Siqing Zhang
Object-IR: Leveraging Object Consistency and Mesh Deformation for Self-Supervised Image Retargeting
Oct 31, 2025Abstract:Eliminating geometric distortion in semantically important regions remains an intractable challenge in image retargeting. This paper presents Object-IR, a self-supervised architecture that reformulates image retargeting as a learning-based mesh warping optimization problem, where the mesh deformation is guided by object appearance consistency and geometric-preserving constraints. Given an input image and a target aspect ratio, we initialize a uniform rigid mesh at the output resolution and use a convolutional neural network to predict the motion of each mesh grid and obtain the deformed mesh. The retargeted result is generated by warping the input image according to the rigid mesh in the input image and the deformed mesh in the output resolution. To mitigate geometric distortion, we design a comprehensive objective function incorporating a) object-consistent loss to ensure that the important semantic objects retain their appearance, b) geometric-preserving loss to constrain simple scale transform of the important meshes, and c) boundary loss to enforce a clean rectangular output. Notably, our self-supervised paradigm eliminates the need for manually annotated retargeting datasets by deriving supervision directly from the input's geometric and semantic properties. Extensive evaluations on the RetargetMe benchmark demonstrate that our Object-IR achieves state-of-the-art performance, outperforming existing methods in quantitative metrics and subjective visual quality assessments. The framework efficiently processes arbitrary input resolutions (average inference time: 0.009s for 1024x683 resolution) while maintaining real-time performance on consumer-grade GPUs. The source code will soon be available at https://github.com/tlliao/Object-IR.
Privacy-Preserving Orthogonal Aggregation for Guaranteeing Gender Fairness in Federated Recommendation
Nov 29, 2024



Abstract:Under stringent privacy constraints, whether federated recommendation systems can achieve group fairness remains an inadequately explored question. Taking gender fairness as a representative issue, we identify three phenomena in federated recommendation systems: performance difference, data imbalance, and preference disparity. We discover that the state-of-the-art methods only focus on the first phenomenon. Consequently, their imposition of inappropriate fairness constraints detrimentally affects the model training. Moreover, due to insufficient sensitive attribute protection of existing works, we can infer the gender of all users with 99.90% accuracy even with the addition of maximal noise. In this work, we propose Privacy-Preserving Orthogonal Aggregation (PPOA), which employs the secure aggregation scheme and quantization technique, to prevent the suppression of minority groups by the majority and preserve the distinct preferences for better group fairness. PPOA can assist different groups in obtaining their respective model aggregation results through a designed orthogonal mapping while keeping their attributes private. Experimental results on three real-world datasets demonstrate that PPOA enhances recommendation effectiveness for both females and males by up to 8.25% and 6.36%, respectively, with a maximum overall improvement of 7.30%, and achieves optimal fairness in most cases. Extensive ablation experiments and visualizations indicate that PPOA successfully maintains preferences for different gender groups.
Unsupervised Person Re-identification via Simultaneous Clustering and Consistency Learning
Apr 01, 2021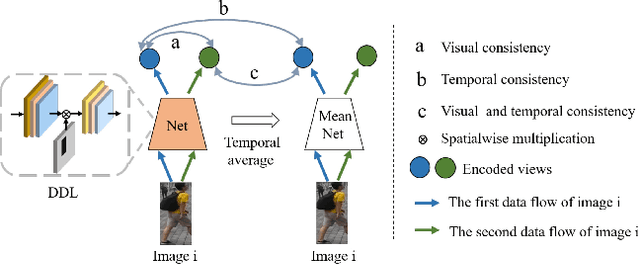
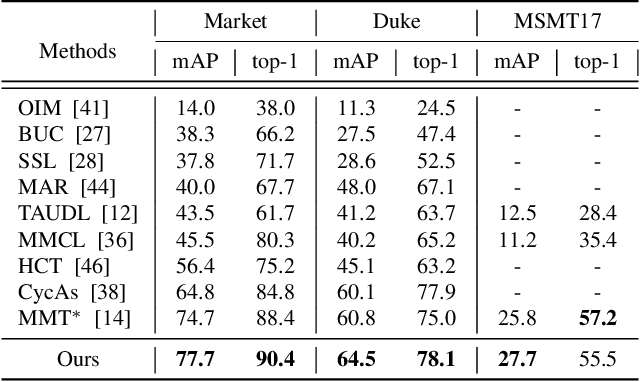
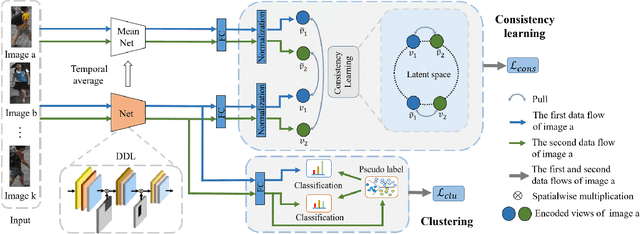
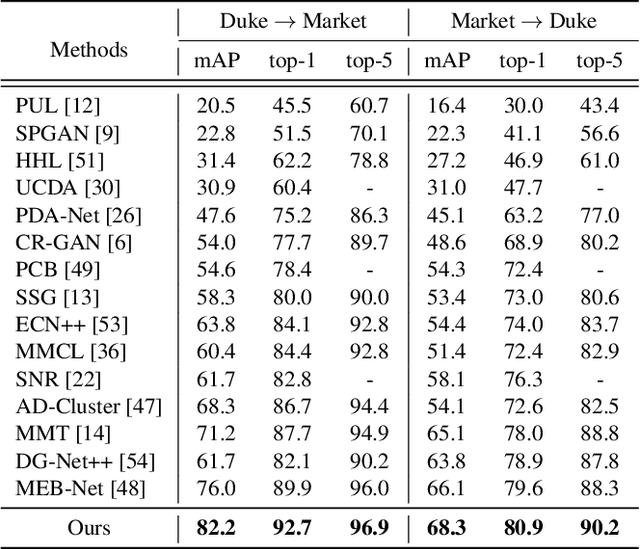
Abstract:Unsupervised person re-identification (re-ID) has become an important topic due to its potential to resolve the scalability problem of supervised re-ID models. However, existing methods simply utilize pseudo labels from clustering for supervision and thus have not yet fully explored the semantic information in data itself, which limits representation capabilities of learned models. To address this problem, we design a pretext task for unsupervised re-ID by learning visual consistency from still images and temporal consistency during training process, such that the clustering network can separate the images into semantic clusters automatically. Specifically, the pretext task learns semantically meaningful representations by maximizing the agreement between two encoded views of the same image via a consistency loss in latent space. Meanwhile, we optimize the model by grouping the two encoded views into same cluster, thus enhancing the visual consistency between views. Experiments on Market-1501, DukeMTMC-reID and MSMT17 datasets demonstrate that our proposed approach outperforms the state-of-the-art methods by large margins.
Knowledge Transfer Based Fine-grained Visual Classification
Dec 21, 2020



Abstract:Fine-grained visual classification (FGVC) aims to distinguish the sub-classes of the same category and its essential solution is to mine the subtle and discriminative regions. Convolution neural networks (CNNs), which employ the cross entropy loss (CE-loss) as the loss function, show poor performance since the model can only learn the most discriminative part and ignore other meaningful regions. Some existing works try to solve this problem by mining more discriminative regions by some detection techniques or attention mechanisms. However, most of them will meet the background noise problem when trying to find more discriminative regions. In this paper, we address it in a knowledge transfer learning manner. Multiple models are trained one by one, and all previously trained models are regarded as teacher models to supervise the training of the current one. Specifically, a orthogonal loss (OR-loss) is proposed to encourage the network to find diverse and meaningful regions. In addition, the first model is trained with only CE-Loss. Finally, all models' outputs with complementary knowledge are combined together for the final prediction result. We demonstrate the superiority of the proposed method and obtain state-of-the-art (SOTA) performances on three popular FGVC datasets.
SSKD: Self-Supervised Knowledge Distillation for Cross Domain Adaptive Person Re-Identification
Sep 13, 2020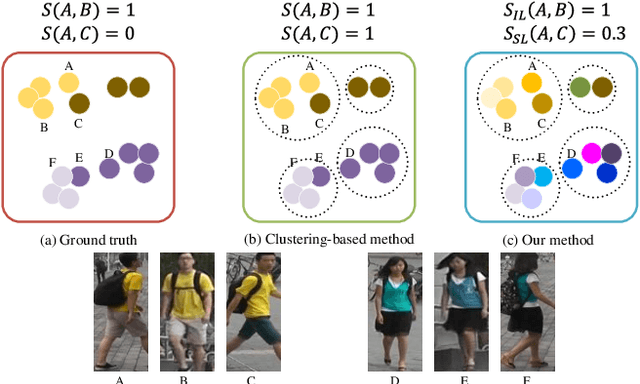
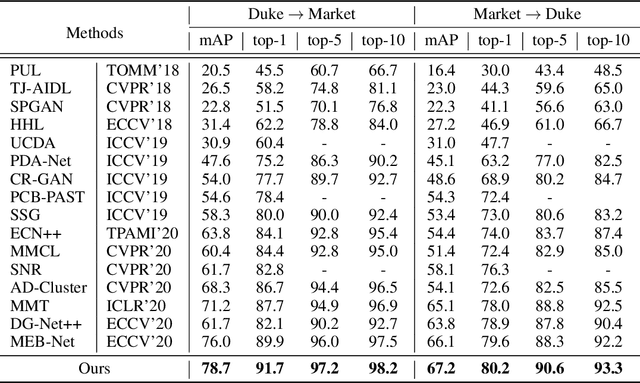
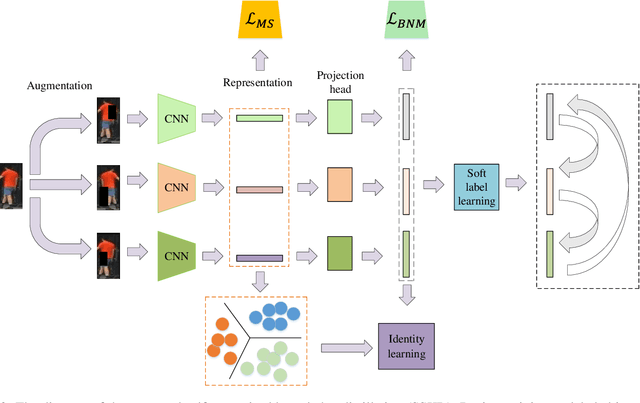
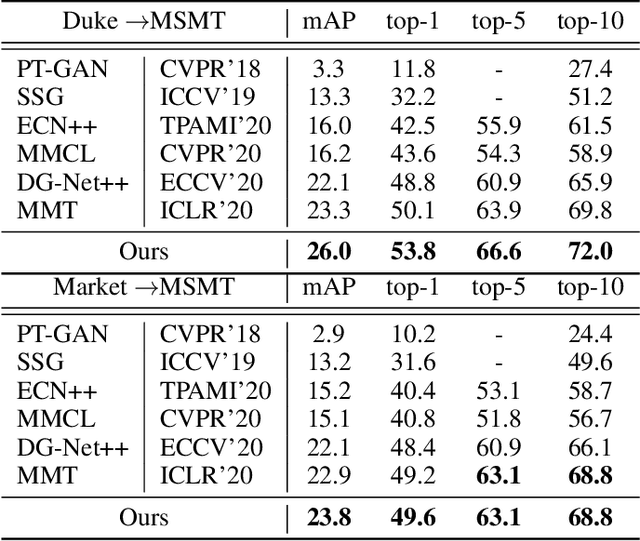
Abstract:Domain adaptive person re-identification (re-ID) is a challenging task due to the large discrepancy between the source domain and the target domain. To reduce the domain discrepancy, existing methods mainly attempt to generate pseudo labels for unlabeled target images by clustering algorithms. However, clustering methods tend to bring noisy labels and the rich fine-grained details in unlabeled images are not sufficiently exploited. In this paper, we seek to improve the quality of labels by capturing feature representation from multiple augmented views of unlabeled images. To this end, we propose a Self-Supervised Knowledge Distillation (SSKD) technique containing two modules, the identity learning and the soft label learning. Identity learning explores the relationship between unlabeled samples and predicts their one-hot labels by clustering to give exact information for confidently distinguished images. Soft label learning regards labels as a distribution and induces an image to be associated with several related classes for training peer network in a self-supervised manner, where the slowly evolving network is a core to obtain soft labels as a gentle constraint for reliable images. Finally, the two modules can resist label noise for re-ID by enhancing each other and systematically integrating label information from unlabeled images. Extensive experiments on several adaptation tasks demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms the current state-of-the-art approaches by large margins.
Dual-attention Guided Dropblock Module for Weakly Supervised Object Localization
Mar 19, 2020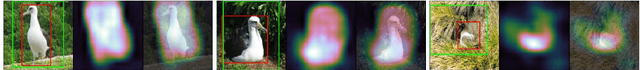
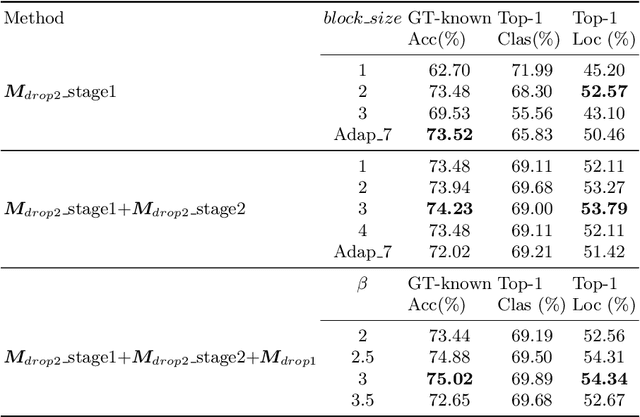
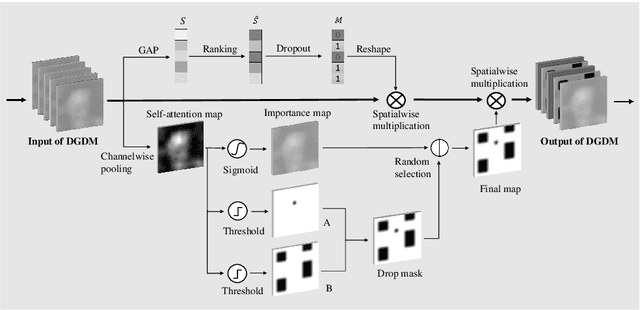
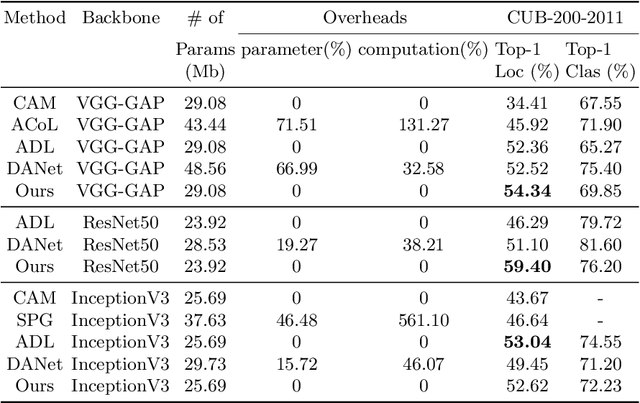
Abstract:In this paper, we present a dual-attention guided dropblock module, and aim at learning the informative and complementary visual features for weakly supervised object localization (WSOL). The attention mechanism is extended to the task of WSOL, and design two types of attention modules to learn the discriminative features for better feature representations. Based on two types of attention mechanism, we propose a channel attention guided dropout (CAGD) and a spatial attention guided dropblock (SAGD). The CAGD ranks channel attention by a measure of importance and consider the top-k largest magnitude attentions as important ones. The SAGD can not only completely remove the information by erasing the contiguous regions of feature maps rather than individual pixels, but also simply distinguish the foreground objects and background regions to alleviate the attention misdirection. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed method achieves new state-of-the-art localization accuracy on a challenging dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge