Qifeng Chen
FastVMT: Eliminating Redundancy in Video Motion Transfer
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Video motion transfer aims to synthesize videos by generating visual content according to a text prompt while transferring the motion pattern observed in a reference video. Recent methods predominantly use the Diffusion Transformer (DiT) architecture. To achieve satisfactory runtime, several methods attempt to accelerate the computations in the DiT, but fail to address structural sources of inefficiency. In this work, we identify and remove two types of computational redundancy in earlier work: motion redundancy arises because the generic DiT architecture does not reflect the fact that frame-to-frame motion is small and smooth; gradient redundancy occurs if one ignores that gradients change slowly along the diffusion trajectory. To mitigate motion redundancy, we mask the corresponding attention layers to a local neighborhood such that interaction weights are not computed unnecessarily distant image regions. To exploit gradient redundancy, we design an optimization scheme that reuses gradients from previous diffusion steps and skips unwarranted gradient computations. On average, FastVMT achieves a 3.43x speedup without degrading the visual fidelity or the temporal consistency of the generated videos.
Show, Don't Tell: Morphing Latent Reasoning into Image Generation
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Text-to-image (T2I) generation has achieved remarkable progress, yet existing methods often lack the ability to dynamically reason and refine during generation--a hallmark of human creativity. Current reasoning-augmented paradigms most rely on explicit thought processes, where intermediate reasoning is decoded into discrete text at fixed steps with frequent image decoding and re-encoding, leading to inefficiencies, information loss, and cognitive mismatches. To bridge this gap, we introduce LatentMorph, a novel framework that seamlessly integrates implicit latent reasoning into the T2I generation process. At its core, LatentMorph introduces four lightweight components: (i) a condenser for summarizing intermediate generation states into compact visual memory, (ii) a translator for converting latent thoughts into actionable guidance, (iii) a shaper for dynamically steering next image token predictions, and (iv) an RL-trained invoker for adaptively determining when to invoke reasoning. By performing reasoning entirely in continuous latent spaces, LatentMorph avoids the bottlenecks of explicit reasoning and enables more adaptive self-refinement. Extensive experiments demonstrate that LatentMorph (I) enhances the base model Janus-Pro by $16\%$ on GenEval and $25\%$ on T2I-CompBench; (II) outperforms explicit paradigms (e.g., TwiG) by $15\%$ and $11\%$ on abstract reasoning tasks like WISE and IPV-Txt, (III) while reducing inference time by $44\%$ and token consumption by $51\%$; and (IV) exhibits $71\%$ cognitive alignment with human intuition on reasoning invocation.
HumanX: Toward Agile and Generalizable Humanoid Interaction Skills from Human Videos
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Enabling humanoid robots to perform agile and adaptive interactive tasks has long been a core challenge in robotics. Current approaches are bottlenecked by either the scarcity of realistic interaction data or the need for meticulous, task-specific reward engineering, which limits their scalability. To narrow this gap, we present HumanX, a full-stack framework that compiles human video into generalizable, real-world interaction skills for humanoids, without task-specific rewards. HumanX integrates two co-designed components: XGen, a data generation pipeline that synthesizes diverse and physically plausible robot interaction data from video while supporting scalable data augmentation; and XMimic, a unified imitation learning framework that learns generalizable interaction skills. Evaluated across five distinct domains--basketball, football, badminton, cargo pickup, and reactive fighting--HumanX successfully acquires 10 different skills and transfers them zero-shot to a physical Unitree G1 humanoid. The learned capabilities include complex maneuvers such as pump-fake turnaround fadeaway jumpshots without any external perception, as well as interactive tasks like sustained human-robot passing sequences over 10 consecutive cycles--learned from a single video demonstration. Our experiments show that HumanX achieves over 8 times higher generalization success than prior methods, demonstrating a scalable and task-agnostic pathway for learning versatile, real-world robot interactive skills.
FlyAware: Inertia-Aware Aerial Manipulation via Vision-Based Estimation and Post-Grasp Adaptation
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Aerial manipulators (AMs) are gaining increasing attention in automated transportation and emergency services due to their superior dexterity compared to conventional multirotor drones. However, their practical deployment is challenged by the complexity of time-varying inertial parameters, which are highly sensitive to payload variations and manipulator configurations. Inspired by human strategies for interacting with unknown objects, this letter presents a novel onboard framework for robust aerial manipulation. The proposed system integrates a vision-based pre-grasp inertia estimation module with a post-grasp adaptation mechanism, enabling real-time estimation and adaptation of inertial dynamics. For control, we develop an inertia-aware adaptive control strategy based on gain scheduling, and assess its robustness via frequency-domain system identification. Our study provides new insights into post-grasp control for AMs, and real-world experiments validate the effectiveness and feasibility of the proposed framework.
TIGaussian: Disentangle Gaussians for Spatial-Awared Text-Image-3D Alignment
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:While visual-language models have profoundly linked features between texts and images, the incorporation of 3D modality data, such as point clouds and 3D Gaussians, further enables pretraining for 3D-related tasks, e.g., cross-modal retrieval, zero-shot classification, and scene recognition. As challenges remain in extracting 3D modal features and bridging the gap between different modalities, we propose TIGaussian, a framework that harnesses 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) characteristics to strengthen cross-modality alignment through multi-branch 3DGS tokenizer and modality-specific 3D feature alignment strategies. Specifically, our multi-branch 3DGS tokenizer decouples the intrinsic properties of 3DGS structures into compact latent representations, enabling more generalizable feature extraction. To further bridge the modality gap, we develop a bidirectional cross-modal alignment strategies: a multi-view feature fusion mechanism that leverages diffusion priors to resolve perspective ambiguity in image-3D alignment, while a text-3D projection module adaptively maps 3D features to text embedding space for better text-3D alignment. Extensive experiments on various datasets demonstrate the state-of-the-art performance of TIGaussian in multiple tasks.
Active Intelligence in Video Avatars via Closed-loop World Modeling
Dec 23, 2025Abstract:Current video avatar generation methods excel at identity preservation and motion alignment but lack genuine agency, they cannot autonomously pursue long-term goals through adaptive environmental interaction. We address this by introducing L-IVA (Long-horizon Interactive Visual Avatar), a task and benchmark for evaluating goal-directed planning in stochastic generative environments, and ORCA (Online Reasoning and Cognitive Architecture), the first framework enabling active intelligence in video avatars. ORCA embodies Internal World Model (IWM) capabilities through two key innovations: (1) a closed-loop OTAR cycle (Observe-Think-Act-Reflect) that maintains robust state tracking under generative uncertainty by continuously verifying predicted outcomes against actual generations, and (2) a hierarchical dual-system architecture where System 2 performs strategic reasoning with state prediction while System 1 translates abstract plans into precise, model-specific action captions. By formulating avatar control as a POMDP and implementing continuous belief updating with outcome verification, ORCA enables autonomous multi-step task completion in open-domain scenarios. Extensive experiments demonstrate that ORCA significantly outperforms open-loop and non-reflective baselines in task success rate and behavioral coherence, validating our IWM-inspired design for advancing video avatar intelligence from passive animation to active, goal-oriented behavior.
LongVideoAgent: Multi-Agent Reasoning with Long Videos
Dec 23, 2025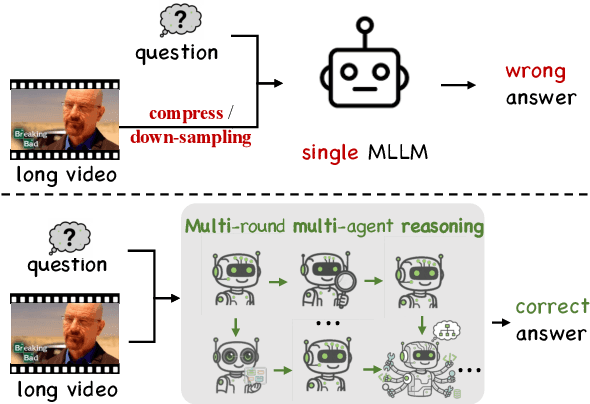


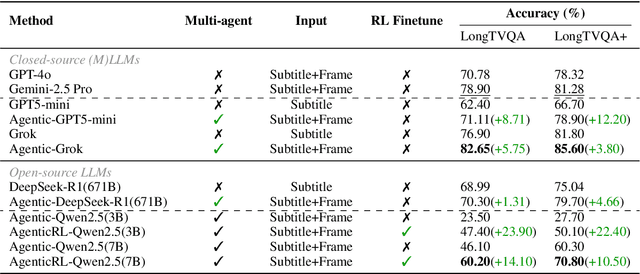
Abstract:Recent advances in multimodal LLMs and systems that use tools for long-video QA point to the promise of reasoning over hour-long episodes. However, many methods still compress content into lossy summaries or rely on limited toolsets, weakening temporal grounding and missing fine-grained cues. We propose a multi-agent framework in which a master LLM coordinates a grounding agent to localize question-relevant segments and a vision agent to extract targeted textual observations. The master agent plans with a step limit, and is trained with reinforcement learning to encourage concise, correct, and efficient multi-agent cooperation. This design helps the master agent focus on relevant clips via grounding, complements subtitles with visual detail, and yields interpretable trajectories. On our proposed LongTVQA and LongTVQA+ which are episode-level datasets aggregated from TVQA/TVQA+, our multi-agent system significantly outperforms strong non-agent baselines. Experiments also show reinforcement learning further strengthens reasoning and planning for the trained agent. Code and data will be shared at https://longvideoagent.github.io/.
Learning Generalizable Hand-Object Tracking from Synthetic Demonstrations
Dec 22, 2025Abstract:We present a system for learning generalizable hand-object tracking controllers purely from synthetic data, without requiring any human demonstrations. Our approach makes two key contributions: (1) HOP, a Hand-Object Planner, which can synthesize diverse hand-object trajectories; and (2) HOT, a Hand-Object Tracker that bridges synthetic-to-physical transfer through reinforcement learning and interaction imitation learning, delivering a generalizable controller conditioned on target hand-object states. Our method extends to diverse object shapes and hand morphologies. Through extensive evaluations, we show that our approach enables dexterous hands to track challenging, long-horizon sequences including object re-arrangement and agile in-hand reorientation. These results represent a significant step toward scalable foundation controllers for manipulation that can learn entirely from synthetic data, breaking the data bottleneck that has long constrained progress in dexterous manipulation.
Robust-R1: Degradation-Aware Reasoning for Robust Visual Understanding
Dec 19, 2025Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models struggle to maintain reliable performance under extreme real-world visual degradations, which impede their practical robustness. Existing robust MLLMs predominantly rely on implicit training/adaptation that focuses solely on visual encoder generalization, suffering from limited interpretability and isolated optimization. To overcome these limitations, we propose Robust-R1, a novel framework that explicitly models visual degradations through structured reasoning chains. Our approach integrates: (i) supervised fine-tuning for degradation-aware reasoning foundations, (ii) reward-driven alignment for accurately perceiving degradation parameters, and (iii) dynamic reasoning depth scaling adapted to degradation intensity. To facilitate this approach, we introduce a specialized 11K dataset featuring realistic degradations synthesized across four critical real-world visual processing stages, each annotated with structured chains connecting degradation parameters, perceptual influence, pristine semantic reasoning chain, and conclusion. Comprehensive evaluations demonstrate state-of-the-art robustness: Robust-R1 outperforms all general and robust baselines on the real-world degradation benchmark R-Bench, while maintaining superior anti-degradation performance under multi-intensity adversarial degradations on MMMB, MMStar, and RealWorldQA.
The World is Your Canvas: Painting Promptable Events with Reference Images, Trajectories, and Text
Dec 18, 2025



Abstract:We present WorldCanvas, a framework for promptable world events that enables rich, user-directed simulation by combining text, trajectories, and reference images. Unlike text-only approaches and existing trajectory-controlled image-to-video methods, our multimodal approach combines trajectories -- encoding motion, timing, and visibility -- with natural language for semantic intent and reference images for visual grounding of object identity, enabling the generation of coherent, controllable events that include multi-agent interactions, object entry/exit, reference-guided appearance and counterintuitive events. The resulting videos demonstrate not only temporal coherence but also emergent consistency, preserving object identity and scene despite temporary disappearance. By supporting expressive world events generation, WorldCanvas advances world models from passive predictors to interactive, user-shaped simulators. Our project page is available at: https://worldcanvas.github.io/.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge