Wanli Ouyang
School of Electrical and Information Engineering, The University of Sydney, Australia
MEMTS: Internalizing Domain Knowledge via Parameterized Memory for Retrieval-Free Domain Adaptation of Time Series Foundation Models
Feb 14, 2026Abstract:While Time Series Foundation Models (TSFMs) have demonstrated exceptional performance in generalized forecasting, their performance often degrades significantly when deployed in real-world vertical domains characterized by temporal distribution shifts and domain-specific periodic structures. Current solutions are primarily constrained by two paradigms: Domain-Adaptive Pretraining (DAPT), which improves short-term domain fitting but frequently disrupts previously learned global temporal patterns due to catastrophic forgetting; and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), which incorporates external knowledge but introduces substantial retrieval overhead. This creates a severe scalability bottleneck that fails to meet the high-efficiency requirements of real-time stream processing. To break this impasse, we propose Memory for Time Series (MEMTS), a lightweight and plug-and-play method for retrieval-free domain adaptation in time series forecasting. The key component of MEMTS is a Knowledge Persistence Module (KPM), which internalizes domain-specific temporal dynamics, such as recurring seasonal patterns and trends into a compact set of learnable latent prototypes. In doing so, it transforms fragmented historical observations into continuous, parameterized knowledge representations. This paradigm shift enables MEMTS to achieve accurate domain adaptation with constant-time inference and near-zero latency, while effectively mitigating catastrophic forgetting of general temporal patterns, all without requiring any architectural modifications to the frozen TSFM backbone. Extensive experiments on multiple datasets demonstrate the SOTA performance of MEMTS.
Equivariant Evidential Deep Learning for Interatomic Potentials
Feb 11, 2026Abstract:Uncertainty quantification (UQ) is critical for assessing the reliability of machine learning interatomic potentials (MLIPs) in molecular dynamics (MD) simulations, identifying extrapolation regimes and enabling uncertainty-aware workflows such as active learning for training dataset construction. Existing UQ approaches for MLIPs are often limited by high computational cost or suboptimal performance. Evidential deep learning (EDL) provides a theoretically grounded single-model alternative that determines both aleatoric and epistemic uncertainty in a single forward pass. However, extending evidential formulations from scalar targets to vector-valued quantities such as atomic forces introduces substantial challenges, particularly in maintaining statistical self-consistency under rotational transformations. To address this, we propose \textit{Equivariant Evidential Deep Learning for Interatomic Potentials} ($\text{e}^2$IP), a backbone-agnostic framework that models atomic forces and their uncertainty jointly by representing uncertainty as a full $3\times3$ symmetric positive definite covariance tensor that transforms equivariantly under rotations. Experiments on diverse molecular benchmarks show that $\text{e}^2$IP provides a stronger accuracy-efficiency-reliability balance than the non-equivariant evidential baseline and the widely used ensemble method. It also achieves better data efficiency through the fully equivariant architecture while retaining single-model inference efficiency.
Charting Empirical Laws for LLM Fine-Tuning in Scientific Multi-Discipline Learning
Feb 11, 2026Abstract:While large language models (LLMs) have achieved strong performance through fine-tuning within individual scientific domains, their learning dynamics in multi-disciplinary contexts remains poorly understood, despite the promise of improved generalization and broader applicability through cross-domain knowledge synergy. In this work, we present the first systematic study of multi-disciplinary LLM fine-tuning, constructing a five-discipline corpus and analyzing learning patterns of full fine-tuning, LoRA, LoRA-MoE, and LoRA compositions. Particularly, our study shows that multi-disciplinary learning is substantially more variable than single-discipline training and distills four consistent empirical laws: (1) Balance-then-Diversity: low-resource disciplines degrade performance unless mitigated via diversity-aware upsampling; (2) Merge-then-Align: restoring instruction-following ability is critical for cross-discipline synergy; (3) Optimize-then-Scale: parameter scaling offers limited gains without prior design optimization; and (4) Share-then-Specialize: asymmetric LoRA-MoE yields robust gains with minimal trainable parameters via shared low-rank projection. Together, these laws form a practical recipe for principled multi-discipline fine-tuning and provide actionable guidance for developing generalizable scientific LLMs.
Vision-DeepResearch Benchmark: Rethinking Visual and Textual Search for Multimodal Large Language Models
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have advanced VQA and now support Vision-DeepResearch systems that use search engines for complex visual-textual fact-finding. However, evaluating these visual and textual search abilities is still difficult, and existing benchmarks have two major limitations. First, existing benchmarks are not visual search-centric: answers that should require visual search are often leaked through cross-textual cues in the text questions or can be inferred from the prior world knowledge in current MLLMs. Second, overly idealized evaluation scenario: On the image-search side, the required information can often be obtained via near-exact matching against the full image, while the text-search side is overly direct and insufficiently challenging. To address these issues, we construct the Vision-DeepResearch benchmark (VDR-Bench) comprising 2,000 VQA instances. All questions are created via a careful, multi-stage curation pipeline and rigorous expert review, designed to assess the behavior of Vision-DeepResearch systems under realistic real-world conditions. Moreover, to address the insufficient visual retrieval capabilities of current MLLMs, we propose a simple multi-round cropped-search workflow. This strategy is shown to effectively improve model performance in realistic visual retrieval scenarios. Overall, our results provide practical guidance for the design of future multimodal deep-research systems. The code will be released in https://github.com/Osilly/Vision-DeepResearch.
Vision-DeepResearch: Incentivizing DeepResearch Capability in Multimodal Large Language Models
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have achieved remarkable success across a broad range of vision tasks. However, constrained by the capacity of their internal world knowledge, prior work has proposed augmenting MLLMs by ``reasoning-then-tool-call'' for visual and textual search engines to obtain substantial gains on tasks requiring extensive factual information. However, these approaches typically define multimodal search in a naive setting, assuming that a single full-level or entity-level image query and few text query suffices to retrieve the key evidence needed to answer the question, which is unrealistic in real-world scenarios with substantial visual noise. Moreover, they are often limited in the reasoning depth and search breadth, making it difficult to solve complex questions that require aggregating evidence from diverse visual and textual sources. Building on this, we propose Vision-DeepResearch, which proposes one new multimodal deep-research paradigm, i.e., performs multi-turn, multi-entity and multi-scale visual and textual search to robustly hit real-world search engines under heavy noise. Our Vision-DeepResearch supports dozens of reasoning steps and hundreds of engine interactions, while internalizing deep-research capabilities into the MLLM via cold-start supervision and RL training, resulting in a strong end-to-end multimodal deep-research MLLM. It substantially outperforming existing multimodal deep-research MLLMs, and workflows built on strong closed-source foundation model such as GPT-5, Gemini-2.5-pro and Claude-4-Sonnet. The code will be released in https://github.com/Osilly/Vision-DeepResearch.
SALAD: Achieve High-Sparsity Attention via Efficient Linear Attention Tuning for Video Diffusion Transformer
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:Diffusion Transformers have recently demonstrated remarkable performance in video generation. However, the long input sequences result in high computational latency due to the quadratic complexity of full attention. Various sparse attention mechanisms have been proposed. Training-free sparse attention is constrained by limited sparsity and thus offers modest acceleration, whereas training-based methods can reach much higher sparsity but demand substantial data and computation for training. In this work, we propose SALAD, introducing a lightweight linear attention branch in parallel with the sparse attention. By incorporating an input-dependent gating mechanism to finely balance the two branches, our method attains 90% sparsity and 1.72x inference speedup, while maintaining generation quality comparable to the full attention baseline. Moreover, our finetuning process is highly efficient, requiring only 2,000 video samples and 1,600 training steps with a batch size of 8.
Reflection Pretraining Enables Token-Level Self-Correction in Biological Sequence Models
Dec 24, 2025



Abstract:Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting has significantly advanced task-solving capabilities in natural language processing with large language models. Unlike standard prompting, CoT encourages the model to generate intermediate reasoning steps, non-answer tokens, that help guide the model toward more accurate final outputs. These intermediate steps enable more complex reasoning processes such as error correction, memory management, future planning, and self-reflection. However, applying CoT to non-natural language domains, such as protein and RNA language models, is not yet possible, primarily due to the limited expressiveness of their token spaces (e.g., amino acid tokens). In this work, we propose and define the concept of language expressiveness: the ability of a given language, using its tokens and grammar, to encode information. We show that the limited expressiveness of protein language severely restricts the applicability of CoT-style reasoning. To overcome this, we introduce reflection pretraining, for the first time in a biological sequence model, which enables the model to engage in intermediate reasoning through the generation of auxiliary "thinking tokens" beyond simple answer tokens. Theoretically, we demonstrate that our augmented token set significantly enhances biological language expressiveness, thereby improving the overall reasoning capacity of the model. Experimentally, our pretraining approach teaches protein models to self-correct and leads to substantial performance gains compared to standard pretraining.
An Agentic Framework for Autonomous Materials Computation
Dec 22, 2025



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have emerged as powerful tools for accelerating scientific discovery, yet their static knowledge and hallucination issues hinder autonomous research applications. Recent advances integrate LLMs into agentic frameworks, enabling retrieval, reasoning, and tool use for complex scientific workflows. Here, we present a domain-specialized agent designed for reliable automation of first-principles materials computations. By embedding domain expertise, the agent ensures physically coherent multi-step workflows and consistently selects convergent, well-posed parameters, thereby enabling reliable end-to-end computational execution. A new benchmark of diverse computational tasks demonstrates that our system significantly outperforms standalone LLMs in both accuracy and robustness. This work establishes a verifiable foundation for autonomous computational experimentation and represents a key step toward fully automated scientific discovery.
Revisiting the Broken Symmetry Phase of Solid Hydrogen: A Neural Network Variational Monte Carlo Study
Dec 19, 2025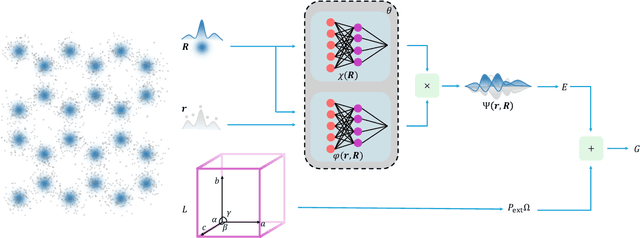
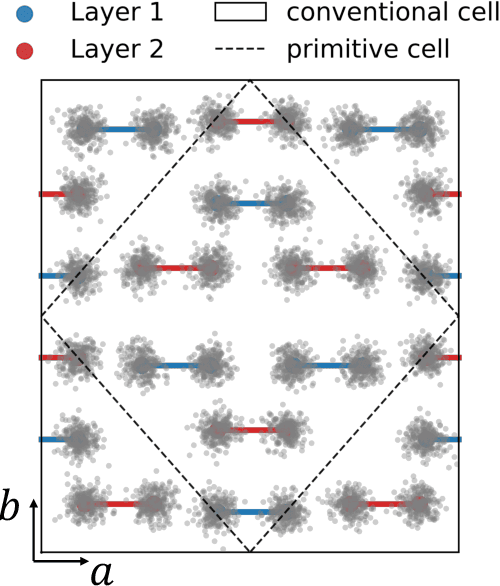
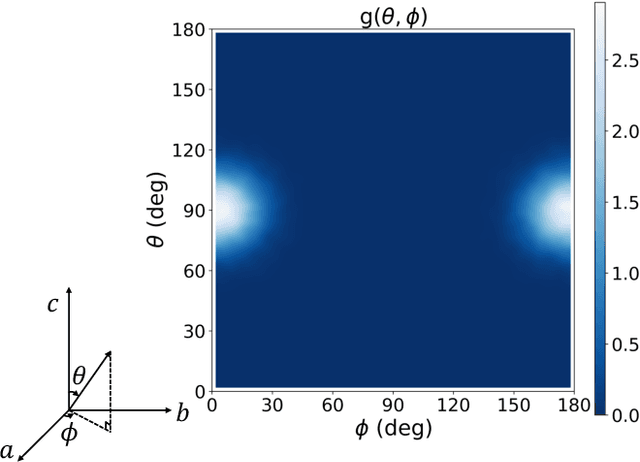
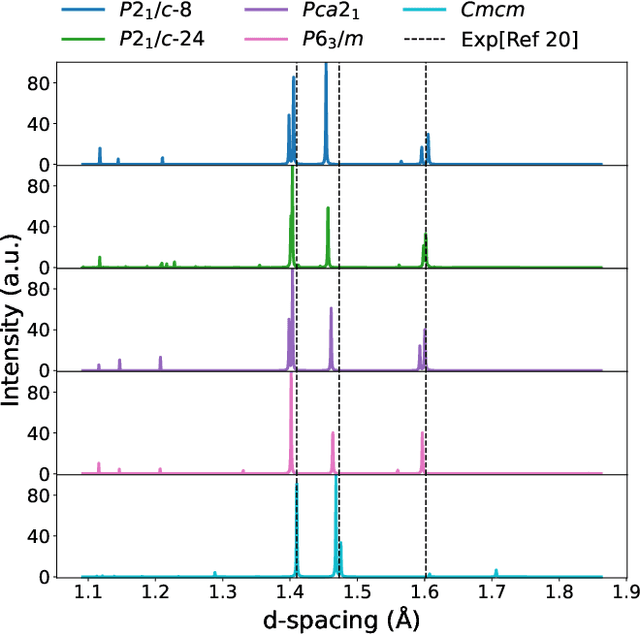
Abstract:The crystal structure of high-pressure solid hydrogen remains a fundamental open problem. Although the research frontier has mostly shifted toward ultra-high pressure phases above 400 GPa, we show that even the broken symmetry phase observed around 130~GPa requires revisiting due to its intricate coupling of electronic and nuclear degrees of freedom. Here, we develop a first principle quantum Monte Carlo framework based on a deep neural network wave function that treats both electrons and nuclei quantum mechanically within the constant pressure ensemble. Our calculations reveal an unreported ground-state structure candidate for the broken symmetry phase with $Cmcm$ space group symmetry, and we test its stability up to 96 atoms. The predicted structure quantitatively matches the experimental equation of state and X-ray diffraction patterns. Furthermore, our group-theoretical analysis shows that the $Cmcm$ structure is compatible with existing Raman and infrared spectroscopic data. Crucially, static density functional theory calculation reveals the $Cmcm$ structure as a dynamically unstable saddle point on the Born-Oppenheimer potential energy surface, demonstrating that a full quantum many-body treatment of the problem is necessary. These results shed new light on the phase diagram of high-pressure hydrogen and call for further experimental verifications.
Probing Scientific General Intelligence of LLMs with Scientist-Aligned Workflows
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:Despite advances in scientific AI, a coherent framework for Scientific General Intelligence (SGI)-the ability to autonomously conceive, investigate, and reason across scientific domains-remains lacking. We present an operational SGI definition grounded in the Practical Inquiry Model (PIM: Deliberation, Conception, Action, Perception) and operationalize it via four scientist-aligned tasks: deep research, idea generation, dry/wet experiments, and experimental reasoning. SGI-Bench comprises over 1,000 expert-curated, cross-disciplinary samples inspired by Science's 125 Big Questions, enabling systematic evaluation of state-of-the-art LLMs. Results reveal gaps: low exact match (10--20%) in deep research despite step-level alignment; ideas lacking feasibility and detail; high code executability but low execution result accuracy in dry experiments; low sequence fidelity in wet protocols; and persistent multimodal comparative-reasoning challenges. We further introduce Test-Time Reinforcement Learning (TTRL), which optimizes retrieval-augmented novelty rewards at inference, enhancing hypothesis novelty without reference answer. Together, our PIM-grounded definition, workflow-centric benchmark, and empirical insights establish a foundation for AI systems that genuinely participate in scientific discovery.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge