Wei Sun
Max
Surveillance Facial Image Quality Assessment: A Multi-dimensional Dataset and Lightweight Model
Feb 07, 2026Abstract:Surveillance facial images are often captured under unconstrained conditions, resulting in severe quality degradation due to factors such as low resolution, motion blur, occlusion, and poor lighting. Although recent face restoration techniques applied to surveillance cameras can significantly enhance visual quality, they often compromise fidelity (i.e., identity-preserving features), which directly conflicts with the primary objective of surveillance images -- reliable identity verification. Existing facial image quality assessment (FIQA) predominantly focus on either visual quality or recognition-oriented evaluation, thereby failing to jointly address visual quality and fidelity, which are critical for surveillance applications. To bridge this gap, we propose the first comprehensive study on surveillance facial image quality assessment (SFIQA), targeting the unique challenges inherent to surveillance scenarios. Specifically, we first construct SFIQA-Bench, a multi-dimensional quality assessment benchmark for surveillance facial images, which consists of 5,004 surveillance facial images captured by three widely deployed surveillance cameras in real-world scenarios. A subjective experiment is conducted to collect six dimensional quality ratings, including noise, sharpness, colorfulness, contrast, fidelity and overall quality, covering the key aspects of SFIQA. Furthermore, we propose SFIQA-Assessor, a lightweight multi-task FIQA model that jointly exploits complementary facial views through cross-view feature interaction, and employs learnable task tokens to guide the unified regression of multiple quality dimensions. The experiment results on the proposed dataset show that our method achieves the best performance compared with the state-of-the-art general image quality assessment (IQA) and FIQA methods, validating its effectiveness for real-world surveillance applications.
Principled Synthetic Data Enables the First Scaling Laws for LLMs in Recommendation
Feb 07, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) represent a promising frontier for recommender systems, yet their development has been impeded by the absence of predictable scaling laws, which are crucial for guiding research and optimizing resource allocation. We hypothesize that this may be attributed to the inherent noise, bias, and incompleteness of raw user interaction data in prior continual pre-training (CPT) efforts. This paper introduces a novel, layered framework for generating high-quality synthetic data that circumvents such issues by creating a curated, pedagogical curriculum for the LLM. We provide powerful, direct evidence for the utility of our curriculum by showing that standard sequential models trained on our principled synthetic data significantly outperform ($+130\%$ on recall@100 for SasRec) models trained on real data in downstream ranking tasks, demonstrating its superiority for learning generalizable user preference patterns. Building on this, we empirically demonstrate, for the first time, robust power-law scaling for an LLM that is continually pre-trained on our high-quality, recommendation-specific data. Our experiments reveal consistent and predictable perplexity reduction across multiple synthetic data modalities. These findings establish a foundational methodology for reliable scaling LLM capabilities in the recommendation domain, thereby shifting the research focus from mitigating data deficiencies to leveraging high-quality, structured information.
EEmo-Logic: A Unified Dataset and Multi-Stage Framework for Comprehensive Image-Evoked Emotion Assessment
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Understanding the multi-dimensional attributes and intensity nuances of image-evoked emotions is pivotal for advancing machine empathy and empowering diverse human-computer interaction applications. However, existing models are still limited to coarse-grained emotion perception or deficient reasoning capabilities. To bridge this gap, we introduce EEmoDB, the largest image-evoked emotion understanding dataset to date. It features $5$ analysis dimensions spanning $5$ distinct task categories, facilitating comprehensive interpretation. Specifically, we compile $1.2M$ question-answering (QA) pairs (EEmoDB-QA) from $125k$ images via automated generation, alongside a $36k$ dataset (EEmoDB-Assess) curated from $25k$ images for fine-grained assessment. Furthermore, we propose EEmo-Logic, an all-in-one multimodal large language model (MLLM) developed via instruction fine-tuning and task-customized group relative preference optimization (GRPO) with novel reward design. Extensive experiments demonstrate that EEmo-Logic achieves robust performance in in-domain and cross-domain datasets, excelling in emotion QA and fine-grained assessment. The code is available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/EEmoLogic.
Physics Informed Reconstruction of Four-Dimensional Atmospheric Wind Fields Using Multi-UAS Swarm Observations in a Synthetic Turbulent Environment
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Accurate reconstruction of atmospheric wind fields is essential for applications such as weather forecasting, hazard prediction, and wind energy assessment, yet conventional instruments leave spatio-temporal gaps within the lower atmospheric boundary layer. Unmanned aircraft systems (UAS) provide flexible in situ measurements, but individual platforms sample wind only along their flight trajectories, limiting full wind-field recovery. This study presents a framework for reconstructing four-dimensional atmospheric wind fields using measurements obtained from a coordinated UAS swarm. A synthetic turbulence environment and high-fidelity multirotor simulation are used to generate training and evaluation data. Local wind components are estimated from UAS dynamics using a bidirectional long short-term memory network (Bi-LSTM) and assimilated into a physics-informed neural network (PINN) to reconstruct a continuous wind field in space and time. For local wind estimation, the bidirectional LSTM achieves root-mean-square errors (RMSE) of 0.064 and 0.062 m/s for the north and east components in low-wind conditions, increasing to 0.122 to 0.129 m/s under moderate winds and 0.271 to 0.273 m/s in high-wind conditions, while the vertical component exhibits higher error, with RMSE values of 0.029 to 0.091 m/s. The physics-informed reconstruction recovers the dominant spatial and temporal structure of the wind field up to 1000 m altitude while preserving mean flow direction and vertical shear. Under moderate wind conditions, the reconstructed mean wind field achieves an overall RMSE between 0.118 and 0.154 m/s across evaluated UAS configurations, with the lowest error obtained using a five-UAS swarm. These results demonstrate that coordinated UAS measurements enable accurate and scalable four-dimensional wind-field reconstruction without dedicated wind sensors or fixed infrastructure.
Automated Safety Benchmarking: A Multi-agent Pipeline for LVLMs
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Large vision-language models (LVLMs) exhibit remarkable capabilities in cross-modal tasks but face significant safety challenges, which undermine their reliability in real-world applications. Efforts have been made to build LVLM safety evaluation benchmarks to uncover their vulnerability. However, existing benchmarks are hindered by their labor-intensive construction process, static complexity, and limited discriminative power. Thus, they may fail to keep pace with rapidly evolving models and emerging risks. To address these limitations, we propose VLSafetyBencher, the first automated system for LVLM safety benchmarking. VLSafetyBencher introduces four collaborative agents: Data Preprocessing, Generation, Augmentation, and Selection agents to construct and select high-quality samples. Experiments validates that VLSafetyBencher can construct high-quality safety benchmarks within one week at a minimal cost. The generated benchmark effectively distinguish safety, with a safety rate disparity of 70% between the most and least safe models.
QualiRAG: Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Visual Quality Understanding
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Visual quality assessment (VQA) is increasingly shifting from scalar score prediction toward interpretable quality understanding -- a paradigm that demands \textit{fine-grained spatiotemporal perception} and \textit{auxiliary contextual information}. Current approaches rely on supervised fine-tuning or reinforcement learning on curated instruction datasets, which involve labor-intensive annotation and are prone to dataset-specific biases. To address these challenges, we propose \textbf{QualiRAG}, a \textit{training-free} \textbf{R}etrieval-\textbf{A}ugmented \textbf{G}eneration \textbf{(RAG)} framework that systematically leverages the latent perceptual knowledge of large multimodal models (LMMs) for visual quality perception. Unlike conventional RAG that retrieves from static corpora, QualiRAG dynamically generates auxiliary knowledge by decomposing questions into structured requests and constructing four complementary knowledge sources: \textit{visual metadata}, \textit{subject localization}, \textit{global quality summaries}, and \textit{local quality descriptions}, followed by relevance-aware retrieval for evidence-grounded reasoning. Extensive experiments show that QualiRAG achieves substantial improvements over open-source general-purpose LMMs and VQA-finetuned LMMs on visual quality understanding tasks, and delivers competitive performance on visual quality comparison tasks, demonstrating robust quality assessment capabilities without any task-specific training. The code will be publicly available at https://github.com/clh124/QualiRAG.
The Llama 4 Herd: Architecture, Training, Evaluation, and Deployment Notes
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:This document consolidates publicly reported technical details about Metas Llama 4 model family. It summarizes (i) released variants (Scout and Maverick) and the broader herd context including the previewed Behemoth teacher model, (ii) architectural characteristics beyond a high-level MoE description covering routed/shared-expert structure, early-fusion multimodality, and long-context design elements reported for Scout (iRoPE and length generalization strategies), (iii) training disclosures spanning pre-training, mid-training for long-context extension, and post-training methodology (lightweight SFT, online RL, and lightweight DPO) as described in release materials, (iv) developer-reported benchmark results for both base and instruction-tuned checkpoints, and (v) practical deployment constraints observed across major serving environments, including provider-specific context limits and quantization packaging. The manuscript also summarizes licensing obligations relevant to redistribution and derivative naming, and reviews publicly described safeguards and evaluation practices. The goal is to provide a compact technical reference for researchers and practitioners who need precise, source-backed facts about Llama 4.
TorchTraceAP: A New Benchmark Dataset for Detecting Performance Anti-Patterns in Computer Vision Models
Dec 16, 2025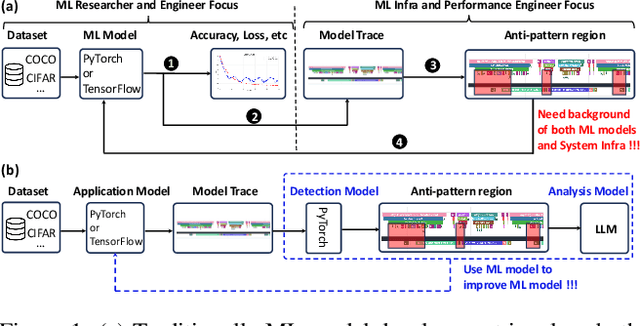
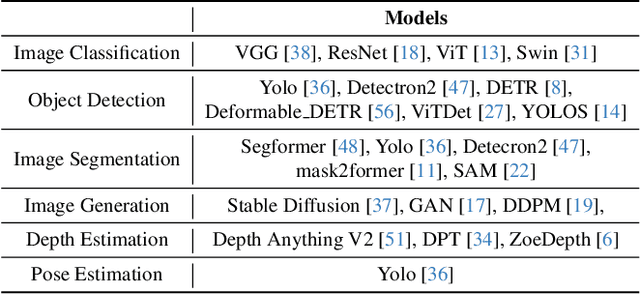
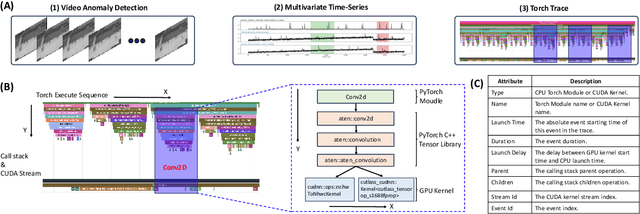
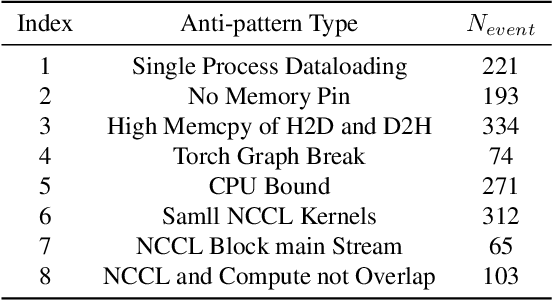
Abstract:Identifying and addressing performance anti-patterns in machine learning (ML) models is critical for efficient training and inference, but it typically demands deep expertise spanning system infrastructure, ML models and kernel development. While large tech companies rely on dedicated ML infrastructure engineers to analyze torch traces and benchmarks, such resource-intensive workflows are largely inaccessible to computer vision researchers in general. Among the challenges, pinpointing problematic trace segments within lengthy execution traces remains the most time-consuming task, and is difficult to automate with current ML models, including LLMs. In this work, we present the first benchmark dataset specifically designed to evaluate and improve ML models' ability to detect anti patterns in traces. Our dataset contains over 600 PyTorch traces from diverse computer vision models classification, detection, segmentation, and generation collected across multiple hardware platforms. We also propose a novel iterative approach: a lightweight ML model first detects trace segments with anti patterns, followed by a large language model (LLM) for fine grained classification and targeted feedback. Experimental results demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms unsupervised clustering and rule based statistical techniques for detecting anti pattern regions. Our method also effectively compensates LLM's limited context length and reasoning inefficiencies.
Shape Deformation Networks for Automated Aortic Valve Finite Element Meshing from 3D CT Images
Nov 05, 2025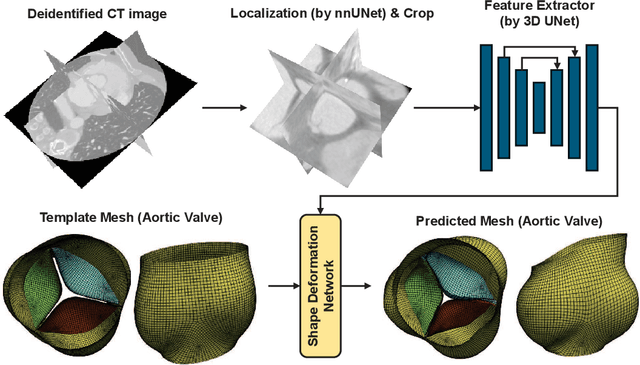
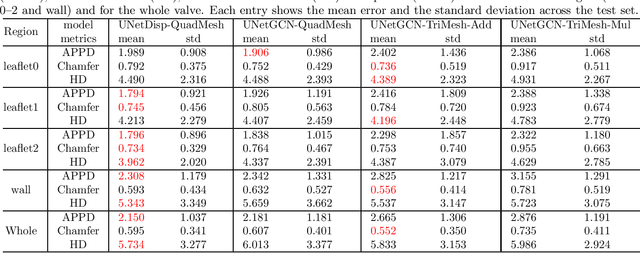
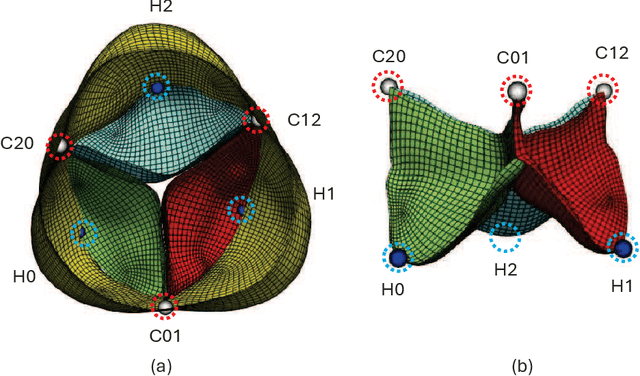
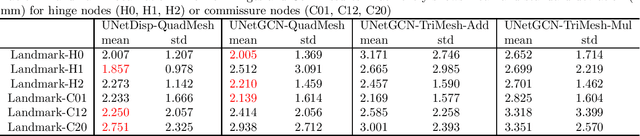
Abstract:Accurate geometric modeling of the aortic valve from 3D CT images is essential for biomechanical analysis and patient-specific simulations to assess valve health or make a preoperative plan. However, it remains challenging to generate aortic valve meshes with both high-quality and consistency across different patients. Traditional approaches often produce triangular meshes with irregular topologies, which can result in poorly shaped elements and inconsistent correspondence due to inter-patient anatomical variation. In this work, we address these challenges by introducing a template-fitting pipeline with deep neural networks to generate structured quad (i.e., quadrilateral) meshes from 3D CT images to represent aortic valve geometries. By remeshing aortic valves of all patients with a common quad mesh template, we ensure a uniform mesh topology with consistent node-to-node and element-to-element correspondence across patients. This consistency enables us to simplify the learning objective of the deep neural networks, by employing a loss function with only two terms (i.e., a geometry reconstruction term and a smoothness regularization term), which is sufficient to preserve mesh smoothness and element quality. Our experiments demonstrate that the proposed approach produces high-quality aortic valve surface meshes with improved smoothness and shape quality, while requiring fewer explicit regularization terms compared to the traditional methods. These results highlight that using structured quad meshes for the template and neural network training not only ensures mesh correspondence and quality but also simplifies the training process, thus enhancing the effectiveness and efficiency of aortic valve modeling.
Contrastive Retrieval Heads Improve Attention-Based Re-Ranking
Oct 02, 2025Abstract:The strong zero-shot and long-context capabilities of recent Large Language Models (LLMs) have paved the way for highly effective re-ranking systems. Attention-based re-rankers leverage attention weights from transformer heads to produce relevance scores, but not all heads are created equally: many contribute noise and redundancy, thus limiting performance. To address this, we introduce CoRe heads, a small set of retrieval heads identified via a contrastive scoring metric that explicitly rewards high attention heads that correlate with relevant documents, while downplaying nodes with higher attention that correlate with irrelevant documents. This relative ranking criterion isolates the most discriminative heads for re-ranking and yields a state-of-the-art list-wise re-ranker. Extensive experiments with three LLMs show that aggregated signals from CoRe heads, constituting less than 1% of all heads, substantially improve re-ranking accuracy over strong baselines. We further find that CoRe heads are concentrated in middle layers, and pruning the computation of final 50% of model layers preserves accuracy while significantly reducing inference time and memory usage.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge