Hyperbolic Deep Learning for Foundation Models: A Survey
Jul 23, 2025Abstract:Foundation models pre-trained on massive datasets, including large language models (LLMs), vision-language models (VLMs), and large multimodal models, have demonstrated remarkable success in diverse downstream tasks. However, recent studies have shown fundamental limitations of these models: (1) limited representational capacity, (2) lower adaptability, and (3) diminishing scalability. These shortcomings raise a critical question: is Euclidean geometry truly the optimal inductive bias for all foundation models, or could incorporating alternative geometric spaces enable models to better align with the intrinsic structure of real-world data and improve reasoning processes? Hyperbolic spaces, a class of non-Euclidean manifolds characterized by exponential volume growth with respect to distance, offer a mathematically grounded solution. These spaces enable low-distortion embeddings of hierarchical structures (e.g., trees, taxonomies) and power-law distributions with substantially fewer dimensions compared to Euclidean counterparts. Recent advances have leveraged these properties to enhance foundation models, including improving LLMs' complex reasoning ability, VLMs' zero-shot generalization, and cross-modal semantic alignment, while maintaining parameter efficiency. This paper provides a comprehensive review of hyperbolic neural networks and their recent development for foundation models. We further outline key challenges and research directions to advance the field.
HEIST: A Graph Foundation Model for Spatial Transcriptomics and Proteomics Data
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:Single-cell transcriptomics has become a great source for data-driven insights into biology, enabling the use of advanced deep learning methods to understand cellular heterogeneity and transcriptional regulation at the single-cell level. With the advent of spatial transcriptomics data we have the promise of learning about cells within a tissue context as it provides both spatial coordinates and transcriptomic readouts. However, existing models either ignore spatial resolution or the gene regulatory information. Gene regulation in cells can change depending on microenvironmental cues from neighboring cells, but existing models neglect gene regulatory patterns with hierarchical dependencies across levels of abstraction. In order to create contextualized representations of cells and genes from spatial transcriptomics data, we introduce HEIST, a hierarchical graph transformer-based foundation model for spatial transcriptomics and proteomics data. HEIST models tissue as spatial cellular neighborhood graphs, and each cell is, in turn, modeled as a gene regulatory network graph. The framework includes a hierarchical graph transformer that performs cross-level message passing and message passing within levels. HEIST is pre-trained on 22.3M cells from 124 tissues across 15 organs using spatially-aware contrastive learning and masked auto-encoding objectives. Unsupervised analysis of HEIST representations of cells, shows that it effectively encodes the microenvironmental influences in cell embeddings, enabling the discovery of spatially-informed subpopulations that prior models fail to differentiate. Further, HEIST achieves state-of-the-art results on four downstream task such as clinical outcome prediction, cell type annotation, gene imputation, and spatially-informed cell clustering across multiple technologies, highlighting the importance of hierarchical modeling and GRN-based representations.
TRACE: Grounding Time Series in Context for Multimodal Embedding and Retrieval
Jun 10, 2025Abstract:The ubiquity of dynamic data in domains such as weather, healthcare, and energy underscores a growing need for effective interpretation and retrieval of time-series data. These data are inherently tied to domain-specific contexts, such as clinical notes or weather narratives, making cross-modal retrieval essential not only for downstream tasks but also for developing robust time-series foundation models by retrieval-augmented generation (RAG). Despite the increasing demand, time-series retrieval remains largely underexplored. Existing methods often lack semantic grounding, struggle to align heterogeneous modalities, and have limited capacity for handling multi-channel signals. To address this gap, we propose TRACE, a generic multimodal retriever that grounds time-series embeddings in aligned textual context. TRACE enables fine-grained channel-level alignment and employs hard negative mining to facilitate semantically meaningful retrieval. It supports flexible cross-modal retrieval modes, including Text-to-Timeseries and Timeseries-to-Text, effectively linking linguistic descriptions with complex temporal patterns. By retrieving semantically relevant pairs, TRACE enriches downstream models with informative context, leading to improved predictive accuracy and interpretability. Beyond a static retrieval engine, TRACE also serves as a powerful standalone encoder, with lightweight task-specific tuning that refines context-aware representations while maintaining strong cross-modal alignment. These representations achieve state-of-the-art performance on downstream forecasting and classification tasks. Extensive experiments across multiple domains highlight its dual utility, as both an effective encoder for downstream applications and a general-purpose retriever to enhance time-series models.
Learning Along the Arrow of Time: Hyperbolic Geometry for Backward-Compatible Representation Learning
Jun 06, 2025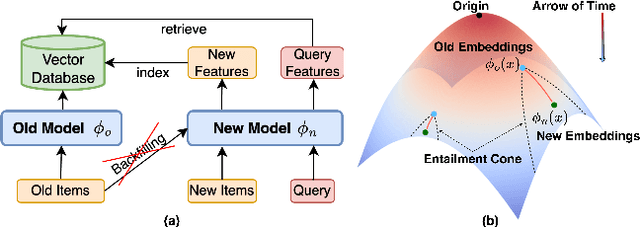
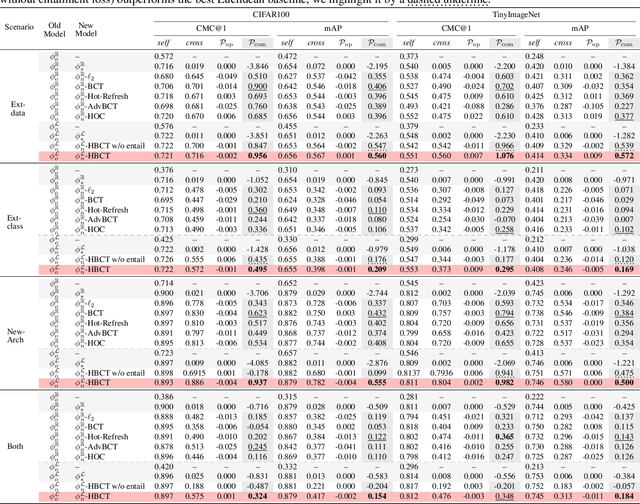
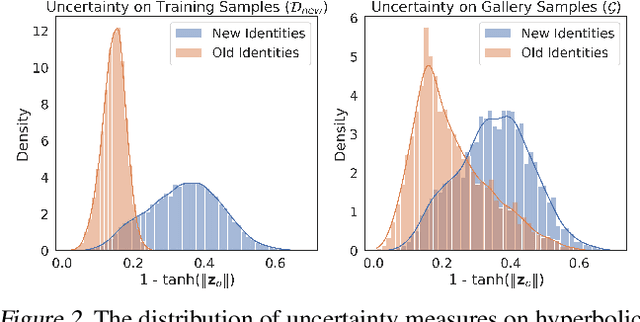
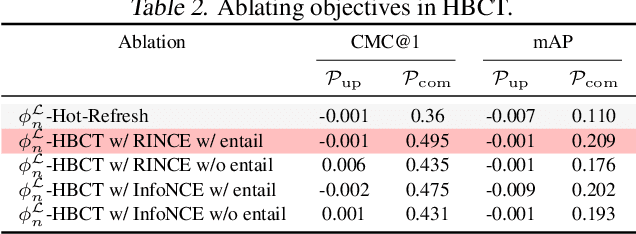
Abstract:Backward compatible representation learning enables updated models to integrate seamlessly with existing ones, avoiding to reprocess stored data. Despite recent advances, existing compatibility approaches in Euclidean space neglect the uncertainty in the old embedding model and force the new model to reconstruct outdated representations regardless of their quality, thereby hindering the learning process of the new model. In this paper, we propose to switch perspectives to hyperbolic geometry, where we treat time as a natural axis for capturing a model's confidence and evolution. By lifting embeddings into hyperbolic space and constraining updated embeddings to lie within the entailment cone of the old ones, we maintain generational consistency across models while accounting for uncertainties in the representations. To further enhance compatibility, we introduce a robust contrastive alignment loss that dynamically adjusts alignment weights based on the uncertainty of the old embeddings. Experiments validate the superiority of the proposed method in achieving compatibility, paving the way for more resilient and adaptable machine learning systems.
HELM: Hyperbolic Large Language Models via Mixture-of-Curvature Experts
May 30, 2025



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have shown great success in text modeling tasks across domains. However, natural language exhibits inherent semantic hierarchies and nuanced geometric structure, which current LLMs do not capture completely owing to their reliance on Euclidean operations. Recent studies have also shown that not respecting the geometry of token embeddings leads to training instabilities and degradation of generative capabilities. These findings suggest that shifting to non-Euclidean geometries can better align language models with the underlying geometry of text. We thus propose to operate fully in Hyperbolic space, known for its expansive, scale-free, and low-distortion properties. We thus introduce HELM, a family of HypErbolic Large Language Models, offering a geometric rethinking of the Transformer-based LLM that addresses the representational inflexibility, missing set of necessary operations, and poor scalability of existing hyperbolic LMs. We additionally introduce a Mixture-of-Curvature Experts model, HELM-MICE, where each expert operates in a distinct curvature space to encode more fine-grained geometric structure from text, as well as a dense model, HELM-D. For HELM-MICE, we further develop hyperbolic Multi-Head Latent Attention (HMLA) for efficient, reduced-KV-cache training and inference. For both models, we develop essential hyperbolic equivalents of rotary positional encodings and RMS normalization. We are the first to train fully hyperbolic LLMs at billion-parameter scale, and evaluate them on well-known benchmarks such as MMLU and ARC, spanning STEM problem-solving, general knowledge, and commonsense reasoning. Our results show consistent gains from our HELM architectures -- up to 4% -- over popular Euclidean architectures used in LLaMA and DeepSeek, highlighting the efficacy and enhanced reasoning afforded by hyperbolic geometry in large-scale LM pretraining.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge