Tao Tang
CATNet: Collaborative Alignment and Transformation Network for Cooperative Perception
Mar 05, 2026Abstract:Cooperative perception significantly enhances scene understanding by integrating complementary information from diverse agents. However, existing research often overlooks critical challenges inherent in real-world multi-source data integration, specifically high temporal latency and multi-source noise. To address these practical limitations, we propose Collaborative Alignment and Transformation Network (CATNet), an adaptive compensation framework that resolves temporal latency and noise interference in multi-agent systems. Our key innovations can be summarized in three aspects. First, we introduce a Spatio-Temporal Recurrent Synchronization (STSync) that aligns asynchronous feature streams via adjacent-frame differential modeling, establishing a temporal-spatially unified representation space. Second, we design a Dual-Branch Wavelet Enhanced Denoiser (WTDen) that suppresses global noise and reconstructs localized feature distortions within aligned representations. Third, we construct an Adaptive Feature Selector (AdpSel) that dynamically focuses on critical perceptual features for robust fusion. Extensive experiments on multiple datasets demonstrate that CATNet consistently outperforms existing methods under complex traffic conditions, proving its superior robustness and adaptability.
DriveCombo: Benchmarking Compositional Traffic Rule Reasoning in Autonomous Driving
Mar 02, 2026Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) are rapidly becoming the intelligence brain of end-to-end autonomous driving systems. A key challenge is to assess whether MLLMs can truly understand and follow complex real-world traffic rules. However, existing benchmarks mainly focus on single-rule scenarios like traffic sign recognition, neglecting the complexity of multi-rule concurrency and conflicts in real driving. Consequently, models perform well on simple tasks but often fail or violate rules in real world complex situations. To bridge this gap, we propose DriveCombo, a text and vision-based benchmark for compositional traffic rule reasoning. Inspired by human drivers' cognitive development, we propose a systematic Five-Level Cognitive Ladder that evaluates reasoning from single-rule understanding to multi-rule integration and conflict resolution, enabling quantitative assessment across cognitive stages. We further propose a Rule2Scene Agent that maps language-based traffic rules to dynamic driving scenes through rule crafting and scene generation, enabling scene-level traffic rule visual reasoning. Evaluations of 14 mainstream MLLMs reveal performance drops as task complexity grows, particularly during rule conflicts. After splitting the dataset and fine-tuning on the training set, we further observe substantial improvements in both traffic rule reasoning and downstream planning capabilities. These results highlight the effectiveness of DriveCombo in advancing compliant and intelligent autonomous driving systems.
Thinking with Geometry: Active Geometry Integration for Spatial Reasoning
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Recent progress in spatial reasoning with Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) increasingly leverages geometric priors from 3D encoders. However, most existing integration strategies remain passive: geometry is exposed as a global stream and fused in an indiscriminate manner, which often induces semantic-geometry misalignment and redundant signals. We propose GeoThinker, a framework that shifts the paradigm from passive fusion to active perception. Instead of feature mixing, GeoThinker enables the model to selectively retrieve geometric evidence conditioned on its internal reasoning demands. GeoThinker achieves this through Spatial-Grounded Fusion applied at carefully selected VLM layers, where semantic visual priors selectively query and integrate task-relevant geometry via frame-strict cross-attention, further calibrated by Importance Gating that biases per-frame attention toward task-relevant structures. Comprehensive evaluation results show that GeoThinker sets a new state-of-the-art in spatial intelligence, achieving a peak score of 72.6 on the VSI-Bench. Furthermore, GeoThinker demonstrates robust generalization and significantly improved spatial perception across complex downstream scenarios, including embodied referring and autonomous driving. Our results indicate that the ability to actively integrate spatial structures is essential for next-generation spatial intelligence. Code can be found at https://github.com/Li-Hao-yuan/GeoThinker.
FairGE: Fairness-Aware Graph Encoding in Incomplete Social Networks
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Graph Transformers (GTs) are increasingly applied to social network analysis, yet their deployment is often constrained by fairness concerns. This issue is particularly critical in incomplete social networks, where sensitive attributes are frequently missing due to privacy and ethical restrictions. Existing solutions commonly generate these incomplete attributes, which may introduce additional biases and further compromise user privacy. To address this challenge, FairGE (Fair Graph Encoding) is introduced as a fairness-aware framework for GTs in incomplete social networks. Instead of generating sensitive attributes, FairGE encodes fairness directly through spectral graph theory. By leveraging the principal eigenvector to represent structural information and padding incomplete sensitive attributes with zeros to maintain independence, FairGE ensures fairness without data reconstruction. Theoretical analysis demonstrates that the method suppresses the influence of non-principal spectral components, thereby enhancing fairness. Extensive experiments on seven real-world social network datasets confirm that FairGE achieves at least a 16% improvement in both statistical parity and equality of opportunity compared with state-of-the-art baselines. The source code is shown in https://github.com/LuoRenqiang/FairGE.
OmniGen: Unified Multimodal Sensor Generation for Autonomous Driving
Dec 16, 2025Abstract:Autonomous driving has seen remarkable advancements, largely driven by extensive real-world data collection. However, acquiring diverse and corner-case data remains costly and inefficient. Generative models have emerged as a promising solution by synthesizing realistic sensor data. However, existing approaches primarily focus on single-modality generation, leading to inefficiencies and misalignment in multimodal sensor data. To address these challenges, we propose OminiGen, which generates aligned multimodal sensor data in a unified framework. Our approach leverages a shared Bird\u2019s Eye View (BEV) space to unify multimodal features and designs a novel generalizable multimodal reconstruction method, UAE, to jointly decode LiDAR and multi-view camera data. UAE achieves multimodal sensor decoding through volume rendering, enabling accurate and flexible reconstruction. Furthermore, we incorporate a Diffusion Transformer (DiT) with a ControlNet branch to enable controllable multimodal sensor generation. Our comprehensive experiments demonstrate that OminiGen achieves desired performances in unified multimodal sensor data generation with multimodal consistency and flexible sensor adjustments.
CorrectAD: A Self-Correcting Agentic System to Improve End-to-end Planning in Autonomous Driving
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:End-to-end planning methods are the de facto standard of the current autonomous driving system, while the robustness of the data-driven approaches suffers due to the notorious long-tail problem (i.e., rare but safety-critical failure cases). In this work, we explore whether recent diffusion-based video generation methods (a.k.a. world models), paired with structured 3D layouts, can enable a fully automated pipeline to self-correct such failure cases. We first introduce an agent to simulate the role of product manager, dubbed PM-Agent, which formulates data requirements to collect data similar to the failure cases. Then, we use a generative model that can simulate both data collection and annotation. However, existing generative models struggle to generate high-fidelity data conditioned on 3D layouts. To address this, we propose DriveSora, which can generate spatiotemporally consistent videos aligned with the 3D annotations requested by PM-Agent. We integrate these components into our self-correcting agentic system, CorrectAD. Importantly, our pipeline is an end-to-end model-agnostic and can be applied to improve any end-to-end planner. Evaluated on both nuScenes and a more challenging in-house dataset across multiple end-to-end planners, CorrectAD corrects 62.5% and 49.8% of failure cases, reducing collision rates by 39% and 27%, respectively.
LiDAR-GS++:Improving LiDAR Gaussian Reconstruction via Diffusion Priors
Nov 15, 2025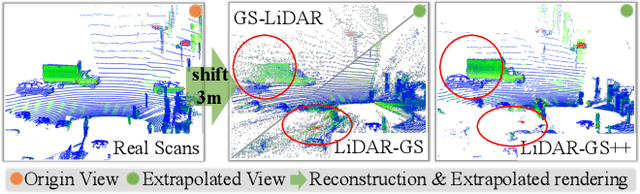
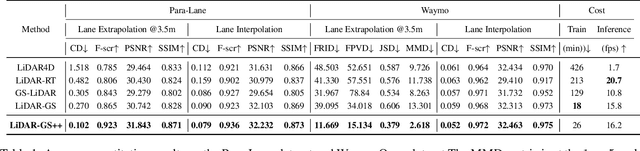
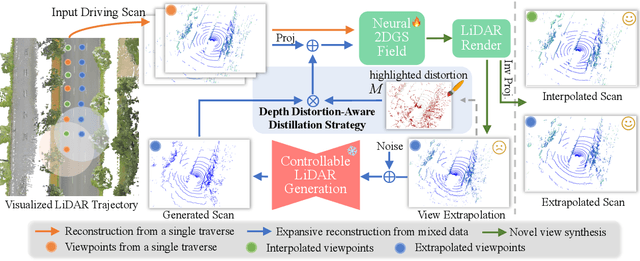
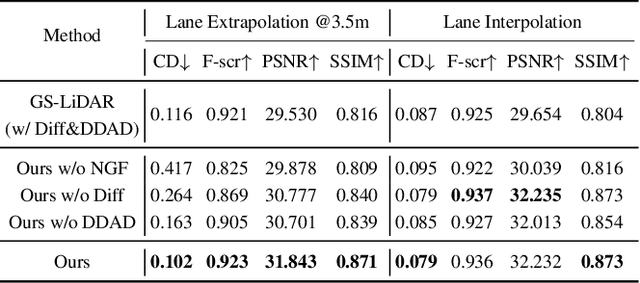
Abstract:Recent GS-based rendering has made significant progress for LiDAR, surpassing Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) in both quality and speed. However, these methods exhibit artifacts in extrapolated novel view synthesis due to the incomplete reconstruction from single traversal scans. To address this limitation, we present LiDAR-GS++, a LiDAR Gaussian Splatting reconstruction method enhanced by diffusion priors for real-time and high-fidelity re-simulation on public urban roads. Specifically, we introduce a controllable LiDAR generation model conditioned on coarsely extrapolated rendering to produce extra geometry-consistent scans and employ an effective distillation mechanism for expansive reconstruction. By extending reconstruction to under-fitted regions, our approach ensures global geometric consistency for extrapolative novel views while preserving detailed scene surfaces captured by sensors. Experiments on multiple public datasets demonstrate that LiDAR-GS++ achieves state-of-the-art performance for both interpolated and extrapolated viewpoints, surpassing existing GS and NeRF-based methods.
Human-in-Context: Unified Cross-Domain 3D Human Motion Modeling via In-Context Learning
Aug 14, 2025Abstract:This paper aims to model 3D human motion across domains, where a single model is expected to handle multiple modalities, tasks, and datasets. Existing cross-domain models often rely on domain-specific components and multi-stage training, which limits their practicality and scalability. To overcome these challenges, we propose a new setting to train a unified cross-domain model through a single process, eliminating the need for domain-specific components and multi-stage training. We first introduce Pose-in-Context (PiC), which leverages in-context learning to create a pose-centric cross-domain model. While PiC generalizes across multiple pose-based tasks and datasets, it encounters difficulties with modality diversity, prompting strategy, and contextual dependency handling. We thus propose Human-in-Context (HiC), an extension of PiC that broadens generalization across modalities, tasks, and datasets. HiC combines pose and mesh representations within a unified framework, expands task coverage, and incorporates larger-scale datasets. Additionally, HiC introduces a max-min similarity prompt sampling strategy to enhance generalization across diverse domains and a network architecture with dual-branch context injection for improved handling of contextual dependencies. Extensive experimental results show that HiC performs better than PiC in terms of generalization, data scale, and performance across a wide range of domains. These results demonstrate the potential of HiC for building a unified cross-domain 3D human motion model with improved flexibility and scalability. The source codes and models are available at https://github.com/BradleyWang0416/Human-in-Context.
MIND: A Noise-Adaptive Denoising Framework for Medical Images Integrating Multi-Scale Transformer
Aug 13, 2025Abstract:The core role of medical images in disease diagnosis makes their quality directly affect the accuracy of clinical judgment. However, due to factors such as low-dose scanning, equipment limitations and imaging artifacts, medical images are often accompanied by non-uniform noise interference, which seriously affects structure recognition and lesion detection. This paper proposes a medical image adaptive denoising model (MI-ND) that integrates multi-scale convolutional and Transformer architecture, introduces a noise level estimator (NLE) and a noise adaptive attention module (NAAB), and realizes channel-spatial attention regulation and cross-modal feature fusion driven by noise perception. Systematic testing is carried out on multimodal public datasets. Experiments show that this method significantly outperforms the comparative methods in image quality indicators such as PSNR, SSIM, and LPIPS, and improves the F1 score and ROC-AUC in downstream diagnostic tasks, showing strong prac-tical value and promotional potential. The model has outstanding benefits in structural recovery, diagnostic sensitivity, and cross-modal robustness, and provides an effective solution for medical image enhancement and AI-assisted diagnosis and treatment.
Does Your 3D Encoder Really Work? When Pretrain-SFT from 2D VLMs Meets 3D VLMs
Jun 06, 2025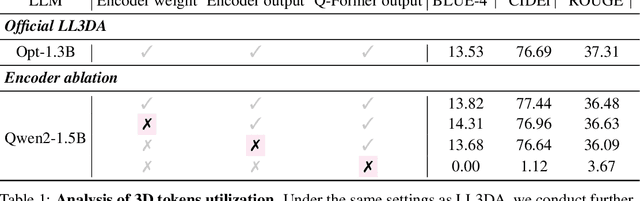
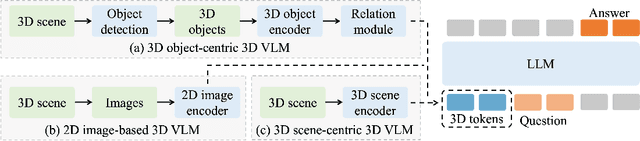

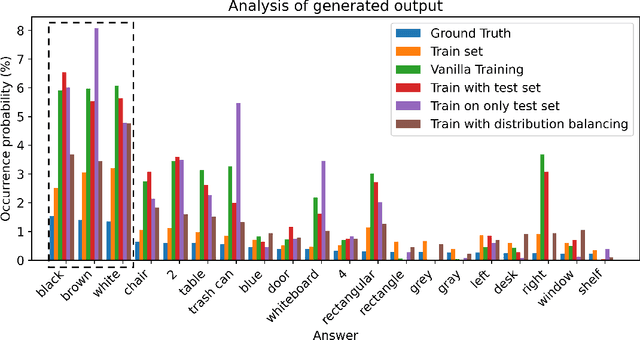
Abstract:Remarkable progress in 2D Vision-Language Models (VLMs) has spurred interest in extending them to 3D settings for tasks like 3D Question Answering, Dense Captioning, and Visual Grounding. Unlike 2D VLMs that typically process images through an image encoder, 3D scenes, with their intricate spatial structures, allow for diverse model architectures. Based on their encoder design, this paper categorizes recent 3D VLMs into 3D object-centric, 2D image-based, and 3D scene-centric approaches. Despite the architectural similarity of 3D scene-centric VLMs to their 2D counterparts, they have exhibited comparatively lower performance compared with the latest 3D object-centric and 2D image-based approaches. To understand this gap, we conduct an in-depth analysis, revealing that 3D scene-centric VLMs show limited reliance on the 3D scene encoder, and the pre-train stage appears less effective than in 2D VLMs. Furthermore, we observe that data scaling benefits are less pronounced on larger datasets. Our investigation suggests that while these models possess cross-modal alignment capabilities, they tend to over-rely on linguistic cues and overfit to frequent answer distributions, thereby diminishing the effective utilization of the 3D encoder. To address these limitations and encourage genuine 3D scene understanding, we introduce a novel 3D Relevance Discrimination QA dataset designed to disrupt shortcut learning and improve 3D understanding. Our findings highlight the need for advanced evaluation and improved strategies for better 3D understanding in 3D VLMs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge