Yibo Guo
Easy Adaptation: An Efficient Task-Specific Knowledge Injection Method for Large Models in Resource-Constrained Environments
Dec 19, 2025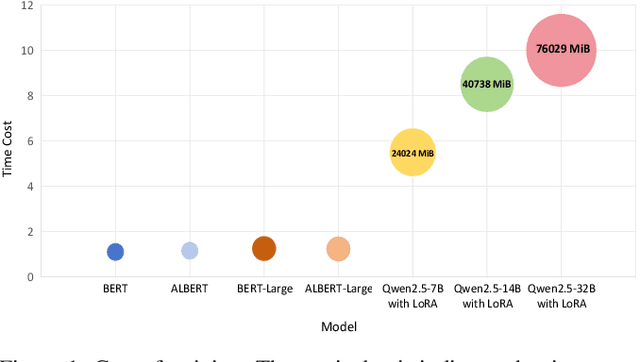
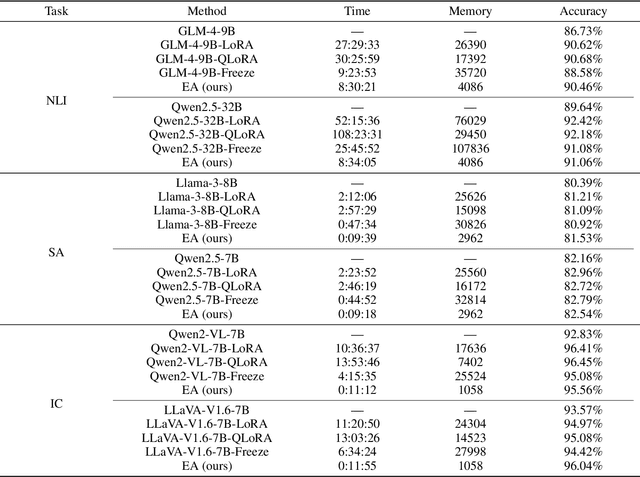
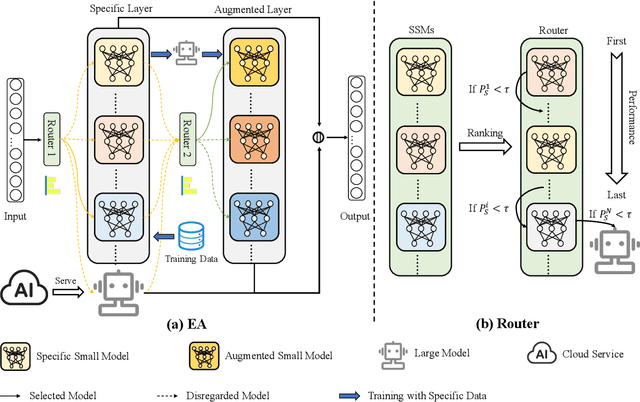
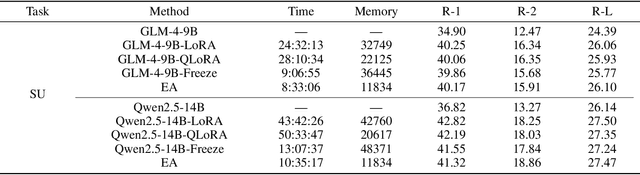
Abstract:While the enormous parameter scale endows Large Models (LMs) with unparalleled performance, it also limits their adaptability across specific tasks. Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT) has emerged as a critical approach for effectively adapting LMs to a diverse range of downstream tasks. However, existing PEFT methods face two primary challenges: (1) High resource cost. Although PEFT methods significantly reduce resource demands compared to full fine-tuning, it still requires substantial time and memory, making it impractical in resource-constrained environments. (2) Parameter dependency. PEFT methods heavily rely on updating a subset of parameters associated with LMs to incorporate task-specific knowledge. Yet, due to increasing competition in the LMs landscape, many companies have adopted closed-source policies for their leading models, offering access only via Application Programming Interface (APIs). Whereas, the expense is often cost-prohibitive and difficult to sustain, as the fine-tuning process of LMs is extremely slow. Even if small models perform far worse than LMs in general, they can achieve superior results on particular distributions while requiring only minimal resources. Motivated by this insight, we propose Easy Adaptation (EA), which designs Specific Small Models (SSMs) to complement the underfitted data distribution for LMs. Extensive experiments show that EA matches the performance of PEFT on diverse tasks without accessing LM parameters, and requires only minimal resources.
AI-powered virtual eye: perspective, challenges and opportunities
May 07, 2025Abstract:We envision the "virtual eye" as a next-generation, AI-powered platform that uses interconnected foundation models to simulate the eye's intricate structure and biological function across all scales. Advances in AI, imaging, and multiomics provide a fertile ground for constructing a universal, high-fidelity digital replica of the human eye. This perspective traces the evolution from early mechanistic and rule-based models to contemporary AI-driven approaches, integrating in a unified model with multimodal, multiscale, dynamic predictive capabilities and embedded feedback mechanisms. We propose a development roadmap emphasizing the roles of large-scale multimodal datasets, generative AI, foundation models, agent-based architectures, and interactive interfaces. Despite challenges in interpretability, ethics, data processing and evaluation, the virtual eye holds the potential to revolutionize personalized ophthalmic care and accelerate research into ocular health and disease.
Emergent Incident Response for Unmanned Warehouses with Multi-agent Systems*
May 29, 2023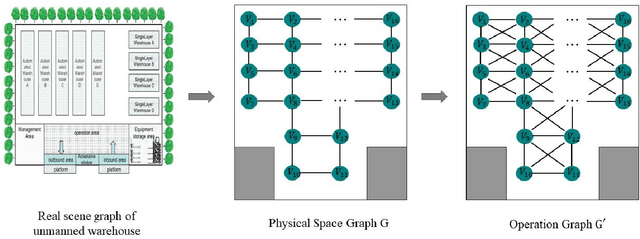
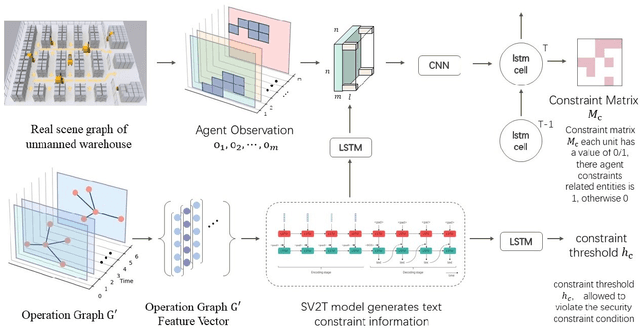
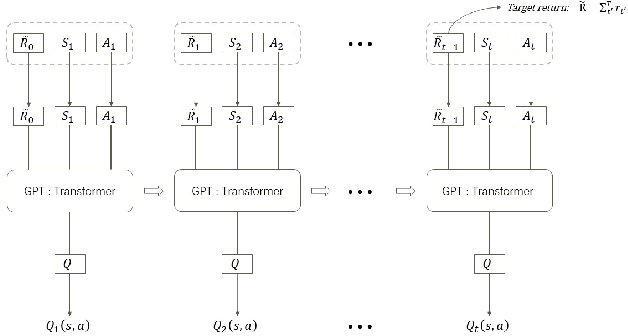
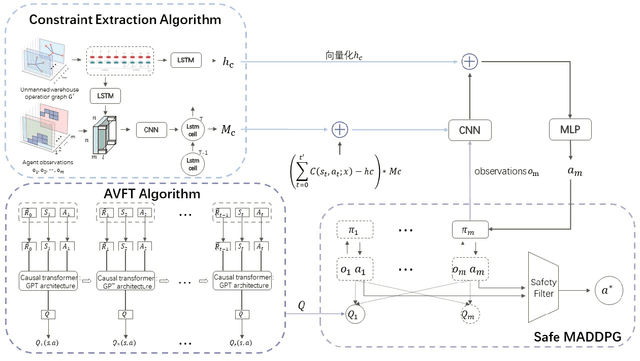
Abstract:Unmanned warehouses are an important part of logistics, and improving their operational efficiency can effectively enhance service efficiency. However, due to the complexity of unmanned warehouse systems and their susceptibility to errors, incidents may occur during their operation, most often in inbound and outbound operations, which can decrease operational efficiency. Hence it is crucial to to improve the response to such incidents. This paper proposes a collaborative optimization algorithm for emergent incident response based on Safe-MADDPG. To meet safety requirements during emergent incident response, we investigated the intrinsic hidden relationships between various factors. By obtaining constraint information of agents during the emergent incident response process and of the dynamic environment of unmanned warehouses on agents, the algorithm reduces safety risks and avoids the occurrence of chain accidents; this enables an unmanned system to complete emergent incident response tasks and achieve its optimization objectives: (1) minimizing the losses caused by emergent incidents; and (2) maximizing the operational efficiency of inbound and outbound operations during the response process. A series of experiments conducted in a simulated unmanned warehouse scenario demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method.
An Emergency Disposal Decision-making Method with Human--Machine Collaboration
May 29, 2023Abstract:Rapid developments in artificial intelligence technology have led to unmanned systems replacing human beings in many fields requiring high-precision predictions and decisions. In modern operational environments, all job plans are affected by emergency events such as equipment failures and resource shortages, making a quick resolution critical. The use of unmanned systems to assist decision-making can improve resolution efficiency, but their decision-making is not interpretable and may make the wrong decisions. Current unmanned systems require human supervision and control. Based on this, we propose a collaborative human--machine method for resolving unplanned events using two phases: task filtering and task scheduling. In the task filtering phase, we propose a human--machine collaborative decision-making algorithm for dynamic tasks. The GACRNN model is used to predict the state of the job nodes, locate the key nodes, and generate a machine-predicted resolution task list. A human decision-maker supervises the list in real time and modifies and confirms the machine-predicted list through the human--machine interface. In the task scheduling phase, we propose a scheduling algorithm that integrates human experience constraints. The steps to resolve an event are inserted into the normal job sequence to schedule the resolution. We propose several human--machine collaboration methods in each phase to generate steps to resolve an unplanned event while minimizing the impact on the original job plan.
Prototype as Query for Few Shot Semantic Segmentation
Nov 27, 2022



Abstract:Few-shot Semantic Segmentation (FSS) was proposed to segment unseen classes in a query image, referring to only a few annotated examples named support images. One of the characteristics of FSS is spatial inconsistency between query and support targets, e.g., texture or appearance. This greatly challenges the generalization ability of methods for FSS, which requires to effectively exploit the dependency of the query image and the support examples. Most existing methods abstracted support features into prototype vectors and implemented the interaction with query features using cosine similarity or feature concatenation. However, this simple interaction may not capture spatial details in query features. To alleviate this limitation, a few methods utilized all pixel-wise support information via computing the pixel-wise correlations between paired query and support features implemented with the attention mechanism of Transformer. These approaches suffer from heavy computation on the dot-product attention between all pixels of support and query features. In this paper, we propose a simple yet effective framework built upon Transformer termed as ProtoFormer to fully capture spatial details in query features. It views the abstracted prototype of the target class in support features as Query and the query features as Key and Value embeddings, which are input to the Transformer decoder. In this way, the spatial details can be better captured and the semantic features of target class in the query image can be focused. The output of the Transformer-based module can be viewed as semantic-aware dynamic kernels to filter out the segmentation mask from the enriched query features. Extensive experiments on PASCAL-$5^{i}$ and COCO-$20^{i}$ show that our ProtoFormer significantly advances the state-of-the-art methods.
Decision-making of Emergent Incident based on P-MADDPG
Mar 19, 2022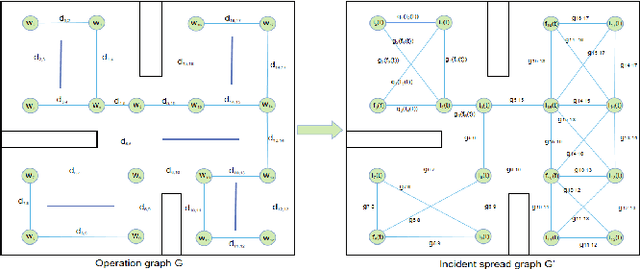
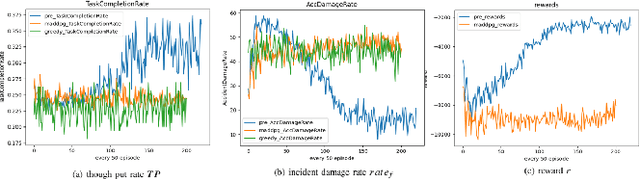
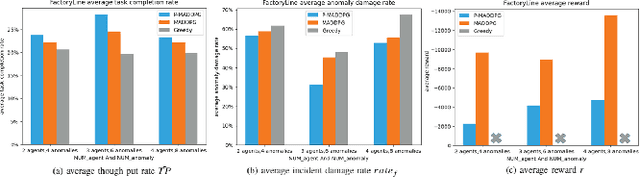
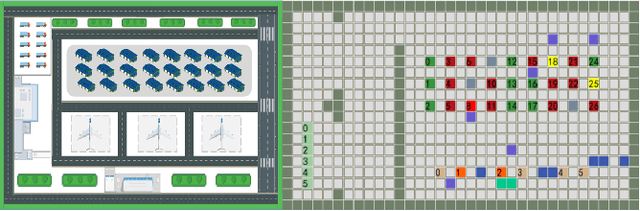
Abstract:In recent years, human casualties and damage to resources caused by emergent incidents have become a serious problem worldwide. In this paper, we model the emergency decision-making problem and use Multi-agent System (MAS) to solve the problem that the decision speed cannot keep up with the spreading speed. MAS can play an important role in the automated execution of these tasks to reduce mission completion time. In this paper, we propose a P-MADDPG algorithm to solve the emergency decision-making problem of emergent incidents, which predicts the nodes where an incident may occur in the next time by GRU model and makes decisions before the incident occurs, thus solving the problem that the decision speed cannot keep up with the spreading speed. A simulation environment was established for realistic scenarios, and three scenarios were selected to test the performance of P-MADDPG in emergency decision-making problems for emergent incidents: unmanned storage, factory assembly line, and civil airport baggage transportation. Simulation results using the P-MADDPG algorithm are compared with the greedy algorithm and the MADDPG algorithm, and the final experimental results show that the P-MADDPG algorithm converges faster and better than the other algorithms in scenarios of different sizes. This shows that the P-MADDP algorithm is effective for emergency decision-making in emergent incident.
Zero-sample surface defect detection and classification based on semantic feedback neural network
Jun 15, 2021



Abstract:Defect detection and classification technology has changed from traditional artificial visual inspection to current intelligent automated inspection, but most of the current defect detection methods are training related detection models based on a data-driven approach, taking into account the difficulty of collecting some sample data in the industrial field. We apply zero-shot learning technology to the industrial field. Aiming at the problem of the existing "Latent Feature Guide Attribute Attention" (LFGAA) zero-shot image classification network, the output latent attributes and artificially defined attributes are different in the semantic space, which leads to the problem of model performance degradation, proposed an LGFAA network based on semantic feedback, and improved model performance by constructing semantic embedded modules and feedback mechanisms. At the same time, for the common domain shift problem in zero-shot learning, based on the idea of co-training algorithm using the difference information between different views of data to learn from each other, we propose an Ensemble Co-training algorithm, which adaptively reduces the prediction error in image tag embedding from multiple angles. Various experiments conducted on the zero-shot dataset and the cylinder liner dataset in the industrial field provide competitive results.
A self-adapting super-resolution structures framework for automatic design of GAN
Jun 10, 2021



Abstract:With the development of deep learning, the single super-resolution image reconstruction network models are becoming more and more complex. Small changes in hyperparameters of the models have a greater impact on model performance. In the existing works, experts have gradually explored a set of optimal model parameters based on empirical values or performing brute-force search. In this paper, we introduce a new super-resolution image reconstruction generative adversarial network framework, and a Bayesian optimization method used to optimizing the hyperparameters of the generator and discriminator. The generator is made by self-calibrated convolution, and discriminator is made by convolution lays. We have defined the hyperparameters such as the number of network layers and the number of neurons. Our method adopts Bayesian optimization as a optimization policy of GAN in our model. Not only can find the optimal hyperparameter solution automatically, but also can construct a super-resolution image reconstruction network, reducing the manual workload. Experiments show that Bayesian optimization can search the optimal solution earlier than the other two optimization algorithms.
Super-Resolution Image Reconstruction Based on Self-Calibrated Convolutional GAN
Jun 10, 2021



Abstract:With the effective application of deep learning in computer vision, breakthroughs have been made in the research of super-resolution images reconstruction. However, many researches have pointed out that the insufficiency of the neural network extraction on image features may bring the deteriorating of newly reconstructed image. On the other hand, the generated pictures are sometimes too artificial because of over-smoothing. In order to solve the above problems, we propose a novel self-calibrated convolutional generative adversarial networks. The generator consists of feature extraction and image reconstruction. Feature extraction uses self-calibrated convolutions, which contains four portions, and each portion has specific functions. It can not only expand the range of receptive fields, but also obtain long-range spatial and inter-channel dependencies. Then image reconstruction is performed, and finally a super-resolution image is reconstructed. We have conducted thorough experiments on different datasets including set5, set14 and BSD100 under the SSIM evaluation method. The experimental results prove the effectiveness of the proposed network.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge