Hui Yang
Department of Mathematical Sciences, University of Essex, Wivenhoe Park, Colchester, CO43SQ, UK, Mondaq Ltd, Bristol, UK
Large Language Model for OWL Proofs
Jan 18, 2026Abstract:The ability of Large Language Models (LLMs) to perform reasoning tasks such as deduction has been widely investigated in recent years. Yet, their capacity to generate proofs-faithful, human-readable explanations of why conclusions follow-remains largely under explored. In this work, we study proof generation in the context of OWL ontologies, which are widely adopted for representing and reasoning over complex knowledge, by developing an automated dataset construction and evaluation framework. Our evaluation encompassing three sequential tasks for complete proving: Extraction, Simplification, and Explanation, as well as an additional task of assessing Logic Completeness of the premise. Through extensive experiments on widely used reasoning LLMs, we achieve important findings including: (1) Some models achieve overall strong results but remain limited on complex cases; (2) Logical complexity, rather than representation format (formal logic language versus natural language), is the dominant factor shaping LLM performance; and (3) Noise and incompleteness in input data substantially diminish LLMs' performance. Together, these results underscore both the promise of LLMs for explanation with rigorous logics and the gap of supporting resilient reasoning under complex or imperfect conditions. Code and data are available at https://github.com/HuiYang1997/LLMOwlR.
xbench: Tracking Agents Productivity Scaling with Profession-Aligned Real-World Evaluations
Jun 16, 2025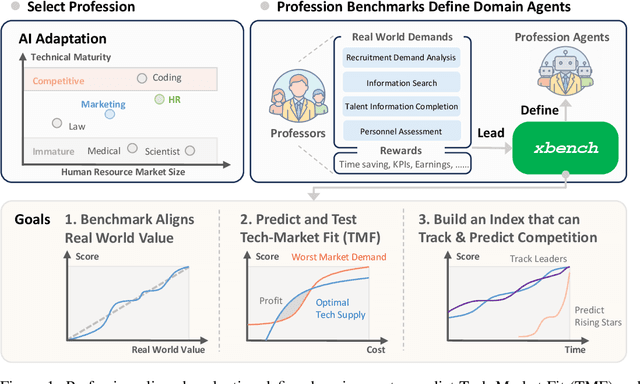
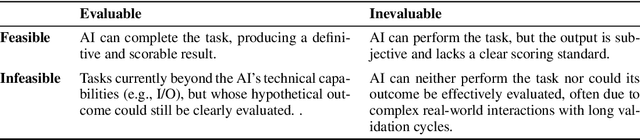
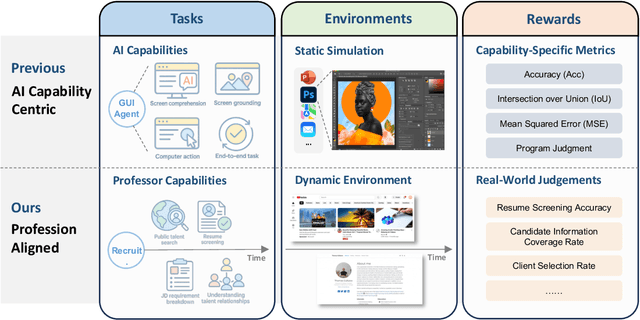
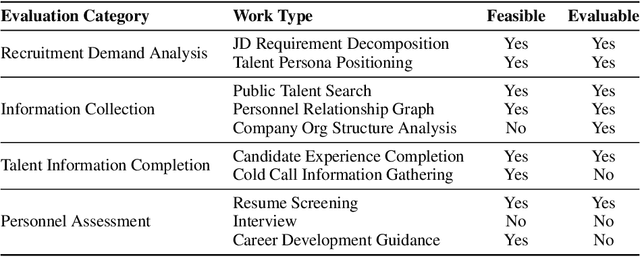
Abstract:We introduce xbench, a dynamic, profession-aligned evaluation suite designed to bridge the gap between AI agent capabilities and real-world productivity. While existing benchmarks often focus on isolated technical skills, they may not accurately reflect the economic value agents deliver in professional settings. To address this, xbench targets commercially significant domains with evaluation tasks defined by industry professionals. Our framework creates metrics that strongly correlate with productivity value, enables prediction of Technology-Market Fit (TMF), and facilitates tracking of product capabilities over time. As our initial implementations, we present two benchmarks: Recruitment and Marketing. For Recruitment, we collect 50 tasks from real-world headhunting business scenarios to evaluate agents' abilities in company mapping, information retrieval, and talent sourcing. For Marketing, we assess agents' ability to match influencers with advertiser needs, evaluating their performance across 50 advertiser requirements using a curated pool of 836 candidate influencers. We present initial evaluation results for leading contemporary agents, establishing a baseline for these professional domains. Our continuously updated evalsets and evaluations are available at https://xbench.org.
Occlusion-Aware 3D Hand-Object Pose Estimation with Masked AutoEncoders
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:Hand-object pose estimation from monocular RGB images remains a significant challenge mainly due to the severe occlusions inherent in hand-object interactions. Existing methods do not sufficiently explore global structural perception and reasoning, which limits their effectiveness in handling occluded hand-object interactions. To address this challenge, we propose an occlusion-aware hand-object pose estimation method based on masked autoencoders, termed as HOMAE. Specifically, we propose a target-focused masking strategy that imposes structured occlusion on regions of hand-object interaction, encouraging the model to learn context-aware features and reason about the occluded structures. We further integrate multi-scale features extracted from the decoder to predict a signed distance field (SDF), capturing both global context and fine-grained geometry. To enhance geometric perception, we combine the implicit SDF with an explicit point cloud derived from the SDF, leveraging the complementary strengths of both representations. This fusion enables more robust handling of occluded regions by combining the global context from the SDF with the precise local geometry provided by the point cloud. Extensive experiments on challenging DexYCB and HO3Dv2 benchmarks demonstrate that HOMAE achieves state-of-the-art performance in hand-object pose estimation. We will release our code and model.
MonoDiff9D: Monocular Category-Level 9D Object Pose Estimation via Diffusion Model
Apr 14, 2025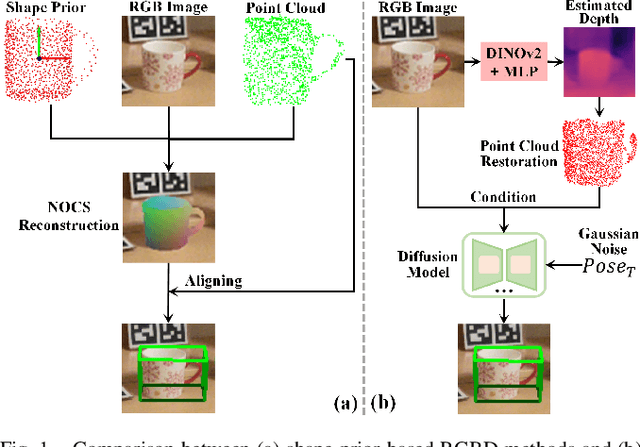
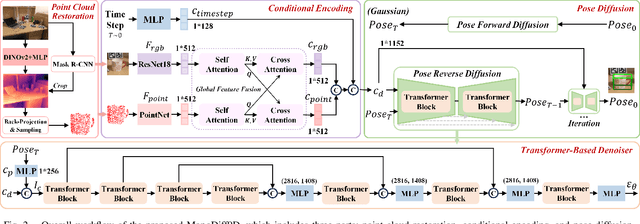

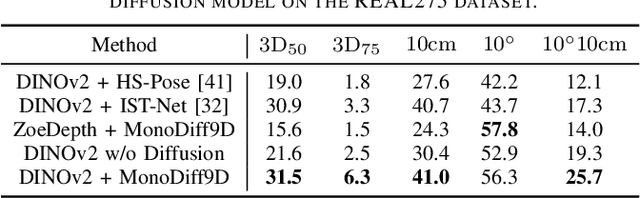
Abstract:Object pose estimation is a core means for robots to understand and interact with their environment. For this task, monocular category-level methods are attractive as they require only a single RGB camera. However, current methods rely on shape priors or CAD models of the intra-class known objects. We propose a diffusion-based monocular category-level 9D object pose generation method, MonoDiff9D. Our motivation is to leverage the probabilistic nature of diffusion models to alleviate the need for shape priors, CAD models, or depth sensors for intra-class unknown object pose estimation. We first estimate coarse depth via DINOv2 from the monocular image in a zero-shot manner and convert it into a point cloud. We then fuse the global features of the point cloud with the input image and use the fused features along with the encoded time step to condition MonoDiff9D. Finally, we design a transformer-based denoiser to recover the object pose from Gaussian noise. Extensive experiments on two popular benchmark datasets show that MonoDiff9D achieves state-of-the-art monocular category-level 9D object pose estimation accuracy without the need for shape priors or CAD models at any stage. Our code will be made public at https://github.com/CNJianLiu/MonoDiff9D.
Novel Object 6D Pose Estimation with a Single Reference View
Mar 07, 2025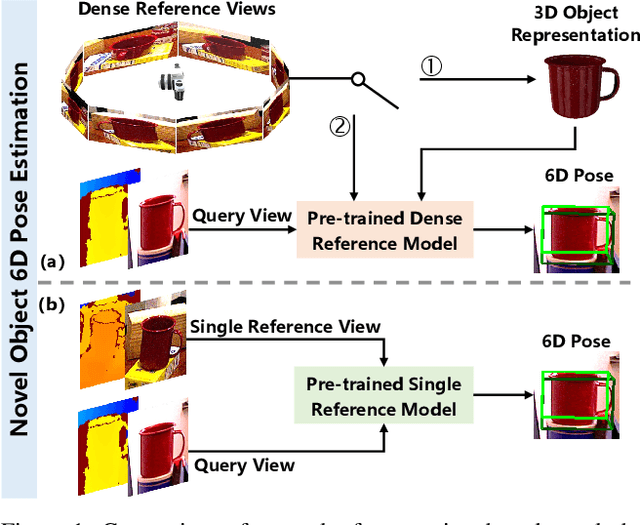
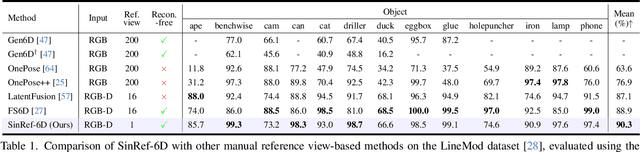
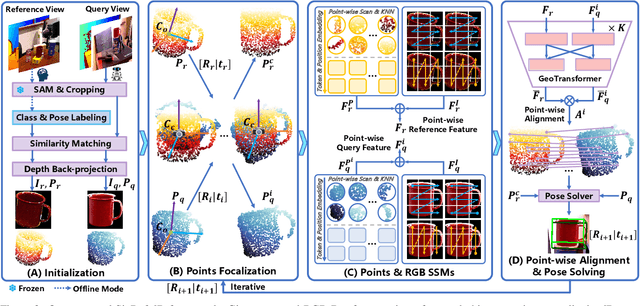
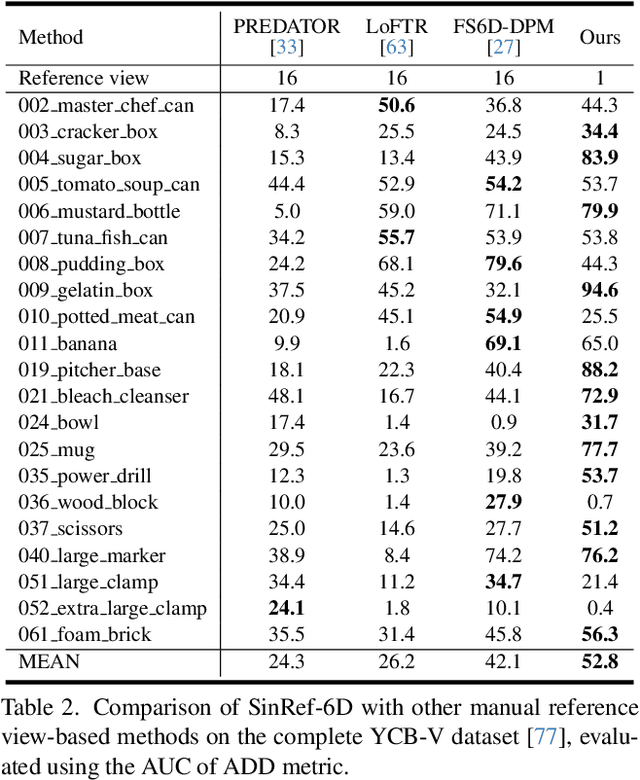
Abstract:Existing novel object 6D pose estimation methods typically rely on CAD models or dense reference views, which are both difficult to acquire. Using only a single reference view is more scalable, but challenging due to large pose discrepancies and limited geometric and spatial information. To address these issues, we propose a Single-Reference-based novel object 6D (SinRef-6D) pose estimation method. Our key idea is to iteratively establish point-wise alignment in the camera coordinate system based on state space models (SSMs). Specifically, iterative camera-space point-wise alignment can effectively handle large pose discrepancies, while our proposed RGB and Points SSMs can capture long-range dependencies and spatial information from a single view, offering linear complexity and superior spatial modeling capability. Once pre-trained on synthetic data, SinRef-6D can estimate the 6D pose of a novel object using only a single reference view, without requiring retraining or a CAD model. Extensive experiments on six popular datasets and real-world robotic scenes demonstrate that we achieve on-par performance with CAD-based and dense reference view-based methods, despite operating in the more challenging single reference setting. Code will be released at https://github.com/CNJianLiu/SinRef-6D.
Diff9D: Diffusion-Based Domain-Generalized Category-Level 9-DoF Object Pose Estimation
Feb 04, 2025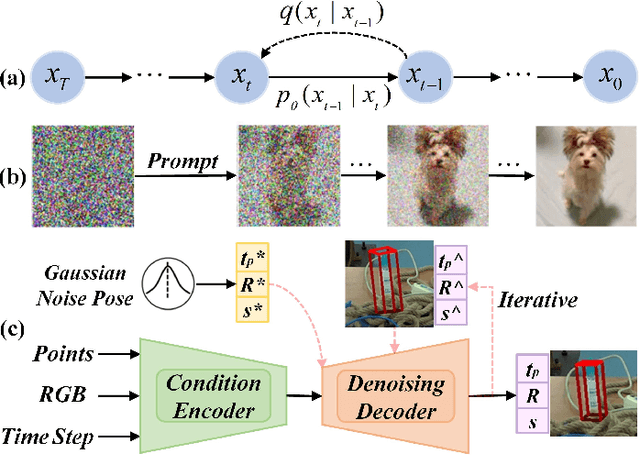
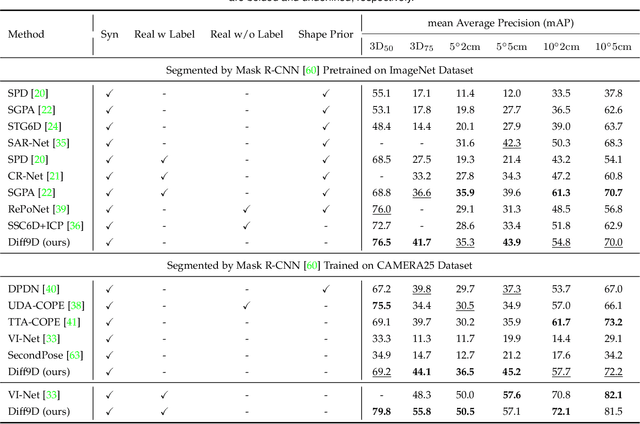
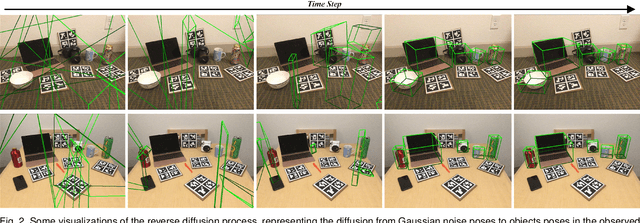
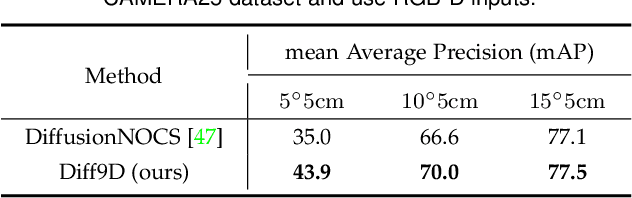
Abstract:Nine-degrees-of-freedom (9-DoF) object pose and size estimation is crucial for enabling augmented reality and robotic manipulation. Category-level methods have received extensive research attention due to their potential for generalization to intra-class unknown objects. However, these methods require manual collection and labeling of large-scale real-world training data. To address this problem, we introduce a diffusion-based paradigm for domain-generalized category-level 9-DoF object pose estimation. Our motivation is to leverage the latent generalization ability of the diffusion model to address the domain generalization challenge in object pose estimation. This entails training the model exclusively on rendered synthetic data to achieve generalization to real-world scenes. We propose an effective diffusion model to redefine 9-DoF object pose estimation from a generative perspective. Our model does not require any 3D shape priors during training or inference. By employing the Denoising Diffusion Implicit Model, we demonstrate that the reverse diffusion process can be executed in as few as 3 steps, achieving near real-time performance. Finally, we design a robotic grasping system comprising both hardware and software components. Through comprehensive experiments on two benchmark datasets and the real-world robotic system, we show that our method achieves state-of-the-art domain generalization performance. Our code will be made public at https://github.com/CNJianLiu/Diff9D.
RegD: Hierarchical Embeddings via Distances over Geometric Regions
Jan 29, 2025



Abstract:Hierarchical data are common in many domains like life sciences and e-commerce, and their embeddings often play a critical role. Although hyperbolic embeddings offer a grounded approach to representing hierarchical structures in low-dimensional spaces, their utility is hindered by optimization difficulties in hyperbolic space and dependence on handcrafted structural constraints. We propose RegD, a novel Euclidean framework that addresses these limitations by representing hierarchical data as geometric regions with two new metrics: (1) depth distance, which preserves the representational power of hyperbolic spaces for hierarchical data, and (2) boundary distance, which explicitly encodes set-inclusion relationships between regions in a general way. Our empirical evaluation on diverse real-world datasets shows consistent performance gains over state-of-the-art methods and demonstrates RegD's potential for broader applications beyond hierarchy alone tasks.
An Efficient Diffusion-based Non-Autoregressive Solver for Traveling Salesman Problem
Jan 23, 2025



Abstract:Recent advances in neural models have shown considerable promise in solving Traveling Salesman Problems (TSPs) without relying on much hand-crafted engineering. However, while non-autoregressive (NAR) approaches benefit from faster inference through parallelism, they typically deliver solutions of inferior quality compared to autoregressive ones. To enhance the solution quality while maintaining fast inference, we propose DEITSP, a diffusion model with efficient iterations tailored for TSP that operates in a NAR manner. Firstly, we introduce a one-step diffusion model that integrates the controlled discrete noise addition process with self-consistency enhancement, enabling optimal solution prediction through simultaneous denoising of multiple solutions. Secondly, we design a dual-modality graph transformer to bolster the extraction and fusion of features from node and edge modalities, while further accelerating the inference with fewer layers. Thirdly, we develop an efficient iterative strategy that alternates between adding and removing noise to improve exploration compared to previous diffusion methods. Additionally, we devise a scheduling framework to progressively refine the solution space by adjusting noise levels, facilitating a smooth search for optimal solutions. Extensive experiments on real-world and large-scale TSP instances demonstrate that DEITSP performs favorably against existing neural approaches in terms of solution quality, inference latency, and generalization ability. Our code is available at $\href{https://github.com/DEITSP/DEITSP}{https://github.com/DEITSP/DEITSP}$.
OOD-HOI: Text-Driven 3D Whole-Body Human-Object Interactions Generation Beyond Training Domains
Nov 27, 2024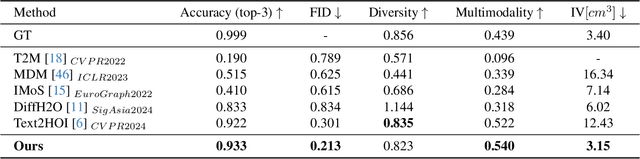
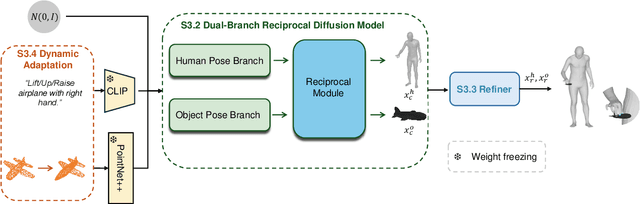
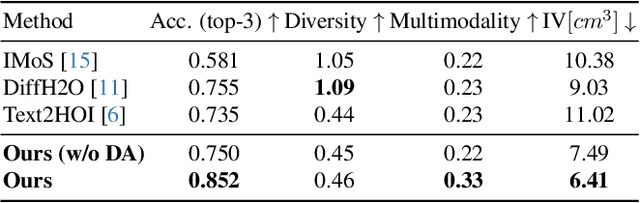
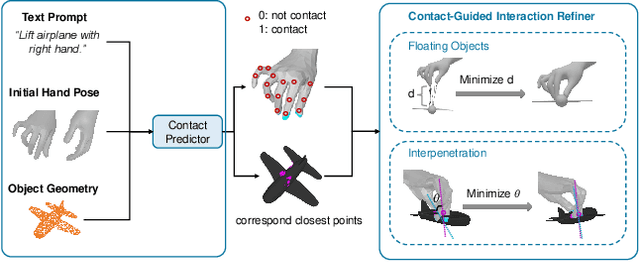
Abstract:Generating realistic 3D human-object interactions (HOIs) from text descriptions is a active research topic with potential applications in virtual and augmented reality, robotics, and animation. However, creating high-quality 3D HOIs remains challenging due to the lack of large-scale interaction data and the difficulty of ensuring physical plausibility, especially in out-of-domain (OOD) scenarios. Current methods tend to focus either on the body or the hands, which limits their ability to produce cohesive and realistic interactions. In this paper, we propose OOD-HOI, a text-driven framework for generating whole-body human-object interactions that generalize well to new objects and actions. Our approach integrates a dual-branch reciprocal diffusion model to synthesize initial interaction poses, a contact-guided interaction refiner to improve physical accuracy based on predicted contact areas, and a dynamic adaptation mechanism which includes semantic adjustment and geometry deformation to improve robustness. Experimental results demonstrate that our OOD-HOI could generate more realistic and physically plausible 3D interaction pose in OOD scenarios compared to existing methods.
TransBox: EL++-closed Ontology Embedding
Oct 18, 2024Abstract:OWL (Web Ontology Language) ontologies, which are able to represent both relational and type facts as standard knowledge graphs and complex domain knowledge in Description Logic (DL) axioms, are widely adopted in domains such as healthcare and bioinformatics. Inspired by the success of knowledge graph embeddings, embedding OWL ontologies has gained significant attention in recent years. Current methods primarily focus on learning embeddings for atomic concepts and roles, enabling the evaluation based on normalized axioms through specially designed score functions. However, they often neglect the embedding of complex concepts, making it difficult to infer with more intricate axioms. This limitation reduces their effectiveness in advanced reasoning tasks, such as Ontology Learning and ontology-mediated Query Answering. In this paper, we propose EL++-closed ontology embeddings which are able to represent any logical expressions in DL via composition. Furthermore, we develop TransBox, an effective EL++-closed ontology embedding method that can handle many-to-one, one-to-many and many-to-many relations. Our extensive experiments demonstrate that TransBox often achieves state-of-the-art performance across various real-world datasets for predicting complex axioms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge