Yixin Ren
AgentIF-OneDay: A Task-level Instruction-Following Benchmark for General AI Agents in Daily Scenarios
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:The capacity of AI agents to effectively handle tasks of increasing duration and complexity continues to grow, demonstrating exceptional performance in coding, deep research, and complex problem-solving evaluations. However, in daily scenarios, the perception of these advanced AI capabilities among general users remains limited. We argue that current evaluations prioritize increasing task difficulty without sufficiently addressing the diversity of agentic tasks necessary to cover the daily work, life, and learning activities of a broad demographic. To address this, we propose AgentIF-OneDay, aimed at determining whether general users can utilize natural language instructions and AI agents to complete a diverse array of daily tasks. These tasks require not only solving problems through dialogue but also understanding various attachment types and delivering tangible file-based results. The benchmark is structured around three user-centric categories: Open Workflow Execution, which assesses adherence to explicit and complex workflows; Latent Instruction, which requires agents to infer implicit instructions from attachments; and Iterative Refinement, which involves modifying or expanding upon ongoing work. We employ instance-level rubrics and a refined evaluation pipeline that aligns LLM-based verification with human judgment, achieving an 80.1% agreement rate using Gemini-3-Pro. AgentIF-OneDay comprises 104 tasks covering 767 scoring points. We benchmarked four leading general AI agents and found that agent products built based on APIs and ChatGPT agents based on agent RL remain in the first tier simultaneously. Leading LLM APIs and open-source models have internalized agentic capabilities, enabling AI application teams to develop cutting-edge Agent products.
BabyVision: Visual Reasoning Beyond Language
Jan 10, 2026Abstract:While humans develop core visual skills long before acquiring language, contemporary Multimodal LLMs (MLLMs) still rely heavily on linguistic priors to compensate for their fragile visual understanding. We uncovered a crucial fact: state-of-the-art MLLMs consistently fail on basic visual tasks that humans, even 3-year-olds, can solve effortlessly. To systematically investigate this gap, we introduce BabyVision, a benchmark designed to assess core visual abilities independent of linguistic knowledge for MLLMs. BabyVision spans a wide range of tasks, with 388 items divided into 22 subclasses across four key categories. Empirical results and human evaluation reveal that leading MLLMs perform significantly below human baselines. Gemini3-Pro-Preview scores 49.7, lagging behind 6-year-old humans and falling well behind the average adult score of 94.1. These results show despite excelling in knowledge-heavy evaluations, current MLLMs still lack fundamental visual primitives. Progress in BabyVision represents a step toward human-level visual perception and reasoning capabilities. We also explore solving visual reasoning with generation models by proposing BabyVision-Gen and automatic evaluation toolkit. Our code and benchmark data are released at https://github.com/UniPat-AI/BabyVision for reproduction.
xbench: Tracking Agents Productivity Scaling with Profession-Aligned Real-World Evaluations
Jun 16, 2025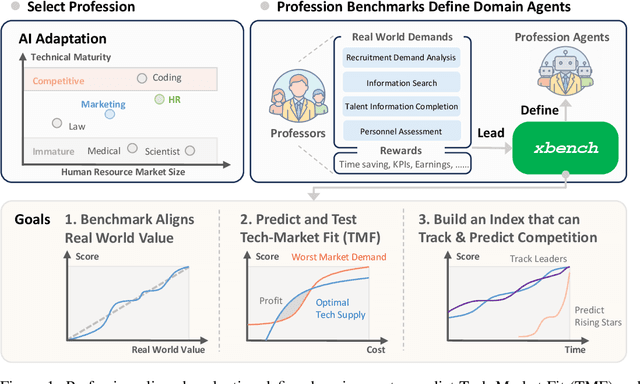
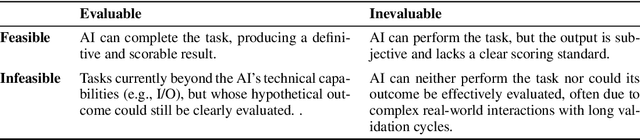
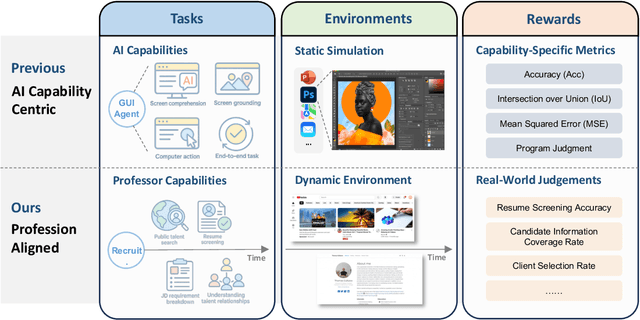
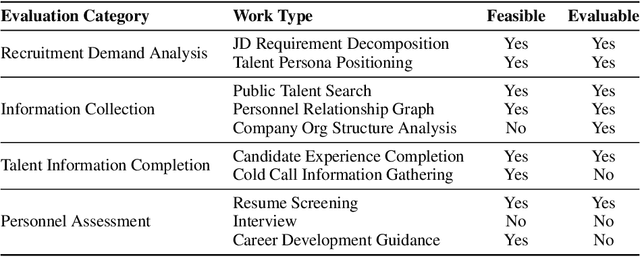
Abstract:We introduce xbench, a dynamic, profession-aligned evaluation suite designed to bridge the gap between AI agent capabilities and real-world productivity. While existing benchmarks often focus on isolated technical skills, they may not accurately reflect the economic value agents deliver in professional settings. To address this, xbench targets commercially significant domains with evaluation tasks defined by industry professionals. Our framework creates metrics that strongly correlate with productivity value, enables prediction of Technology-Market Fit (TMF), and facilitates tracking of product capabilities over time. As our initial implementations, we present two benchmarks: Recruitment and Marketing. For Recruitment, we collect 50 tasks from real-world headhunting business scenarios to evaluate agents' abilities in company mapping, information retrieval, and talent sourcing. For Marketing, we assess agents' ability to match influencers with advertiser needs, evaluating their performance across 50 advertiser requirements using a curated pool of 836 candidate influencers. We present initial evaluation results for leading contemporary agents, establishing a baseline for these professional domains. Our continuously updated evalsets and evaluations are available at https://xbench.org.
Score-based Generative Modeling for Conditional Independence Testing
May 29, 2025Abstract:Determining conditional independence (CI) relationships between random variables is a fundamental yet challenging task in machine learning and statistics, especially in high-dimensional settings. Existing generative model-based CI testing methods, such as those utilizing generative adversarial networks (GANs), often struggle with undesirable modeling of conditional distributions and training instability, resulting in subpar performance. To address these issues, we propose a novel CI testing method via score-based generative modeling, which achieves precise Type I error control and strong testing power. Concretely, we first employ a sliced conditional score matching scheme to accurately estimate conditional score and use Langevin dynamics conditional sampling to generate null hypothesis samples, ensuring precise Type I error control. Then, we incorporate a goodness-of-fit stage into the method to verify generated samples and enhance interpretability in practice. We theoretically establish the error bound of conditional distributions modeled by score-based generative models and prove the validity of our CI tests. Extensive experiments on both synthetic and real-world datasets show that our method significantly outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods, providing a promising way to revitalize generative model-based CI testing.
Fast Causal Discovery by Approximate Kernel-based Generalized Score Functions with Linear Computational Complexity
Dec 23, 2024



Abstract:Score-based causal discovery methods can effectively identify causal relationships by evaluating candidate graphs and selecting the one with the highest score. One popular class of scores is kernel-based generalized score functions, which can adapt to a wide range of scenarios and work well in practice because they circumvent assumptions about causal mechanisms and data distributions. Despite these advantages, kernel-based generalized score functions pose serious computational challenges in time and space, with a time complexity of $\mathcal{O}(n^3)$ and a memory complexity of $\mathcal{O}(n^2)$, where $n$ is the sample size. In this paper, we propose an approximate kernel-based generalized score function with $\mathcal{O}(n)$ time and space complexities by using low-rank technique and designing a set of rules to handle the complex composite matrix operations required to calculate the score, as well as developing sampling algorithms for different data types to benefit the handling of diverse data types efficiently. Our extensive causal discovery experiments on both synthetic and real-world data demonstrate that compared to the state-of-the-art method, our method can not only significantly reduce computational costs, but also achieve comparable accuracy, especially for large datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge