Xinyue Li
ELIQ: A Label-Free Framework for Quality Assessment of Evolving AI-Generated Images
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Generative text-to-image models are advancing at an unprecedented pace, continuously shifting the perceptual quality ceiling and rendering previously collected labels unreliable for newer generations. To address this, we present ELIQ, a Label-free Framework for Quality Assessment of Evolving AI-generated Images. Specifically, ELIQ focuses on visual quality and prompt-image alignment, automatically constructs positive and aspect-specific negative pairs to cover both conventional distortions and AIGC-specific distortion modes, enabling transferable supervision without human annotations. Building on these pairs, ELIQ adapts a pre-trained multimodal model into a quality-aware critic via instruction tuning and predicts two-dimensional quality using lightweight gated fusion and a Quality Query Transformer. Experiments across multiple benchmarks demonstrate that ELIQ consistently outperforms existing label-free methods, generalizes from AI-generated content (AIGC) to user-generated content (UGC) scenarios without modification, and paves the way for scalable and label-free quality assessment under continuously evolving generative models. The code will be released upon publication.
Decoupling Perception and Calibration: Label-Efficient Image Quality Assessment Framework
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Recent multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have demonstrated strong capabilities in image quality assessment (IQA) tasks. However, adapting such large-scale models is computationally expensive and still relies on substantial Mean Opinion Score (MOS) annotations. We argue that for MLLM-based IQA, the core bottleneck lies not in the quality perception capacity of MLLMs, but in MOS scale calibration. Therefore, we propose LEAF, a Label-Efficient Image Quality Assessment Framework that distills perceptual quality priors from an MLLM teacher into a lightweight student regressor, enabling MOS calibration with minimal human supervision. Specifically, the teacher conducts dense supervision through point-wise judgments and pair-wise preferences, with an estimate of decision reliability. Guided by these signals, the student learns the teacher's quality perception patterns through joint distillation and is calibrated on a small MOS subset to align with human annotations. Experiments on both user-generated and AI-generated IQA benchmarks demonstrate that our method significantly reduces the need for human annotations while maintaining strong MOS-aligned correlations, making lightweight IQA practical under limited annotation budgets.
Q-Bench-Portrait: Benchmarking Multimodal Large Language Models on Portrait Image Quality Perception
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Recent advances in multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have demonstrated impressive performance on existing low-level vision benchmarks, which primarily focus on generic images. However, their capabilities to perceive and assess portrait images, a domain characterized by distinct structural and perceptual properties, remain largely underexplored. To this end, we introduce Q-Bench-Portrait, the first holistic benchmark specifically designed for portrait image quality perception, comprising 2,765 image-question-answer triplets and featuring (1) diverse portrait image sources, including natural, synthetic distortion, AI-generated, artistic, and computer graphics images; (2) comprehensive quality dimensions, covering technical distortions, AIGC-specific distortions, and aesthetics; and (3) a range of question formats, including single-choice, multiple-choice, true/false, and open-ended questions, at both global and local levels. Based on Q-Bench-Portrait, we evaluate 20 open-source and 5 closed-source MLLMs, revealing that although current models demonstrate some competence in portrait image perception, their performance remains limited and imprecise, with a clear gap relative to human judgments. We hope that the proposed benchmark will foster further research into enhancing the portrait image perception capabilities of both general-purpose and domain-specific MLLMs.
VQualA 2025 Challenge on Visual Quality Comparison for Large Multimodal Models: Methods and Results
Sep 11, 2025
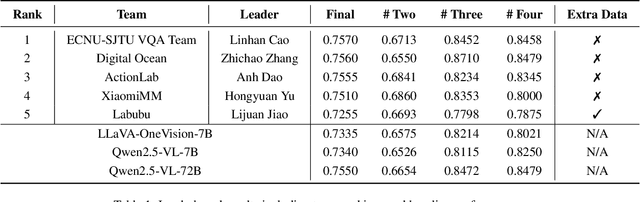
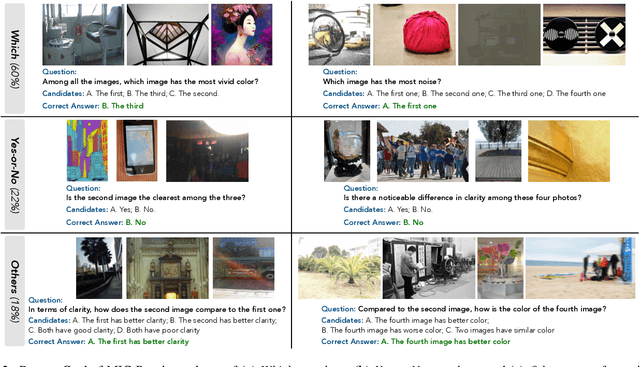
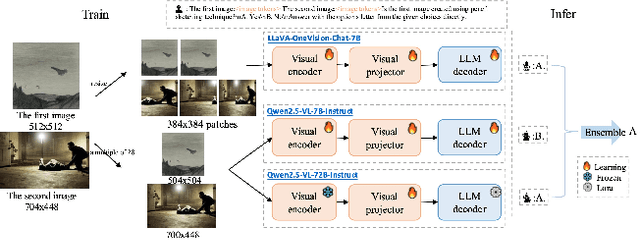
Abstract:This paper presents a summary of the VQualA 2025 Challenge on Visual Quality Comparison for Large Multimodal Models (LMMs), hosted as part of the ICCV 2025 Workshop on Visual Quality Assessment. The challenge aims to evaluate and enhance the ability of state-of-the-art LMMs to perform open-ended and detailed reasoning about visual quality differences across multiple images. To this end, the competition introduces a novel benchmark comprising thousands of coarse-to-fine grained visual quality comparison tasks, spanning single images, pairs, and multi-image groups. Each task requires models to provide accurate quality judgments. The competition emphasizes holistic evaluation protocols, including 2AFC-based binary preference and multi-choice questions (MCQs). Around 100 participants submitted entries, with five models demonstrating the emerging capabilities of instruction-tuned LMMs on quality assessment. This challenge marks a significant step toward open-domain visual quality reasoning and comparison and serves as a catalyst for future research on interpretable and human-aligned quality evaluation systems.
Sekai: A Video Dataset towards World Exploration
Jun 18, 2025Abstract:Video generation techniques have made remarkable progress, promising to be the foundation of interactive world exploration. However, existing video generation datasets are not well-suited for world exploration training as they suffer from some limitations: limited locations, short duration, static scenes, and a lack of annotations about exploration and the world. In this paper, we introduce Sekai (meaning ``world'' in Japanese), a high-quality first-person view worldwide video dataset with rich annotations for world exploration. It consists of over 5,000 hours of walking or drone view (FPV and UVA) videos from over 100 countries and regions across 750 cities. We develop an efficient and effective toolbox to collect, pre-process and annotate videos with location, scene, weather, crowd density, captions, and camera trajectories. Experiments demonstrate the quality of the dataset. And, we use a subset to train an interactive video world exploration model, named YUME (meaning ``dream'' in Japanese). We believe Sekai will benefit the area of video generation and world exploration, and motivate valuable applications.
Training Superior Sparse Autoencoders for Instruct Models
Jun 09, 2025Abstract:As large language models (LLMs) grow in scale and capability, understanding their internal mechanisms becomes increasingly critical. Sparse autoencoders (SAEs) have emerged as a key tool in mechanistic interpretability, enabling the extraction of human-interpretable features from LLMs. However, existing SAE training methods are primarily designed for base models, resulting in reduced reconstruction quality and interpretability when applied to instruct models. To bridge this gap, we propose $\underline{\textbf{F}}$inetuning-$\underline{\textbf{a}}$ligned $\underline{\textbf{S}}$equential $\underline{\textbf{T}}$raining ($\textit{FAST}$), a novel training method specifically tailored for instruct models. $\textit{FAST}$ aligns the training process with the data distribution and activation patterns characteristic of instruct models, resulting in substantial improvements in both reconstruction and feature interpretability. On Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct, $\textit{FAST}$ achieves a mean squared error of 0.6468 in token reconstruction, significantly outperforming baseline methods with errors of 5.1985 and 1.5096. In feature interpretability, $\textit{FAST}$ yields a higher proportion of high-quality features, for Llama3.2-3B-Instruct, $21.1\%$ scored in the top range, compared to $7.0\%$ and $10.2\%$ for $\textit{BT(P)}$ and $\textit{BT(F)}$. Surprisingly, we discover that intervening on the activations of special tokens via the SAEs leads to improvements in output quality, suggesting new opportunities for fine-grained control of model behavior. Code, data, and 240 trained SAEs are available at https://github.com/Geaming2002/FAST.
NTIRE 2025 challenge on Text to Image Generation Model Quality Assessment
May 22, 2025Abstract:This paper reports on the NTIRE 2025 challenge on Text to Image (T2I) generation model quality assessment, which will be held in conjunction with the New Trends in Image Restoration and Enhancement Workshop (NTIRE) at CVPR 2025. The aim of this challenge is to address the fine-grained quality assessment of text-to-image generation models. This challenge evaluates text-to-image models from two aspects: image-text alignment and image structural distortion detection, and is divided into the alignment track and the structural track. The alignment track uses the EvalMuse-40K, which contains around 40K AI-Generated Images (AIGIs) generated by 20 popular generative models. The alignment track has a total of 371 registered participants. A total of 1,883 submissions are received in the development phase, and 507 submissions are received in the test phase. Finally, 12 participating teams submitted their models and fact sheets. The structure track uses the EvalMuse-Structure, which contains 10,000 AI-Generated Images (AIGIs) with corresponding structural distortion mask. A total of 211 participants have registered in the structure track. A total of 1155 submissions are received in the development phase, and 487 submissions are received in the test phase. Finally, 8 participating teams submitted their models and fact sheets. Almost all methods have achieved better results than baseline methods, and the winning methods in both tracks have demonstrated superior prediction performance on T2I model quality assessment.
OmniCaptioner: One Captioner to Rule Them All
Apr 09, 2025Abstract:We propose OmniCaptioner, a versatile visual captioning framework for generating fine-grained textual descriptions across a wide variety of visual domains. Unlike prior methods limited to specific image types (e.g., natural images or geometric visuals), our framework provides a unified solution for captioning natural images, visual text (e.g., posters, UIs, textbooks), and structured visuals (e.g., documents, tables, charts). By converting low-level pixel information into semantically rich textual representations, our framework bridges the gap between visual and textual modalities. Our results highlight three key advantages: (i) Enhanced Visual Reasoning with LLMs, where long-context captions of visual modalities empower LLMs, particularly the DeepSeek-R1 series, to reason effectively in multimodal scenarios; (ii) Improved Image Generation, where detailed captions improve tasks like text-to-image generation and image transformation; and (iii) Efficient Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT), which enables faster convergence with less data. We believe the versatility and adaptability of OmniCaptioner can offer a new perspective for bridging the gap between language and visual modalities.
Lumina-Image 2.0: A Unified and Efficient Image Generative Framework
Mar 27, 2025



Abstract:We introduce Lumina-Image 2.0, an advanced text-to-image generation framework that achieves significant progress compared to previous work, Lumina-Next. Lumina-Image 2.0 is built upon two key principles: (1) Unification - it adopts a unified architecture (Unified Next-DiT) that treats text and image tokens as a joint sequence, enabling natural cross-modal interactions and allowing seamless task expansion. Besides, since high-quality captioners can provide semantically well-aligned text-image training pairs, we introduce a unified captioning system, Unified Captioner (UniCap), specifically designed for T2I generation tasks. UniCap excels at generating comprehensive and accurate captions, accelerating convergence and enhancing prompt adherence. (2) Efficiency - to improve the efficiency of our proposed model, we develop multi-stage progressive training strategies and introduce inference acceleration techniques without compromising image quality. Extensive evaluations on academic benchmarks and public text-to-image arenas show that Lumina-Image 2.0 delivers strong performances even with only 2.6B parameters, highlighting its scalability and design efficiency. We have released our training details, code, and models at https://github.com/Alpha-VLLM/Lumina-Image-2.0.
LeX-Art: Rethinking Text Generation via Scalable High-Quality Data Synthesis
Mar 27, 2025Abstract:We introduce LeX-Art, a comprehensive suite for high-quality text-image synthesis that systematically bridges the gap between prompt expressiveness and text rendering fidelity. Our approach follows a data-centric paradigm, constructing a high-quality data synthesis pipeline based on Deepseek-R1 to curate LeX-10K, a dataset of 10K high-resolution, aesthetically refined 1024$\times$1024 images. Beyond dataset construction, we develop LeX-Enhancer, a robust prompt enrichment model, and train two text-to-image models, LeX-FLUX and LeX-Lumina, achieving state-of-the-art text rendering performance. To systematically evaluate visual text generation, we introduce LeX-Bench, a benchmark that assesses fidelity, aesthetics, and alignment, complemented by Pairwise Normalized Edit Distance (PNED), a novel metric for robust text accuracy evaluation. Experiments demonstrate significant improvements, with LeX-Lumina achieving a 79.81% PNED gain on CreateBench, and LeX-FLUX outperforming baselines in color (+3.18%), positional (+4.45%), and font accuracy (+3.81%). Our codes, models, datasets, and demo are publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge