Jiancheng Yang
Learning Topology-Aware Implicit Field for Unified Pulmonary Tree Modeling with Incomplete Topological Supervision
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Pulmonary trees extracted from CT images frequently exhibit topological incompleteness, such as missing or disconnected branches, which substantially degrades downstream anatomical analysis and limits the applicability of existing pulmonary tree modeling pipelines. Current approaches typically rely on dense volumetric processing or explicit graph reasoning, leading to limited efficiency and reduced robustness under realistic structural corruption. We propose TopoField, a topology-aware implicit modeling framework that treats topology repair as a first-class modeling problem and enables unified multi-task inference for pulmonary tree analysis. TopoField represents pulmonary anatomy using sparse surface and skeleton point clouds and learns a continuous implicit field that supports topology repair without relying on complete or explicit disconnection annotations, by training on synthetically introduced structural disruptions over \textit{already} incomplete trees. Building upon the repaired implicit representation, anatomical labeling and lung segment reconstruction are jointly inferred through task-specific implicit functions within a single forward pass.Extensive experiments on the Lung3D+ dataset demonstrate that TopoField consistently improves topological completeness and achieves accurate anatomical labeling and lung segment reconstruction under challenging incomplete scenarios. Owing to its implicit formulation, TopoField attains high computational efficiency, completing all tasks in just over one second per case, highlighting its practicality for large-scale and time-sensitive clinical applications. Code and data will be available at https://github.com/HINTLab/TopoField.
Bonnet: Ultra-fast whole-body bone segmentation from CT scans
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:This work proposes Bonnet, an ultra-fast sparse-volume pipeline for whole-body bone segmentation from CT scans. Accurate bone segmentation is important for surgical planning and anatomical analysis, but existing 3D voxel-based models such as nnU-Net and STU-Net require heavy computation and often take several minutes per scan, which limits time-critical use. The proposed Bonnet addresses this by integrating a series of novel framework components including HU-based bone thresholding, patch-wise inference with a sparse spconv-based U-Net, and multi-window fusion into a full-volume prediction. Trained on TotalSegmentator and evaluated without additional tuning on RibSeg, CT-Pelvic1K, and CT-Spine1K, Bonnet achieves high Dice across ribs, pelvis, and spine while running in only 2.69 seconds per scan on an RTX A6000. Compared to strong voxel baselines, Bonnet attains a similar accuracy but reduces inference time by roughly 25x on the same hardware and tiling setup. The toolkit and pre-trained models will be released at https://github.com/HINTLab/Bonnet.
AortaDiff: A Unified Multitask Diffusion Framework For Contrast-Free AAA Imaging
Oct 01, 2025Abstract:While contrast-enhanced CT (CECT) is standard for assessing abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAA), the required iodinated contrast agents pose significant risks, including nephrotoxicity, patient allergies, and environmental harm. To reduce contrast agent use, recent deep learning methods have focused on generating synthetic CECT from non-contrast CT (NCCT) scans. However, most adopt a multi-stage pipeline that first generates images and then performs segmentation, which leads to error accumulation and fails to leverage shared semantic and anatomical structures. To address this, we propose a unified deep learning framework that generates synthetic CECT images from NCCT scans while simultaneously segmenting the aortic lumen and thrombus. Our approach integrates conditional diffusion models (CDM) with multi-task learning, enabling end-to-end joint optimization of image synthesis and anatomical segmentation. Unlike previous multitask diffusion models, our approach requires no initial predictions (e.g., a coarse segmentation mask), shares both encoder and decoder parameters across tasks, and employs a semi-supervised training strategy to learn from scans with missing segmentation labels, a common constraint in real-world clinical data. We evaluated our method on a cohort of 264 patients, where it consistently outperformed state-of-the-art single-task and multi-stage models. For image synthesis, our model achieved a PSNR of 25.61 dB, compared to 23.80 dB from a single-task CDM. For anatomical segmentation, it improved the lumen Dice score to 0.89 from 0.87 and the challenging thrombus Dice score to 0.53 from 0.48 (nnU-Net). These segmentation enhancements led to more accurate clinical measurements, reducing the lumen diameter MAE to 4.19 mm from 5.78 mm and the thrombus area error to 33.85% from 41.45% when compared to nnU-Net. Code is available at https://github.com/yuxuanou623/AortaDiff.git.
Benchmarking Large Multimodal Models for Ophthalmic Visual Question Answering with OphthalWeChat
May 26, 2025Abstract:Purpose: To develop a bilingual multimodal visual question answering (VQA) benchmark for evaluating VLMs in ophthalmology. Methods: Ophthalmic image posts and associated captions published between January 1, 2016, and December 31, 2024, were collected from WeChat Official Accounts. Based on these captions, bilingual question-answer (QA) pairs in Chinese and English were generated using GPT-4o-mini. QA pairs were categorized into six subsets by question type and language: binary (Binary_CN, Binary_EN), single-choice (Single-choice_CN, Single-choice_EN), and open-ended (Open-ended_CN, Open-ended_EN). The benchmark was used to evaluate the performance of three VLMs: GPT-4o, Gemini 2.0 Flash, and Qwen2.5-VL-72B-Instruct. Results: The final OphthalWeChat dataset included 3,469 images and 30,120 QA pairs across 9 ophthalmic subspecialties, 548 conditions, 29 imaging modalities, and 68 modality combinations. Gemini 2.0 Flash achieved the highest overall accuracy (0.548), outperforming GPT-4o (0.522, P < 0.001) and Qwen2.5-VL-72B-Instruct (0.514, P < 0.001). It also led in both Chinese (0.546) and English subsets (0.550). Subset-specific performance showed Gemini 2.0 Flash excelled in Binary_CN (0.687), Single-choice_CN (0.666), and Single-choice_EN (0.646), while GPT-4o ranked highest in Binary_EN (0.717), Open-ended_CN (BLEU-1: 0.301; BERTScore: 0.382), and Open-ended_EN (BLEU-1: 0.183; BERTScore: 0.240). Conclusions: This study presents the first bilingual VQA benchmark for ophthalmology, distinguished by its real-world context and inclusion of multiple examinations per patient. The dataset reflects authentic clinical decision-making scenarios and enables quantitative evaluation of VLMs, supporting the development of accurate, specialized, and trustworthy AI systems for eye care.
Template-Guided Reconstruction of Pulmonary Segments with Neural Implicit Functions
May 13, 2025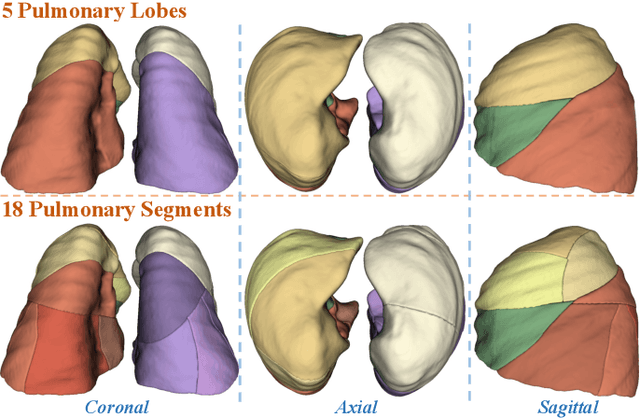
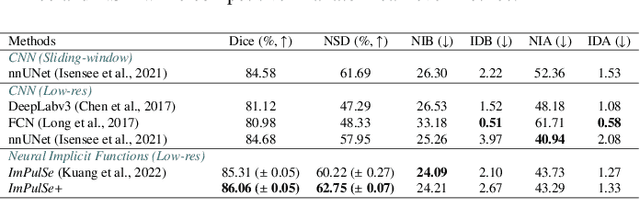
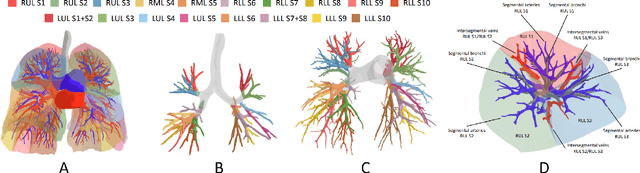
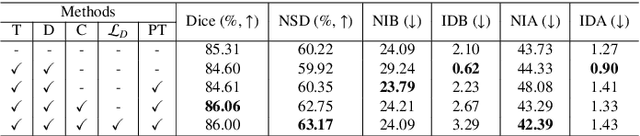
Abstract:High-quality 3D reconstruction of pulmonary segments plays a crucial role in segmentectomy and surgical treatment planning for lung cancer. Due to the resolution requirement of the target reconstruction, conventional deep learning-based methods often suffer from computational resource constraints or limited granularity. Conversely, implicit modeling is favored due to its computational efficiency and continuous representation at any resolution. We propose a neural implicit function-based method to learn a 3D surface to achieve anatomy-aware, precise pulmonary segment reconstruction, represented as a shape by deforming a learnable template. Additionally, we introduce two clinically relevant evaluation metrics to assess the reconstruction comprehensively. Further, due to the absence of publicly available shape datasets to benchmark reconstruction algorithms, we developed a shape dataset named Lung3D, including the 3D models of 800 labeled pulmonary segments and the corresponding airways, arteries, veins, and intersegmental veins. We demonstrate that the proposed approach outperforms existing methods, providing a new perspective for pulmonary segment reconstruction. Code and data will be available at https://github.com/M3DV/ImPulSe.
AI-powered virtual eye: perspective, challenges and opportunities
May 07, 2025Abstract:We envision the "virtual eye" as a next-generation, AI-powered platform that uses interconnected foundation models to simulate the eye's intricate structure and biological function across all scales. Advances in AI, imaging, and multiomics provide a fertile ground for constructing a universal, high-fidelity digital replica of the human eye. This perspective traces the evolution from early mechanistic and rule-based models to contemporary AI-driven approaches, integrating in a unified model with multimodal, multiscale, dynamic predictive capabilities and embedded feedback mechanisms. We propose a development roadmap emphasizing the roles of large-scale multimodal datasets, generative AI, foundation models, agent-based architectures, and interactive interfaces. Despite challenges in interpretability, ethics, data processing and evaluation, the virtual eye holds the potential to revolutionize personalized ophthalmic care and accelerate research into ocular health and disease.
DiffAtlas: GenAI-fying Atlas Segmentation via Image-Mask Diffusion
Mar 09, 2025Abstract:Accurate medical image segmentation is crucial for precise anatomical delineation. Deep learning models like U-Net have shown great success but depend heavily on large datasets and struggle with domain shifts, complex structures, and limited training samples. Recent studies have explored diffusion models for segmentation by iteratively refining masks. However, these methods still retain the conventional image-to-mask mapping, making them highly sensitive to input data, which hampers stability and generalization. In contrast, we introduce DiffAtlas, a novel generative framework that models both images and masks through diffusion during training, effectively ``GenAI-fying'' atlas-based segmentation. During testing, the model is guided to generate a specific target image-mask pair, from which the corresponding mask is obtained. DiffAtlas retains the robustness of the atlas paradigm while overcoming its scalability and domain-specific limitations. Extensive experiments on CT and MRI across same-domain, cross-modality, varying-domain, and different data-scale settings using the MMWHS and TotalSegmentator datasets demonstrate that our approach outperforms existing methods, particularly in limited-data and zero-shot modality segmentation. Code is available at https://github.com/M3DV/DiffAtlas.
Fundus2Globe: Generative AI-Driven 3D Digital Twins for Personalized Myopia Management
Feb 18, 2025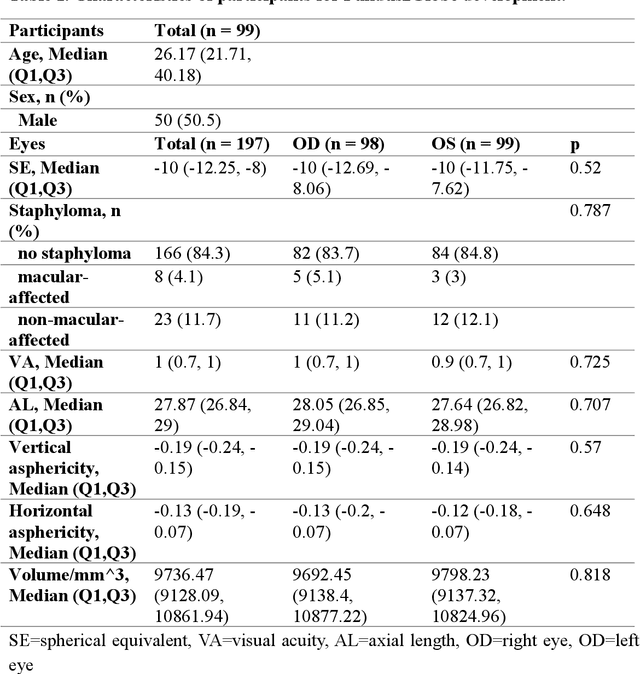
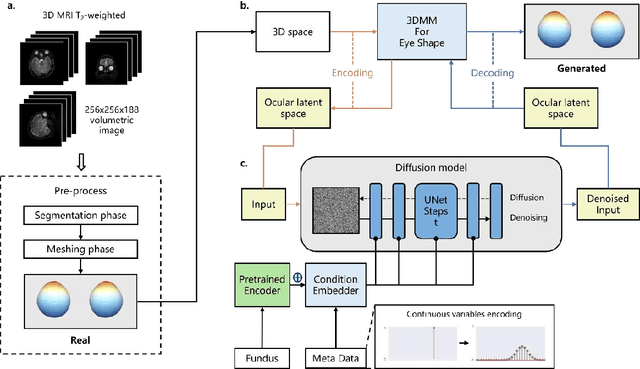
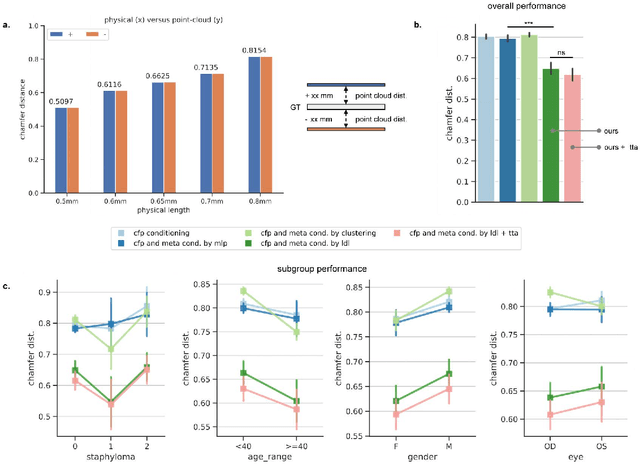
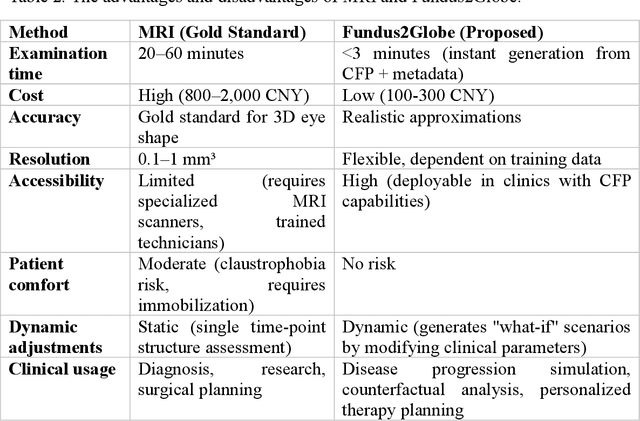
Abstract:Myopia, projected to affect 50% population globally by 2050, is a leading cause of vision loss. Eyes with pathological myopia exhibit distinctive shape distributions, which are closely linked to the progression of vision-threatening complications. Recent understanding of eye-shape-based biomarkers requires magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), however, it is costly and unrealistic in routine ophthalmology clinics. We present Fundus2Globe, the first AI framework that synthesizes patient-specific 3D eye globes from ubiquitous 2D color fundus photographs (CFPs) and routine metadata (axial length, spherical equivalent), bypassing MRI dependency. By integrating a 3D morphable eye model (encoding biomechanical shape priors) with a latent diffusion model, our approach achieves submillimeter accuracy in reconstructing posterior ocular anatomy efficiently. Fundus2Globe uniquely quantifies how vision-threatening lesions (e.g., staphylomas) in CFPs correlate with MRI-validated 3D shape abnormalities, enabling clinicians to simulate posterior segment changes in response to refractive shifts. External validation demonstrates its robust generation performance, ensuring fairness across underrepresented groups. By transforming 2D fundus imaging into 3D digital replicas of ocular structures, Fundus2Globe is a gateway for precision ophthalmology, laying the foundation for AI-driven, personalized myopia management.
MedTet: An Online Motion Model for 4D Heart Reconstruction
Dec 03, 2024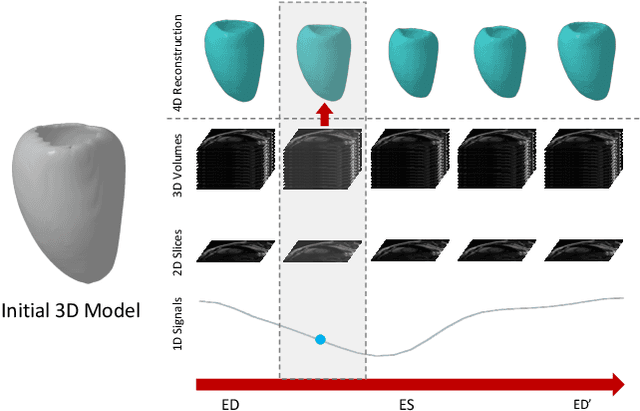
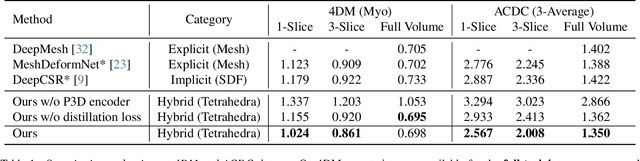
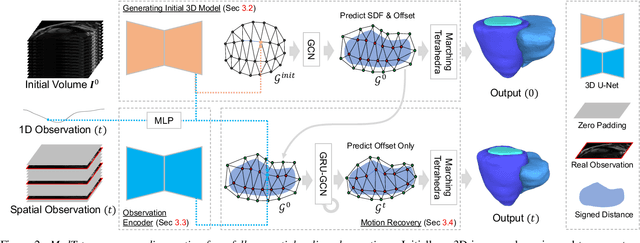
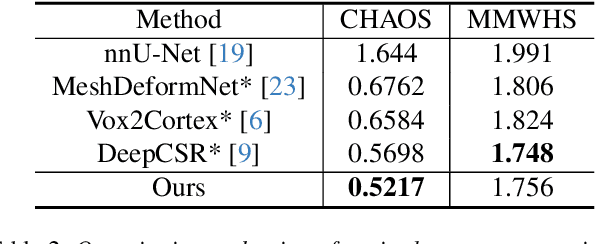
Abstract:We present a novel approach to reconstruction of 3D cardiac motion from sparse intraoperative data. While existing methods can accurately reconstruct 3D organ geometries from full 3D volumetric imaging, they cannot be used during surgical interventions where usually limited observed data, such as a few 2D frames or 1D signals, is available in real-time. We propose a versatile framework for reconstructing 3D motion from such partial data. It discretizes the 3D space into a deformable tetrahedral grid with signed distance values, providing implicit unlimited resolution while maintaining explicit control over motion dynamics. Given an initial 3D model reconstructed from pre-operative full volumetric data, our system, equipped with an universal observation encoder, can reconstruct coherent 3D cardiac motion from full 3D volumes, a few 2D MRI slices or even 1D signals. Extensive experiments on cardiac intervention scenarios demonstrate our ability to generate plausible and anatomically consistent 3D motion reconstructions from various sparse real-time observations, highlighting its potential for multimodal cardiac imaging. Our code and model will be made available at https://github.com/Scalsol/MedTet.
Fundus to Fluorescein Angiography Video Generation as a Retinal Generative Foundation Model
Oct 17, 2024



Abstract:Fundus fluorescein angiography (FFA) is crucial for diagnosing and monitoring retinal vascular issues but is limited by its invasive nature and restricted accessibility compared to color fundus (CF) imaging. Existing methods that convert CF images to FFA are confined to static image generation, missing the dynamic lesional changes. We introduce Fundus2Video, an autoregressive generative adversarial network (GAN) model that generates dynamic FFA videos from single CF images. Fundus2Video excels in video generation, achieving an FVD of 1497.12 and a PSNR of 11.77. Clinical experts have validated the fidelity of the generated videos. Additionally, the model's generator demonstrates remarkable downstream transferability across ten external public datasets, including blood vessel segmentation, retinal disease diagnosis, systemic disease prediction, and multimodal retrieval, showcasing impressive zero-shot and few-shot capabilities. These findings position Fundus2Video as a powerful, non-invasive alternative to FFA exams and a versatile retinal generative foundation model that captures both static and temporal retinal features, enabling the representation of complex inter-modality relationships.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge