Pumeng Lyu
ReconMOST: Multi-Layer Sea Temperature Reconstruction with Observations-Guided Diffusion
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:Accurate reconstruction of ocean is essential for reflecting global climate dynamics and supporting marine meteorological research. Conventional methods face challenges due to sparse data, algorithmic complexity, and high computational costs, while increasing usage of machine learning (ML) method remains limited to reconstruction problems at the sea surface and local regions, struggling with issues like cloud occlusion. To address these limitations, this paper proposes ReconMOST, a data-driven guided diffusion model framework for multi-layer sea temperature reconstruction. Specifically, we first pre-train an unconditional diffusion model using a large collection of historical numerical simulation data, enabling the model to attain physically consistent distribution patterns of ocean temperature fields. During the generation phase, sparse yet high-accuracy in-situ observational data are utilized as guidance points for the reverse diffusion process, generating accurate reconstruction results. Importantly, in regions lacking direct observational data, the physically consistent spatial distribution patterns learned during pre-training enable implicitly guided and physically plausible reconstructions. Our method extends ML-based SST reconstruction to a global, multi-layer setting, handling over 92.5% missing data while maintaining reconstruction accuracy, spatial resolution, and superior generalization capability. We pre-train our model on CMIP6 numerical simulation data and conduct guided reconstruction experiments on CMIP6 and EN4 analysis data. The results of mean squared error (MSE) values achieve 0.049 on guidance, 0.680 on reconstruction, and 0.633 on total, respectively, demonstrating the effectiveness and robustness of the proposed framework. Our source code is available at https://github.com/norsheep/ReconMOST.
ORCA: A Global Ocean Emulator for Multi-year to Decadal Predictions
May 24, 2024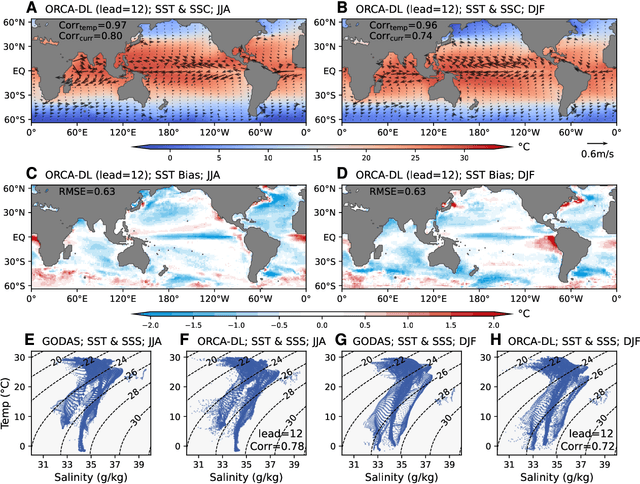
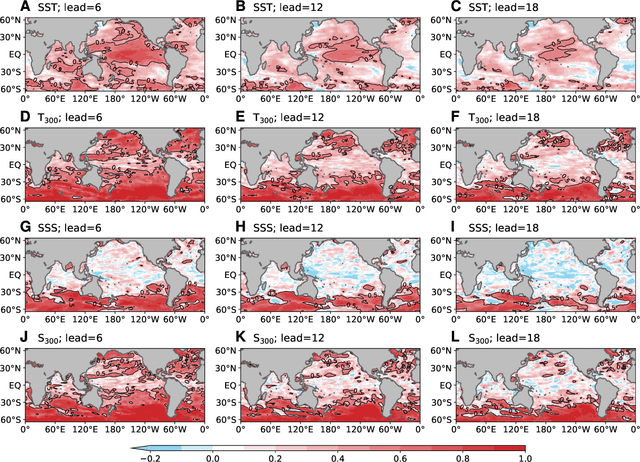
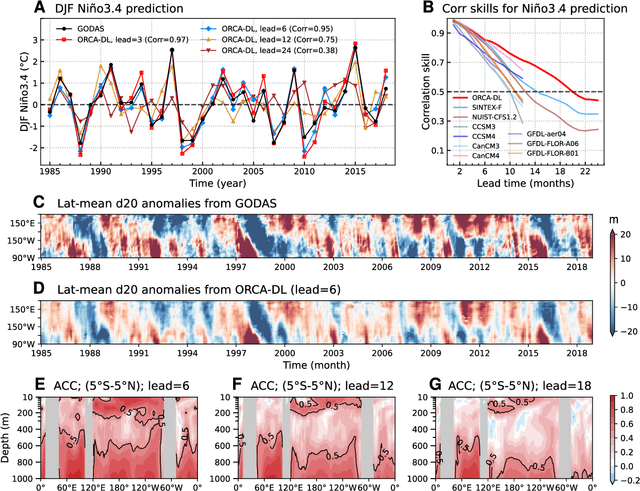
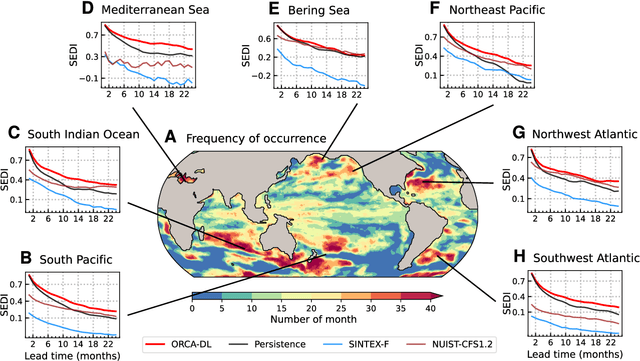
Abstract:Ocean dynamics plays a crucial role in driving global weather and climate patterns. Accurate and efficient modeling of ocean dynamics is essential for improved understanding of complex ocean circulation and processes, for predicting climate variations and their associated teleconnections, and for addressing the challenges of climate change. While great efforts have been made to improve numerical Ocean General Circulation Models (OGCMs), accurate forecasting of global oceanic variations for multi-year remains to be a long-standing challenge. Here, we introduce ORCA (Oceanic Reliable foreCAst), the first data-driven model predicting global ocean circulation from multi-year to decadal time scales. ORCA accurately simulates the three-dimensional circulations and dynamics of the global ocean with high physical consistency. Hindcasts of key oceanic variables demonstrate ORCA's remarkable prediction skills in predicting ocean variations compared with state-of-the-art numerical OGCMs and abilities in capturing occurrences of extreme events at the subsurface ocean and ENSO vertical patterns. These results demonstrate the potential of data-driven ocean models for providing cheap, efficient, and accurate global ocean modeling and prediction. Moreover, ORCA stably and faithfully emulates ocean dynamics at decadal timescales, demonstrating its potential even for climate projections. The model will be available at https://github.com/OpenEarthLab/ORCA.
MLP Can Be A Good Transformer Learner
Apr 08, 2024Abstract:Self-attention mechanism is the key of the Transformer but often criticized for its computation demands. Previous token pruning works motivate their methods from the view of computation redundancy but still need to load the full network and require same memory costs. This paper introduces a novel strategy that simplifies vision transformers and reduces computational load through the selective removal of non-essential attention layers, guided by entropy considerations. We identify that regarding the attention layer in bottom blocks, their subsequent MLP layers, i.e. two feed-forward layers, can elicit the same entropy quantity. Meanwhile, the accompanied MLPs are under-exploited since they exhibit smaller feature entropy compared to those MLPs in the top blocks. Therefore, we propose to integrate the uninformative attention layers into their subsequent counterparts by degenerating them into identical mapping, yielding only MLP in certain transformer blocks. Experimental results on ImageNet-1k show that the proposed method can remove 40% attention layer of DeiT-B, improving throughput and memory bound without performance compromise. Code is available at https://github.com/sihaoevery/lambda_vit.
ResoNet: Robust and Explainable ENSO Forecasts with Hybrid Convolution and Transformer Networks
Dec 16, 2023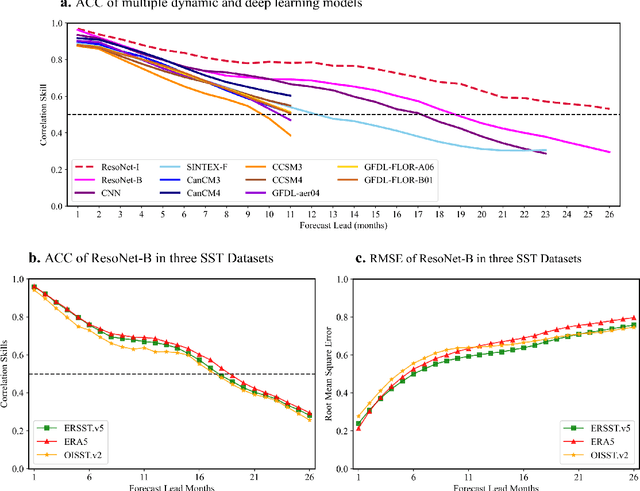
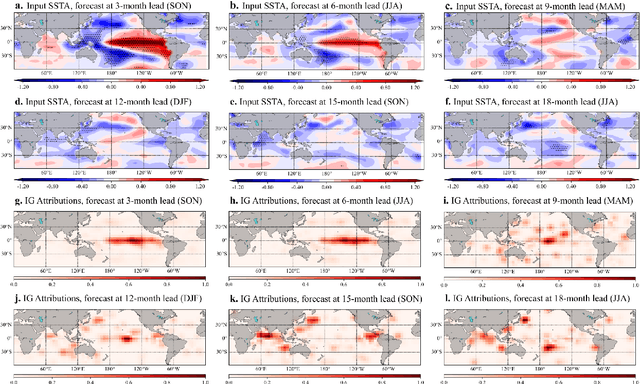
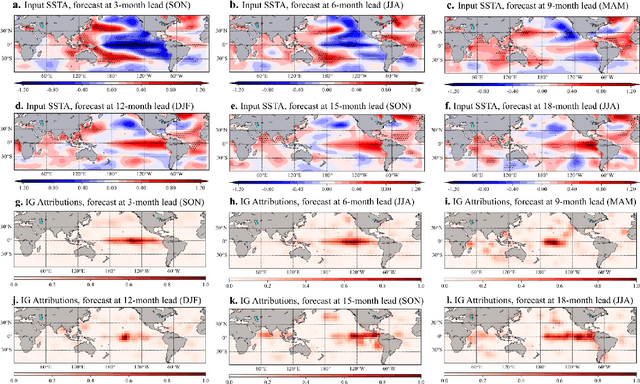
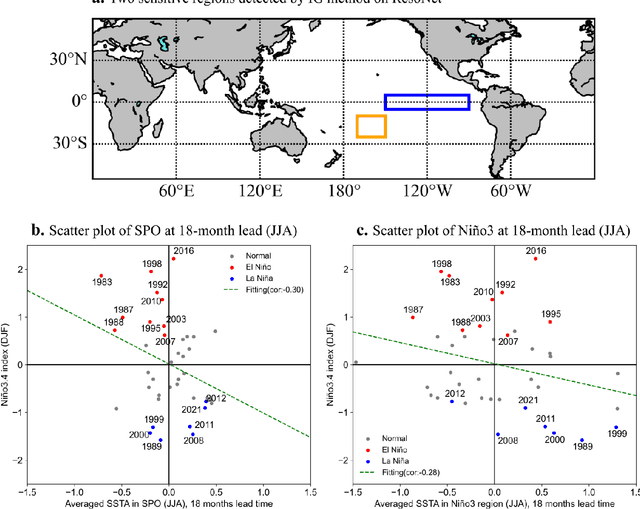
Abstract:Recent studies have shown that deep learning (DL) models can skillfully predict the El Ni\~no-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) forecasts over 1.5 years ahead. However, concerns regarding the reliability of predictions made by DL methods persist, including potential overfitting issues and lack of interpretability. Here, we propose ResoNet, a DL model that combines convolutional neural network (CNN) and Transformer architectures. This hybrid architecture design enables our model to adequately capture local SSTA as well as long-range inter-basin interactions across oceans. We show that ResoNet can robustly predict ESNO at lead times between 19 and 26 months, thus outperforming existing approaches in terms of the forecast horizon. According to an explainability method applied to ResoNet predictions of El Ni\~no and La Ni\~na events from 1- to 18-month lead, we find that it predicts the Ni\~no3.4 index based on multiple physically reasonable mechanisms, such as the Recharge Oscillator concept, Seasonal Footprint Mechanism, and Indian Ocean capacitor effect. Moreover, we demonstrate that for the first time, the asymmetry between El Ni\~no and La Ni\~na development can be captured by ResoNet. Our results could help alleviate skepticism about applying DL models for ENSO prediction and encourage more attempts to discover and predict climate phenomena using AI methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge