Haoyu Lu
Kimi K2.5: Visual Agentic Intelligence
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:We introduce Kimi K2.5, an open-source multimodal agentic model designed to advance general agentic intelligence. K2.5 emphasizes the joint optimization of text and vision so that two modalities enhance each other. This includes a series of techniques such as joint text-vision pre-training, zero-vision SFT, and joint text-vision reinforcement learning. Building on this multimodal foundation, K2.5 introduces Agent Swarm, a self-directed parallel agent orchestration framework that dynamically decomposes complex tasks into heterogeneous sub-problems and executes them concurrently. Extensive evaluations show that Kimi K2.5 achieves state-of-the-art results across various domains including coding, vision, reasoning, and agentic tasks. Agent Swarm also reduces latency by up to $4.5\times$ over single-agent baselines. We release the post-trained Kimi K2.5 model checkpoint to facilitate future research and real-world applications of agentic intelligence.
WorldVQA: Measuring Atomic World Knowledge in Multimodal Large Language Models
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:We introduce WorldVQA, a benchmark designed to evaluate the atomic visual world knowledge of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs). Unlike current evaluations, which often conflate visual knowledge retrieval with reasoning, WorldVQA decouples these capabilities to strictly measure "what the model memorizes." The benchmark assesses the atomic capability of grounding and naming visual entities across a stratified taxonomy, spanning from common head-class objects to long-tail rarities. We expect WorldVQA to serve as a rigorous test for visual factuality, thereby establishing a standard for assessing the encyclopedic breadth and hallucination rates of current and next-generation frontier models.
Towards Pixel-Level VLM Perception via Simple Points Prediction
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:We present SimpleSeg, a strikingly simple yet highly effective approach to endow Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) with native pixel-level perception. Our method reframes segmentation as a simple sequence generation problem: the model directly predicts sequences of points (textual coordinates) delineating object boundaries, entirely within its language space. To achieve high fidelity, we introduce a two-stage SF$\to$RL training pipeline, where Reinforcement Learning with an IoU-based reward refines the point sequences to accurately match ground-truth contours. We find that the standard MLLM architecture possesses a strong, inherent capacity for low-level perception that can be unlocked without any specialized architecture. On segmentation benchmarks, SimpleSeg achieves performance that is comparable to, and often surpasses, methods relying on complex, task-specific designs. This work lays out that precise spatial understanding can emerge from simple point prediction, challenging the prevailing need for auxiliary components and paving the way for more unified and capable VLMs. Homepage: https://simpleseg.github.io/
BabyVision: Visual Reasoning Beyond Language
Jan 10, 2026Abstract:While humans develop core visual skills long before acquiring language, contemporary Multimodal LLMs (MLLMs) still rely heavily on linguistic priors to compensate for their fragile visual understanding. We uncovered a crucial fact: state-of-the-art MLLMs consistently fail on basic visual tasks that humans, even 3-year-olds, can solve effortlessly. To systematically investigate this gap, we introduce BabyVision, a benchmark designed to assess core visual abilities independent of linguistic knowledge for MLLMs. BabyVision spans a wide range of tasks, with 388 items divided into 22 subclasses across four key categories. Empirical results and human evaluation reveal that leading MLLMs perform significantly below human baselines. Gemini3-Pro-Preview scores 49.7, lagging behind 6-year-old humans and falling well behind the average adult score of 94.1. These results show despite excelling in knowledge-heavy evaluations, current MLLMs still lack fundamental visual primitives. Progress in BabyVision represents a step toward human-level visual perception and reasoning capabilities. We also explore solving visual reasoning with generation models by proposing BabyVision-Gen and automatic evaluation toolkit. Our code and benchmark data are released at https://github.com/UniPat-AI/BabyVision for reproduction.
HyperVL: An Efficient and Dynamic Multimodal Large Language Model for Edge Devices
Dec 16, 2025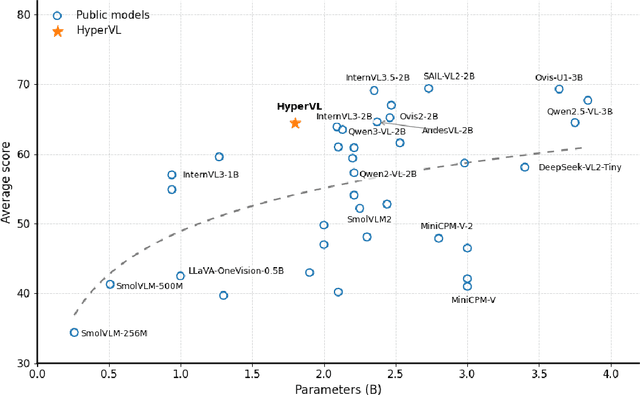

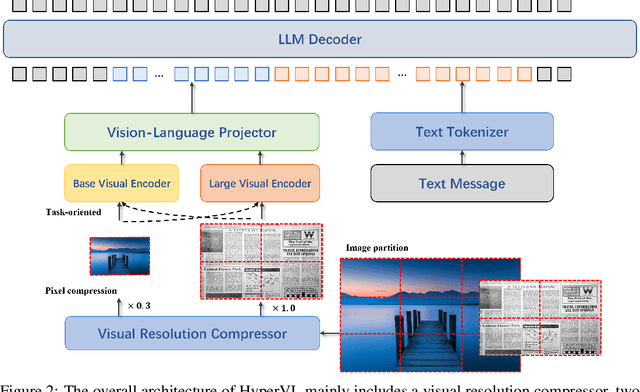
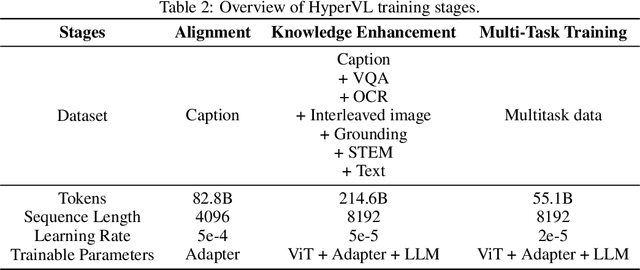
Abstract:Current multimodal large lanauge models possess strong perceptual and reasoning capabilities, however high computational and memory requirements make them difficult to deploy directly on on-device environments. While small-parameter models are progressively endowed with strong general capabilities, standard Vision Transformer (ViT) encoders remain a critical bottleneck, suffering from excessive latency and memory consumption when processing high-resolution inputs.To address these challenges, we introduce HyperVL, an efficient multimodal large language model tailored for on-device inference. HyperVL adopts an image-tiling strategy to cap peak memory usage and incorporates two novel techniques: (1) a Visual Resolution Compressor (VRC) that adaptively predicts optimal encoding resolutions to eliminate redundant computation, and (2) Dual Consistency Learning (DCL), which aligns multi-scale ViT encoders within a unified framework, enabling dynamic switching between visual branches under a shared LLM. Extensive experiments demonstrate that HyperVL achieves state-of-the-art performance among models of comparable size across multiple benchmarks. Furthermore, it significantly significantly reduces latency and power consumption on real mobile devices, demonstrating its practicality for on-device multimodal inference.
Physics-Constrained Diffusion Reconstruction with Posterior Correction for Quantitative and Fast PET Imaging
Aug 20, 2025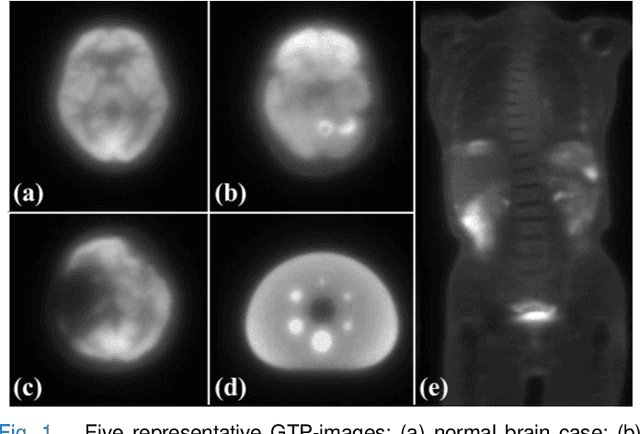
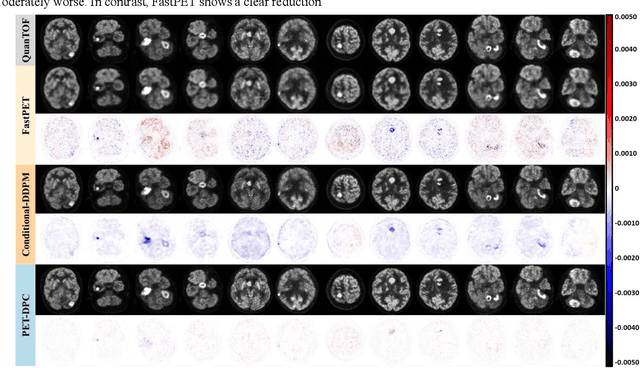
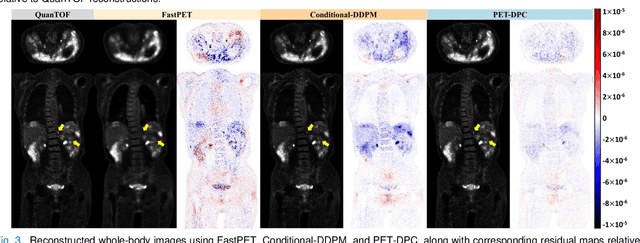
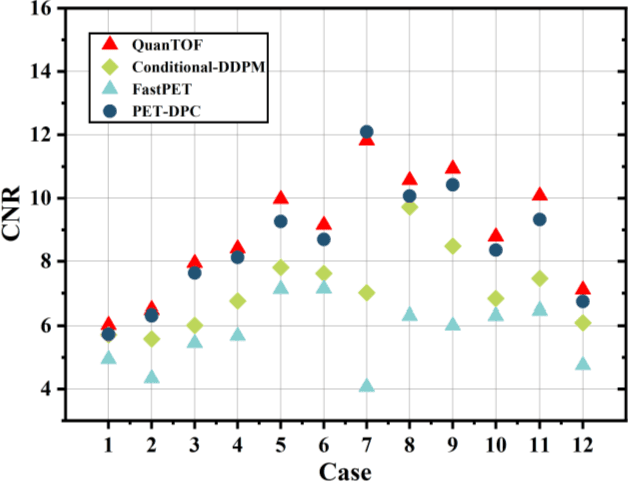
Abstract:Deep learning-based reconstruction of positron emission tomography(PET) data has gained increasing attention in recent years. While these methods achieve fast reconstruction,concerns remain regarding quantitative accuracy and the presence of artifacts,stemming from limited model interpretability,data driven dependence, and overfitting risks.These challenges have hindered clinical adoption.To address them,we propose a conditional diffusion model with posterior physical correction (PET-DPC) for PET image reconstruction. An innovative normalization procedure generates the input Geometric TOF Probabilistic Image (GTP-image),while physical information is incorporated during the diffusion sampling process to perform posterior scatter,attenuation,and random corrections. The model was trained and validated on 300 brain and 50 whole-body PET datasets,a physical phantom,and 20 simulated brain datasets. PET-DPC produced reconstructions closely aligned with fully corrected OSEM images,outperforming end-to-end deep learning models in quantitative metrics and,in some cases, surpassing traditional iterative methods. The model also generalized well to out-of-distribution(OOD) data. Compared to iterative methods,PET-DPC reduced reconstruction time by 50% for brain scans and 85% for whole-body scans. Ablation studies confirmed the critical role of posterior correction in implementing scatter and attenuation corrections,enhancing reconstruction accuracy. Experiments with physical phantoms further demonstrated PET-DPC's ability to preserve background uniformity and accurately reproduce tumor-to-background intensity ratios. Overall,these results highlight PET-DPC as a promising approach for rapid, quantitatively accurate PET reconstruction,with strong potential to improve clinical imaging workflows.
Kimi-VL Technical Report
Apr 10, 2025
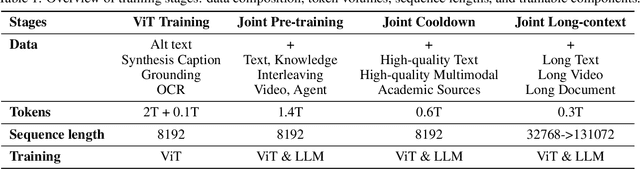
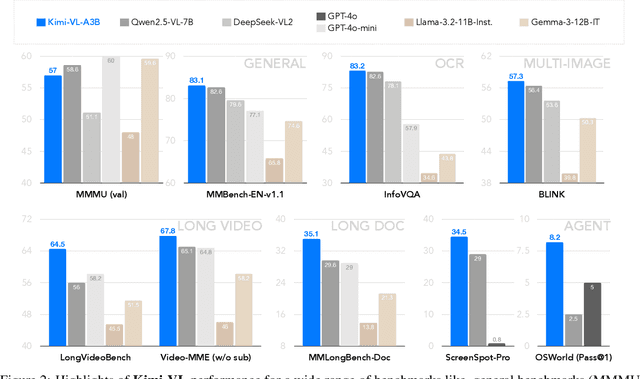
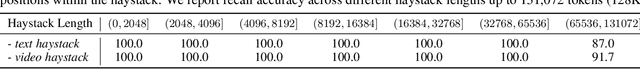
Abstract:We present Kimi-VL, an efficient open-source Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) vision-language model (VLM) that offers advanced multimodal reasoning, long-context understanding, and strong agent capabilities - all while activating only 2.8B parameters in its language decoder (Kimi-VL-A3B). Kimi-VL demonstrates strong performance across challenging domains: as a general-purpose VLM, Kimi-VL excels in multi-turn agent tasks (e.g., OSWorld), matching flagship models. Furthermore, it exhibits remarkable capabilities across diverse challenging vision language tasks, including college-level image and video comprehension, OCR, mathematical reasoning, and multi-image understanding. In comparative evaluations, it effectively competes with cutting-edge efficient VLMs such as GPT-4o-mini, Qwen2.5-VL-7B, and Gemma-3-12B-IT, while surpassing GPT-4o in several key domains. Kimi-VL also advances in processing long contexts and perceiving clearly. With a 128K extended context window, Kimi-VL can process diverse long inputs, achieving impressive scores of 64.5 on LongVideoBench and 35.1 on MMLongBench-Doc. Its native-resolution vision encoder, MoonViT, further allows it to see and understand ultra-high-resolution visual inputs, achieving 83.2 on InfoVQA and 34.5 on ScreenSpot-Pro, while maintaining lower computational cost for common tasks. Building upon Kimi-VL, we introduce an advanced long-thinking variant: Kimi-VL-Thinking. Developed through long chain-of-thought (CoT) supervised fine-tuning (SFT) and reinforcement learning (RL), this model exhibits strong long-horizon reasoning capabilities. It achieves scores of 61.7 on MMMU, 36.8 on MathVision, and 71.3 on MathVista while maintaining the compact 2.8B activated LLM parameters, setting a new standard for efficient multimodal thinking models. Code and models are publicly accessible at https://github.com/MoonshotAI/Kimi-VL.
Efficient Motion-Aware Video MLLM
Mar 17, 2025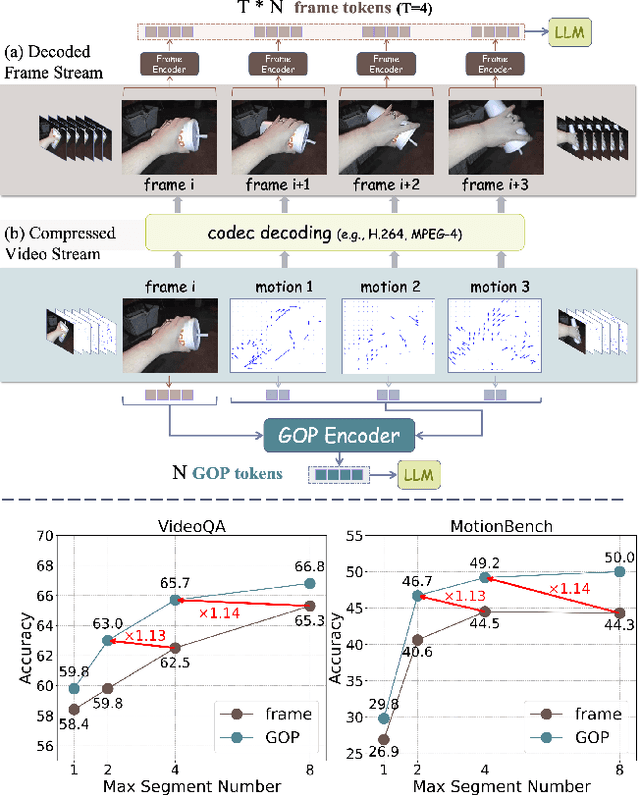
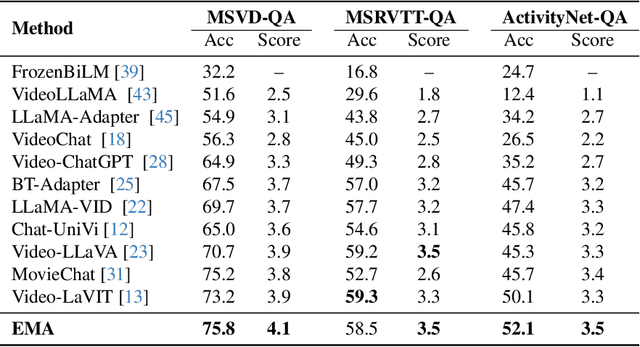
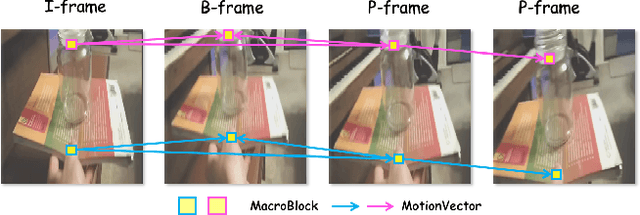
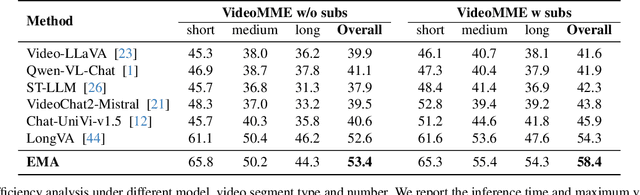
Abstract:Most current video MLLMs rely on uniform frame sampling and image-level encoders, resulting in inefficient data processing and limited motion awareness. To address these challenges, we introduce EMA, an Efficient Motion-Aware video MLLM that utilizes compressed video structures as inputs. We propose a motion-aware GOP (Group of Pictures) encoder that fuses spatial and motion information within a GOP unit in the compressed video stream, generating compact, informative visual tokens. By integrating fewer but denser RGB frames with more but sparser motion vectors in this native slow-fast input architecture, our approach reduces redundancy and enhances motion representation. Additionally, we introduce MotionBench, a benchmark for evaluating motion understanding across four motion types: linear, curved, rotational, and contact-based. Experimental results show that EMA achieves state-of-the-art performance on both MotionBench and popular video question answering benchmarks, while reducing inference costs. Moreover, EMA demonstrates strong scalability, as evidenced by its competitive performance on long video understanding benchmarks.
R1-Onevision: Advancing Generalized Multimodal Reasoning through Cross-Modal Formalization
Mar 13, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models have demonstrated remarkable reasoning capability in complex textual tasks. However, multimodal reasoning, which requires integrating visual and textual information, remains a significant challenge. Existing visual-language models often struggle to effectively analyze and reason visual content, resulting in suboptimal performance on complex reasoning tasks. Moreover, the absence of comprehensive benchmarks hinders the accurate assessment of multimodal reasoning capabilities. In this paper, we introduce R1-Onevision, a multimodal reasoning model designed to bridge the gap between visual perception and deep reasoning. To achieve this, we propose a cross-modal reasoning pipeline that transforms images into formal textural representations, enabling precise language-based reasoning. Leveraging this pipeline, we construct the R1-Onevision dataset which provides detailed, step-by-step multimodal reasoning annotations across diverse domains. We further develop the R1-Onevision model through supervised fine-tuning and reinforcement learning to cultivate advanced reasoning and robust generalization abilities. To comprehensively evaluate multimodal reasoning performance across different grades, we introduce R1-Onevision-Bench, a benchmark aligned with human educational stages, covering exams from junior high school to university and beyond. Experimental results show that R1-Onevision achieves state-of-the-art performance, outperforming models such as GPT-4o and Qwen2.5-VL on multiple challenging multimodal reasoning benchmarks.
Beyond Filtering: Adaptive Image-Text Quality Enhancement for MLLM Pretraining
Oct 21, 2024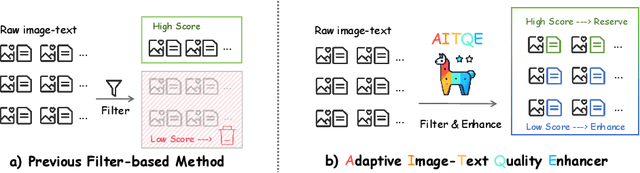



Abstract:Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have made significant strides by integrating visual and textual modalities. A critical factor in training MLLMs is the quality of image-text pairs within multimodal pretraining datasets. However, $\textit {de facto}$ filter-based data quality enhancement paradigms often discard a substantial portion of high-quality image data due to inadequate semantic alignment between images and texts, leading to inefficiencies in data utilization and scalability. In this paper, we propose the Adaptive Image-Text Quality Enhancer (AITQE), a model that dynamically assesses and enhances the quality of image-text pairs. AITQE employs a text rewriting mechanism for low-quality pairs and incorporates a negative sample learning strategy to improve evaluative capabilities by integrating deliberately selected low-quality samples during training. Unlike prior approaches that significantly alter text distributions, our method minimally adjusts text to preserve data volume while enhancing quality. Experimental results demonstrate that AITQE surpasses existing methods on various benchmark, effectively leveraging raw data and scaling efficiently with increasing data volumes. We hope our work will inspire future works. The code and model are available at: https://github.com/hanhuang22/AITQE.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge