Jingbo Wang
FRAPPE: Infusing World Modeling into Generalist Policies via Multiple Future Representation Alignment
Feb 19, 2026Abstract:Enabling VLA models to predict environmental dynamics, known as world modeling, has been recognized as essential for improving robotic reasoning and generalization. However, current approaches face two main issues: 1. The training objective forces models to over-emphasize pixel-level reconstruction, which constrains semantic learning and generalization 2. Reliance on predicted future observations during inference often leads to error accumulation. To address these challenges, we introduce Future Representation Alignment via Parallel Progressive Expansion (FRAPPE). Our method adopts a two-stage fine-tuning strategy: In the mid-training phase, the model learns to predict the latent representations of future observations; In the post-training phase, we expand the computational workload in parallel and align the representation simultaneously with multiple different visual foundation models. By significantly improving fine-tuning efficiency and reducing dependence on action-annotated data, FRAPPE provides a scalable and data-efficient pathway to enhance world-awareness in generalist robotic policies. Experiments on the RoboTwin benchmark and real-world tasks demonstrate that FRAPPE outperforms state-of-the-art approaches and shows strong generalization in long-horizon and unseen scenarios.
Quantum Reservoir Computing with Neutral Atoms on a Small, Complex, Medical Dataset
Feb 16, 2026Abstract:Biomarker-based prediction of clinical outcomes is challenging due to nonlinear relationships, correlated features, and the limited size of many medical datasets. Classical machine-learning methods can struggle under these conditions, motivating the search for alternatives. In this work, we investigate quantum reservoir computing (QRC), using both noiseless emulation and hardware execution on the neutral-atom Rydberg processor \textit{Aquila}. We evaluate performance with six classical machine-learning models and use SHAP to generate feature subsets. We find that models trained on emulated quantum features achieve mean test accuracies comparable to those trained on classical features, but have higher training accuracies and greater variability over data splits, consistent with overfitting. When comparing hardware execution of QRC to noiseless emulation, the models are more robust over different data splits and often exhibit statistically significant improvements in mean test accuracy. This combination of improved accuracy and increased stability is suggestive of a regularising effect induced by hardware execution. To investigate the origin of this behaviour, we examine the statistical differences between hardware and emulated quantum feature distributions. We find that hardware execution applies a structured, time-dependent transformation characterised by compression toward the mean and a progressive reduction in mutual information relative to emulation.
CLOT: Closed-Loop Global Motion Tracking for Whole-Body Humanoid Teleoperation
Feb 13, 2026Abstract:Long-horizon whole-body humanoid teleoperation remains challenging due to accumulated global pose drift, particularly on full-sized humanoids. Although recent learning-based tracking methods enable agile and coordinated motions, they typically operate in the robot's local frame and neglect global pose feedback, leading to drift and instability during extended execution. In this work, we present CLOT, a real-time whole-body humanoid teleoperation system that achieves closed-loop global motion tracking via high-frequency localization feedback. CLOT synchronizes operator and robot poses in a closed loop, enabling drift-free human-to-humanoid mimicry over long timehorizons. However, directly imposing global tracking rewards in reinforcement learning, often results in aggressive and brittle corrections. To address this, we propose a data-driven randomization strategy that decouples observation trajectories from reward evaluation, enabling smooth and stable global corrections. We further regularize the policy with an adversarial motion prior to suppress unnatural behaviors. To support CLOT, we collect 20 hours of carefully curated human motion data for training the humanoid teleoperation policy. We design a transformer-based policy and train it for over 1300 GPU hours. The policy is deployed on a full-sized humanoid with 31 DoF (excluding hands). Both simulation and real-world experiments verify high-dynamic motion, high-precision tracking, and strong robustness in sim-to-real humanoid teleoperation. Motion data, demos and code can be found in our website.
Scalable and General Whole-Body Control for Cross-Humanoid Locomotion
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Learning-based whole-body controllers have become a key driver for humanoid robots, yet most existing approaches require robot-specific training. In this paper, we study the problem of cross-embodiment humanoid control and show that a single policy can robustly generalize across a wide range of humanoid robot designs with one-time training. We introduce XHugWBC, a novel cross-embodiment training framework that enables generalist humanoid control through: (1) physics-consistent morphological randomization, (2) semantically aligned observation and action spaces across diverse humanoid robots, and (3) effective policy architectures modeling morphological and dynamical properties. XHugWBC is not tied to any specific robot. Instead, it internalizes a broad distribution of morphological and dynamical characteristics during training. By learning motion priors from diverse randomized embodiments, the policy acquires a strong structural bias that supports zero-shot transfer to previously unseen robots. Experiments on twelve simulated humanoids and seven real-world robots demonstrate the strong generalization and robustness of the resulting universal controller.
HumanX: Toward Agile and Generalizable Humanoid Interaction Skills from Human Videos
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Enabling humanoid robots to perform agile and adaptive interactive tasks has long been a core challenge in robotics. Current approaches are bottlenecked by either the scarcity of realistic interaction data or the need for meticulous, task-specific reward engineering, which limits their scalability. To narrow this gap, we present HumanX, a full-stack framework that compiles human video into generalizable, real-world interaction skills for humanoids, without task-specific rewards. HumanX integrates two co-designed components: XGen, a data generation pipeline that synthesizes diverse and physically plausible robot interaction data from video while supporting scalable data augmentation; and XMimic, a unified imitation learning framework that learns generalizable interaction skills. Evaluated across five distinct domains--basketball, football, badminton, cargo pickup, and reactive fighting--HumanX successfully acquires 10 different skills and transfers them zero-shot to a physical Unitree G1 humanoid. The learned capabilities include complex maneuvers such as pump-fake turnaround fadeaway jumpshots without any external perception, as well as interactive tasks like sustained human-robot passing sequences over 10 consecutive cycles--learned from a single video demonstration. Our experiments show that HumanX achieves over 8 times higher generalization success than prior methods, demonstrating a scalable and task-agnostic pathway for learning versatile, real-world robot interactive skills.
RoboStriker: Hierarchical Decision-Making for Autonomous Humanoid Boxing
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Achieving human-level competitive intelligence and physical agility in humanoid robots remains a major challenge, particularly in contact-rich and highly dynamic tasks such as boxing. While Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL) offers a principled framework for strategic interaction, its direct application to humanoid control is hindered by high-dimensional contact dynamics and the absence of strong physical motion priors. We propose RoboStriker, a hierarchical three-stage framework that enables fully autonomous humanoid boxing by decoupling high-level strategic reasoning from low-level physical execution. The framework first learns a comprehensive repertoire of boxing skills by training a single-agent motion tracker on human motion capture data. These skills are subsequently distilled into a structured latent manifold, regularized by projecting the Gaussian-parameterized distribution onto a unit hypersphere. This topological constraint effectively confines exploration to the subspace of physically plausible motions. In the final stage, we introduce Latent-Space Neural Fictitious Self-Play (LS-NFSP), where competing agents learn competitive tactics by interacting within the latent action space rather than the raw motor space, significantly stabilizing multi-agent training. Experimental results demonstrate that RoboStriker achieves superior competitive performance in simulation and exhibits sim-to-real transfer. Our website is available at RoboStriker.
Orchestrating Intelligence: Confidence-Aware Routing for Efficient Multi-Agent Collaboration across Multi-Scale Models
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:While multi-agent systems (MAS) have demonstrated superior performance over single-agent approaches in complex reasoning tasks, they often suffer from significant computational inefficiencies. Existing frameworks typically deploy large language models (LLMs) uniformly across all agent roles, failing to account for the varying cognitive demands of different reasoning stages. We address this inefficiency by proposing OI-MAS framework, a novel multi-agent framework that implements an adaptive model-selection policy across a heterogeneous pool of multi-scale LLMs. Specifically, OI-MAS introduces a state-dependent routing mechanism that dynamically selects agent roles and model scales throughout the reasoning process. In addition, we introduce a confidence-aware mechanism that selects appropriate model scales conditioned on task complexity, thus reducing unnecessary reliance on large-scale models. Experimental results show that OI-MAS consistently outperforms baseline multi-agent systems, improving accuracy by up to 12.88\% while reducing cost by up to 79.78\%.
EgoReAct: Egocentric Video-Driven 3D Human Reaction Generation
Dec 28, 2025Abstract:Humans exhibit adaptive, context-sensitive responses to egocentric visual input. However, faithfully modeling such reactions from egocentric video remains challenging due to the dual requirements of strictly causal generation and precise 3D spatial alignment. To tackle this problem, we first construct the Human Reaction Dataset (HRD) to address data scarcity and misalignment by building a spatially aligned egocentric video-reaction dataset, as existing datasets (e.g., ViMo) suffer from significant spatial inconsistency between the egocentric video and reaction motion, e.g., dynamically moving motions are always paired with fixed-camera videos. Leveraging HRD, we present EgoReAct, the first autoregressive framework that generates 3D-aligned human reaction motions from egocentric video streams in real-time. We first compress the reaction motion into a compact yet expressive latent space via a Vector Quantised-Variational AutoEncoder and then train a Generative Pre-trained Transformer for reaction generation from the visual input. EgoReAct incorporates 3D dynamic features, i.e., metric depth, and head dynamics during the generation, which effectively enhance spatial grounding. Extensive experiments demonstrate that EgoReAct achieves remarkably higher realism, spatial consistency, and generation efficiency compared with prior methods, while maintaining strict causality during generation. We will release code, models, and data upon acceptance.
Learning Generalizable Hand-Object Tracking from Synthetic Demonstrations
Dec 22, 2025Abstract:We present a system for learning generalizable hand-object tracking controllers purely from synthetic data, without requiring any human demonstrations. Our approach makes two key contributions: (1) HOP, a Hand-Object Planner, which can synthesize diverse hand-object trajectories; and (2) HOT, a Hand-Object Tracker that bridges synthetic-to-physical transfer through reinforcement learning and interaction imitation learning, delivering a generalizable controller conditioned on target hand-object states. Our method extends to diverse object shapes and hand morphologies. Through extensive evaluations, we show that our approach enables dexterous hands to track challenging, long-horizon sequences including object re-arrangement and agile in-hand reorientation. These results represent a significant step toward scalable foundation controllers for manipulation that can learn entirely from synthetic data, breaking the data bottleneck that has long constrained progress in dexterous manipulation.
Maritime object classification with SAR imagery using quantum kernel methods
Dec 12, 2025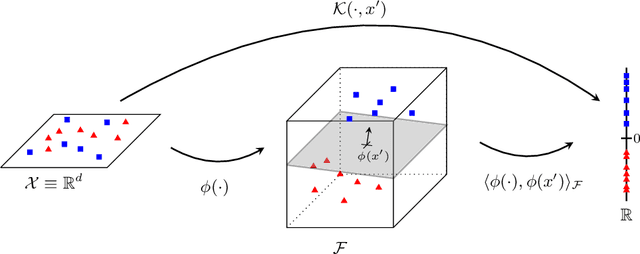
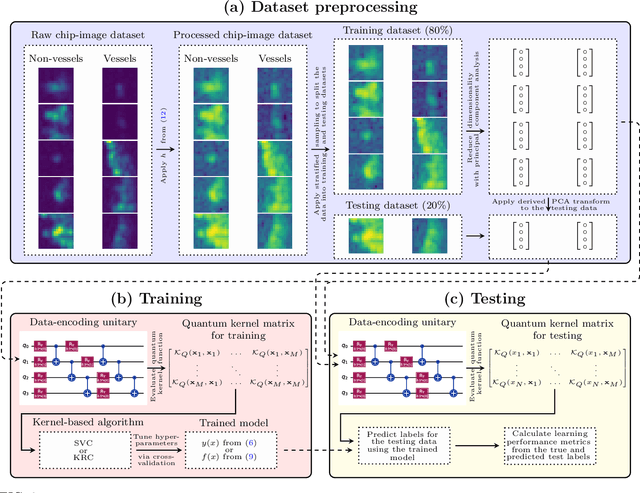
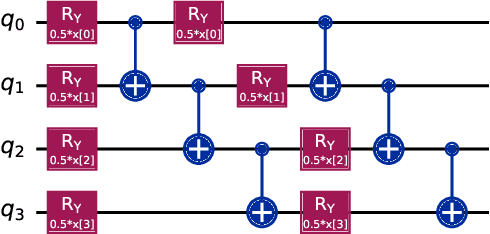
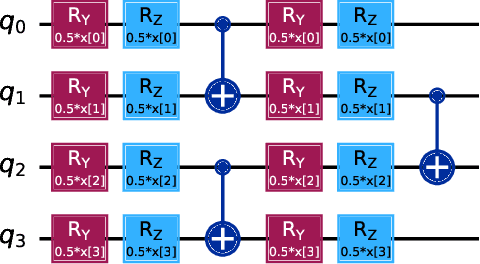
Abstract:Illegal, unreported, and unregulated (IUU) fishing causes global economic losses of \$10-25 billion annually and undermines marine sustainability and governance. Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) provides reliable maritime surveillance under all weather and lighting conditions, but classifying small maritime objects in SAR imagery remains challenging. We investigate quantum machine learning for this task, focusing on Quantum Kernel Methods (QKMs) applied to real and complex SAR chips extracted from the SARFish dataset. We tackle two binary classification problems, the first for distinguishing vessels from non-vessels, and the second for distinguishing fishing vessels from other types of vessels. We compare QKMs applied to real and complex SAR chips against classical Laplacian, RBF, and linear kernels applied to real SAR chips. Using noiseless numerical simulations of the quantum kernels, we find that QKMs are capable of obtaining equal or better performance than the classical kernel on these tasks in the best case, but do not demonstrate a clear advantage for the complex SAR data. This work presents the first application of QKMs to maritime classification in SAR imagery and offers insight into the potential and current limitations of quantum-enhanced learning for maritime surveillance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge