Hong Liu
School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK, USA
IDPruner: Harmonizing Importance and Diversity in Visual Token Pruning for MLLMs
Feb 10, 2026Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have demonstrated impressive capabilities, yet they encounter significant computational bottlenecks due to the massive volume of visual tokens. Consequently, visual token pruning, which substantially reduces the token count, has emerged as a critical technique for accelerating MLLM inference. Existing approaches focus on token importance, diversity, or an intuitive combination of both, without a principled framework for their optimal integration. To address this issue, we first conduct a systematic analysis to characterize the trade-off between token importance and semantic diversity. Guided by this analysis, we propose the \textbf{I}mportance and \textbf{D}iversity Pruner (\textbf{IDPruner}), which leverages the Maximal Marginal Relevance (MMR) algorithm to achieve a Pareto-optimal balance between these two objectives. Crucially, our method operates without requiring attention maps, ensuring full compatibility with FlashAttention and efficient deployment via one-shot pruning. We conduct extensive experiments across various model architectures and multimodal benchmarks, demonstrating that IDPruner achieves state-of-the-art performance and superior generalization across diverse architectures and tasks. Notably, on Qwen2.5-VL-7B-Instruct, IDPruner retains 95.18\% of baseline performance when pruning 75\% of the tokens, and still maintains 86.40\% even under an extreme 90\% pruning ratio. Our code is available at https://github.com/Tencent/AngelSlim.
PA-MIL: Phenotype-Aware Multiple Instance Learning Guided by Language Prompting and Genotype-to-Phenotype Relationships
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Deep learning has been extensively researched in the analysis of pathology whole-slide images (WSIs). However, most existing methods are limited to providing prediction interpretability by locating the model's salient areas in a post-hoc manner, failing to offer more reliable and accountable explanations. In this work, we propose Phenotype-Aware Multiple Instance Learning (PA-MIL), a novel ante-hoc interpretable framework that identifies cancer-related phenotypes from WSIs and utilizes them for cancer subtyping. To facilitate PA-MIL in learning phenotype-aware features, we 1) construct a phenotype knowledge base containing cancer-related phenotypes and their associated genotypes. 2) utilize the morphological descriptions of phenotypes as language prompting to aggregate phenotype-related features. 3) devise the Genotype-to-Phenotype Neural Network (GP-NN) grounded in genotype-to-phenotype relationships, which provides multi-level guidance for PA-MIL. Experimental results on multiple datasets demonstrate that PA-MIL achieves competitive performance compared to existing MIL methods while offering improved interpretability. PA-MIL leverages phenotype saliency as evidence and, using a linear classifier, achieves competitive results compared to state-of-the-art methods. Additionally, we thoroughly analyze the genotype-phenotype relationships, as well as cohort-level and case-level interpretability, demonstrating the reliability and accountability of PA-MIL.
Scaling Embeddings Outperforms Scaling Experts in Language Models
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:While Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architectures have become the standard for sparsity scaling in large language models, they increasingly face diminishing returns and system-level bottlenecks. In this work, we explore embedding scaling as a potent, orthogonal dimension for scaling sparsity. Through a comprehensive analysis and experiments, we identify specific regimes where embedding scaling achieves a superior Pareto frontier compared to expert scaling. We systematically characterize the critical architectural factors governing this efficacy -- ranging from parameter budgeting to the interplay with model width and depth. Moreover, by integrating tailored system optimizations and speculative decoding, we effectively convert this sparsity into tangible inference speedups. Guided by these insights, we introduce LongCat-Flash-Lite, a 68.5B parameter model with ~3B activated trained from scratch. Despite allocating over 30B parameters to embeddings, LongCat-Flash-Lite not only surpasses parameter-equivalent MoE baselines but also exhibits exceptional competitiveness against existing models of comparable scale, particularly in agentic and coding domains.
Trustworthy Evaluation of Robotic Manipulation: A New Benchmark and AutoEval Methods
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Driven by the rapid evolution of Vision-Action and Vision-Language-Action models, imitation learning has significantly advanced robotic manipulation capabilities. However, evaluation methodologies have lagged behind, hindering the establishment of Trustworthy Evaluation for these behaviors. Current paradigms rely on binary success rates, failing to address the critical dimensions of trust: Source Authenticity (i.e., distinguishing genuine policy behaviors from human teleoperation) and Execution Quality (e.g., smoothness and safety). To bridge these gaps, we propose a solution that combines the Eval-Actions benchmark and the AutoEval architecture. First, we construct the Eval-Actions benchmark to support trustworthiness analysis. Distinct from existing datasets restricted to successful human demonstrations, Eval-Actions integrates VA and VLA policy execution trajectories alongside human teleoperation data, explicitly including failure scenarios. This dataset is structured around three core supervision signals: Expert Grading (EG), Rank-Guided preferences (RG), and Chain-of-Thought (CoT). Building on this, we propose the AutoEval architecture: AutoEval leverages Spatio-Temporal Aggregation for semantic assessment, augmented by an auxiliary Kinematic Calibration Signal to refine motion smoothness; AutoEval Plus (AutoEval-P) incorporates the Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) paradigm to enhance logical reasoning capabilities. Experiments show AutoEval achieves Spearman's Rank Correlation Coefficients (SRCC) of 0.81 and 0.84 under the EG and RG protocols, respectively. Crucially, the framework possesses robust source discrimination capabilities, distinguishing between policy-generated and teleoperated videos with 99.6% accuracy, thereby establishing a rigorous standard for trustworthy robotic evaluation. Our project and code are available at https://term-bench.github.io/.
HDCNet: A Hybrid Depth Completion Network for Grasping Transparent and Reflective Objects
Nov 10, 2025Abstract:Depth perception of transparent and reflective objects has long been a critical challenge in robotic manipulation.Conventional depth sensors often fail to provide reliable measurements on such surfaces, limiting the performance of robots in perception and grasping tasks. To address this issue, we propose a novel depth completion network,HDCNet,which integrates the complementary strengths of Transformer,CNN and Mamba architectures.Specifically,the encoder is designed as a dual-branch Transformer-CNN framework to extract modality-specific features. At the shallow layers of the encoder, we introduce a lightweight multimodal fusion module to effectively integrate low-level features. At the network bottleneck,a Transformer-Mamba hybrid fusion module is developed to achieve deep integration of high-level semantic and global contextual information, significantly enhancing depth completion accuracy and robustness. Extensive evaluations on multiple public datasets demonstrate that HDCNet achieves state-of-the-art(SOTA) performance in depth completion tasks.Furthermore,robotic grasping experiments show that HDCNet substantially improves grasp success rates for transparent and reflective objects,achieving up to a 60% increase.
Every Step Evolves: Scaling Reinforcement Learning for Trillion-Scale Thinking Model
Oct 21, 2025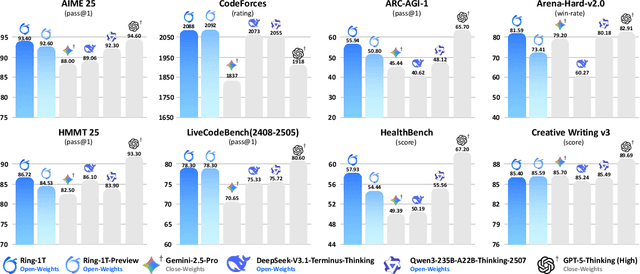
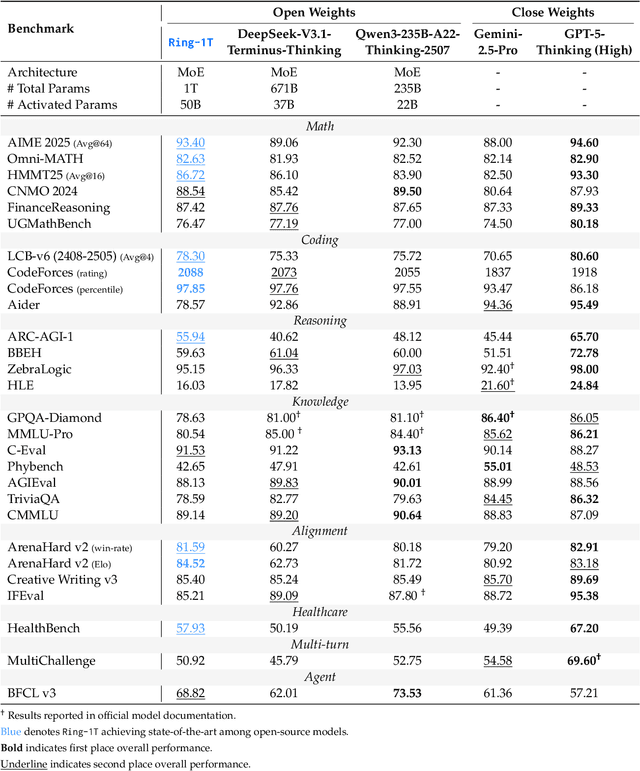
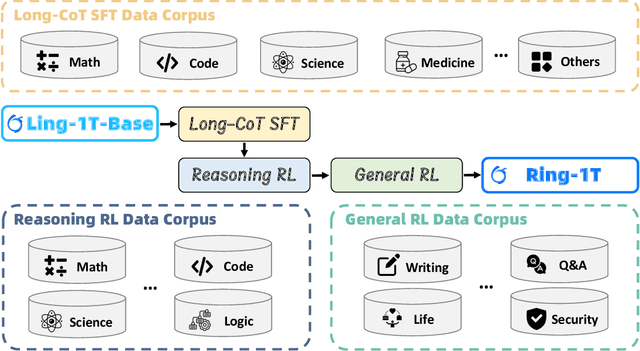
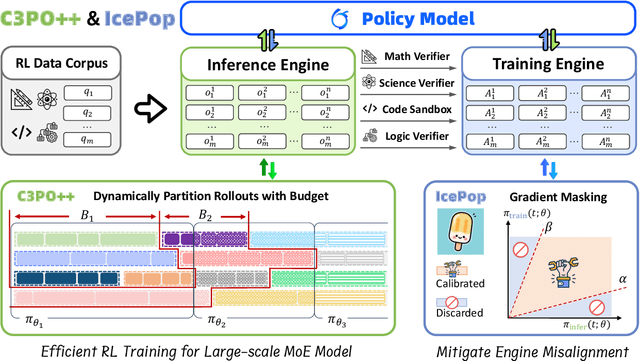
Abstract:We present Ring-1T, the first open-source, state-of-the-art thinking model with a trillion-scale parameter. It features 1 trillion total parameters and activates approximately 50 billion per token. Training such models at a trillion-parameter scale introduces unprecedented challenges, including train-inference misalignment, inefficiencies in rollout processing, and bottlenecks in the RL system. To address these, we pioneer three interconnected innovations: (1) IcePop stabilizes RL training via token-level discrepancy masking and clipping, resolving instability from training-inference mismatches; (2) C3PO++ improves resource utilization for long rollouts under a token budget by dynamically partitioning them, thereby obtaining high time efficiency; and (3) ASystem, a high-performance RL framework designed to overcome the systemic bottlenecks that impede trillion-parameter model training. Ring-1T delivers breakthrough results across critical benchmarks: 93.4 on AIME-2025, 86.72 on HMMT-2025, 2088 on CodeForces, and 55.94 on ARC-AGI-v1. Notably, it attains a silver medal-level result on the IMO-2025, underscoring its exceptional reasoning capabilities. By releasing the complete 1T parameter MoE model to the community, we provide the research community with direct access to cutting-edge reasoning capabilities. This contribution marks a significant milestone in democratizing large-scale reasoning intelligence and establishes a new baseline for open-source model performance.
PANICL: Mitigating Over-Reliance on Single Prompt in Visual In-Context Learning
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:Visual In-Context Learning (VICL) uses input-output image pairs, referred to as in-context pairs (or examples), as prompts alongside query images to guide models in performing diverse vision tasks. However, VICL often suffers from over-reliance on a single in-context pair, which can lead to biased and unstable predictions. We introduce PAtch-based $k$-Nearest neighbor visual In-Context Learning (PANICL), a general training-free framework that mitigates this issue by leveraging multiple in-context pairs. PANICL smooths assignment scores across pairs, reducing bias without requiring additional training. Extensive experiments on a variety of tasks, including foreground segmentation, single object detection, colorization, multi-object segmentation, and keypoint detection, demonstrate consistent improvements over strong baselines. Moreover, PANICL exhibits strong robustness to domain shifts, including dataset-level shift (e.g., from COCO to Pascal) and label-space shift (e.g., FSS-1000), and generalizes well to other VICL models such as SegGPT, Painter, and LVM, highlighting its versatility and broad applicability.
Enhancing WSI-Based Survival Analysis with Report-Auxiliary Self-Distillation
Sep 19, 2025Abstract:Survival analysis based on Whole Slide Images (WSIs) is crucial for evaluating cancer prognosis, as they offer detailed microscopic information essential for predicting patient outcomes. However, traditional WSI-based survival analysis usually faces noisy features and limited data accessibility, hindering their ability to capture critical prognostic features effectively. Although pathology reports provide rich patient-specific information that could assist analysis, their potential to enhance WSI-based survival analysis remains largely unexplored. To this end, this paper proposes a novel Report-auxiliary self-distillation (Rasa) framework for WSI-based survival analysis. First, advanced large language models (LLMs) are utilized to extract fine-grained, WSI-relevant textual descriptions from original noisy pathology reports via a carefully designed task prompt. Next, a self-distillation-based pipeline is designed to filter out irrelevant or redundant WSI features for the student model under the guidance of the teacher model's textual knowledge. Finally, a risk-aware mix-up strategy is incorporated during the training of the student model to enhance both the quantity and diversity of the training data. Extensive experiments carried out on our collected data (CRC) and public data (TCGA-BRCA) demonstrate the superior effectiveness of Rasa against state-of-the-art methods. Our code is available at https://github.com/zhengwang9/Rasa.
Synthetic bootstrapped pretraining
Sep 17, 2025Abstract:We introduce Synthetic Bootstrapped Pretraining (SBP), a language model (LM) pretraining procedure that first learns a model of relations between documents from the pretraining dataset and then leverages it to synthesize a vast new corpus for joint training. While the standard pretraining teaches LMs to learn causal correlations among tokens within a single document, it is not designed to efficiently model the rich, learnable inter-document correlations that can potentially lead to better performance. We validate SBP by designing a compute-matched pretraining setup and pretrain a 3B-parameter model on up to 1T tokens from scratch. We find SBP consistently improves upon a strong repetition baseline and delivers a significant fraction of performance improvement attainable by an oracle upper bound with access to 20x more unique data. Qualitative analysis reveals that the synthesized documents go beyond mere paraphrases -- SBP first abstracts a core concept from the seed material and then crafts a new narration on top of it. Besides strong empirical performance, SBP admits a natural Bayesian interpretation: the synthesizer implicitly learns to abstract the latent concepts shared between related documents.
MAESTRO: Multi-modal Adaptive Ensemble for Spectro-Temporal Robust Optimization
Sep 10, 2025Abstract:Timely and robust influenza incidence forecasting is critical for public health decision-making. To address this, we present MAESTRO, a Multi-modal Adaptive Ensemble for Spectro-Temporal Robust Optimization. MAESTRO achieves robustness by adaptively fusing multi-modal inputs-including surveillance, web search trends, and meteorological data-and leveraging a comprehensive spectro-temporal architecture. The model first decomposes time series into seasonal and trend components. These are then processed through a hybrid feature enhancement pipeline combining Transformer-based encoders, a Mamba state-space model for long-range dependencies, multi-scale temporal convolutions, and a frequency-domain analysis module. A cross-channel attention mechanism further integrates information across the different data modalities. Finally, a temporal projection head performs sequence-to-sequence forecasting, with an optional estimator to quantify prediction uncertainty. Evaluated on over 11 years of Hong Kong influenza data (excluding the COVID-19 period), MAESTRO shows strong competitive performance, demonstrating a superior model fit and relative accuracy, achieving a state-of-the-art R-square of 0.956. Extensive ablations confirm the significant contributions of both multi-modal fusion and the spectro-temporal components. Our modular and reproducible pipeline is made publicly available to facilitate deployment and extension to other regions and pathogens.Our publicly available pipeline presents a powerful, unified framework, demonstrating the critical synergy of advanced spectro-temporal modeling and multi-modal data fusion for robust epidemiological forecasting.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge