Ruoyi Du
VisualCloze: A Universal Image Generation Framework via Visual In-Context Learning
Apr 10, 2025Abstract:Recent progress in diffusion models significantly advances various image generation tasks. However, the current mainstream approach remains focused on building task-specific models, which have limited efficiency when supporting a wide range of different needs. While universal models attempt to address this limitation, they face critical challenges, including generalizable task instruction, appropriate task distributions, and unified architectural design. To tackle these challenges, we propose VisualCloze, a universal image generation framework, which supports a wide range of in-domain tasks, generalization to unseen ones, unseen unification of multiple tasks, and reverse generation. Unlike existing methods that rely on language-based task instruction, leading to task ambiguity and weak generalization, we integrate visual in-context learning, allowing models to identify tasks from visual demonstrations. Meanwhile, the inherent sparsity of visual task distributions hampers the learning of transferable knowledge across tasks. To this end, we introduce Graph200K, a graph-structured dataset that establishes various interrelated tasks, enhancing task density and transferable knowledge. Furthermore, we uncover that our unified image generation formulation shared a consistent objective with image infilling, enabling us to leverage the strong generative priors of pre-trained infilling models without modifying the architectures.
Lumina-Image 2.0: A Unified and Efficient Image Generative Framework
Mar 27, 2025



Abstract:We introduce Lumina-Image 2.0, an advanced text-to-image generation framework that achieves significant progress compared to previous work, Lumina-Next. Lumina-Image 2.0 is built upon two key principles: (1) Unification - it adopts a unified architecture (Unified Next-DiT) that treats text and image tokens as a joint sequence, enabling natural cross-modal interactions and allowing seamless task expansion. Besides, since high-quality captioners can provide semantically well-aligned text-image training pairs, we introduce a unified captioning system, Unified Captioner (UniCap), specifically designed for T2I generation tasks. UniCap excels at generating comprehensive and accurate captions, accelerating convergence and enhancing prompt adherence. (2) Efficiency - to improve the efficiency of our proposed model, we develop multi-stage progressive training strategies and introduce inference acceleration techniques without compromising image quality. Extensive evaluations on academic benchmarks and public text-to-image arenas show that Lumina-Image 2.0 delivers strong performances even with only 2.6B parameters, highlighting its scalability and design efficiency. We have released our training details, code, and models at https://github.com/Alpha-VLLM/Lumina-Image-2.0.
IMAGINE-E: Image Generation Intelligence Evaluation of State-of-the-art Text-to-Image Models
Jan 23, 2025



Abstract:With the rapid development of diffusion models, text-to-image(T2I) models have made significant progress, showcasing impressive abilities in prompt following and image generation. Recently launched models such as FLUX.1 and Ideogram2.0, along with others like Dall-E3 and Stable Diffusion 3, have demonstrated exceptional performance across various complex tasks, raising questions about whether T2I models are moving towards general-purpose applicability. Beyond traditional image generation, these models exhibit capabilities across a range of fields, including controllable generation, image editing, video, audio, 3D, and motion generation, as well as computer vision tasks like semantic segmentation and depth estimation. However, current evaluation frameworks are insufficient to comprehensively assess these models' performance across expanding domains. To thoroughly evaluate these models, we developed the IMAGINE-E and tested six prominent models: FLUX.1, Ideogram2.0, Midjourney, Dall-E3, Stable Diffusion 3, and Jimeng. Our evaluation is divided into five key domains: structured output generation, realism, and physical consistency, specific domain generation, challenging scenario generation, and multi-style creation tasks. This comprehensive assessment highlights each model's strengths and limitations, particularly the outstanding performance of FLUX.1 and Ideogram2.0 in structured and specific domain tasks, underscoring the expanding applications and potential of T2I models as foundational AI tools. This study provides valuable insights into the current state and future trajectory of T2I models as they evolve towards general-purpose usability. Evaluation scripts will be released at https://github.com/jylei16/Imagine-e.
I-Max: Maximize the Resolution Potential of Pre-trained Rectified Flow Transformers with Projected Flow
Oct 10, 2024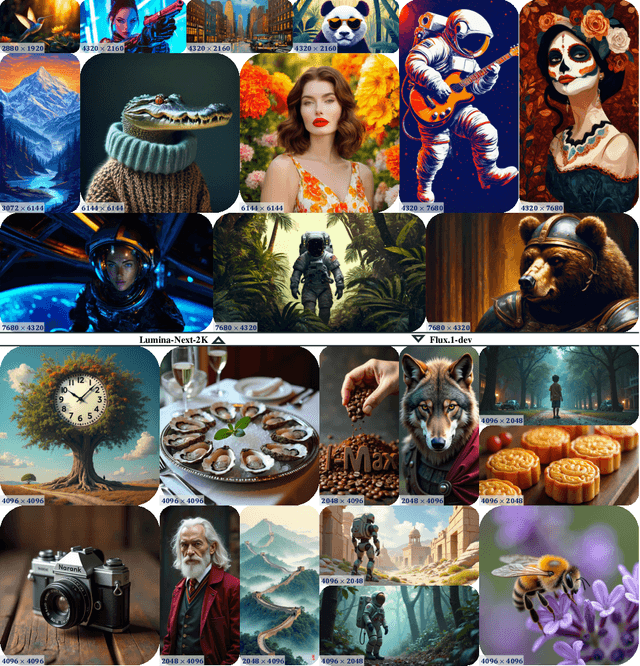

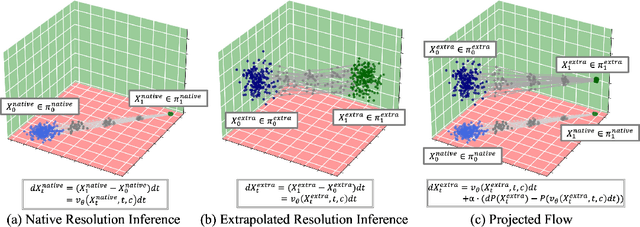
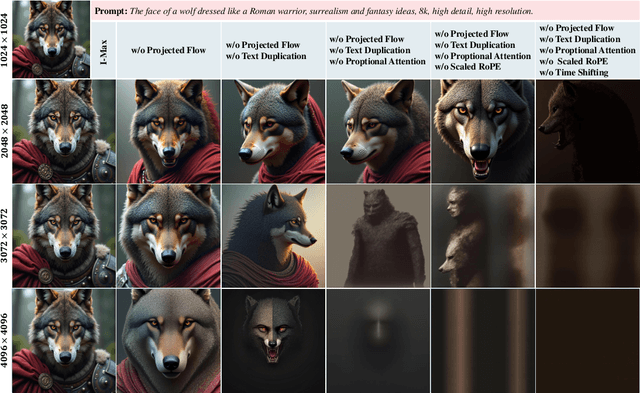
Abstract:Rectified Flow Transformers (RFTs) offer superior training and inference efficiency, making them likely the most viable direction for scaling up diffusion models. However, progress in generation resolution has been relatively slow due to data quality and training costs. Tuning-free resolution extrapolation presents an alternative, but current methods often reduce generative stability, limiting practical application. In this paper, we review existing resolution extrapolation methods and introduce the I-Max framework to maximize the resolution potential of Text-to-Image RFTs. I-Max features: (i) a novel Projected Flow strategy for stable extrapolation and (ii) an advanced inference toolkit for generalizing model knowledge to higher resolutions. Experiments with Lumina-Next-2K and Flux.1-dev demonstrate I-Max's ability to enhance stability in resolution extrapolation and show that it can bring image detail emergence and artifact correction, confirming the practical value of tuning-free resolution extrapolation.
Zero-Shot Audio Captioning Using Soft and Hard Prompts
Jun 10, 2024



Abstract:In traditional audio captioning methods, a model is usually trained in a fully supervised manner using a human-annotated dataset containing audio-text pairs and then evaluated on the test sets from the same dataset. Such methods have two limitations. First, these methods are often data-hungry and require time-consuming and expensive human annotations to obtain audio-text pairs. Second, these models often suffer from performance degradation in cross-domain scenarios, i.e., when the input audio comes from a different domain than the training set, which, however, has received little attention. We propose an effective audio captioning method based on the contrastive language-audio pre-training (CLAP) model to address these issues. Our proposed method requires only textual data for training, enabling the model to generate text from the textual feature in the cross-modal semantic space.In the inference stage, the model generates the descriptive text for the given audio from the audio feature by leveraging the audio-text alignment from CLAP.We devise two strategies to mitigate the discrepancy between text and audio embeddings: a mixed-augmentation-based soft prompt and a retrieval-based acoustic-aware hard prompt. These approaches are designed to enhance the generalization performance of our proposed model, facilitating the model to generate captions more robustly and accurately. Extensive experiments on AudioCaps and Clotho benchmarks show the effectiveness of our proposed method, which outperforms other zero-shot audio captioning approaches for in-domain scenarios and outperforms the compared methods for cross-domain scenarios, underscoring the generalization ability of our method.
Lumina-T2X: Transforming Text into Any Modality, Resolution, and Duration via Flow-based Large Diffusion Transformers
May 09, 2024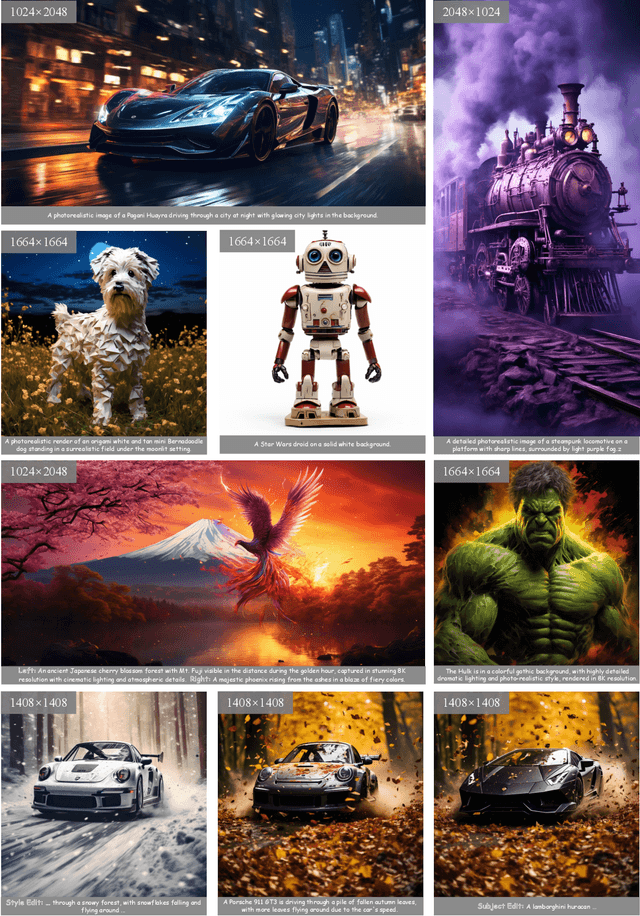
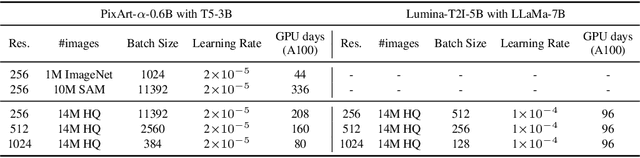
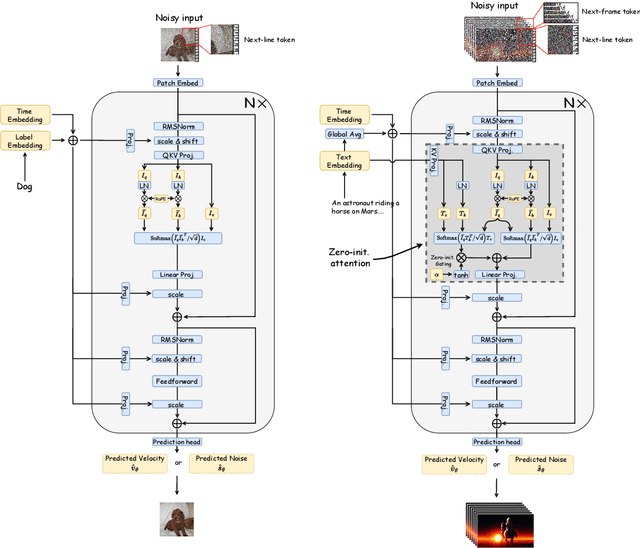
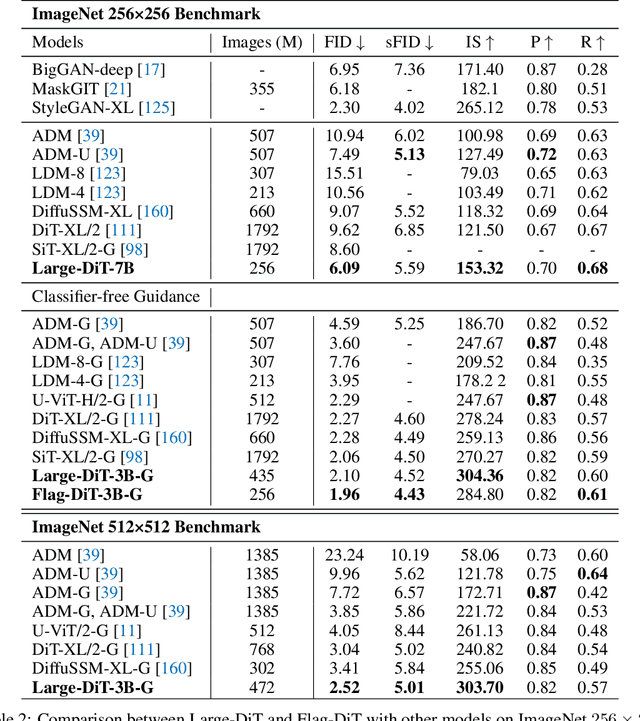
Abstract:Sora unveils the potential of scaling Diffusion Transformer for generating photorealistic images and videos at arbitrary resolutions, aspect ratios, and durations, yet it still lacks sufficient implementation details. In this technical report, we introduce the Lumina-T2X family - a series of Flow-based Large Diffusion Transformers (Flag-DiT) equipped with zero-initialized attention, as a unified framework designed to transform noise into images, videos, multi-view 3D objects, and audio clips conditioned on text instructions. By tokenizing the latent spatial-temporal space and incorporating learnable placeholders such as [nextline] and [nextframe] tokens, Lumina-T2X seamlessly unifies the representations of different modalities across various spatial-temporal resolutions. This unified approach enables training within a single framework for different modalities and allows for flexible generation of multimodal data at any resolution, aspect ratio, and length during inference. Advanced techniques like RoPE, RMSNorm, and flow matching enhance the stability, flexibility, and scalability of Flag-DiT, enabling models of Lumina-T2X to scale up to 7 billion parameters and extend the context window to 128K tokens. This is particularly beneficial for creating ultra-high-definition images with our Lumina-T2I model and long 720p videos with our Lumina-T2V model. Remarkably, Lumina-T2I, powered by a 5-billion-parameter Flag-DiT, requires only 35% of the training computational costs of a 600-million-parameter naive DiT. Our further comprehensive analysis underscores Lumina-T2X's preliminary capability in resolution extrapolation, high-resolution editing, generating consistent 3D views, and synthesizing videos with seamless transitions. We expect that the open-sourcing of Lumina-T2X will further foster creativity, transparency, and diversity in the generative AI community.
DemoFusion: Democratising High-Resolution Image Generation With No $$$
Nov 24, 2023Abstract:High-resolution image generation with Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) has immense potential but, due to the enormous capital investment required for training, it is increasingly centralised to a few large corporations, and hidden behind paywalls. This paper aims to democratise high-resolution GenAI by advancing the frontier of high-resolution generation while remaining accessible to a broad audience. We demonstrate that existing Latent Diffusion Models (LDMs) possess untapped potential for higher-resolution image generation. Our novel DemoFusion framework seamlessly extends open-source GenAI models, employing Progressive Upscaling, Skip Residual, and Dilated Sampling mechanisms to achieve higher-resolution image generation. The progressive nature of DemoFusion requires more passes, but the intermediate results can serve as "previews", facilitating rapid prompt iteration.
Multi-View Active Fine-Grained Recognition
Jun 02, 2022



Abstract:As fine-grained visual classification (FGVC) being developed for decades, great works related have exposed a key direction -- finding discriminative local regions and revealing subtle differences. However, unlike identifying visual contents within static images, for recognizing objects in the real physical world, discriminative information is not only present within seen local regions but also hides in other unseen perspectives. In other words, in addition to focusing on the distinguishable part from the whole, for efficient and accurate recognition, it is required to infer the key perspective with a few glances, e.g., people may recognize a "Benz AMG GT" with a glance of its front and then know that taking a look at its exhaust pipe can help to tell which year's model it is. In this paper, back to reality, we put forward the problem of active fine-grained recognition (AFGR) and complete this study in three steps: (i) a hierarchical, multi-view, fine-grained vehicle dataset is collected as the testbed, (ii) a simple experiment is designed to verify that different perspectives contribute differently for FGVC and different categories own different discriminative perspective, (iii) a policy-gradient-based framework is adopted to achieve efficient recognition with active view selection. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed method delivers a better performance-efficient trade-off than previous FGVC methods and advanced neural networks.
Learning Invariant Visual Representations for Compositional Zero-Shot Learning
Jun 02, 2022



Abstract:Compositional Zero-Shot Learning (CZSL) aims to recognize novel compositions using knowledge learned from seen attribute-object compositions in the training set. Previous works mainly project an image and a composition into a common embedding space to measure their compatibility score. However, both attributes and objects share the visual representations learned above, leading the model to exploit spurious correlations and bias towards seen pairs. Instead, we reconsider CZSL as an out-of-distribution generalization problem. If an object is treated as a domain, we can learn object-invariant features to recognize the attributes attached to any object reliably. Similarly, attribute-invariant features can also be learned when recognizing the objects with attributes as domains. Specifically, we propose an invariant feature learning framework to align different domains at the representation and gradient levels to capture the intrinsic characteristics associated with the tasks. Experiments on two CZSL benchmarks demonstrate that the proposed method significantly outperforms the previous state-of-the-art.
Caption Feature Space Regularization for Audio Captioning
Apr 18, 2022



Abstract:Audio captioning aims at describing the content of audio clips with human language. Due to the ambiguity of audio, different people may perceive the same audio differently, resulting in caption disparities (i.e., one audio may correlate to several captions with diverse semantics). For that, general audio captioning models achieve the one-to-many training by randomly selecting a correlated caption as the ground truth for each audio. However, it leads to a significant variation in the optimization directions and weakens the model stability. To eliminate this negative effect, in this paper, we propose a two-stage framework for audio captioning: (i) in the first stage, via the contrastive learning, we construct a proxy feature space to reduce the distances between captions correlated to the same audio, and (ii) in the second stage, the proxy feature space is utilized as additional supervision to encourage the model to be optimized in the direction that benefits all the correlated captions. We conducted extensive experiments on two datasets using four commonly used encoder and decoder architectures. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method. The code is available at https://github.com/PRIS-CV/Caption-Feature-Space-Regularization.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge