Mingxuan Ju
Plain Transformers are Surprisingly Powerful Link Predictors
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Link prediction is a core challenge in graph machine learning, demanding models that capture rich and complex topological dependencies. While Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) are the standard solution, state-of-the-art pipelines often rely on explicit structural heuristics or memory-intensive node embeddings -- approaches that struggle to generalize or scale to massive graphs. Emerging Graph Transformers (GTs) offer a potential alternative but often incur significant overhead due to complex structural encodings, hindering their applications to large-scale link prediction. We challenge these sophisticated paradigms with PENCIL, an encoder-only plain Transformer that replaces hand-crafted priors with attention over sampled local subgraphs, retaining the scalability and hardware efficiency of standard Transformers. Through experimental and theoretical analysis, we show that PENCIL extracts richer structural signals than GNNs, implicitly generalizing a broad class of heuristics and subgraph-based expressivity. Empirically, PENCIL outperforms heuristic-informed GNNs and is far more parameter-efficient than ID-embedding--based alternatives, while remaining competitive across diverse benchmarks -- even without node features. Our results challenge the prevailing reliance on complex engineering techniques, demonstrating that simple design choices are potentially sufficient to achieve the same capabilities.
Threshold Differential Attention for Sink-Free, Ultra-Sparse, and Non-Dispersive Language Modeling
Jan 17, 2026Abstract:Softmax attention struggles with long contexts due to structural limitations: the strict sum-to-one constraint forces attention sinks on irrelevant tokens, and probability mass disperses as sequence lengths increase. We tackle these problems with Threshold Differential Attention (TDA), a sink-free attention mechanism that achieves ultra-sparsity and improved robustness at longer sequence lengths without the computational overhead of projection methods or the performance degradation caused by noise accumulation of standard rectified attention. TDA applies row-wise extreme-value thresholding with a length-dependent gate, retaining only exceedances. Inspired by the differential transformer, TDA also subtracts an inhibitory view to enhance expressivity. Theoretically, we prove that TDA controls the expected number of spurious survivors per row to $O(1)$ and that consensus spurious matches across independent views vanish as context grows. Empirically, TDA produces $>99\%$ exact zeros and eliminates attention sinks while maintaining competitive performance on standard and long-context benchmarks.
Hierarchical Token Prepending: Enhancing Information Flow in Decoder-based LLM Embeddings
Nov 18, 2025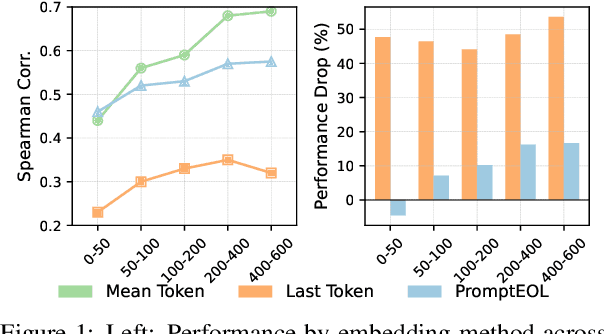
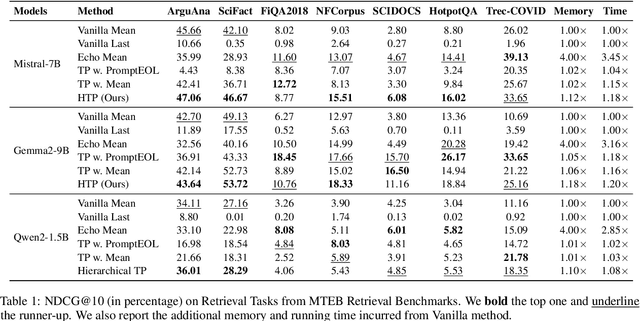
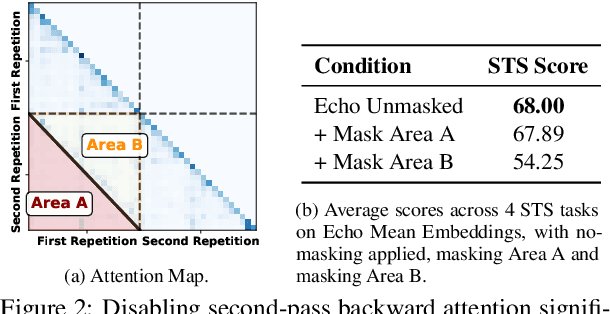
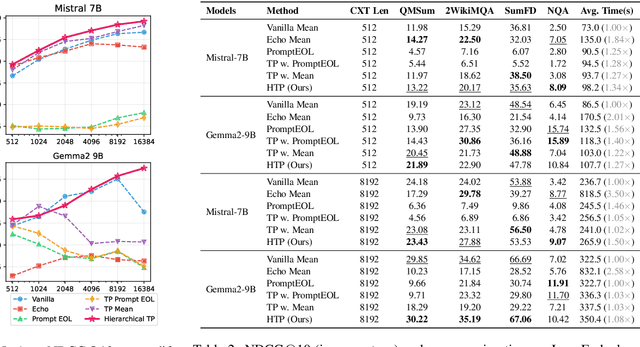
Abstract:Large language models produce powerful text embeddings, but their causal attention mechanism restricts the flow of information from later to earlier tokens, degrading representation quality. While recent methods attempt to solve this by prepending a single summary token, they over-compress information, hence harming performance on long documents. We propose Hierarchical Token Prepending (HTP), a method that resolves two critical bottlenecks. To mitigate attention-level compression, HTP partitions the input into blocks and prepends block-level summary tokens to subsequent blocks, creating multiple pathways for backward information flow. To address readout-level over-squashing, we replace last-token pooling with mean-pooling, a choice supported by theoretical analysis. HTP achieves consistent performance gains across 11 retrieval datasets and 30 general embedding benchmarks, especially in long-context settings. As a simple, architecture-agnostic method, HTP enhances both zero-shot and finetuned models, offering a scalable route to superior long-document embeddings.
Learning Along the Arrow of Time: Hyperbolic Geometry for Backward-Compatible Representation Learning
Jun 06, 2025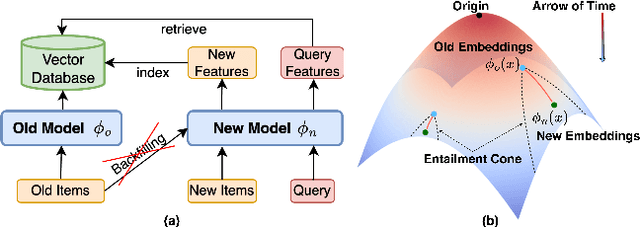
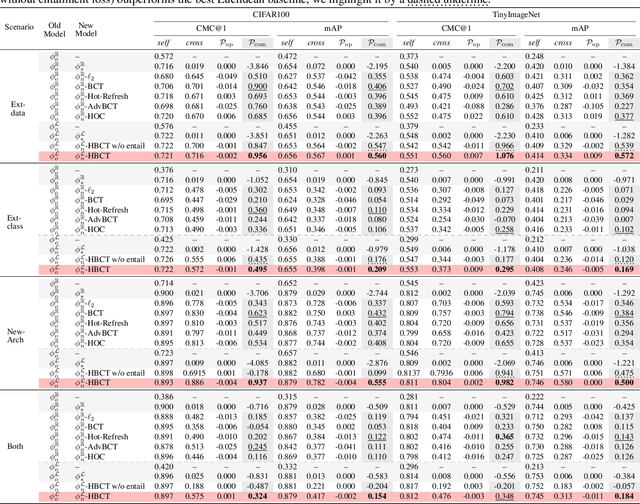
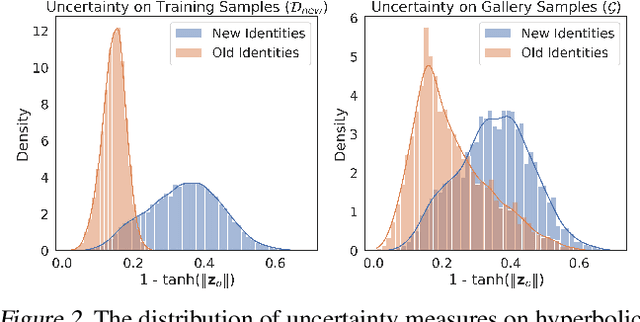
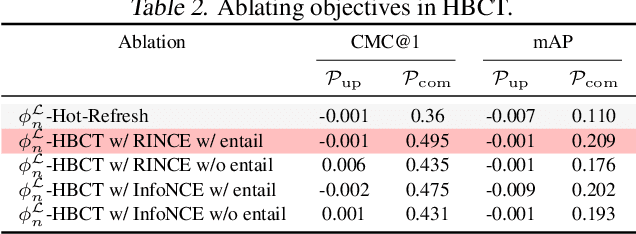
Abstract:Backward compatible representation learning enables updated models to integrate seamlessly with existing ones, avoiding to reprocess stored data. Despite recent advances, existing compatibility approaches in Euclidean space neglect the uncertainty in the old embedding model and force the new model to reconstruct outdated representations regardless of their quality, thereby hindering the learning process of the new model. In this paper, we propose to switch perspectives to hyperbolic geometry, where we treat time as a natural axis for capturing a model's confidence and evolution. By lifting embeddings into hyperbolic space and constraining updated embeddings to lie within the entailment cone of the old ones, we maintain generational consistency across models while accounting for uncertainties in the representations. To further enhance compatibility, we introduce a robust contrastive alignment loss that dynamically adjusts alignment weights based on the uncertainty of the old embeddings. Experiments validate the superiority of the proposed method in achieving compatibility, paving the way for more resilient and adaptable machine learning systems.
On the Role of Weight Decay in Collaborative Filtering: A Popularity Perspective
May 16, 2025Abstract:Collaborative filtering (CF) enables large-scale recommendation systems by encoding information from historical user-item interactions into dense ID-embedding tables. However, as embedding tables grow, closed-form solutions become impractical, often necessitating the use of mini-batch gradient descent for training. Despite extensive work on designing loss functions to train CF models, we argue that one core component of these pipelines is heavily overlooked: weight decay. Attaining high-performing models typically requires careful tuning of weight decay, regardless of loss, yet its necessity is not well understood. In this work, we question why weight decay is crucial in CF pipelines and how it impacts training. Through theoretical and empirical analysis, we surprisingly uncover that weight decay's primary function is to encode popularity information into the magnitudes of the embedding vectors. Moreover, we find that tuning weight decay acts as a coarse, non-linear knob to influence preference towards popular or unpopular items. Based on these findings, we propose PRISM (Popularity-awaRe Initialization Strategy for embedding Magnitudes), a straightforward yet effective solution to simplify the training of high-performing CF models. PRISM pre-encodes the popularity information typically learned through weight decay, eliminating its necessity. Our experiments show that PRISM improves performance by up to 4.77% and reduces training times by 38.48%, compared to state-of-the-art training strategies. Additionally, we parameterize PRISM to modulate the initialization strength, offering a cost-effective and meaningful strategy to mitigate popularity bias.
Heuristic Methods are Good Teachers to Distill MLPs for Graph Link Prediction
Apr 08, 2025



Abstract:Link prediction is a crucial graph-learning task with applications including citation prediction and product recommendation. Distilling Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) teachers into Multi-Layer Perceptrons (MLPs) students has emerged as an effective approach to achieve strong performance and reducing computational cost by removing graph dependency. However, existing distillation methods only use standard GNNs and overlook alternative teachers such as specialized model for link prediction (GNN4LP) and heuristic methods (e.g., common neighbors). This paper first explores the impact of different teachers in GNN-to-MLP distillation. Surprisingly, we find that stronger teachers do not always produce stronger students: MLPs distilled from GNN4LP can underperform those distilled from simpler GNNs, while weaker heuristic methods can teach MLPs to near-GNN performance with drastically reduced training costs. Building on these insights, we propose Ensemble Heuristic-Distilled MLPs (EHDM), which eliminates graph dependencies while effectively integrating complementary signals via a gating mechanism. Experiments on ten datasets show an average 7.93% improvement over previous GNN-to-MLP approaches with 1.95-3.32 times less training time, indicating EHDM is an efficient and effective link prediction method.
Beyond Unimodal Boundaries: Generative Recommendation with Multimodal Semantics
Mar 30, 2025Abstract:Generative recommendation (GR) has become a powerful paradigm in recommendation systems that implicitly links modality and semantics to item representation, in contrast to previous methods that relied on non-semantic item identifiers in autoregressive models. However, previous research has predominantly treated modalities in isolation, typically assuming item content is unimodal (usually text). We argue that this is a significant limitation given the rich, multimodal nature of real-world data and the potential sensitivity of GR models to modality choices and usage. Our work aims to explore the critical problem of Multimodal Generative Recommendation (MGR), highlighting the importance of modality choices in GR nframeworks. We reveal that GR models are particularly sensitive to different modalities and examine the challenges in achieving effective GR when multiple modalities are available. By evaluating design strategies for effectively leveraging multiple modalities, we identify key challenges and introduce MGR-LF++, an enhanced late fusion framework that employs contrastive modality alignment and special tokens to denote different modalities, achieving a performance improvement of over 20% compared to single-modality alternatives.
Enhancing Item Tokenization for Generative Recommendation through Self-Improvement
Dec 22, 2024



Abstract:Generative recommendation systems, driven by large language models (LLMs), present an innovative approach to predicting user preferences by modeling items as token sequences and generating recommendations in a generative manner. A critical challenge in this approach is the effective tokenization of items, ensuring that they are represented in a form compatible with LLMs. Current item tokenization methods include using text descriptions, numerical strings, or sequences of discrete tokens. While text-based representations integrate seamlessly with LLM tokenization, they are often too lengthy, leading to inefficiencies and complicating accurate generation. Numerical strings, while concise, lack semantic depth and fail to capture meaningful item relationships. Tokenizing items as sequences of newly defined tokens has gained traction, but it often requires external models or algorithms for token assignment. These external processes may not align with the LLM's internal pretrained tokenization schema, leading to inconsistencies and reduced model performance. To address these limitations, we propose a self-improving item tokenization method that allows the LLM to refine its own item tokenizations during training process. Our approach starts with item tokenizations generated by any external model and periodically adjusts these tokenizations based on the LLM's learned patterns. Such alignment process ensures consistency between the tokenization and the LLM's internal understanding of the items, leading to more accurate recommendations. Furthermore, our method is simple to implement and can be integrated as a plug-and-play enhancement into existing generative recommendation systems. Experimental results on multiple datasets and using various initial tokenization strategies demonstrate the effectiveness of our method, with an average improvement of 8\% in recommendation performance.
MOPI-HFRS: A Multi-objective Personalized Health-aware Food Recommendation System with LLM-enhanced Interpretation
Dec 12, 2024



Abstract:The prevalence of unhealthy eating habits has become an increasingly concerning issue in the United States. However, major food recommendation platforms (e.g., Yelp) continue to prioritize users' dietary preferences over the healthiness of their choices. Although efforts have been made to develop health-aware food recommendation systems, the personalization of such systems based on users' specific health conditions remains under-explored. In addition, few research focus on the interpretability of these systems, which hinders users from assessing the reliability of recommendations and impedes the practical deployment of these systems. In response to this gap, we first establish two large-scale personalized health-aware food recommendation benchmarks at the first attempt. We then develop a novel framework, Multi-Objective Personalized Interpretable Health-aware Food Recommendation System (MOPI-HFRS), which provides food recommendations by jointly optimizing the three objectives: user preference, personalized healthiness and nutritional diversity, along with an large language model (LLM)-enhanced reasoning module to promote healthy dietary knowledge through the interpretation of recommended results. Specifically, this holistic graph learning framework first utilizes two structure learning and a structure pooling modules to leverage both descriptive features and health data. Then it employs Pareto optimization to achieve designed multi-facet objectives. Finally, to further promote the healthy dietary knowledge and awareness, we exploit an LLM by utilizing knowledge-infusion, prompting the LLMs with knowledge obtained from the recommendation model for interpretation.
One Model for One Graph: A New Perspective for Pretraining with Cross-domain Graphs
Nov 30, 2024



Abstract:Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have emerged as a powerful tool to capture intricate network patterns, achieving success across different domains. However, existing GNNs require careful domain-specific architecture designs and training from scratch on each dataset, leading to an expertise-intensive process with difficulty in generalizing across graphs from different domains. Therefore, it can be hard for practitioners to infer which GNN model can generalize well to graphs from their domains. To address this challenge, we propose a novel cross-domain pretraining framework, "one model for one graph," which overcomes the limitations of previous approaches that failed to use a single GNN to capture diverse graph patterns across domains with significant gaps. Specifically, we pretrain a bank of expert models, with each one corresponding to a specific dataset. When inferring to a new graph, gating functions choose a subset of experts to effectively integrate prior model knowledge while avoiding negative transfer. Extensive experiments consistently demonstrate the superiority of our proposed method on both link prediction and node classification tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge