Hao Fei
Unveiling the Cognitive Compass: Theory-of-Mind-Guided Multimodal Emotion Reasoning
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Despite rapid progress in multimodal large language models (MLLMs), their capability for deep emotional understanding remains limited. We argue that genuine affective intelligence requires explicit modeling of Theory of Mind (ToM), the cognitive substrate from which emotions arise. To this end, we introduce HitEmotion, a ToM-grounded hierarchical benchmark that diagnoses capability breakpoints across increasing levels of cognitive depth. Second, we propose a ToM-guided reasoning chain that tracks mental states and calibrates cross-modal evidence to achieve faithful emotional reasoning. We further introduce TMPO, a reinforcement learning method that uses intermediate mental states as process-level supervision to guide and strengthen model reasoning. Extensive experiments show that HitEmotion exposes deep emotional reasoning deficits in state-of-the-art models, especially on cognitively demanding tasks. In evaluation, the ToM-guided reasoning chain and TMPO improve end-task accuracy and yield more faithful, more coherent rationales. In conclusion, our work provides the research community with a practical toolkit for evaluating and enhancing the cognition-based emotional understanding capabilities of MLLMs. Our dataset and code are available at: https://HitEmotion.github.io/.
SAMTok: Representing Any Mask with Two Words
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Pixel-wise capabilities are essential for building interactive intelligent systems. However, pixel-wise multi-modal LLMs (MLLMs) remain difficult to scale due to complex region-level encoders, specialized segmentation decoders, and incompatible training objectives. To address these challenges, we present SAMTok, a discrete mask tokenizer that converts any region mask into two special tokens and reconstructs the mask using these tokens with high fidelity. By treating masks as new language tokens, SAMTok enables base MLLMs (such as the QwenVL series) to learn pixel-wise capabilities through standard next-token prediction and simple reinforcement learning, without architectural modifications and specialized loss design. SAMTok builds on SAM2 and is trained on 209M diverse masks using a mask encoder and residual vector quantizer to produce discrete, compact, and information-rich tokens. With 5M SAMTok-formatted mask understanding and generation data samples, QwenVL-SAMTok attains state-of-the-art or comparable results on region captioning, region VQA, grounded conversation, referring segmentation, scene graph parsing, and multi-round interactive segmentation. We further introduce a textual answer-matching reward that enables efficient reinforcement learning for mask generation, delivering substantial improvements on GRES and GCG benchmarks. Our results demonstrate a scalable and straightforward paradigm for equipping MLLMs with strong pixel-wise capabilities. Our code and models are available.
JavisGPT: A Unified Multi-modal LLM for Sounding-Video Comprehension and Generation
Dec 28, 2025Abstract:This paper presents JavisGPT, the first unified multimodal large language model (MLLM) for Joint Audio-Video (JAV) comprehension and generation. JavisGPT adopts a concise encoder-LLM-decoder architecture, featuring a SyncFusion module for spatio-temporal audio-video fusion and synchrony-aware learnable queries to bridge a pretrained JAV-DiT generator. This design enables temporally coherent video-audio understanding and generation from multimodal instructions. We design an effective three-stage training pipeline consisting of multimodal pretraining, audio-video fine-tuning, and large-scale instruction-tuning, to progressively build multimodal comprehension and generation from existing vision-language models. To support this, we further construct JavisInst-Omni, a high-quality instruction dataset with over 200K GPT-4o-curated audio-video-text dialogues that span diverse and multi-level comprehension and generation scenarios. Extensive experiments on JAV comprehension and generation benchmarks show that JavisGPT outperforms existing MLLMs, particularly in complex and temporally synchronized settings.
Event Extraction in Large Language Model
Dec 22, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) and multimodal LLMs are changing event extraction (EE): prompting and generation can often produce structured outputs in zero shot or few shot settings. Yet LLM based pipelines face deployment gaps, including hallucinations under weak constraints, fragile temporal and causal linking over long contexts and across documents, and limited long horizon knowledge management within a bounded context window. We argue that EE should be viewed as a system component that provides a cognitive scaffold for LLM centered solutions. Event schemas and slot constraints create interfaces for grounding and verification; event centric structures act as controlled intermediate representations for stepwise reasoning; event links support relation aware retrieval with graph based RAG; and event stores offer updatable episodic and agent memory beyond the context window. This survey covers EE in text and multimodal settings, organizing tasks and taxonomy, tracing method evolution from rule based and neural models to instruction driven and generative frameworks, and summarizing formulations, decoding strategies, architectures, representations, datasets, and evaluation. We also review cross lingual, low resource, and domain specific settings, and highlight open challenges and future directions for reliable event centric systems. Finally, we outline open challenges and future directions that are central to the LLM era, aiming to evolve EE from static extraction into a structurally reliable, agent ready perception and memory layer for open world systems.
Training LLMs with LogicReward for Faithful and Rigorous Reasoning
Dec 20, 2025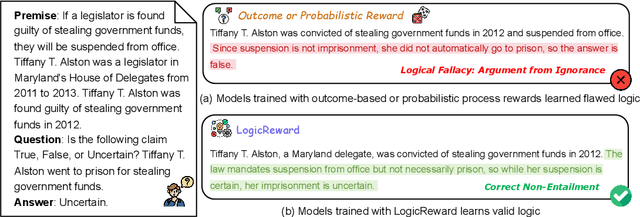
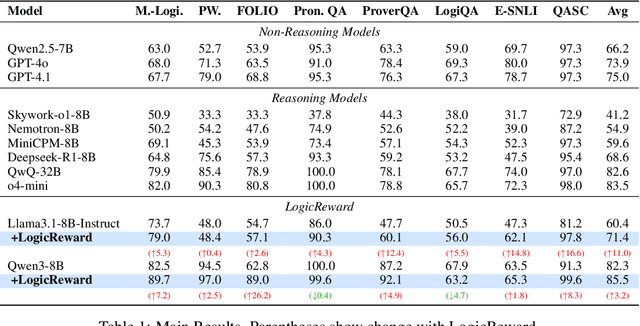
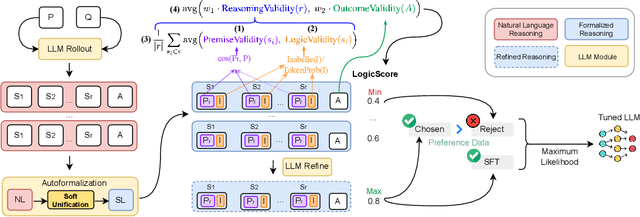
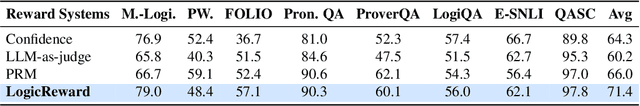
Abstract:Although LLMs exhibit strong reasoning capabilities, existing training methods largely depend on outcome-based feedback, which can produce correct answers with flawed reasoning. Prior work introduces supervision on intermediate steps but still lacks guarantees of logical soundness, which is crucial in high-stakes scenarios where logical consistency is paramount. To address this, we propose LogicReward, a novel reward system that guides model training by enforcing step-level logical correctness with a theorem prover. We further introduce Autoformalization with Soft Unification, which reduces natural language ambiguity and improves formalization quality, enabling more effective use of the theorem prover. An 8B model trained on data constructed with LogicReward surpasses GPT-4o and o4-mini by 11.6\% and 2\% on natural language inference and logical reasoning tasks with simple training procedures. Further analysis shows that LogicReward enhances reasoning faithfulness, improves generalizability to unseen tasks such as math and commonsense reasoning, and provides a reliable reward signal even without ground-truth labels. We will release all data and code at https://llm-symbol.github.io/LogicReward.
UniVA: Universal Video Agent towards Open-Source Next-Generation Video Generalist
Nov 11, 2025Abstract:While specialized AI models excel at isolated video tasks like generation or understanding, real-world applications demand complex, iterative workflows that combine these capabilities. To bridge this gap, we introduce UniVA, an open-source, omni-capable multi-agent framework for next-generation video generalists that unifies video understanding, segmentation, editing, and generation into cohesive workflows. UniVA employs a Plan-and-Act dual-agent architecture that drives a highly automated and proactive workflow: a planner agent interprets user intentions and decomposes them into structured video-processing steps, while executor agents execute these through modular, MCP-based tool servers (for analysis, generation, editing, tracking, etc.). Through a hierarchical multi-level memory (global knowledge, task context, and user-specific preferences), UniVA sustains long-horizon reasoning, contextual continuity, and inter-agent communication, enabling interactive and self-reflective video creation with full traceability. This design enables iterative and any-conditioned video workflows (e.g., text/image/video-conditioned generation $\rightarrow$ multi-round editing $\rightarrow$ object segmentation $\rightarrow$ compositional synthesis) that were previously cumbersome to achieve with single-purpose models or monolithic video-language models. We also introduce UniVA-Bench, a benchmark suite of multi-step video tasks spanning understanding, editing, segmentation, and generation, to rigorously evaluate such agentic video systems. Both UniVA and UniVA-Bench are fully open-sourced, aiming to catalyze research on interactive, agentic, and general-purpose video intelligence for the next generation of multimodal AI systems. (https://univa.online/)
MCM-DPO: Multifaceted Cross-Modal Direct Preference Optimization for Alt-text Generation
Oct 01, 2025Abstract:The alt-text generation task produces concise, context-relevant descriptions of images, enabling blind and low-vision users to access online images. Despite the capabilities of large vision-language models, alt-text generation performance remains limited due to noisy user annotations, inconsistent standards, and MLLMs' insensitivity to contextual information. Previous efforts to fine-tune MLLMs using supervised fine-tuning (SFT) have struggled, as SFT relies on accurate target annotations, which are often flawed in user-generated alt-text. To address this, we propose Multi-faceted Cross-modal Direct Preference Optimization (MCM-DPO), which improves alt-text generation by learning to identify better options in preference pairs without requiring precise annotations. MCM-DPO optimizes preferences across single, paired, and multi-preference dimensions, covering textual, visual, and cross-modal factors. In light of the scarcity of high-quality annotated and preference-labeled datasets for alt-text, we constructed two large-scale, high-quality datasets named TAlt and PAlt, sourced from Twitter and Pinterest. These datasets include 202k annotated alt-text samples and 18k preference pairs that cover diverse preference dimensions, aiming to support further research in this domain. Experimental results show that our proposed MCM-DPO method consistently outperforms both DPO and SFT, establishing a new state of the art in alt-text generation. We release the code and data here: https://github.com/LVUGAI/MCM-DPO
Enhancing Hyperbole and Metaphor Detection with Their Bidirectional Dynamic Interaction and Emotion Knowledge
Jun 18, 2025Abstract:Text-based hyperbole and metaphor detection are of great significance for natural language processing (NLP) tasks. However, due to their semantic obscurity and expressive diversity, it is rather challenging to identify them. Existing methods mostly focus on superficial text features, ignoring the associations of hyperbole and metaphor as well as the effect of implicit emotion on perceiving these rhetorical devices. To implement these hypotheses, we propose an emotion-guided hyperbole and metaphor detection framework based on bidirectional dynamic interaction (EmoBi). Firstly, the emotion analysis module deeply mines the emotion connotations behind hyperbole and metaphor. Next, the emotion-based domain mapping module identifies the target and source domains to gain a deeper understanding of the implicit meanings of hyperbole and metaphor. Finally, the bidirectional dynamic interaction module enables the mutual promotion between hyperbole and metaphor. Meanwhile, a verification mechanism is designed to ensure detection accuracy and reliability. Experiments show that EmoBi outperforms all baseline methods on four datasets. Specifically, compared to the current SoTA, the F1 score increased by 28.1% for hyperbole detection on the TroFi dataset and 23.1% for metaphor detection on the HYPO-L dataset. These results, underpinned by in-depth analyses, underscore the effectiveness and potential of our approach for advancing hyperbole and metaphor detection.
Uncertainty-o: One Model-agnostic Framework for Unveiling Uncertainty in Large Multimodal Models
Jun 09, 2025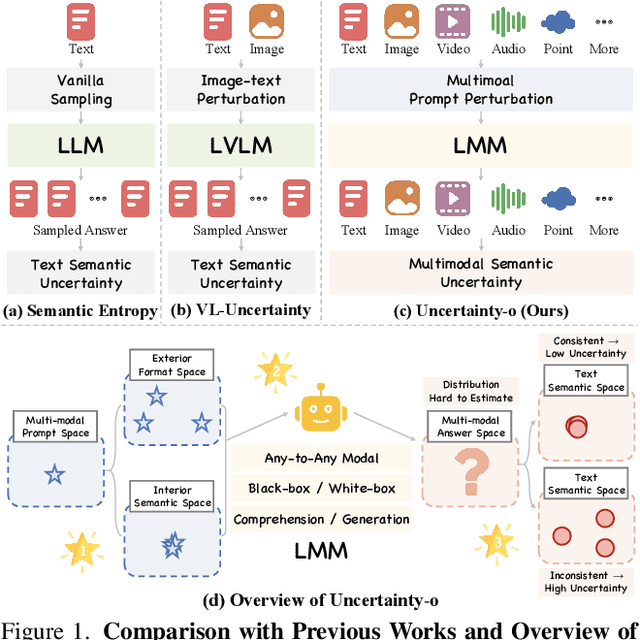
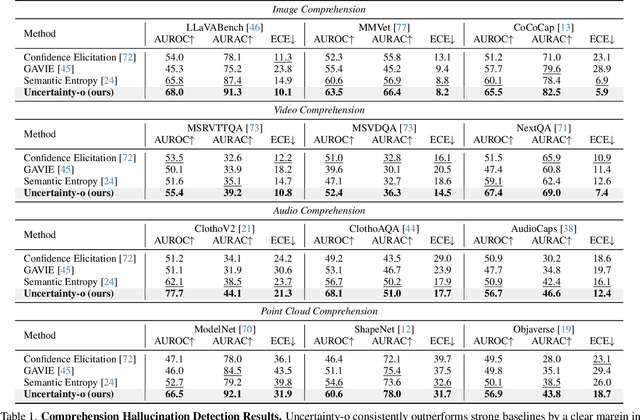
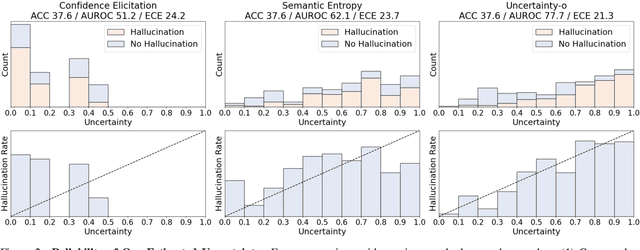

Abstract:Large Multimodal Models (LMMs), harnessing the complementarity among diverse modalities, are often considered more robust than pure Language Large Models (LLMs); yet do LMMs know what they do not know? There are three key open questions remaining: (1) how to evaluate the uncertainty of diverse LMMs in a unified manner, (2) how to prompt LMMs to show its uncertainty, and (3) how to quantify uncertainty for downstream tasks. In an attempt to address these challenges, we introduce Uncertainty-o: (1) a model-agnostic framework designed to reveal uncertainty in LMMs regardless of their modalities, architectures, or capabilities, (2) an empirical exploration of multimodal prompt perturbations to uncover LMM uncertainty, offering insights and findings, and (3) derive the formulation of multimodal semantic uncertainty, which enables quantifying uncertainty from multimodal responses. Experiments across 18 benchmarks spanning various modalities and 10 LMMs (both open- and closed-source) demonstrate the effectiveness of Uncertainty-o in reliably estimating LMM uncertainty, thereby enhancing downstream tasks such as hallucination detection, hallucination mitigation, and uncertainty-aware Chain-of-Thought reasoning.
DragNeXt: Rethinking Drag-Based Image Editing
Jun 09, 2025

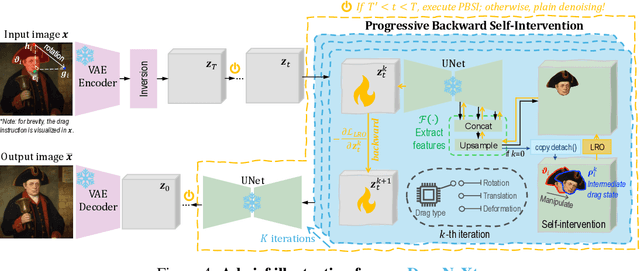

Abstract:Drag-Based Image Editing (DBIE), which allows users to manipulate images by directly dragging objects within them, has recently attracted much attention from the community. However, it faces two key challenges: (\emph{\textcolor{magenta}{i}}) point-based drag is often highly ambiguous and difficult to align with users' intentions; (\emph{\textcolor{magenta}{ii}}) current DBIE methods primarily rely on alternating between motion supervision and point tracking, which is not only cumbersome but also fails to produce high-quality results. These limitations motivate us to explore DBIE from a new perspective -- redefining it as deformation, rotation, and translation of user-specified handle regions. Thereby, by requiring users to explicitly specify both drag areas and types, we can effectively address the ambiguity issue. Furthermore, we propose a simple-yet-effective editing framework, dubbed \textcolor{SkyBlue}{\textbf{DragNeXt}}. It unifies DBIE as a Latent Region Optimization (LRO) problem and solves it through Progressive Backward Self-Intervention (PBSI), simplifying the overall procedure of DBIE while further enhancing quality by fully leveraging region-level structure information and progressive guidance from intermediate drag states. We validate \textcolor{SkyBlue}{\textbf{DragNeXt}} on our NextBench, and extensive experiments demonstrate that our proposed method can significantly outperform existing approaches. Code will be released on github.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge