Ran Wang
PandaPose: 3D Human Pose Lifting from a Single Image via Propagating 2D Pose Prior to 3D Anchor Space
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:3D human pose lifting from a single RGB image is a challenging task in 3D vision. Existing methods typically establish a direct joint-to-joint mapping from 2D to 3D poses based on 2D features. This formulation suffers from two fundamental limitations: inevitable error propagation from input predicted 2D pose to 3D predictions and inherent difficulties in handling self-occlusion cases. In this paper, we propose PandaPose, a 3D human pose lifting approach via propagating 2D pose prior to 3D anchor space as the unified intermediate representation. Specifically, our 3D anchor space comprises: (1) Joint-wise 3D anchors in the canonical coordinate system, providing accurate and robust priors to mitigate 2D pose estimation inaccuracies. (2) Depth-aware joint-wise feature lifting that hierarchically integrates depth information to resolve self-occlusion ambiguities. (3) The anchor-feature interaction decoder that incorporates 3D anchors with lifted features to generate unified anchor queries encapsulating joint-wise 3D anchor set, visual cues and geometric depth information. The anchor queries are further employed to facilitate anchor-to-joint ensemble prediction. Experiments on three well-established benchmarks (i.e., Human3.6M, MPI-INF-3DHP and 3DPW) demonstrate the superiority of our proposition. The substantial reduction in error by $14.7\%$ compared to SOTA methods on the challenging conditions of Human3.6M and qualitative comparisons further showcase the effectiveness and robustness of our approach.
Numina-Lean-Agent: An Open and General Agentic Reasoning System for Formal Mathematics
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Agentic systems have recently become the dominant paradigm for formal theorem proving, achieving strong performance by coordinating multiple models and tools. However, existing approaches often rely on task-specific pipelines and trained formal provers, limiting their flexibility and reproducibility. In this paper, we propose the paradigm that directly uses a general coding agent as a formal math reasoner. This paradigm is motivated by (1) A general coding agent provides a natural interface for diverse reasoning tasks beyond proving, (2) Performance can be improved by simply replacing the underlying base model, without training, and (3) MCP enables flexible extension and autonomous calling of specialized tools, avoiding complex design. Based on this paradigm, we introduce Numina-Lean-Agent, which combines Claude Code with Numina-Lean-MCP to enable autonomous interaction with Lean, retrieval of relevant theorems, informal proving and auxiliary reasoning tools. Using Claude Opus 4.5 as the base model, Numina-Lean-Agent solves all problems in Putnam 2025 (12 / 12), matching the best closed-source system. Beyond benchmark evaluation, we further demonstrate its generality by interacting with mathematicians to successfully formalize the Brascamp-Lieb theorem. We release Numina-Lean-Agent and all solutions at https://github.com/project-numina/numina-lean-agent.
Object-IR: Leveraging Object Consistency and Mesh Deformation for Self-Supervised Image Retargeting
Oct 31, 2025Abstract:Eliminating geometric distortion in semantically important regions remains an intractable challenge in image retargeting. This paper presents Object-IR, a self-supervised architecture that reformulates image retargeting as a learning-based mesh warping optimization problem, where the mesh deformation is guided by object appearance consistency and geometric-preserving constraints. Given an input image and a target aspect ratio, we initialize a uniform rigid mesh at the output resolution and use a convolutional neural network to predict the motion of each mesh grid and obtain the deformed mesh. The retargeted result is generated by warping the input image according to the rigid mesh in the input image and the deformed mesh in the output resolution. To mitigate geometric distortion, we design a comprehensive objective function incorporating a) object-consistent loss to ensure that the important semantic objects retain their appearance, b) geometric-preserving loss to constrain simple scale transform of the important meshes, and c) boundary loss to enforce a clean rectangular output. Notably, our self-supervised paradigm eliminates the need for manually annotated retargeting datasets by deriving supervision directly from the input's geometric and semantic properties. Extensive evaluations on the RetargetMe benchmark demonstrate that our Object-IR achieves state-of-the-art performance, outperforming existing methods in quantitative metrics and subjective visual quality assessments. The framework efficiently processes arbitrary input resolutions (average inference time: 0.009s for 1024x683 resolution) while maintaining real-time performance on consumer-grade GPUs. The source code will soon be available at https://github.com/tlliao/Object-IR.
WGRAMMAR: Leverage Prior Knowledge to Accelerate Structured Decoding
Jul 22, 2025Abstract:Structured decoding enables large language models (LLMs) to generate outputs in formats required by downstream systems, such as HTML or JSON. However, existing methods suffer from efficiency bottlenecks due to grammar compilation, state tracking, and mask creation. We observe that many real-world tasks embed strong prior knowledge about output structure. Leveraging this, we propose a decomposition of constraints into static and dynamic components -- precompiling static structures offline and instantiating dynamic arguments at runtime using grammar snippets. Instead of relying on pushdown automata, we employ a compositional set of operators to model regular formats, achieving lower transition latency. We introduce wgrammar, a lightweight decoding engine that integrates domain-aware simplification, constraint decomposition, and mask caching, achieving up to 250x speedup over existing systems. wgrammar's source code is publicly available at https://github.com/wrran/wgrammar.
Unify Graph Learning with Text: Unleashing LLM Potentials for Session Search
May 20, 2025Abstract:Session search involves a series of interactive queries and actions to fulfill user's complex information need. Current strategies typically prioritize sequential modeling for deep semantic understanding, overlooking the graph structure in interactions. While some approaches focus on capturing structural information, they use a generalized representation for documents, neglecting the word-level semantic modeling. In this paper, we propose Symbolic Graph Ranker (SGR), which aims to take advantage of both text-based and graph-based approaches by leveraging the power of recent Large Language Models (LLMs). Concretely, we first introduce a set of symbolic grammar rules to convert session graph into text. This allows integrating session history, interaction process, and task instruction seamlessly as inputs for the LLM. Moreover, given the natural discrepancy between LLMs pre-trained on textual corpora, and the symbolic language we produce using our graph-to-text grammar, our objective is to enhance LLMs' ability to capture graph structures within a textual format. To achieve this, we introduce a set of self-supervised symbolic learning tasks including link prediction, node content generation, and generative contrastive learning, to enable LLMs to capture the topological information from coarse-grained to fine-grained. Experiment results and comprehensive analysis on two benchmark datasets, AOL and Tiangong-ST, confirm the superiority of our approach. Our paradigm also offers a novel and effective methodology that bridges the gap between traditional search strategies and modern LLMs.
Kimina-Prover Preview: Towards Large Formal Reasoning Models with Reinforcement Learning
Apr 15, 2025Abstract:We introduce Kimina-Prover Preview, a large language model that pioneers a novel reasoning-driven exploration paradigm for formal theorem proving, as showcased in this preview release. Trained with a large-scale reinforcement learning pipeline from Qwen2.5-72B, Kimina-Prover demonstrates strong performance in Lean 4 proof generation by employing a structured reasoning pattern we term \textit{formal reasoning pattern}. This approach allows the model to emulate human problem-solving strategies in Lean, iteratively generating and refining proof steps. Kimina-Prover sets a new state-of-the-art on the miniF2F benchmark, reaching 80.7% with pass@8192. Beyond improved benchmark performance, our work yields several key insights: (1) Kimina-Prover exhibits high sample efficiency, delivering strong results even with minimal sampling (pass@1) and scaling effectively with computational budget, stemming from its unique reasoning pattern and RL training; (2) we demonstrate clear performance scaling with model size, a trend previously unobserved for neural theorem provers in formal mathematics; (3) the learned reasoning style, distinct from traditional search algorithms, shows potential to bridge the gap between formal verification and informal mathematical intuition. We open source distilled versions with 1.5B and 7B parameters of Kimina-Prover
Feature Statistics with Uncertainty Help Adversarial Robustness
Mar 26, 2025Abstract:Despite the remarkable success of deep neural networks (DNNs), the security threat of adversarial attacks poses a significant challenge to the reliability of DNNs. By introducing randomness into different parts of DNNs, stochastic methods can enable the model to learn some uncertainty, thereby improving model robustness efficiently. In this paper, we theoretically discover a universal phenomenon that adversarial attacks will shift the distributions of feature statistics. Motivated by this theoretical finding, we propose a robustness enhancement module called Feature Statistics with Uncertainty (FSU). It resamples channel-wise feature means and standard deviations of examples from multivariate Gaussian distributions, which helps to reconstruct the attacked examples and calibrate the shifted distributions. The calibration recovers some domain characteristics of the data for classification, thereby mitigating the influence of perturbations and weakening the ability of attacks to deceive models. The proposed FSU module has universal applicability in training, attacking, predicting and fine-tuning, demonstrating impressive robustness enhancement ability at trivial additional time cost. For example, against powerful optimization-based CW attacks, by incorporating FSU into attacking and predicting phases, it endows many collapsed state-of-the-art models with 50%-80% robust accuracy on CIFAR10, CIFAR100 and SVHN.
Similarity and Dissimilarity Guided Co-association Matrix Construction for Ensemble Clustering
Nov 01, 2024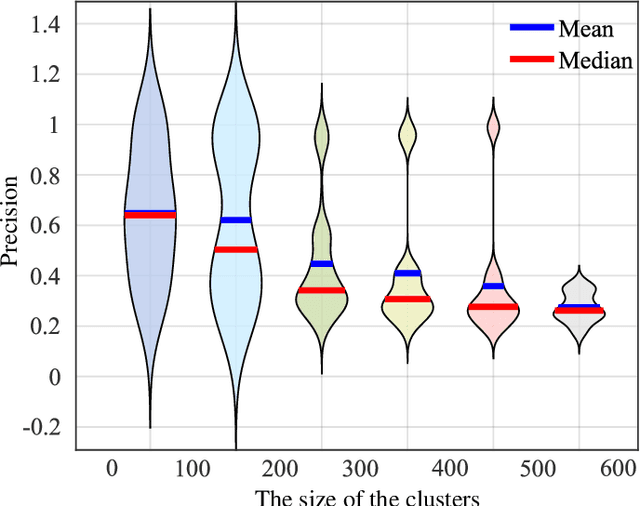
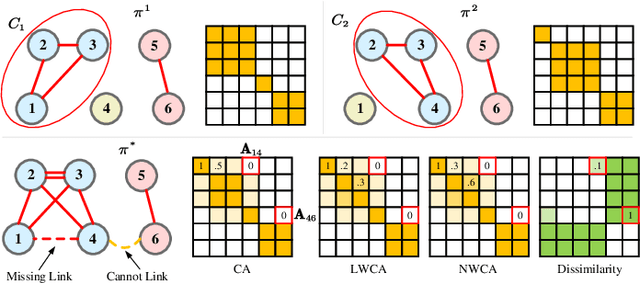
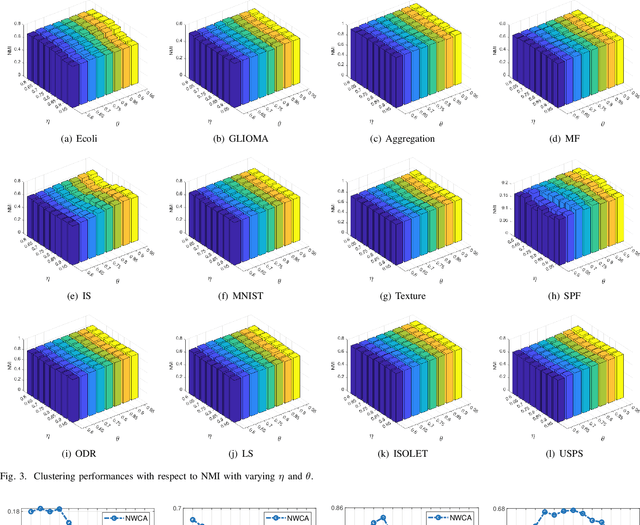
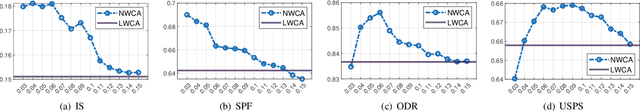
Abstract:Ensemble clustering aggregates multiple weak clusterings to achieve a more accurate and robust consensus result. The Co-Association matrix (CA matrix) based method is the mainstream ensemble clustering approach that constructs the similarity relationships between sample pairs according the weak clustering partitions to generate the final clustering result. However, the existing methods neglect that the quality of cluster is related to its size, i.e., a cluster with smaller size tends to higher accuracy. Moreover, they also do not consider the valuable dissimilarity information in the base clusterings which can reflect the varying importance of sample pairs that are completely disconnected. To this end, we propose the Similarity and Dissimilarity Guided Co-association matrix (SDGCA) to achieve ensemble clustering. First, we introduce normalized ensemble entropy to estimate the quality of each cluster, and construct a similarity matrix based on this estimation. Then, we employ the random walk to explore high-order proximity of base clusterings to construct a dissimilarity matrix. Finally, the adversarial relationship between the similarity matrix and the dissimilarity matrix is utilized to construct a promoted CA matrix for ensemble clustering. We compared our method with 13 state-of-the-art methods across 12 datasets, and the results demonstrated the superiority clustering ability and robustness of the proposed approach. The code is available at https://github.com/xuz2019/SDGCA.
Subgoal-based Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning for Multi-Agent Collaboration
Aug 21, 2024Abstract:Recent advancements in reinforcement learning have made significant impacts across various domains, yet they often struggle in complex multi-agent environments due to issues like algorithm instability, low sampling efficiency, and the challenges of exploration and dimensionality explosion. Hierarchical reinforcement learning (HRL) offers a structured approach to decompose complex tasks into simpler sub-tasks, which is promising for multi-agent settings. This paper advances the field by introducing a hierarchical architecture that autonomously generates effective subgoals without explicit constraints, enhancing both flexibility and stability in training. We propose a dynamic goal generation strategy that adapts based on environmental changes. This method significantly improves the adaptability and sample efficiency of the learning process. Furthermore, we address the critical issue of credit assignment in multi-agent systems by synergizing our hierarchical architecture with a modified QMIX network, thus improving overall strategy coordination and efficiency. Comparative experiments with mainstream reinforcement learning algorithms demonstrate the superior convergence speed and performance of our approach in both single-agent and multi-agent environments, confirming its effectiveness and flexibility in complex scenarios. Our code is open-sourced at: \url{https://github.com/SICC-Group/GMAH}.
Multiobjective Vehicle Routing Optimization with Time Windows: A Hybrid Approach Using Deep Reinforcement Learning and NSGA-II
Jul 18, 2024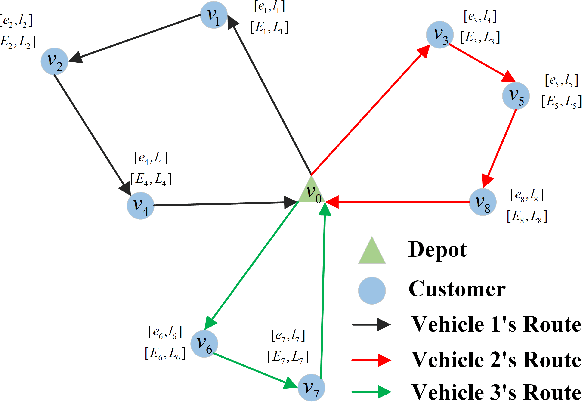
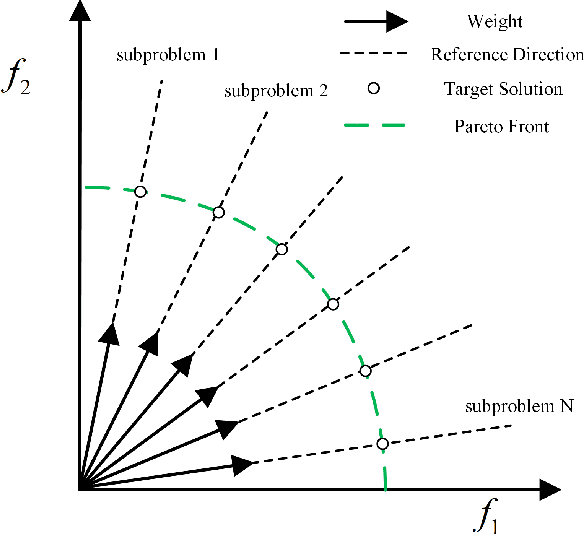
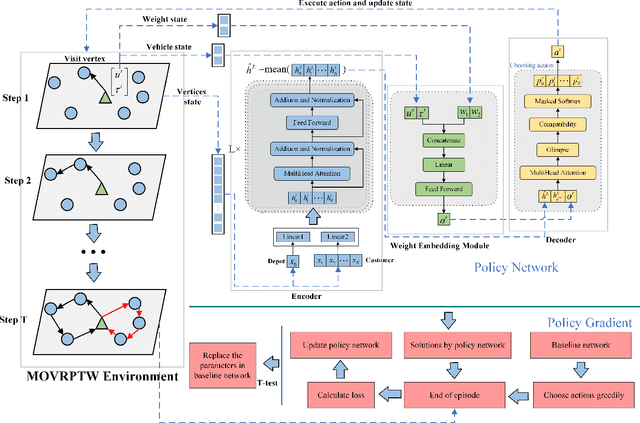
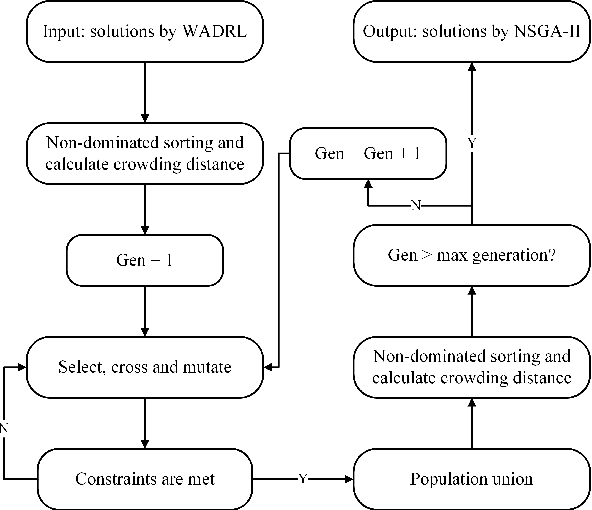
Abstract:This paper proposes a weight-aware deep reinforcement learning (WADRL) approach designed to address the multiobjective vehicle routing problem with time windows (MOVRPTW), aiming to use a single deep reinforcement learning (DRL) model to solve the entire multiobjective optimization problem. The Non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm-II (NSGA-II) method is then employed to optimize the outcomes produced by the WADRL, thereby mitigating the limitations of both approaches. Firstly, we design an MOVRPTW model to balance the minimization of travel cost and the maximization of customer satisfaction. Subsequently, we present a novel DRL framework that incorporates a transformer-based policy network. This network is composed of an encoder module, a weight embedding module where the weights of the objective functions are incorporated, and a decoder module. NSGA-II is then utilized to optimize the solutions generated by WADRL. Finally, extensive experimental results demonstrate that our method outperforms the existing and traditional methods. Due to the numerous constraints in VRPTW, generating initial solutions of the NSGA-II algorithm can be time-consuming. However, using solutions generated by the WADRL as initial solutions for NSGA-II significantly reduces the time required for generating initial solutions. Meanwhile, the NSGA-II algorithm can enhance the quality of solutions generated by WADRL, resulting in solutions with better scalability. Notably, the weight-aware strategy significantly reduces the training time of DRL while achieving better results, enabling a single DRL model to solve the entire multiobjective optimization problem.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge