Yifan Li
Probability-Entropy Calibration: An Elastic Indicator for Adaptive Fine-tuning
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Token-level reweighting is a simple yet effective mechanism for controlling supervised fine-tuning, but common indicators are largely one-dimensional: the ground-truth probability reflects downstream alignment, while token entropy reflects intrinsic uncertainty induced by the pre-training prior. Ignoring entropy can misidentify noisy or easily replaceable tokens as learning-critical, while ignoring probability fails to reflect target-specific alignment. RankTuner introduces a probability--entropy calibration signal, the Relative Rank Indicator, which compares the rank of the ground-truth token with its expected rank under the prediction distribution. The inverse indicator is used as a token-wise Relative Scale to reweight the fine-tuning objective, focusing updates on truly under-learned tokens without over-penalizing intrinsically uncertain positions. Experiments on multiple backbones show consistent improvements on mathematical reasoning benchmarks, transfer gains on out-of-distribution reasoning, and pre code generation performance over probability-only or entropy-only reweighting baselines.
Multi-Perspective Subimage CLIP with Keyword Guidance for Remote Sensing Image-Text Retrieval
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Vision-Language Pre-training (VLP) models like CLIP have significantly advanced Remote Sensing Image-Text Retrieval (RSITR). However, existing methods predominantly rely on coarse-grained global alignment, which often overlooks the dense, multi-scale semantics inherent in overhead imagery. Moreover, adapting these heavy models via full fine-tuning incurs prohibitive computational costs and risks catastrophic forgetting. To address these challenges, we propose MPS-CLIP, a parameter-efficient framework designed to shift the retrieval paradigm from global matching to keyword-guided fine-grained alignment. Specifically, we leverage a Large Language Model (LLM) to extract core semantic keywords, guiding the Segment Anything Model (SamGeo) to generate semantically relevant sub-perspectives. To efficiently adapt the frozen backbone, we introduce a Gated Global Attention (G^2A) adapter, which captures global context and long-range dependencies with minimal overhead. Furthermore, a Multi-Perspective Representation (MPR) module aggregates these local cues into robust multi-perspective embeddings. The framework is optimized via a hybrid objective combining multi-perspective contrastive and weighted triplet losses, which dynamically selects maximum-response perspectives to suppress noise and enforce precise semantic matching. Extensive experiments on the RSICD and RSITMD benchmarks demonstrate that MPS-CLIP achieves state-of-the-art performance with 35.18% and 48.40% mean Recall (mR), respectively, significantly outperforming full fine-tuning baselines and recent competitive methods. Code is available at https://github.com/Lcrucial1f/MPS-CLIP.
KDCM: Reducing Hallucination in LLMs through Explicit Reasoning Structures
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:To mitigate hallucinations in large language models (LLMs), we propose a framework that focuses on errors induced by prompts. Our method extends a chain-style knowledge distillation approach by incorporating a programmable module that guides knowledge graph exploration. This module is embedded as executable code within the reasoning prompt, allowing the model to leverage external structured knowledge during inference. Based on this design, we develop an enhanced distillation-based reasoning framework that explicitly regulates intermediate reasoning steps, resulting in more reliable predictions. We evaluate the proposed approach on multiple public benchmarks using GPT-4 and LLaMA-3.3. Experimental results show that code-guided reasoning significantly improves contextual modeling and reduces prompt-induced hallucinations. Specifically, HIT@1, HIT@3, and HIT@5 increase by 15.64%, 13.38%, and 13.28%, respectively, with scores exceeding 95% across several evaluation settings. These findings indicate that the proposed method effectively constrains erroneous reasoning while improving both accuracy and interpretability.
Mitigating Prompt-Induced Hallucinations in Large Language Models via Structured Reasoning
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:To address hallucination issues in large language models (LLMs), this paper proposes a method for mitigating prompt-induced hallucinations. Building on a knowledge distillation chain-style model, we introduce a code module to guide knowledge-graph exploration and incorporate code as part of the chain-of-thought prompt, forming an external knowledge input that provides more accurate and structured information to the model. Based on this design, we develop an improved knowledge distillation chain-style model and leverage it to analyze and constrain the reasoning process of LLMs, thereby improving inference accuracy. We empirically evaluate the proposed approach using GPT-4 and LLaMA-3.3 on multiple public datasets. Experimental results demonstrate that incorporating code modules significantly enhances the model's ability to capture contextual information and effectively mitigates prompt-induced hallucinations. Specifically, HIT@1, HIT@3, and HIT@5 improve by 15.64%, 13.38%, and 13.28%, respectively. Moreover, the proposed method achieves HIT@1, HIT@3, and HIT@5 scores exceeding 95% across several evaluation settings. These results indicate that the proposed approach substantially reduces hallucination behavior while improving the accuracy and verifiability of large language models.
VIPER: Process-aware Evaluation for Generative Video Reasoning
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:Recent breakthroughs in video generation have demonstrated an emerging capability termed Chain-of-Frames (CoF) reasoning, where models resolve complex tasks through the generation of continuous frames. While these models show promise for Generative Video Reasoning (GVR), existing evaluation frameworks often rely on single-frame assessments, which can lead to outcome-hacking, where a model reaches a correct conclusion through an erroneous process. To address this, we propose a process-aware evaluation paradigm. We introduce VIPER, a comprehensive benchmark spanning 16 tasks across temporal, structural, symbolic, spatial, physics, and planning reasoning. Furthermore, we propose Process-outcome Consistency (POC@r), a new metric that utilizes VLM-as-Judge with a hierarchical rubric to evaluate both the validity of the intermediate steps and the final result. Our experiments reveal that state-of-the-art video models achieve only about 20% POC@1.0 and exhibit a significant outcome-hacking. We further explore the impact of test-time scaling and sampling robustness, highlighting a substantial gap between current video generation and true generalized visual reasoning. Our benchmark will be publicly released.
HY-Motion 1.0: Scaling Flow Matching Models for Text-To-Motion Generation
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:We present HY-Motion 1.0, a series of state-of-the-art, large-scale, motion generation models capable of generating 3D human motions from textual descriptions. HY-Motion 1.0 represents the first successful attempt to scale up Diffusion Transformer (DiT)-based flow matching models to the billion-parameter scale within the motion generation domain, delivering instruction-following capabilities that significantly outperform current open-source benchmarks. Uniquely, we introduce a comprehensive, full-stage training paradigm -- including large-scale pretraining on over 3,000 hours of motion data, high-quality fine-tuning on 400 hours of curated data, and reinforcement learning from both human feedback and reward models -- to ensure precise alignment with the text instruction and high motion quality. This framework is supported by our meticulous data processing pipeline, which performs rigorous motion cleaning and captioning. Consequently, our model achieves the most extensive coverage, spanning over 200 motion categories across 6 major classes. We release HY-Motion 1.0 to the open-source community to foster future research and accelerate the transition of 3D human motion generation models towards commercial maturity.
Asynchronous Fast-Slow Vision-Language-Action Policies for Whole-Body Robotic Manipulation
Dec 23, 2025
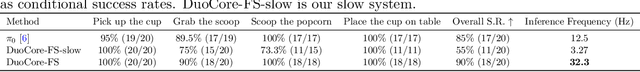
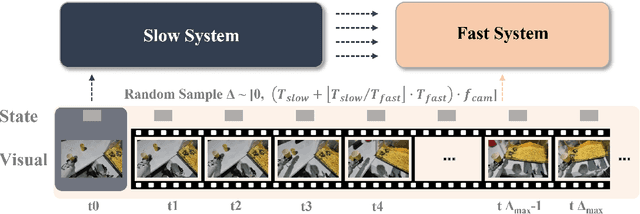
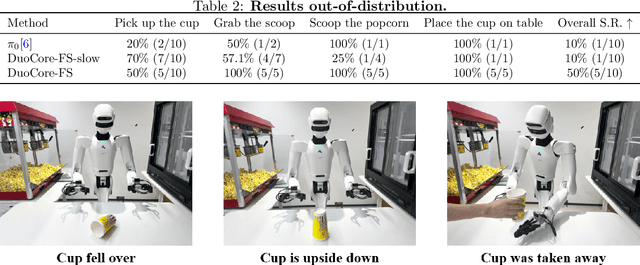
Abstract:Most Vision-Language-Action (VLA) systems integrate a Vision-Language Model (VLM) for semantic reasoning with an action expert generating continuous action signals, yet both typically run at a single unified frequency. As a result, policy performance is constrained by the low inference speed of large VLMs. This mandatory synchronous execution severely limits control stability and real-time performance in whole-body robotic manipulation, which involves more joints, larger motion spaces, and dynamically changing views. We introduce a truly asynchronous Fast-Slow VLA framework (DuoCore-FS), organizing the system into a fast pathway for high-frequency action generation and a slow pathway for rich VLM reasoning. The system is characterized by two key features. First, a latent representation buffer bridges the slow and fast systems. It stores instruction semantics and action-reasoning representation aligned with the scene-instruction context, providing high-level guidance to the fast pathway. Second, a whole-body action tokenizer provides a compact, unified representation of whole-body actions. Importantly, the VLM and action expert are still jointly trained end-to-end, preserving unified policy learning while enabling asynchronous execution. DuoCore-FS supports a 3B-parameter VLM while achieving 30 Hz whole-body action-chunk generation, approximately three times as fast as prior VLA models with comparable model sizes. Real-world whole-body manipulation experiments demonstrate improved task success rates and significantly enhanced responsiveness compared to synchronous Fast-Slow VLA baselines. The implementation of DuoCore-FS, including training, inference, and deployment, is provided to commercial users by Astribot as part of the Astribot robotic platform.
DEVAL: A Framework for Evaluating and Improving the Derivation Capability of Large Language Models
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:Assessing the reasoning ability of Large Language Models (LLMs) over data remains an open and pressing research question. Compared with LLMs, human reasoning can derive corresponding modifications to the output based on certain kinds of changes to the input. This reasoning pattern, which relies on abstract rules that govern relationships between changes of data, has not been comprehensively described or evaluated in LLMs. In this paper, we formally define this reasoning pattern as the Derivation Relation (DR) and introduce the concept of Derivation Capability (DC), i.e. applying DR by making the corresponding modification to the output whenever the input takes certain changes. To assess DC, a systematically constructed evaluation framework named DEVAL is proposed and used to evaluate five popular LLMs and one Large Reasoning Model in seven mainstream tasks. The evaluation results show that mainstream LLMs, such as GPT-4o and Claude3.5, exhibit moderate DR recognition capabilities but reveal significant drop-offs on applying DR effectively in problem-solving scenarios. To improve this, we propose a novel prompt engineering approach called Derivation Prompting (DP). It achieves an average improvement of 15.2% in DC for all tested LLMs, outperforming commonly used prompt engineering techniques.
Hunyuan3D Studio: End-to-End AI Pipeline for Game-Ready 3D Asset Generation
Sep 16, 2025



Abstract:The creation of high-quality 3D assets, a cornerstone of modern game development, has long been characterized by labor-intensive and specialized workflows. This paper presents Hunyuan3D Studio, an end-to-end AI-powered content creation platform designed to revolutionize the game production pipeline by automating and streamlining the generation of game-ready 3D assets. At its core, Hunyuan3D Studio integrates a suite of advanced neural modules (such as Part-level 3D Generation, Polygon Generation, Semantic UV, etc.) into a cohesive and user-friendly system. This unified framework allows for the rapid transformation of a single concept image or textual description into a fully-realized, production-quality 3D model complete with optimized geometry and high-fidelity PBR textures. We demonstrate that assets generated by Hunyuan3D Studio are not only visually compelling but also adhere to the stringent technical requirements of contemporary game engines, significantly reducing iteration time and lowering the barrier to entry for 3D content creation. By providing a seamless bridge from creative intent to technical asset, Hunyuan3D Studio represents a significant leap forward for AI-assisted workflows in game development and interactive media.
VQualA 2025 Challenge on Visual Quality Comparison for Large Multimodal Models: Methods and Results
Sep 11, 2025
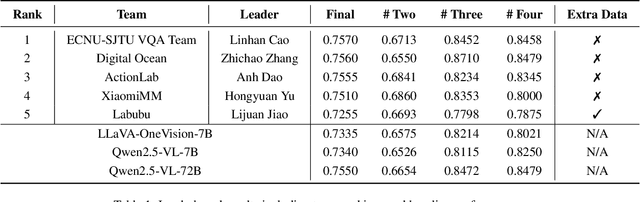
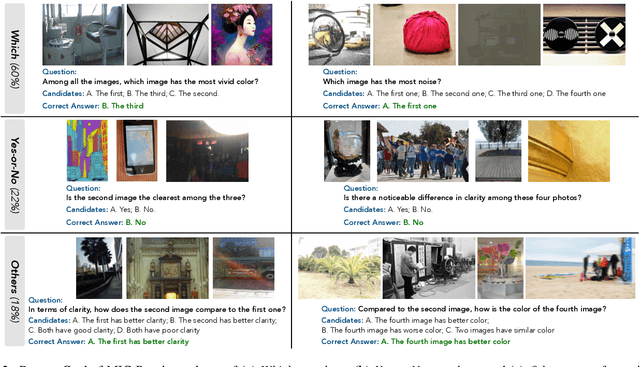
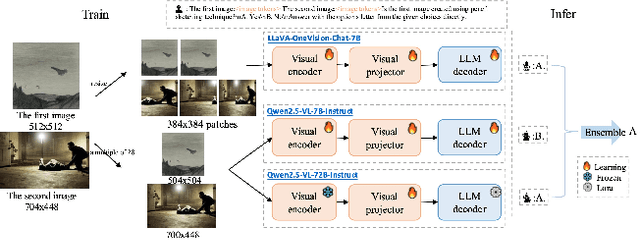
Abstract:This paper presents a summary of the VQualA 2025 Challenge on Visual Quality Comparison for Large Multimodal Models (LMMs), hosted as part of the ICCV 2025 Workshop on Visual Quality Assessment. The challenge aims to evaluate and enhance the ability of state-of-the-art LMMs to perform open-ended and detailed reasoning about visual quality differences across multiple images. To this end, the competition introduces a novel benchmark comprising thousands of coarse-to-fine grained visual quality comparison tasks, spanning single images, pairs, and multi-image groups. Each task requires models to provide accurate quality judgments. The competition emphasizes holistic evaluation protocols, including 2AFC-based binary preference and multi-choice questions (MCQs). Around 100 participants submitted entries, with five models demonstrating the emerging capabilities of instruction-tuned LMMs on quality assessment. This challenge marks a significant step toward open-domain visual quality reasoning and comparison and serves as a catalyst for future research on interpretable and human-aligned quality evaluation systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge