Haojian Huang
EvoEmpirBench: Dynamic Spatial Reasoning with Agent-ExpVer
Sep 16, 2025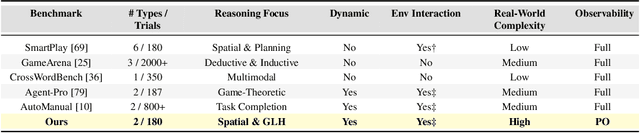
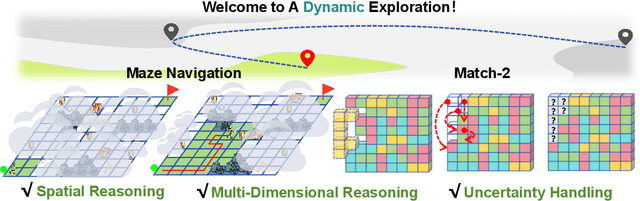
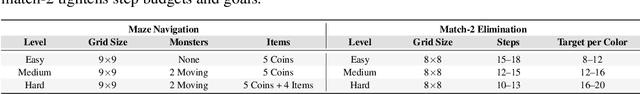
Abstract:Most existing spatial reasoning benchmarks focus on static or globally observable environments, failing to capture the challenges of long-horizon reasoning and memory utilization under partial observability and dynamic changes. We introduce two dynamic spatial benchmarks, locally observable maze navigation and match-2 elimination that systematically evaluate models' abilities in spatial understanding and adaptive planning when local perception, environment feedback, and global objectives are tightly coupled. Each action triggers structural changes in the environment, requiring continuous update of cognition and strategy. We further propose a subjective experience-based memory mechanism for cross-task experience transfer and validation. Experiments show that our benchmarks reveal key limitations of mainstream models in dynamic spatial reasoning and long-term memory, providing a comprehensive platform for future methodological advances. Our code and data are available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/EvoEmpirBench-143C/.
FakeHunter: Multimodal Step-by-Step Reasoning for Explainable Video Forensics
Aug 20, 2025Abstract:FakeHunter is a multimodal deepfake detection framework that combines memory-guided retrieval, chain-of-thought (Observation-Thought-Action) reasoning, and tool-augmented verification to provide accurate and interpretable video forensics. FakeHunter encodes visual content using CLIP and audio using CLAP, generating joint audio-visual embeddings that retrieve semantically similar real exemplars from a FAISS-indexed memory bank for contextual grounding. Guided by the retrieved context, the system iteratively reasons over evidence to localize manipulations and explain them. When confidence is low, it automatically invokes specialized tools-such as zoom-in image forensics or mel-spectrogram inspection-for fine-grained verification. Built on Qwen2.5-Omni-7B, FakeHunter produces structured JSON verdicts that specify what was modified, where it occurs, and why it is judged fake. We also introduce X-AVFake, a benchmark comprising 5.7k+ manipulated and real videos (950+ min) annotated with manipulation type, region/entity, violated reasoning category, and free-form justification. On X-AVFake, FakeHunter achieves an accuracy of 34.75%, outperforming the vanilla Qwen2.5-Omni-7B by 16.87 percentage points and MiniCPM-2.6 by 25.56 percentage points. Ablation studies reveal that memory retrieval contributes a 7.75 percentage point gain, and tool-based inspection improves low-confidence cases to 46.50%. Despite its multi-stage design, the pipeline processes a 10-minute clip in 8 minutes on a single NVIDIA A800 (0.8x real-time) or 2 minutes on four GPUs (0.2x), demonstrating practical deployability.
VistaDPO: Video Hierarchical Spatial-Temporal Direct Preference Optimization for Large Video Models
Apr 17, 2025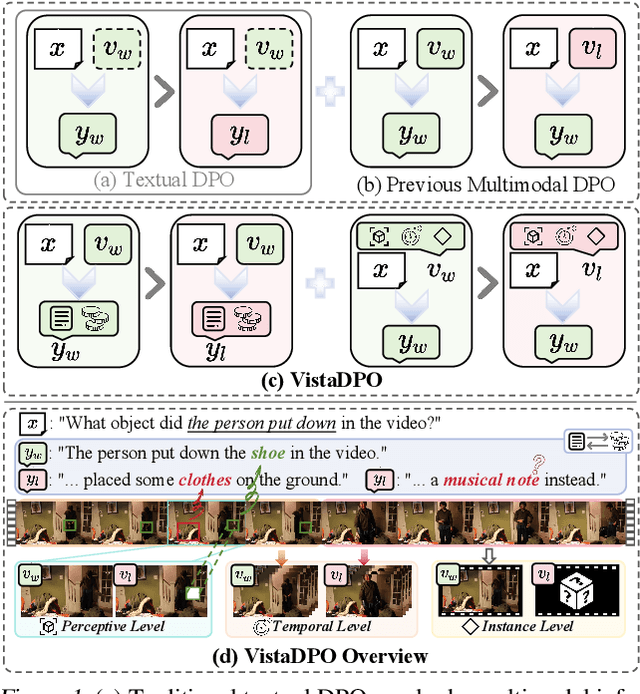
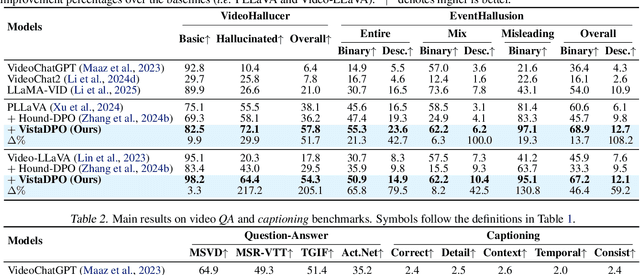
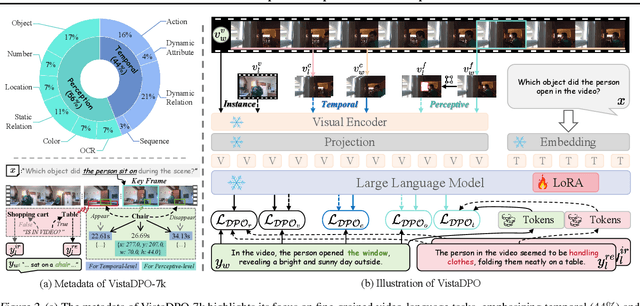
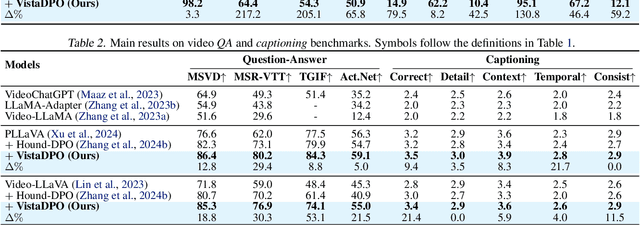
Abstract:Large Video Models (LVMs) built upon Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown promise in video understanding but often suffer from misalignment with human intuition and video hallucination issues. To address these challenges, we introduce VistaDPO, a novel framework for Video Hierarchical Spatial-Temporal Direct Preference Optimization. VistaDPO enhances text-video preference alignment across three hierarchical levels: i) Instance Level, aligning overall video content with responses; ii) Temporal Level, aligning video temporal semantics with event descriptions; and iii) Perceptive Level, aligning spatial objects with language tokens. Given the lack of datasets for fine-grained video-language preference alignment, we construct VistaDPO-7k, a dataset of 7.2K QA pairs annotated with chosen and rejected responses, along with spatial-temporal grounding information such as timestamps, keyframes, and bounding boxes. Extensive experiments on benchmarks such as Video Hallucination, Video QA, and Captioning performance tasks demonstrate that VistaDPO significantly improves the performance of existing LVMs, effectively mitigating video-language misalignment and hallucination. The code and data are available at https://github.com/HaroldChen19/VistaDPO.
VideoGen-of-Thought: Step-by-step generating multi-shot video with minimal manual intervention
Mar 20, 2025Abstract:Current video generation models excel at short clips but fail to produce cohesive multi-shot narratives due to disjointed visual dynamics and fractured storylines. Existing solutions either rely on extensive manual scripting/editing or prioritize single-shot fidelity over cross-scene continuity, limiting their practicality for movie-like content. We introduce VideoGen-of-Thought (VGoT), a step-by-step framework that automates multi-shot video synthesis from a single sentence by systematically addressing three core challenges: (1) Narrative Fragmentation: Existing methods lack structured storytelling. We propose dynamic storyline modeling, which first converts the user prompt into concise shot descriptions, then elaborates them into detailed, cinematic specifications across five domains (character dynamics, background continuity, relationship evolution, camera movements, HDR lighting), ensuring logical narrative progression with self-validation. (2) Visual Inconsistency: Existing approaches struggle with maintaining visual consistency across shots. Our identity-aware cross-shot propagation generates identity-preserving portrait (IPP) tokens that maintain character fidelity while allowing trait variations (expressions, aging) dictated by the storyline. (3) Transition Artifacts: Abrupt shot changes disrupt immersion. Our adjacent latent transition mechanisms implement boundary-aware reset strategies that process adjacent shots' features at transition points, enabling seamless visual flow while preserving narrative continuity. VGoT generates multi-shot videos that outperform state-of-the-art baselines by 20.4% in within-shot face consistency and 17.4% in style consistency, while achieving over 100% better cross-shot consistency and 10x fewer manual adjustments than alternatives.
Temporal Regularization Makes Your Video Generator Stronger
Mar 19, 2025Abstract:Temporal quality is a critical aspect of video generation, as it ensures consistent motion and realistic dynamics across frames. However, achieving high temporal coherence and diversity remains challenging. In this work, we explore temporal augmentation in video generation for the first time, and introduce FluxFlow for initial investigation, a strategy designed to enhance temporal quality. Operating at the data level, FluxFlow applies controlled temporal perturbations without requiring architectural modifications. Extensive experiments on UCF-101 and VBench benchmarks demonstrate that FluxFlow significantly improves temporal coherence and diversity across various video generation models, including U-Net, DiT, and AR-based architectures, while preserving spatial fidelity. These findings highlight the potential of temporal augmentation as a simple yet effective approach to advancing video generation quality.
DependEval: Benchmarking LLMs for Repository Dependency Understanding
Mar 09, 2025Abstract:While large language models (LLMs) have shown considerable promise in code generation, real-world software development demands advanced repository-level reasoning. This includes understanding dependencies, project structures, and managing multi-file changes. However, the ability of LLMs to effectively comprehend and handle complex code repositories has yet to be fully explored. To address challenges, we introduce a hierarchical benchmark designed to evaluate repository dependency understanding (DependEval). Benchmark is based on 15,576 repositories collected from real-world websites. It evaluates models on three core tasks: Dependency Recognition, Repository Construction, and Multi-file Editing, across 8 programming languages from actual code repositories. Our evaluation of over 25 LLMs reveals substantial performance gaps and provides valuable insights into repository-level code understanding.
VideoGen-of-Thought: A Collaborative Framework for Multi-Shot Video Generation
Dec 03, 2024Abstract:Current video generation models excel at generating short clips but still struggle with creating multi-shot, movie-like videos. Existing models trained on large-scale data on the back of rich computational resources are unsurprisingly inadequate for maintaining a logical storyline and visual consistency across multiple shots of a cohesive script since they are often trained with a single-shot objective. To this end, we propose VideoGen-of-Thought (VGoT), a collaborative and training-free architecture designed specifically for multi-shot video generation. VGoT is designed with three goals in mind as follows. Multi-Shot Video Generation: We divide the video generation process into a structured, modular sequence, including (1) Script Generation, which translates a curt story into detailed prompts for each shot; (2) Keyframe Generation, responsible for creating visually consistent keyframes faithful to character portrayals; and (3) Shot-Level Video Generation, which transforms information from scripts and keyframes into shots; (4) Smoothing Mechanism that ensures a consistent multi-shot output. Reasonable Narrative Design: Inspired by cinematic scriptwriting, our prompt generation approach spans five key domains, ensuring logical consistency, character development, and narrative flow across the entire video. Cross-Shot Consistency: We ensure temporal and identity consistency by leveraging identity-preserving (IP) embeddings across shots, which are automatically created from the narrative. Additionally, we incorporate a cross-shot smoothing mechanism, which integrates a reset boundary that effectively combines latent features from adjacent shots, resulting in smooth transitions and maintaining visual coherence throughout the video. Our experiments demonstrate that VGoT surpasses existing video generation methods in producing high-quality, coherent, multi-shot videos.
Recent Trends of Multimodal Affective Computing: A Survey from NLP Perspective
Sep 11, 2024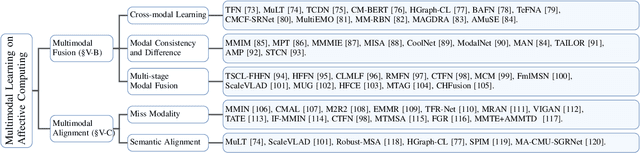
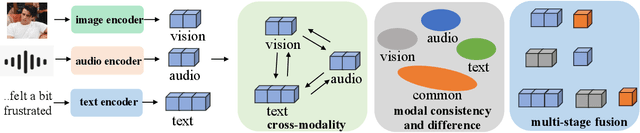

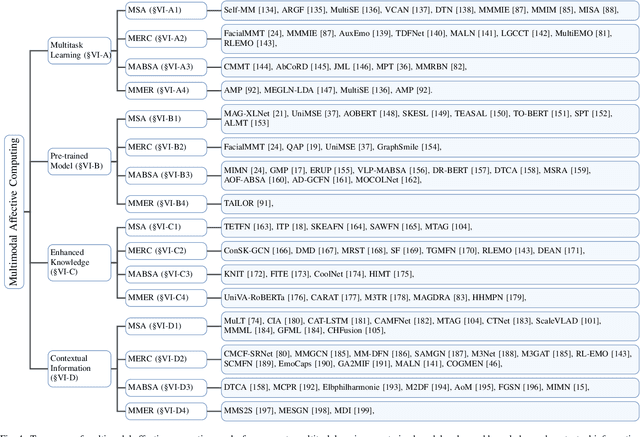
Abstract:Multimodal affective computing (MAC) has garnered increasing attention due to its broad applications in analyzing human behaviors and intentions, especially in text-dominated multimodal affective computing field. This survey presents the recent trends of multimodal affective computing from NLP perspective through four hot tasks: multimodal sentiment analysis, multimodal emotion recognition in conversation, multimodal aspect-based sentiment analysis and multimodal multi-label emotion recognition. The goal of this survey is to explore the current landscape of multimodal affective research, identify development trends, and highlight the similarities and differences across various tasks, offering a comprehensive report on the recent progress in multimodal affective computing from an NLP perspective. This survey covers the formalization of tasks, provides an overview of relevant works, describes benchmark datasets, and details the evaluation metrics for each task. Additionally, it briefly discusses research in multimodal affective computing involving facial expressions, acoustic signals, physiological signals, and emotion causes. Additionally, we discuss the technical approaches, challenges, and future directions in multimodal affective computing. To support further research, we released a repository that compiles related works in multimodal affective computing, providing detailed resources and references for the community.
Towards Robust Uncertainty-Aware Incomplete Multi-View Classification
Sep 10, 2024



Abstract:Handling incomplete data in multi-view classification is challenging, especially when traditional imputation methods introduce biases that compromise uncertainty estimation. Existing Evidential Deep Learning (EDL) based approaches attempt to address these issues, but they often struggle with conflicting evidence due to the limitations of the Dempster-Shafer combination rule, leading to unreliable decisions. To address these challenges, we propose the Alternating Progressive Learning Network (APLN), specifically designed to enhance EDL-based methods in incomplete MVC scenarios. Our approach mitigates bias from corrupted observed data by first applying coarse imputation, followed by mapping the data to a latent space. In this latent space, we progressively learn an evidence distribution aligned with the target domain, incorporating uncertainty considerations through EDL. Additionally, we introduce a conflict-aware Dempster-Shafer combination rule (DSCR) to better handle conflicting evidence. By sampling from the learned distribution, we optimize the latent representations of missing views, reducing bias and enhancing decision-making robustness. Extensive experiments demonstrate that APLN, combined with DSCR, significantly outperforms traditional methods, particularly in environments characterized by high uncertainty and conflicting evidence, establishing it as a promising solution for incomplete multi-view classification.
Trusted Unified Feature-Neighborhood Dynamics for Multi-View Classification
Sep 01, 2024Abstract:Multi-view classification (MVC) faces inherent challenges due to domain gaps and inconsistencies across different views, often resulting in uncertainties during the fusion process. While Evidential Deep Learning (EDL) has been effective in addressing view uncertainty, existing methods predominantly rely on the Dempster-Shafer combination rule, which is sensitive to conflicting evidence and often neglects the critical role of neighborhood structures within multi-view data. To address these limitations, we propose a Trusted Unified Feature-NEighborhood Dynamics (TUNED) model for robust MVC. This method effectively integrates local and global feature-neighborhood (F-N) structures for robust decision-making. Specifically, we begin by extracting local F-N structures within each view. To further mitigate potential uncertainties and conflicts in multi-view fusion, we employ a selective Markov random field that adaptively manages cross-view neighborhood dependencies. Additionally, we employ a shared parameterized evidence extractor that learns global consensus conditioned on local F-N structures, thereby enhancing the global integration of multi-view features. Experiments on benchmark datasets show that our method improves accuracy and robustness over existing approaches, particularly in scenarios with high uncertainty and conflicting views. The code will be made available at https://github.com/JethroJames/TUNED.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge