Zeyu Lu
ScaMo: Exploring the Scaling Law in Autoregressive Motion Generation Model
Dec 19, 2024Abstract:The scaling law has been validated in various domains, such as natural language processing (NLP) and massive computer vision tasks; however, its application to motion generation remains largely unexplored. In this paper, we introduce a scalable motion generation framework that includes the motion tokenizer Motion FSQ-VAE and a text-prefix autoregressive transformer. Through comprehensive experiments, we observe the scaling behavior of this system. For the first time, we confirm the existence of scaling laws within the context of motion generation. Specifically, our results demonstrate that the normalized test loss of our prefix autoregressive models adheres to a logarithmic law in relation to compute budgets. Furthermore, we also confirm the power law between Non-Vocabulary Parameters, Vocabulary Parameters, and Data Tokens with respect to compute budgets respectively. Leveraging the scaling law, we predict the optimal transformer size, vocabulary size, and data requirements for a compute budget of $1e18$. The test loss of the system, when trained with the optimal model size, vocabulary size, and required data, aligns precisely with the predicted test loss, thereby validating the scaling law.
FiTv2: Scalable and Improved Flexible Vision Transformer for Diffusion Model
Oct 17, 2024


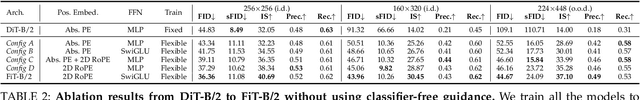
Abstract:\textit{Nature is infinitely resolution-free}. In the context of this reality, existing diffusion models, such as Diffusion Transformers, often face challenges when processing image resolutions outside of their trained domain. To address this limitation, we conceptualize images as sequences of tokens with dynamic sizes, rather than traditional methods that perceive images as fixed-resolution grids. This perspective enables a flexible training strategy that seamlessly accommodates various aspect ratios during both training and inference, thus promoting resolution generalization and eliminating biases introduced by image cropping. On this basis, we present the \textbf{Flexible Vision Transformer} (FiT), a transformer architecture specifically designed for generating images with \textit{unrestricted resolutions and aspect ratios}. We further upgrade the FiT to FiTv2 with several innovative designs, includingthe Query-Key vector normalization, the AdaLN-LoRA module, a rectified flow scheduler, and a Logit-Normal sampler. Enhanced by a meticulously adjusted network structure, FiTv2 exhibits $2\times$ convergence speed of FiT. When incorporating advanced training-free extrapolation techniques, FiTv2 demonstrates remarkable adaptability in both resolution extrapolation and diverse resolution generation. Additionally, our exploration of the scalability of the FiTv2 model reveals that larger models exhibit better computational efficiency. Furthermore, we introduce an efficient post-training strategy to adapt a pre-trained model for the high-resolution generation. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate the exceptional performance of FiTv2 across a broad range of resolutions. We have released all the codes and models at \url{https://github.com/whlzy/FiT} to promote the exploration of diffusion transformer models for arbitrary-resolution image generation.
Diffusion Models Need Visual Priors for Image Generation
Oct 11, 2024



Abstract:Conventional class-guided diffusion models generally succeed in generating images with correct semantic content, but often struggle with texture details. This limitation stems from the usage of class priors, which only provide coarse and limited conditional information. To address this issue, we propose Diffusion on Diffusion (DoD), an innovative multi-stage generation framework that first extracts visual priors from previously generated samples, then provides rich guidance for the diffusion model leveraging visual priors from the early stages of diffusion sampling. Specifically, we introduce a latent embedding module that employs a compression-reconstruction approach to discard redundant detail information from the conditional samples in each stage, retaining only the semantic information for guidance. We evaluate DoD on the popular ImageNet-$256 \times 256$ dataset, reducing 7$\times$ training cost compared to SiT and DiT with even better performance in terms of the FID-50K score. Our largest model DoD-XL achieves an FID-50K score of 1.83 with only 1 million training steps, which surpasses other state-of-the-art methods without bells and whistles during inference.
GenAgent: Build Collaborative AI Systems with Automated Workflow Generation -- Case Studies on ComfyUI
Sep 02, 2024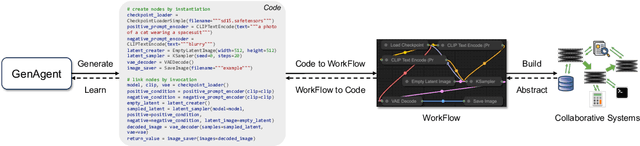
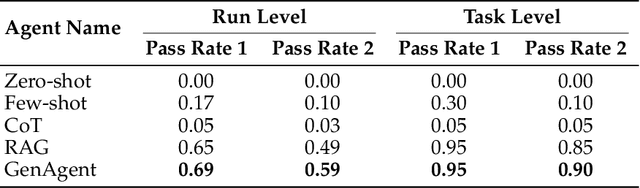


Abstract:Much previous AI research has focused on developing monolithic models to maximize their intelligence and capability, with the primary goal of enhancing performance on specific tasks. In contrast, this paper explores an alternative approach: collaborative AI systems that use workflows to integrate models, data sources, and pipelines to solve complex and diverse tasks. We introduce GenAgent, an LLM-based framework that automatically generates complex workflows, offering greater flexibility and scalability compared to monolithic models. The core innovation of GenAgent lies in representing workflows with code, alongside constructing workflows with collaborative agents in a step-by-step manner. We implement GenAgent on the ComfyUI platform and propose a new benchmark, OpenComfy. The results demonstrate that GenAgent outperforms baseline approaches in both run-level and task-level evaluations, showing its capability to generate complex workflows with superior effectiveness and stability.
PredBench: Benchmarking Spatio-Temporal Prediction across Diverse Disciplines
Jul 11, 2024

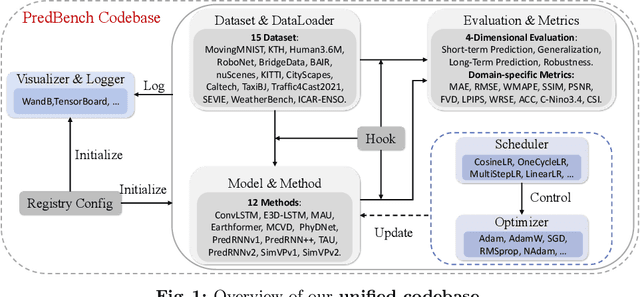

Abstract:In this paper, we introduce PredBench, a benchmark tailored for the holistic evaluation of spatio-temporal prediction networks. Despite significant progress in this field, there remains a lack of a standardized framework for a detailed and comparative analysis of various prediction network architectures. PredBench addresses this gap by conducting large-scale experiments, upholding standardized and appropriate experimental settings, and implementing multi-dimensional evaluations. This benchmark integrates 12 widely adopted methods with 15 diverse datasets across multiple application domains, offering extensive evaluation of contemporary spatio-temporal prediction networks. Through meticulous calibration of prediction settings across various applications, PredBench ensures evaluations relevant to their intended use and enables fair comparisons. Moreover, its multi-dimensional evaluation framework broadens the analysis with a comprehensive set of metrics, providing deep insights into the capabilities of models. The findings from our research offer strategic directions for future developments in the field. Our codebase is available at https://github.com/WZDTHU/PredBench.
Plot2Code: A Comprehensive Benchmark for Evaluating Multi-modal Large Language Models in Code Generation from Scientific Plots
May 13, 2024



Abstract:The remarkable progress of Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs) has attracted significant attention due to their superior performance in visual contexts. However, their capabilities in turning visual figure to executable code, have not been evaluated thoroughly. To address this, we introduce Plot2Code, a comprehensive visual coding benchmark designed for a fair and in-depth assessment of MLLMs. We carefully collect 132 manually selected high-quality matplotlib plots across six plot types from publicly available matplotlib galleries. For each plot, we carefully offer its source code, and an descriptive instruction summarized by GPT-4. This approach enables Plot2Code to extensively evaluate MLLMs' code capabilities across various input modalities. Furthermore, we propose three automatic evaluation metrics, including code pass rate, text-match ratio, and GPT-4V overall rating, for a fine-grained assessment of the output code and rendered images. Instead of simply judging pass or fail, we employ GPT-4V to make an overall judgement between the generated and reference images, which has been shown to be consistent with human evaluation. The evaluation results, which include analyses of 14 MLLMs such as the proprietary GPT-4V, Gemini-Pro, and the open-sourced Mini-Gemini, highlight the substantial challenges presented by Plot2Code. With Plot2Code, we reveal that most existing MLLMs struggle with visual coding for text-dense plots, heavily relying on textual instruction. We hope that the evaluation results from Plot2Code on visual coding will guide the future development of MLLMs. All data involved with Plot2Code are available at https://huggingface.co/datasets/TencentARC/Plot2Code.
A Survey on Long Video Generation: Challenges, Methods, and Prospects
Mar 25, 2024



Abstract:Video generation is a rapidly advancing research area, garnering significant attention due to its broad range of applications. One critical aspect of this field is the generation of long-duration videos, which presents unique challenges and opportunities. This paper presents the first survey of recent advancements in long video generation and summarises them into two key paradigms: divide and conquer temporal autoregressive. We delve into the common models employed in each paradigm, including aspects of network design and conditioning techniques. Furthermore, we offer a comprehensive overview and classification of the datasets and evaluation metrics which are crucial for advancing long video generation research. Concluding with a summary of existing studies, we also discuss the emerging challenges and future directions in this dynamic field. We hope that this survey will serve as an essential reference for researchers and practitioners in the realm of long video generation.
FiT: Flexible Vision Transformer for Diffusion Model
Feb 19, 2024



Abstract:Nature is infinitely resolution-free. In the context of this reality, existing diffusion models, such as Diffusion Transformers, often face challenges when processing image resolutions outside of their trained domain. To overcome this limitation, we present the Flexible Vision Transformer (FiT), a transformer architecture specifically designed for generating images with unrestricted resolutions and aspect ratios. Unlike traditional methods that perceive images as static-resolution grids, FiT conceptualizes images as sequences of dynamically-sized tokens. This perspective enables a flexible training strategy that effortlessly adapts to diverse aspect ratios during both training and inference phases, thus promoting resolution generalization and eliminating biases induced by image cropping. Enhanced by a meticulously adjusted network structure and the integration of training-free extrapolation techniques, FiT exhibits remarkable flexibility in resolution extrapolation generation. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate the exceptional performance of FiT across a broad range of resolutions, showcasing its effectiveness both within and beyond its training resolution distribution. Repository available at https://github.com/whlzy/FiT.
LLaMA Pro: Progressive LLaMA with Block Expansion
Jan 04, 2024



Abstract:Humans generally acquire new skills without compromising the old; however, the opposite holds for Large Language Models (LLMs), e.g., from LLaMA to CodeLLaMA. To this end, we propose a new post-pretraining method for LLMs with an expansion of Transformer blocks. We tune the expanded blocks using only new corpus, efficiently and effectively improving the model's knowledge without catastrophic forgetting. In this paper, we experiment on the corpus of code and math, yielding LLaMA Pro-8.3B, a versatile foundation model initialized from LLaMA2-7B, excelling in general tasks, programming, and mathematics. LLaMA Pro and its instruction-following counterpart (LLaMA Pro-Instruct) achieve advanced performance among various benchmarks, demonstrating superiority over existing open models in the LLaMA family and the immense potential of reasoning and addressing diverse tasks as an intelligent agent. Our findings provide valuable insights into integrating natural and programming languages, laying a solid foundation for developing advanced language agents that operate effectively in various environments.
$π$-Tuning: Transferring Multimodal Foundation Models with Optimal Multi-task Interpolation
Apr 28, 2023Abstract:Foundation models have achieved great advances in multi-task learning with a unified interface of unimodal and multimodal tasks. However, the potential of such multi-task learners has not been exploited during transfer learning. In this work, we present a universal parameter-efficient transfer learning method, termed Predict-Interpolate Tuning ($\pi$-Tuning), for vision, language, and vision-language tasks. It aggregates the parameters of lightweight task-specific experts learned from similar tasks to aid the target downstream task. The task similarities are predicted in a unified modality-independent space, yielding a scalable graph to demonstrate task relationships. $\pi$-Tuning has several appealing benefits. First, it flexibly explores both intra- and inter-modal transferability between similar tasks to improve the accuracy and robustness of transfer learning, especially in data-scarce scenarios. Second, it offers a systematical solution for transfer learning with multi-task prediction-and-then-interpolation, compatible with diverse types of parameter-efficient experts, such as prompt and adapter. Third, an extensive study of task-level mutual benefits on 14 unimodal and 6 multimodal datasets shows that $\pi$-Tuning surpasses fine-tuning and other parameter-efficient transfer learning methods both in full-shot and low-shot regimes. The task graph also enables an in-depth interpretable analysis of task transferability across modalities.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge